New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
1. NAFLD: An Emerging Multifactorial Liver Disease
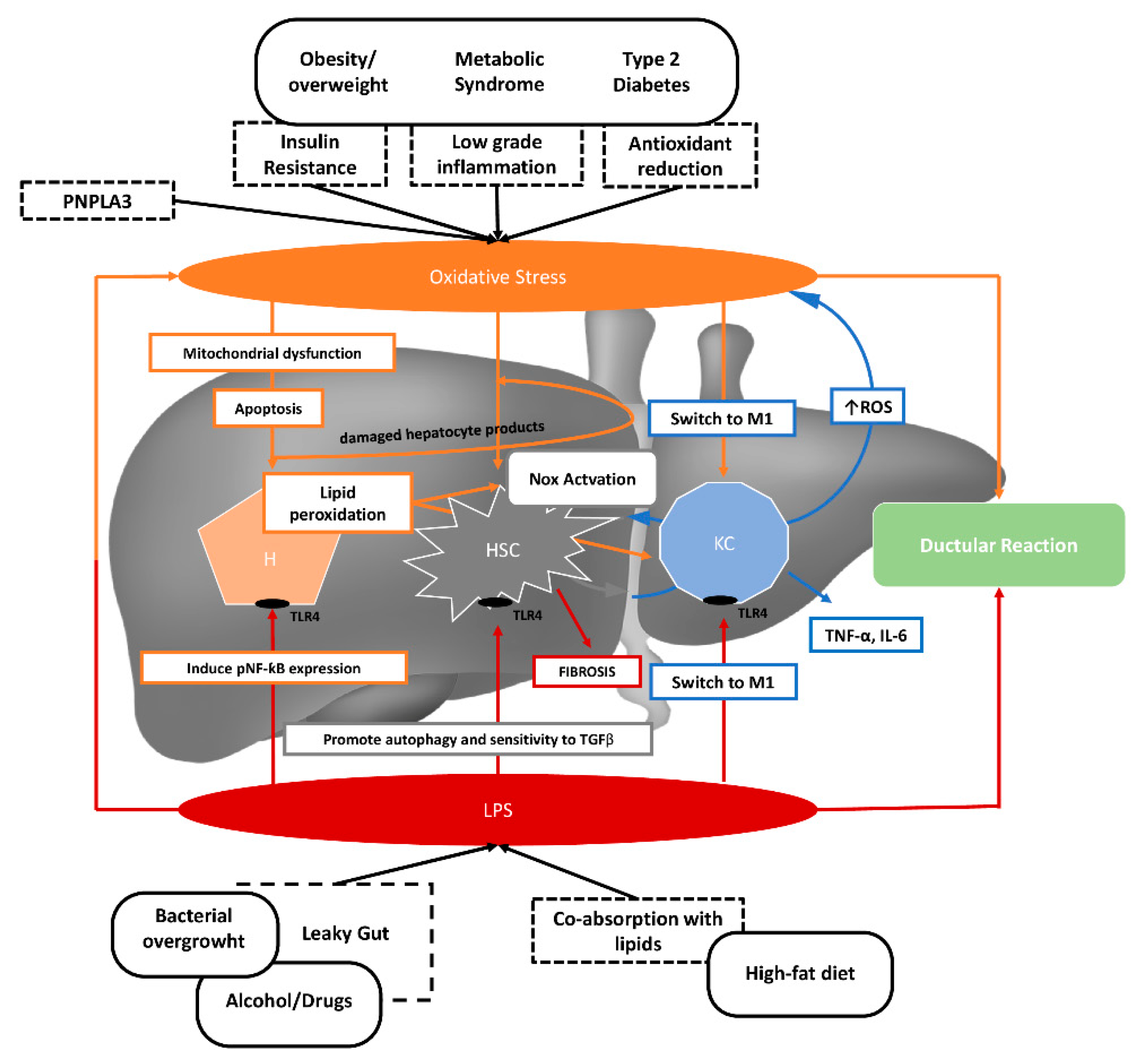
2. NAFLD Pathogenesis
2.1. Gut Microbiota
2.2. Oxidative Stress
3. Lipopolysaccharide and Oxidative Stress
4. Therapeutic Approach to Reduce Oxidative Stress and Lipopolysaccharide in NAFLD
4.1. Therapeutic Approach to Reducing Lipopolysaccharides in NAFLD
4.2. Therapeutic Approach to Reducing Oxidative Stress in NAFLD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vernon, G.; Baranova, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Systematic Review: The Epidemiology and Natural History of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Adults. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.P.; Younossi, Z.M.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Practice Guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2017, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Tiribelli, C.; Marchesini, G.; Bellentani, S. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Dionysos Nutrition and Liver Study. Hepatology 2005, 42, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.G.; Saibara, T.; Chitturi, S.; Kim, B.I.; Sung, J.J.; Chutaputti, A.; Asia–Pacific Working Party for NAFLD. What Are the Risk Factors and Settings for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Asia?Pacific? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddin, M.; Vipani, A.; Bresee, C.; Todo, T.; Kim, I.K.; Alkhouri, N.; Setiawan, V.W.; Tran, T.; Ayoub, W.S.; Lu, S.C.; et al. NASH Leading Cause of Liver Transplant in Women: Updated Analysis of Indications For Liver Transplant and Ethnic and Gender Variances. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shanab, A.; Quigley, E.M.M. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The Gut Microbiota as an Environmental Factor That Regulates Fat Storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolo, A.P.; Teodoro, J.S.; Palmeira, C.M. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Free Radic. Boil. Med. 2012, 52, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serviddio, G.; Bellanti, F.; Vendemiale, G. Free Radical Biology for Medicine: Learning from Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Free Radic. Boil. Med. 2013, 65, 952–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Multiple Parallel Hits Hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD Development and Therapeutic Strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, A.; Kawai, D.; Yamamoto, K. Multiple Hits, Including Oxidative Stress, As Pathogenesis and Treatment Target in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20704–20728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Ben, M.; Baratta, F.; Polimeni, L.; Angelico, F. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Epidemiological, Clinical and Pathophysiological Evidences. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2012, 7, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Lonardo, A.; Zoppini, G.; Barbui, C. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, F.; Ding, Y.; Hou, J.; Bi, J.; Zhang, Z. Association of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease With Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Day, C.P.; Bonora, E. Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastori, D.; Loffredo, L.; Perri, L.; Baratta, F.; Scardella, L.; Polimeni, L.; Pani, A.; Brancorsini, M.; Albanese, F.; Catasca, E.; et al. Relation of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Framingham Risk Score to Flow-Mediated Dilation in Patients With Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinn, D.H.; Kang, D.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Gu, S.; Kim, H.; Seong, D.; Cho, S.J.; Yi, B.K.; Park, H.D.; et al. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Progression of Coronary Artery Calcium Score: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Gut 2016, 66, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, A.; D’Erasmo, L.; Polimeni, L.; Baratta, F.; Coletta, P.; Di Martino, M.; Loffredo, L.; Perri, L.; Ceci, F.; Montali, A.; et al. