Association between Unhealthy Dietary Habits and Proteinuria Onset in a Japanese General Population: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Measurements of Study Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Subjects
3.2. Changes in BMI and WtHR According to Baseline Unhealthy Dietary Habits
3.3. Unhealthy Dietary Habits and Risks for Proteinuria Onset
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Bolton, K.; Culleton, B.; Harvey, K.S.; Ikizler, T.A.; Johnson, C.A.; Kausz, A.; Kimmel, P.L.; Kusek, J.; et al. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, S1–S266. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata, K.; Yagisawa, T.; Nakai, S.; Nakayama, M.; Imai, E.; Hattori, M.; Iseki, K.; Akiba, T. Prevalence and incidence of chronic kidney disease stage G5 in Japan. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.; Covic, A.; Fliser, D.; Fouque, D.; Goldsmith, D.; Kanbay, M.; Mallamaci, F.; Massy, Z.A.; Rossignol, P.; Vanholder, R.; et al. Epidemiology, contributors to, and clinical trials of mortality risk in chronic kidney failure. Lancet 2014, 383, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Diabetes and hypertension have become leading causes of CKD in Chinese elderly patients: A comparison between 1990–1991 and 2009–2010. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2012, 44, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Juncos, L.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, J.E. Obesity, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Q.; Pu, Y.; Guo, M.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, W.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y. Skipping breakfast is associated with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, C.F.; Miklich, M.A.; Patel, R.S.; Fink, J.C. Medication Safety Principles and Practice in CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Nakamura, U.; Iwase, M.; Ide, H.; Fujii, H.; Jodai, T.; Kaizu, S.; Kikuchi, Y.; Idewaki, Y.; Sumi, A.; et al. Effects of smoking and its cessation on creatinine- and cystatin C-based estimated glomerular filtration rates and albuminuria in male patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Fukuoka Diabetes Registry. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuleman, Y.; Hoekstra, T.; Dekker, F.W.; Navis, G.; Vogt, L.; van der Boog, P.J.M.; Bos, W.J.W.; van Montfrans, G.A.; van Dijk, S.; Group, E.S. Sodium Restriction in Patients With CKD: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Self-management Support. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, K.U.; Kasiske, B.L. Foreword. Kidney Int. 2009, 76113, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rughooputh, M.S.; Zeng, R.; Yao, Y. Protein Diet Restriction Slows Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in Non-Diabetic and in Type 1 Diabetic Patients, but Not in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Using Glomerular Filtration Rate as a Surrogate. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheer, F.A.; Hilton, M.F.