The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Body Composition, Strength, and Endurance Performance in Healthy Young Males: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
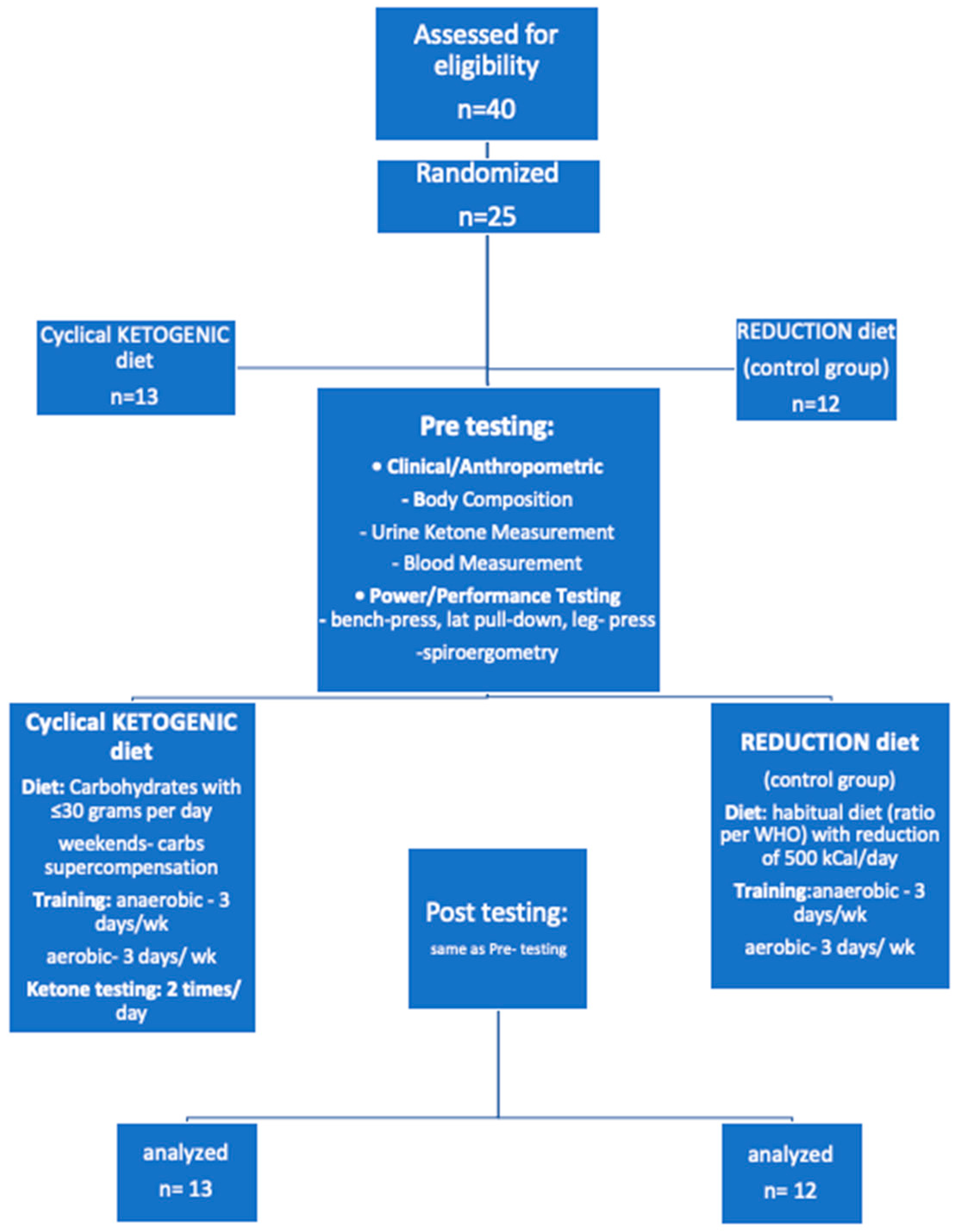
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Baseline and Postinterventional Testing
2.1.1. Biochemical and Anthropometric Examination
2.1.2. Strength and Aerobic Performance Testing
2.1.3. Methodology of Strength Testing
2.1.4. Aerobic Performance Testing
2.2. Diet Protocol
2.2.1. Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet
2.2.2. Reduction Diet
2.3. Training Protocol
2.3.1. Development of Strength Skills
- Focused on chest—bench press.
- Focused on the muscles of the lower limbs—leg press.