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Subclinical Atherosclerosis: A Comparison of Metabolically- Versus Genetically-Driven Excess Fat Hepatic Storage. Atherosclerosis 2017, 257, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Ben, M.; Polimeni, L.; Brancorsini, M.; Di Costanzo, A.; D’Erasmo, L.; Baratta, F.; Loffredo, L.; Pastori, D.; Pignatelli, P.; Violi, F.; et al. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Metabolic Syndrome and Patatin-Like Phospholipase Domain-Containing Protein3 Gene Variants. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Gut Microbiota Shapes Intestinal Immune Responses During Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigg, A.J.; Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Dymock, R.B.; McCarthy, P.J.; Grose, R.H.; Cummins, A.G. The Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth, Intestinal Permeability, Endotoxaemia, and Tumour Necrosis Factor α in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gut 2001, 48, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzaki, M.; Comelli, E.M.; Arendt, B.M.; Bonengel, J.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; McGilvray, I.D.; Allard, J.P. Intestinal Microbiota in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Determines Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. Gut 2012, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamparast, T.; Poustchi, H.; Zamani, F.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic Supplementation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, Z.; Gibson, D.L.; Hekmatdoost, A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, the Gut Microbiome, and Diet. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Castagliuolo, I.; Di Leo, V.; Buda, A.; Pinzani, M.; Palù, G.; Martines, D. Increased Intestinal Permeability in Obese Mice: New Evidence in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G518–G525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.B.; Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Roncon-Albuquerque, R., Jr.; Leite-Moreira, A.F. The Role of lipopolysaccharide/Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling in Chronic Liver Diseases. Hepatol. Int. 2010, 4, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Del Ben, M.; Pastori, D.; Carnevale, R.; Baratta, F.; Overi, D.; Francis, H.; Cardinale, V.; Onori, P.; Safarikia, S.; et al. Increased Liver Localization of Lipopolysaccharides in Human and Experimental NAFLD. Hepatology 2020, 72, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Bartimoccia, S.; Cammisotto, V.; Cocomello, N.; Colantoni, A.; Nocella, C.; Carnevale, R.; Ferro, D.; Angelico, F.; et al. Poor Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Serum Lipopolysaccharide Are Associated With Oxidative Stress in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 17232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Role of the Normal Gut Microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.M.; Stefano, J.T.; Oliveira, C.P. Microbiota and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NAFLD/NASH). Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Mascianà, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G.; et al. Increased Intestinal Permeability and Tight Junction Alterations in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohr, M.W.; Narasimhulu, C.A.; Rudeski-Rohr, T.A.; Parthasarathy, S. Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet on Intestinal Permeability: A Review. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 11, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awada, M.; Soulage, C.O.; Meynier, A.; Debard, C.; Plaisancié, P.; Benoit, B.; Picard, G.; Loizon, E.; Chauvin, M.A.; Estienne, M.; et al. Dietary Oxidizedn-3 PUFA Induce Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Role of Intestinal Absorption of 4-HHE and Reactivity in Intestinal Cells. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2069–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenman, L.K.; Holma, R.; Korpela, R. High-Fat-Induced Intestinal Permeability Dysfunction Associated With Altered Fecal Bile Acids. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, F.; Santoro, P.; Barone, M.V.; Pappacoda, S.; Barretta, M.L.; Nanayakkara, M.; Apicella, C.; Capasso, L.; Paludetto, R. Bile Acids Modulate Tight Junction Structure and Barrier Function of Caco-2 Monolayers via EGFR Activation. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G906–G913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, S.; Witta, J.; Zhong, J.; De Villiers, W.; Eckhardt, E. Chylomicrons Promote Intestinal Absorption of Lipopolysaccharides. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 50, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vors, C.; Pineau, G.; Drai, J.; Meugnier, E.; Pesenti, S.; Laville, M.; Laugerette, F.; Malpuech-Brugère, C.; Vidal, H.; Michalski, M. Postprandial Endotoxemia Linked With Chylomicrons and Lipopolysaccharides Handling in Obese Versus Lean Men: A Lipid Dose-Effect Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3427–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic Endotoxemia Initiates Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Oxidative Stress: From Basic Research to Clinical Application. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, S31–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, R.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Free. Radic. Boil. Med. 2020, 152, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, A.; Gattolliat, C.H.; Asselah, T. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Signaling in Chronic Liver Diseases. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurutaş, E.B. The Importance of Antioxidants Which Play the Role in Cellular Response Against oxidative/nitrosative Stress: Current State. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The Liver. Curr. Boil. 2017, 27, R1147–R1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichoz-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative Stress as a Crucial Factor in Liver Diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polimeni, L.; Del Ben, M.; Baratta, F.; Perri, L.; Albanese, F.; Pastori, D.; Violi, F.; Angelico, F. Oxidative Stress: New Insights on the Association of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Atherosclerosis. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A. The Role of NADPH Oxidases (NOXs) in Liver Fibrosis and the Activation of Myofibroblasts. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Ben, M.; Polimeni, L.; Carnevale, R.; Bartimoccia, S.; Nocella, C.; Baratta, F.; Loffredo, L.; Pignatelli, P.; Violi, F.; Angelico, F. NOX2-Generated Oxidative Stress Is Associated With Severity of Ultrasound Liver Steatosis in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Ben, M.; Polimeni, L.; Baratta, F.; Bartimoccia, S.; Carnevale, R.; Loffredo, L.; Pignatelli, P.; Violi, F.; Angelico, F. Serum Cytokeratin-18 Is Associated With NOX2-Generated Oxidative Stress in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver. Int. J. Hepatol. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastori, D.; Baratta, F.; Carnevale, R.; Cangemi, R.; Del Ben, M.; Bucci, T.; Polimeni, L.; Labbadia, G.; Nocella, C.; Scardella, L.; et al. Similar Reduction of Cholesterol-Adjusted Vitamin E Serum Levels in Simple Steatosis and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevale, R.; Nocella, C.; Petrozza, V.; Cammisotto, V.; Pacini, L.; Sorrentino, V.; Martinelli, O.; Irace, L.; Sciarretta, S.; Frati, G.; et al. Localization of Lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia Coli into Human Atherosclerotic Plaque. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, L.; Ettorre, E.; Zicari, A.M.; Inghilleri, M.; Nocella, C.; Perri, L.; Spalice, A.; Fossati, C.; De Lucia, M.C.; Pigozzi, F.; et al. Neurodegenerative Disease study group. Oxidative Stress and Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides in Neurodegenerative Disease: Role of NOX2. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8630275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neish, A.S.; Jones, R.M. Redox Signaling Mediated by the Gut Microbiota. Free. Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.; Leoni, G.; Quiros, M.; Wu, H.; Desai, C.; Nishio, H.; Jones, R.M.; Nusrat, A.; Neish, A.S. The Microenvironment of Injured Murine Gut Elicits a Local Pro-Restitutive Microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbach, S.H.; Schönfelder, T.; Brandão, I.; Wilms, E.; Hörmann, N.; Jäckel, S.; Schüler, R.; Finger, S.; Knorr, M.; Lagrange, J.; et al. Gut Microbiota Promote Angiotensin II–Induced Arterial Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2016, 5, e003698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastori, D.; Carnevale, R.; Nocella, C.; Novo, M.; Santulli, M.; Cammisotto, V.; Menichelli, D.; Pignatelli, P.; Violi, F. Gut-Derived Serum Lipopolysaccharide Is Associated With Enhanced Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation: Effect of Adherence to Mediterranean Diet. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2017, 6, e005784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale, R.; Pastori, D.; Nocella, C.; Cammisotto, V.; Bartimoccia, S.; Novo, M.; Del Ben, M.; Farcomeni, A.; Angelico, F.; Violi, F. Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides Increase Post-Prandial Oxidative Stress via Nox2 Activation in Patients With Impaired Fasting Glucose Tolerance: Effect of Extra-Virgin Olive Oil. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 58, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Pastori, D.; Baratta, F.; Overi, D.; Labbadia, G.; Polimeni, L.; Di Costanzo, A.; Pannitteri, G.; Carnevale, R.; Del Ben, M.; et al. PNPLA3 Variant and portal/periportal Histological Pattern in Patients With Biopsy-Proven Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Possible Role for Oxidative Stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.A.; Holscher, H.D. Microbiome-Mediated Effects of the Mediterranean Diet on Inflammation. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nymark, M.; Pussinen, P.; Tuomainen, A.M.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.H.; Lehto, M. Serum Lipopolysaccharide Activity Is Associated With the Progression of Kidney Disease in Finnish Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009, 32, 1689–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendyala, S.; Walker, J.M.; Holt, P.R. A High-Fat Diet Is Associated With Endotoxemia That Originates from the Gut. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1100–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umoh, F.I.; Kato, I.; Ren, J.; Wachowiak, P.L.; Ruffin, I.M.T.; Turgeon, D.K.; Sen, A.; Brenner, D.E.; Djuric, Z. Markers of Systemic Exposures to Products of Intestinal Bacteria in a Dietary Intervention Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 55, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Hollis, J.H.; Gabler, N.K. Dietary Oil Composition Differentially Modulates Intestinal Endotoxin Transport and Postprandial Endotoxemia. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyte, J.M.; Gabler, N.K.; Hollis, J.H. Postprandial Serum Endotoxin in Healthy Humans Is Modulated by Dietary Fat in a Randomized, Controlled, Cross-over Study. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erridge, C.; Attinà, T.; Spickett, C.M.; Webb, D.J. A High-Fat Meal Induces Low-Grade Endotoxemia: Evidence of a Novel Mechanism of Postprandial Inflammation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugerette, F.; Vors, C.; Peretti, N.; Michalski, M. Complex Links between Dietary Lipids, Endogenous Endotoxins and Metabolic Inflammation. Biochimie 2011, 93, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; He, J.; Gao, N.; Lu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Probiotics May Delay the Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Restoring the Gut Microbiota Structure and Improving Intestinal Endotoxemia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamparast, T.; Eghtesad, S.