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Shea, S.A. Adverse metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of circadian misalignment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, S.; Fukui, M.; Kajiyama, S. Effect of eating vegetables before carbohydrates on glucose excursions in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 54, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bi, H.; Gan, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Tong, X.; Lu, Z. Breakfast skipping and the risk of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 3013–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutsuma, A.; Nakajima, K.; Suwa, K. Potential Association between Breakfast Skipping and Concomitant Late-Night-Dinner Eating with Metabolic Syndrome and Proteinuria in the Japanese Population. Scientifica 2014, 2014, 253581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, A.; World Health, A. WHO global strategy on diet, physical activity and health. Food Nutr. Bull. 2004, 25, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, T.; Furuichi, K.; Ninomiya, T.; Shimizu, M.; Hara, A.; Iwata, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Wada, T. The impacts of albuminuria and low eGFR on the risk of cardiovascular death, all-cause mortality, and renal events in diabetic patients: Meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Cole, T.J.; Dixon, A.K. Ratio of waist circumference to height is strong predictor of intra-abdominal fat. BMJ 1996, 313, 559–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, S.; Imai, E.; Horio, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Tomita, K.; Nitta, K.; Yamagata, K.; Tomino, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Hishida, A.; et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, M.D.; Sheehan, N.A.; Scurrah, K.J.; Burton, P.R. Adjusting for treatment effects in studies of quantitative traits: Antihypertensive therapy and systolic blood pressure. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 2911–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, S13–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, S.P.; McClellan, W.; Port, F.K.; Hsu, S.I. Risk factors for proteinuria in a large, multiracial, southeast Asian population. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kuma, A.; Uchino, B.; Ochiai, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Enta, K.; Tamura, M.; Otsuji, Y.; Kato, A. Relationship between abdominal adiposity and incident chronic kidney disease in young- to middle-aged working men: A retrospective cohort study. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, E.; Horio, M.; Watanabe, T.; Iseki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Hara, S.; Ura, N.; Kiyohara, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ando, Y.; et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the Japanese general population. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2009, 13, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagata, K.; Ishida, K.; Sairenchi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ohba, S.; Shiigai, T.; Narita, M.; Koyama, A. Risk factors for chronic kidney disease in a community-based population: A 10-year follow-up study. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.K.; Tang, T.S. When’s dinner? Does timing of dinner affect the cardiometabolic risk profiles of South-Asian Canadians at risk for diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekary, R.A.; Giovannucci, E.; Willett, W.C.; van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B. Eating patterns and type 2 diabetes risk in men: Breakfast omission, eating frequency, and snacking. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekary, R.A.; Giovannucci, E.; Cahill, L.; Willett, W.C.; van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B. Eating patterns and type 2 diabetes risk in older women: Breakfast consumption and eating frequency. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Yoshita, K.; Nakamura, K.; Miura, K.; Takamura, T.; Nagasawa, S.Y.; Morikawa, Y.; Kido, T.; Naruse, Y.; Nogawa, K.; et al. Skipping breakfast and 5-year changes in body mass index and waist circumference in Japanese men and women. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2017, 3, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, J.; Eguchi, E.; Nagaoka, K.; Ito, T.; Ogino, K. Association of night eating habits with metabolic syndrome and its components: A longitudinal study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakopoulos, V.; Franzen, S.; Svensson, A.M.; Sattar, N.; Miftaraj, M.; Bjorck, S.; Ottosson, J.; Naslund, I.; Gudbjornsdottir, S.; Eliasson, B. Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes After Weight Loss From Gastric Bypass Surgery in Type 2 Diabetes: Cardiorenal Risk Reductions Exceed Atherosclerotic Benefits. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujibayashi, K.; Fukuda, H.; Yokokawa, H.; Haniu, T.; Oka, F.; Ooike, M.; Gunji, T.; Sasabe, N.; Okumura, M.; Iijima, K.; et al. Associations between healthy lifestyle behaviors and proteinuria and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). J. Atheroscler Thromb. 2012, 19, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michishita, R.; Matsuda, T.; Kawakami, S.; Kiyonaga, A.; Tanaka, H.; Morito, N.; Higaki, Y. The Association Between Unhealthy Lifestyle Behaviors and the Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Middle-Aged and Older Men. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birketvedt, G.S.; Florholmen, J.; Sundsfjord, J.; Osterud, B.; Dinges, D.; Bilker, W.; Stunkard, A. Behavioral and neuroendocrine characteristics of the night-eating syndrome. JAMA 1999, 282, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.-W.; Lu, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Lee, C.-S.; Kao, W.-P.; Lee, H.-C.; Voon, W.-C.; Lai, W.-T.; Sheu, S.-H. A-002 Association of Lower Endogenous Cortisol Level with Higher Blood Pressure Load in Untreated Hypertensive Patients. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witbracht, M.; Keim, N.L.; Forester, S.; Widaman, A.; Laugero, K. Female breakfast skippers display a disrupted cortisol rhythm and elevated blood pressure. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 140, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, K.D.; Robertson, I.K.; Ball, M.J. Acute effects of food on postprandial blood pressure and measures of arterial stiffness in healthy humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Brereton, N.; Schweitzer, A.; Cotter, M.; Duan, D.; Borsheim, E.; Wolfe, R.R.; Pham, L.V.; Polotsky, V.Y.; Jun, J.C. Metabolic Effects of Late Dinner in Healthy Volunteers-A Randomized Crossover Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafidis, P.A.; Khosla, N.; Bakris, G.L. Antihypertensive therapy in the presence of proteinuria. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Sasako, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Kato, M.; Okahata, S.; Katsuyama, H.; Haraguchi, M.; Morita, A.; Ohashi, K.; Hara, K.; et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J-DOIT3): An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