- Focused on the back muscles—lat pull-down.
2.3.2. Development of Endurance Skills
2.3.3. Supervision of Adherence to Training and Diet Protocols
2.4. Post-Intervention Testing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
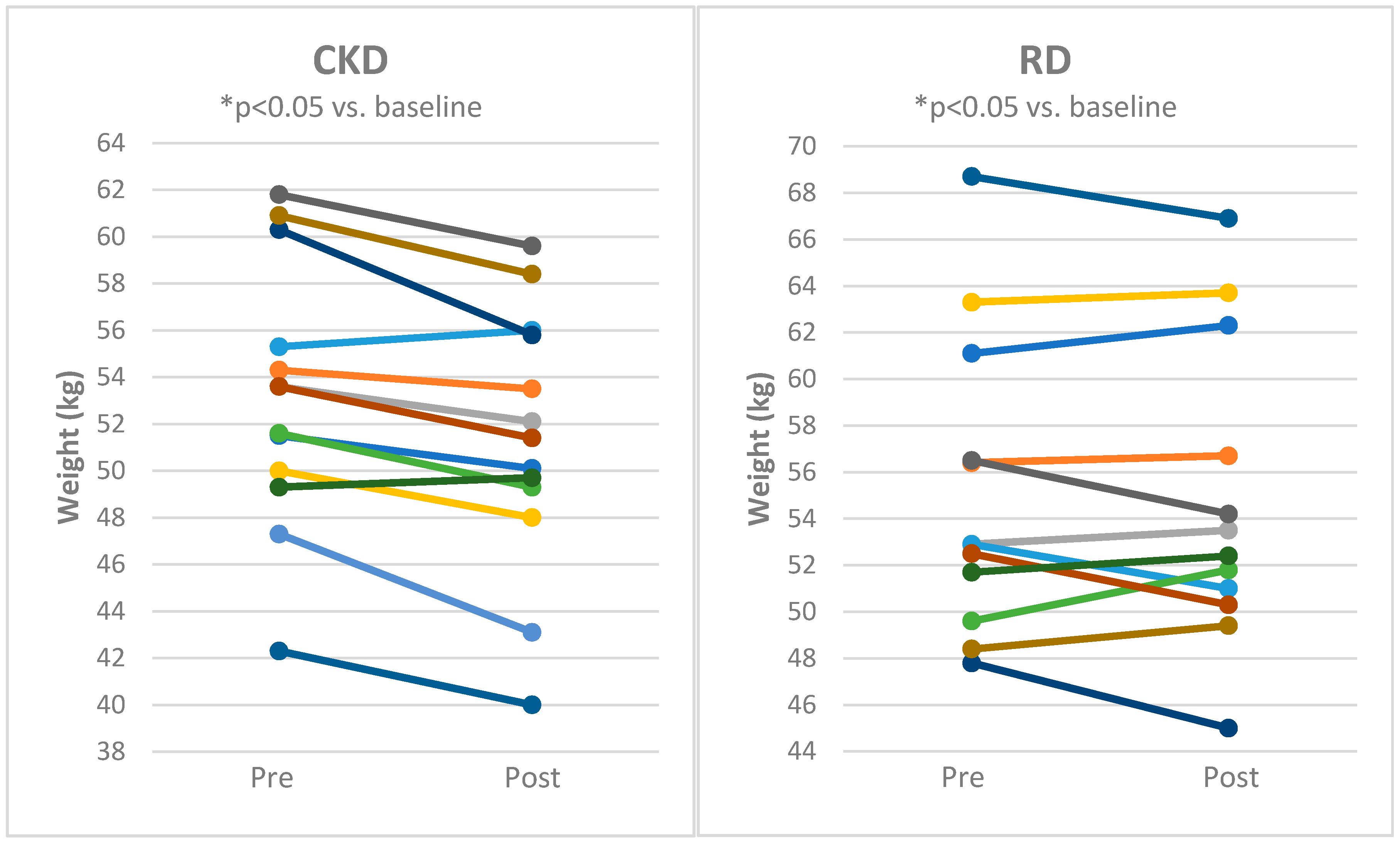
3.1. The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters
3.2. The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Muscle Strength Parameters
3.3. The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Spiroergometric Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mozaffarian, D. Dietary and Policy Priorities for Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Obesity: A Comprehensive Review. Circulation 2016, 133, 187–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.M.; Kiens, B.; Ivy, J.L. Carbohydrates and fat for training and recovery. J. Sports Sci. 2004, 22, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaspar, M.B.; Austin, K.; Huecker, M.; Sarav, M. Ketogenic Diet: From the Historical Records to Use in Elite Athletes. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2019, 8, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.A.; Brouns, F.; Jeukendrup, A. Strategies to enhance fat utilisation during exercise. Sports Med. 1998, 25, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilis, K.; Pilis, A.; Stec, K.; Pilis, W.; Langfort, J.; Letkiewicz, S.; Michalski, C.; Czuba, M.; Zych, M.; Chalimoniuk, M. Three-Year Chronic Consumption of Low-Carbohydrate Diet Impairs Exercise Performance and Has a Small Unfavorable Effect on Lipid Profile in Middle-Aged Men. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westman, E.C.; Feinman, R.D.; Mavropoulos, J.C.; Vernon, M.C.; Volek, J.S.; Wortman, J.A.; Yancy, W.S.; Phinney, S.D. Low-carbohydrate nutrition and metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.C.; Swart, J.; Noakes, T.D.; Smith, J.A. A Carbohydrate Ingestion Intervention in an Elite Athlete Who Follows a Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noakes, T.D.; Windt, J. Evidence that supports the prescription of low-carbohydrate high-fat diets: A narrative review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.L.; Wolfe, R.R. Physical exercise as a modulator of adaptation to low and high carbohydrate and low and high fat intakes. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53 (Suppl. 1), S112–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinckaers, P.J.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Bailey, D.; van Loon, L.J. Ketone Bodies and Exercise Performance: The Next Magic Bullet or Merely Hype? Sports Med. 2017, 47, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McSwiney, F.T.; Doyle, L.; Plews, D.J.; Zinn, C. Impact of Ketogenic Diet on Athletes: Current Insights. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2019, 10, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heatherly, A.J.; Killen, L.G.; Smith, A.F.; Waldman, H.S.; Seltmann, C.L.; Hollingsworth, A.; O’Neal, E.K. Effects of Ad libitum Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Dieting in Middle-Age Male Runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.M. Re-Examining High-Fat Diets for Sports Performance: Did We Call the “Nail in the Coffin” Too Soon? Sports Med. 2015, 45 (Suppl. 1), S33–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, W.K.; Carey, A.L.; Burke, L.; Spriet, L.L.; Hawley, J.A. Fat adaptation in well-trained athletes: Effects on cell metabolism. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 36, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, S.D.; Bistrian, B.R.; Evans, W.J.; Gervino, E.; Blackburn, G.L. The human metabolic response to chronic ketosis without caloric restriction: Preservation of submaximal exercise capability with reduced carbohydrate oxidation. Metabolism 1983, 32, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.P.; Hennessy, E. A review of the ketogenic diet for endurance athletes: Performance enhancer or placebo effect? J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.A.; Burke, L.M.; Phillips, S.M.; Spriet, L.L. Nutritional modulation of training-induced skeletal muscle adaptations. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 110, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Huang, Q.; Tominaga, T.; Liu, C.; Suzuki, K. An 8-Week Ketogenic Diet Alternated Interleukin-6, Ketolytic and Lipolytic Gene Expression, and Enhanced Exercise Capacity in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolla, A.M.; Caretto, A.; Laurenzi, A.; Scavini, M.; Piemonti, L. Low-Carb and Ketogenic Diets in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazzano, L.A.; Hu, T.; Reynolds, K.; Yao, L.; Bunol, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.S.; Klag, M.J.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Effects of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 161, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.; Unwin, D.; Finucane, F. Low-Carbohydrate Diets in the Management of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: A Review from Clinicians Using the Approach in Practice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouns, F. Overweight and diabetes prevention: Is a low-carbohydrate-high-fat diet recommendable? Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, D.; Schaitel, K.; Pennefather, A.; Gernigon, M.; Keiller, D.; Barnes, R. The incidence of plateau at VO(2max) is affected by a bout of prior-priming exercise. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2012, 32, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merra, G.; Miranda, R.; Barrucco, S.; Gualtieri, P.; Mazza, M.; Moriconi, E.; Marchetti, M.; Chang, T.F.; De Lorenzo, A.; Di Renzo, L. Very-low-calorie ketogenic diet with aminoacid supplement versus very low restricted-calorie diet for preserving muscle mass during weight loss: A pilot double-blind study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol Sci. 2016, 20, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moreno, B.; Bellido, D.; Sajoux, I.; Goday, A.; Saavedra, D.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F. Comparison of a very low-calorie-ketogenic diet with a standard low-calorie diet in the treatment of obesity. Endocrine 2014, 47, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissiou, M.; Borkoles, E.; Kobayashi, K.; Polman, R. The Effect of an 8 Week Prescribed Exercise and Low-Carbohydrate Diet on Cardiorespiratory Fitness, Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Obese Individuals: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vargas, S.; Romance, R.; Petro, J.L.; Bonilla, D.A.; Galancho, I.; Espinar, S.; Kreider, R.B.; Benitez-Porres, J. Efficacy of ketogenic diet on body composition during resistance training in trained men: A randomized controlled trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greene, D.A.; Varley, B.J.; Hartwig, T.B.; Chapman, P.; Rigney, M. A Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet Reduces Body Mass Without Compromising Performance in Powerlifting and Olympic Weightlifting Athletes. J. Strength Cond Res. 2018, 32, 3373–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Lowery, R.P.; Roberts, M.D.; Sharp, M.H.; Joy, J.M.; Shields, K.A.; Partl, J.; Volek, J.S.; D’Agostino, D. The Effects of Ketogenic Dieting on Body Composition, Strength, Power, and Hormonal Profiles in Resistance Training Males. J. Strength Cond Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kephart, W.C.; Pledge, C.D.; Roberson, P.A.; Mumford, P.W.; Romero, M.A.; Mobley, C.B.; Martin, J.S.; Young, K.C.; Lowery, R.P.; Wilson, J.M.; et al. The Three-Month Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Blood Parameters, and Performance Metrics in CrossFit Trainees: A Pilot Study. Sports 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McSwiney, F.T.; Wardrop, B.; Hyde, P.N.; Lafountain, R.A.; Volek, J.S.; Doyle, L. Keto-adaptation enhances exercise performance and body composition responses to training in endurance athletes. Metabolism 2018, 81, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubini, A.; Bosco, G.; Lodi, A.; Cenci, L.; Parmagnani, A.; Grimaldi, K.; Zhongjin, Y.; Paoli, A. Effects of Twenty Days of the Ketogenic Diet on Metabolic and Respiratory Parameters in Healthy Subjects. Lung 2015, 193, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burke, L.M.; Ross, M.L.; Garvican-Lewis, L.A.; Welvaert, M.; Heikura, I.A.; Forbes, S.G.; Mirtschin, J.G.; Cato, L.E.; Strobel, N.; Sharma, A.P.; et al. Low carbohydrate, high fat diet impairs exercise economy and negates the performance benefit from intensified training in elite race walkers. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2785–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burke, L.M.; Sharma, A.P.; Heikura, I.A.; Forbes, S.F.; Holloway, M.; McKay, A.K.A.; Bone, J.L.; Leckey, J.J.; Welvaert, M.; Ross, M.L. Crisis of confidence averted: Impairment of exercise economy and performance in elite race walkers by ketogenic low carbohydrate, high fat (LCHF) diet is reproducible. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, S.D.; Horton, E.S.; Sims, E.A.; Hanson, J.S.; Danforth, E., Jr.; LaGrange, B.M. Capacity for moderate exercise in obese subjects after adaptation to a hypocaloric, ketogenic diet. J. Clin. Invest. 1980, 66, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K.L.; Holcomb, L.E.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr. Ketogenic Diets and Exercise Performance. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, B.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise metabolism and the molecular regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, M.; Cogan, K.E.; Egan, B. Metabolism of ketone bodies during exercise and training: Physiological basis for exogenous supplementation. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2857–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD) | Reduction Diet (RD) | ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1-before | V2-after | V1-before | V2-after | ||
| Number (n) | 13 | 13 | 12 | 12 | |
| Age (year) | 23 ± 5 | NA | 24 ± 4 | NA | NS |
| Height (cm) | 181 ± 6 | NA | 186 ± 10 | NA | NS |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.1 ± 3.7 | 24.6 ± 3.3 * | 26.9 ± 4.3 | 25.5 ± 4.2 * | NS |