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Poustchi, H. Probiotics and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Middle East J. Dig. Dis. 2013, 5, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Ding, Z.; Shi, H.; Qian, W.; Hou, X.; Lin, R. The Role of Probiotics in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Autophagy in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 2464–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lin, A.; Kong, M.; Yao, X.; Yin, M.; Xia, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Intestinal Microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 55, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.C.; Zhao, W.; Li, S. Small Intestinal Bacteria Overgrowth Decreases Small Intestinal Motility in the NASH Rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpignato, C.; Pelosini, I. Rifaximin, a Poorly Absorbed Antibiotic: Pharmacology and Clinical Potential. Chemotherapy 2005, 51, 36–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangarapu, V.; Ince, A.T.; Baysal, B.; Kayar, Y.; Klç, U.; Gök, Ö.; Uysal, O.; Senturk, H. Efficacy of Rifaximin on Circulating Endotoxins and Cytokines in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Razik, A.; Mousa, N.; Shabana, W.; Refaey, M.; Elzehery, R.; Elhelaly, R.; Zalata, K.; Abdelsalam, M.; Eldeeb, A.A.; Awad, M.; et al. Rifaximin in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Zocco, M.A.; D’Aversa, F.; Pompili, M.; Gasbarrini, A. Eubiotic Properties of Rifaximin: Disruption of the Traditional Concepts in Gut Microbiota Modulation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P.; DiNicolantonio, J.J. Mediterranean Diet: ω-6 and ω-3 Fatty Acids and Diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 953–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Camargo, A.; Delgado-Casado, N.; Cruz-Teno, C.; Santos-Gonzalez, M.; Rodriguez-Cantalejo, F.; Castaño, J.P.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Supplemented With Coenzyme Q10 Induces Postprandial Changes in p53 in Response to Oxidative DNA Damage in Elderly Subjects. AGE 2011, 34, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, F.; Cuevas, A.; Guasch, V.; Pérez, D.D.; Strobel, P.; Martín, A.S.; Urzua, U.; Díez, M.S.; Foncea, R.; Castillo, O.; et al. Plasma Polyphenols and Antioxidants, Oxidative DNA Damage and Endothelial Function in a Diet and Wine Intervention Study in Humans. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1999, 25, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barona, J.; Jones, J.J.; Kopec, R.E.; Comperatore, M.; Andersen, C.; Schwartz, S.J.; Lerman, R.H.; Fernandez, M.L. A Mediterranean-Style Low-Glycemic-Load Diet Increases Plasma Carotenoids and Decreases LDL Oxidation in Women with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fíto, M.; Guxens, M.; Corella, D.; Saez, G.; Estruch, R.; De La Torre, R.; Francés, F.; Cabezas, C.; López-Sabater, M.C.; Marrugat, J.; et al. for the PREDIMED Study Investigators. Effect of a Traditional Mediterranean Diet on Lipoprotein Oxidation. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Di Palo, C.; Maiorino, M.I.; Petrizzo, M.; Bellastella, G.; Siniscalchi, I.; Giugliano, D. Long-Term Effect of Mediterranean-Style Diet and Calorie Restriction on Biomarkers of Longevity and Oxidative Stress in Overweight Men. Cardiol. Res. Pr. 2010, 2011, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Comperatore, M.; Barona, J.; Calle, M.C.; Andersen, C.; McIntosh, M.; Najm, W.; Lerman, R.H.; Fernandez, M.L. A Mediterranean-Style, low–glycemic-Load Diet Decreases Atherogenic Lipoproteins and Reduces Lipoprotein (a) and Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Women with Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolism 2012, 61, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Willett, W.; Wang, M.; Wu, T.; Jensen, M.; Hankinson, S.E.; Eliassen, A.H. Healthy Dietary Patterns and Oxidative Stress As Measured by Fluorescent Oxidation Products in Nurses’ Health Study. Nutrients 2016, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative Stress, Aging, and Diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging. 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.K.; Riley, M.A.; Hobbs, S.; Cortez-Cooper, M.; Robinson, V.J. Can ?