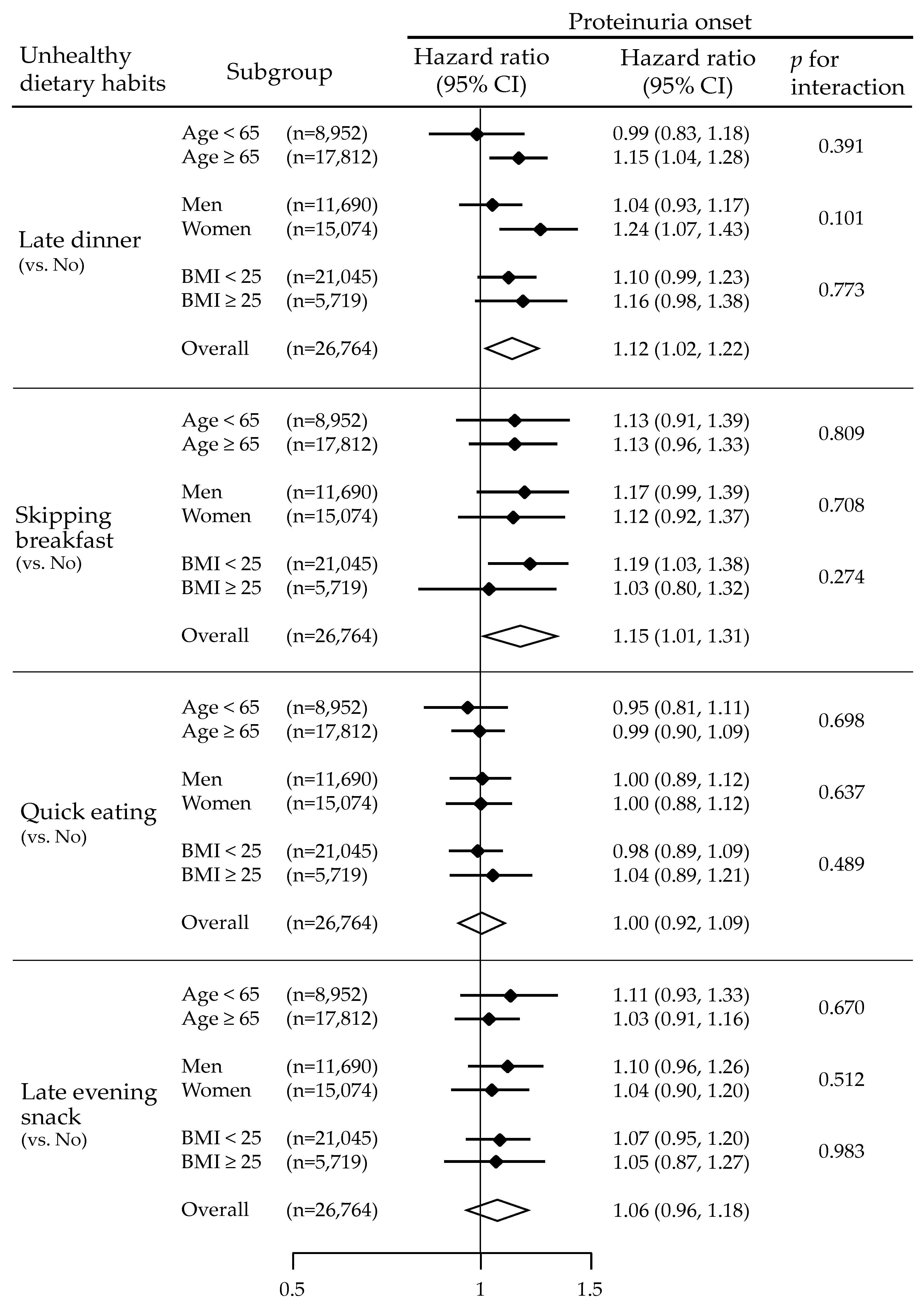
| Variables | All |
|---|---|
| N | 26,764 |
| Age, year | 68 (9) |
| Men, n (%) | 11,690 (44) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.8 (3.1) |
| Waist circumference, cm | 83 (9) |
| Waist-to-height ratio, cm/cm | 0.53 (0.06) |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 132 (18) |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 77 (11) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 77 (12) |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.6 (1.4) |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 103 (74, 146) |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 204 (33) |
| HbA1c, % | 5.2 (5.0, 5.5) |
| Quick eating (yes), n (%) | 7659 (29) |
| Late dinner (yes), n (%) | 5157 (19) |
| Late evening snack (yes), n (%) | 4218 (16) |
| Skipping breakfast (yes), n (%) | 2350 (9) |
| Daily drinking (yes), n (%) | 9225 (34) |
| Current smoking (yes), n (%) | 3792 (14) |
| Overall | ||||
| Number of events | 2844 (10.6%) | |||
| Person-years | 86,903 | |||
| Events per 1000 person-years | 32.7 | |||
| Quick Eating | Late Dinner | |||
| Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| Number of events | 805 (10.5%) | 2039 (10.7%) | 625 (12.1%) | 2219 (10.3%) |
| Person-years | 24,882 | 62,020 | 16,582 | 70,321 |
| Events per 1000 person-years | 32.4 | 32.9 | 37.7 | 32.5 |
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI; p-value) (vs. No) | 0.98 (0.91, 1.07; p = 0.711) | 1.19 (1.09, 1.30; p < 0.001) | ||
| Late Evening Snack | Skipping Breakfast | |||
| Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| Number of events | 469 (11.1%) | 2375 (10.5%) | 265 (11.3%) | 2579 (10.6%) |
| Person-years | 13,783 | 73,120 | 7314 | 79,589 |
| Events per 1000 person-years | 34.0 | 32.5 | 36.2 | 32.4 |
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI; p-value) (vs. No) | 1.04 (0.95, 1.15; p = 0.396) | 1.12 (0.99, 1,27; p = 0.078) | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tokumaru, T.; Toyama, T.; Hara, A.; Kitagawa, K.; Yamamura, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Oshima, M.; Miyagawa, T.; Sato, K.; Ogura, H.; et al. Association between Unhealthy Dietary Habits and Proteinuria Onset in a Japanese General Population: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092511
Tokumaru T, Toyama T, Hara A, Kitagawa K, Yamamura Y, Nakagawa S, Oshima M, Miyagawa T, Sato K, Ogura H, et al. Association between Unhealthy Dietary Habits and Proteinuria Onset in a Japanese General Population: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092511
Chicago/Turabian StyleTokumaru, Toshiaki, Tadashi Toyama, Akinori Hara, Kiyoki Kitagawa, Yuta Yamamura, Shiori Nakagawa, Megumi Oshima, Taro Miyagawa, Koichi Sato, Hisayuki Ogura, and et al. 2020. "Association between Unhealthy Dietary Habits and Proteinuria Onset in a Japanese General Population: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092511
APA StyleTokumaru, T., Toyama, T., Hara, A., Kitagawa, K., Yamamura, Y., Nakagawa, S., Oshima, M., Miyagawa, T., Sato, K., Ogura, H., Kitajima, S., Iwata, Y., Sakai, N., Shimizu, M., Furuichi, K., Hashiba, A., & Wada, T. (2020). Association between Unhealthy Dietary Habits and Proteinuria Onset in a Japanese General Population: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients, 12(9), 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092511