| WEIGHT (kg) | 85.6 ± 13.4 | 81.0 ± 12.0 * | 93.0 ± 17.5 | 88.5 ± 17.4 * | NS |
| MUSCLES (kg) | 41.8 ± 4.5 | 40.0 ± 4.6 * | 43.5 ± 5.3 | 43.1 ± 5.3 | NS |
| FAT (kg) | 12.9 ± 6.9 | 11.0 ± 5.8 * | 17.6 ± 9.8 | 13.6 ± 9.0 * | NS |
| % FAT | 14.5 ± 5.5 | 13.0 ± 5.1 * | 17.9 ± 6.9 | 14.2 ± 6.9 * | NS |
| WATER (kg) | 53.2 ± 5.6 | 51.0 ± 5.6 * | 55.1 ± 6.4 | 54.8 ± 6.5 | NS |
| CK (ukat/L) | 4.40 ± 2.81 | 2.81 ± 1.21 | 3.80 ± 2.03 | 3.03 ± 2.03 | NS |
| LDH (ukat/L) | 2.68 ± 0.60 | 2.47 ± 0.42 | 2.74 ± 0.44 | 2.55 ± 0.33 | NS |
| β-OH-butyrate (mmol/L) | 0.2 ± 0.07 | 0.38 ± 0.25 * | 0.24 ± 0.12 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | NS |
| Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD) | Reduction Diet (RD) | ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1-before | V2-after | V1-before | V2-after | ||
| Bench press (BP) | 90.0 ± 24.2 | 90.0 ± 23.7 | 84.2 ± 21.8 | 87.7 ± 20.1 | NS |
| Lat pull-down (LPD) | 74.2 ± 15.7 | 76.0 ± 15.0 | 70.4 ± 14.8 | 75.2 ± 17.1 * | NS |
| Leg press (LP) | 138.0 ± 21.1 | 142.0 ± 16.3 | 127.8 ± 22.0 | 140 ± 22.8 * | NS |
| Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD) | Reduction Diet (RD) | ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1-before | V2-after | V1-before | V2-after | ||
| TFmax | 180.9 ± 10.2 | 178.0 ± 11.3 | 178.9 ± 11.8 | 179.0 ± 10.2 | NS |
| Rmax | 1.27 ± 0.08 | 1.2 ± 0.12 * | 1.21 ± 0.04 | 1.16 ± 0.10 | 0.04 |
| Wmax | 297.0 ± 48.5 | 298.0 ± 54.3 | 282.1 ± 34.3 | 296.0 ± 35.9 * | NS |
| VEmax | 121.0 ± 28.5 | 136.0 ± 30.0 | 113.2 ± 20.3 | 124.0 ± 21.3 | NS |
| VO2max/kg | 40.2 ± 4.1 | 43.0 ± 5.4 | 35.2 ± 6.0 | 38.2 ± 6.3 * | 0.007 |
| VO2max/TF | 19.0 ± 3.3 | 20.0 ± 3.4 | 18.0 ± 1.9 | 18.9 ± 1.6 | NS |
| Wmax/kg | 3.53 ± 0.42 | 3.6 ± 0.39 | 3.13 ± 0.52 | 3.36 ± 0.59 * | NS |
| W170max/kg | 3.27 ± 0.65 | 3.4 ± 0.37 | 2.8 ± 0.74 | 3.06 ± 0.83 * | NS |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kysel, P.; Haluzíková, D.; Doležalová, R.P.; Laňková, I.; Lacinová, Z.; Kasperová, B.J.; Trnovská, J.; Hrádková, V.; Mráz, M.; Vilikus, Z.; et al. The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Body Composition, Strength, and Endurance Performance in Healthy Young Males: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092832
Kysel P, Haluzíková D, Doležalová RP, Laňková I, Lacinová Z, Kasperová BJ, Trnovská J, Hrádková V, Mráz M, Vilikus Z, et al. The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Body Composition, Strength, and Endurance Performance in Healthy Young Males: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092832
Chicago/Turabian StyleKysel, Pavel, Denisa Haluzíková, Radka Petráková Doležalová, Ivana Laňková, Zdeňka Lacinová, Barbora Judita Kasperová, Jaroslava Trnovská, Viktorie Hrádková, Miloš Mráz, Zdeněk Vilikus, and et al. 2020. "The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Body Composition, Strength, and Endurance Performance in Healthy Young Males: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092832
APA StyleKysel, P., Haluzíková, D., Doležalová, R. P., Laňková, I., Lacinová, Z., Kasperová, B. J., Trnovská, J., Hrádková, V., Mráz, M., Vilikus, Z., & Haluzík, M. (2020). The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Body Composition, Strength, and Endurance Performance in Healthy Young Males: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 12(9), 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092832