-Lipoic Acid Mitigate Progression of Aging-Related Decline Caused by Oxidative Stress? South. Med J. 2014, 107, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska, J.; Gębczyński, A.K.; Konarzewski, M. Metabolic Risk Factors in Mice Divergently Selected for BMR Fed High Fat and High Carb Diets. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, J.I.; Hord, N.G.; Ghosh, S.; Gurzell, E.A. Immunomodulation by Dietary Long Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids and the Potential for Adverse Health Outcomes. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids. 2013, 89, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fernández-Galilea, M.; Martínez-Fernández, L.; González-Muniesa, P.; Pérez-Chávez, A.; Martínez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. Oxidative Stress and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; LaVine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Ünalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, Vitamin E, or Placebo for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schürks, M.; Glynn, R.J.; Rist, P.M.; Tzourio, C.; Kurth, T. Effects of Vitamin E on Stroke Subtypes: Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ 2010, 341, c5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Wei, J.; Citronberg, J.; Hartman, T.; Fedirko, V.; Goodman, M. Relation of Vitamin E and Selenium Exposure to Prostate Cancer Risk by Smoking Status: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 4983–4996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- LaVine, J.E.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Van Natta, M.L.; Molleston, J.P.; Murray, K.F.; Rosenthal, P.; Abrams, S.H.; Scheimann, A.O.; Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; et al. for the Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Effect of Vitamin E or Metformin for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents. JAMA 2011, 305, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, V.; Manco, M.; DeVito, R.; Di Ciommo, V.; Comparcola, D.; Sartorelli, M.R.; Piemonte, F.; Marcellini, M.; Angulo, P. Lifestyle Intervention and Antioxidant Therapy in Children With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Hepatology 2008, 48, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Fliss-Isakov, N.; Salomone, F.; Webb, M.; Shibolet, O.; Kariv, R.; Zelber-Sagi, S. Dietary Vitamin E and C Intake Is Inversely Associated With the Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, H.; Omidian, K.; Bandy, B. Dietary Polyphenols Protect Against Oleic Acid-Induced Steatosis in an in Vitro Model of NAFLD by Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Improving Mitochondrial Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Fan, Y.; Yan, Q.; Fan, X.; Wu, B.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Niu, J. The Therapeutic Effect of Silymarin in the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Disease. Medicine 2017, 96, e9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.; Belle, S.H.; D’Amato, M.; Adfhal, N.; Brunt, E.M.; Fried, M.W.; Reddy, K.R.; Wahed, A.S.; Harrison, S.; Silymarin in NASH and C Hepatitis (SyNCH) Study Group. Silymarin in Non-Cirrhotics with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE. 2019, 14, e0221683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferro, D.; Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Cocomello, N.; Colantoni, A.; Angelico, F.; Del Ben, M. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092762
Ferro D, Baratta F, Pastori D, Cocomello N, Colantoni A, Angelico F, Del Ben M. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092762
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerro, Domenico, Francesco Baratta, Daniele Pastori, Nicholas Cocomello, Alessandra Colantoni, Francesco Angelico, and Maria Del Ben. 2020. "New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides and Oxidative Stress" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092762
APA StyleFerro, D., Baratta, F., Pastori, D., Cocomello, N., Colantoni, A., Angelico, F., & Del Ben, M. (2020). New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients, 12(9), 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092762







