A National e-Health Program for the Prevention and Management of Overweight and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence in Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
2.3. Assessment and Interventions
2.4. Assays
2.5. Statistical Analyses
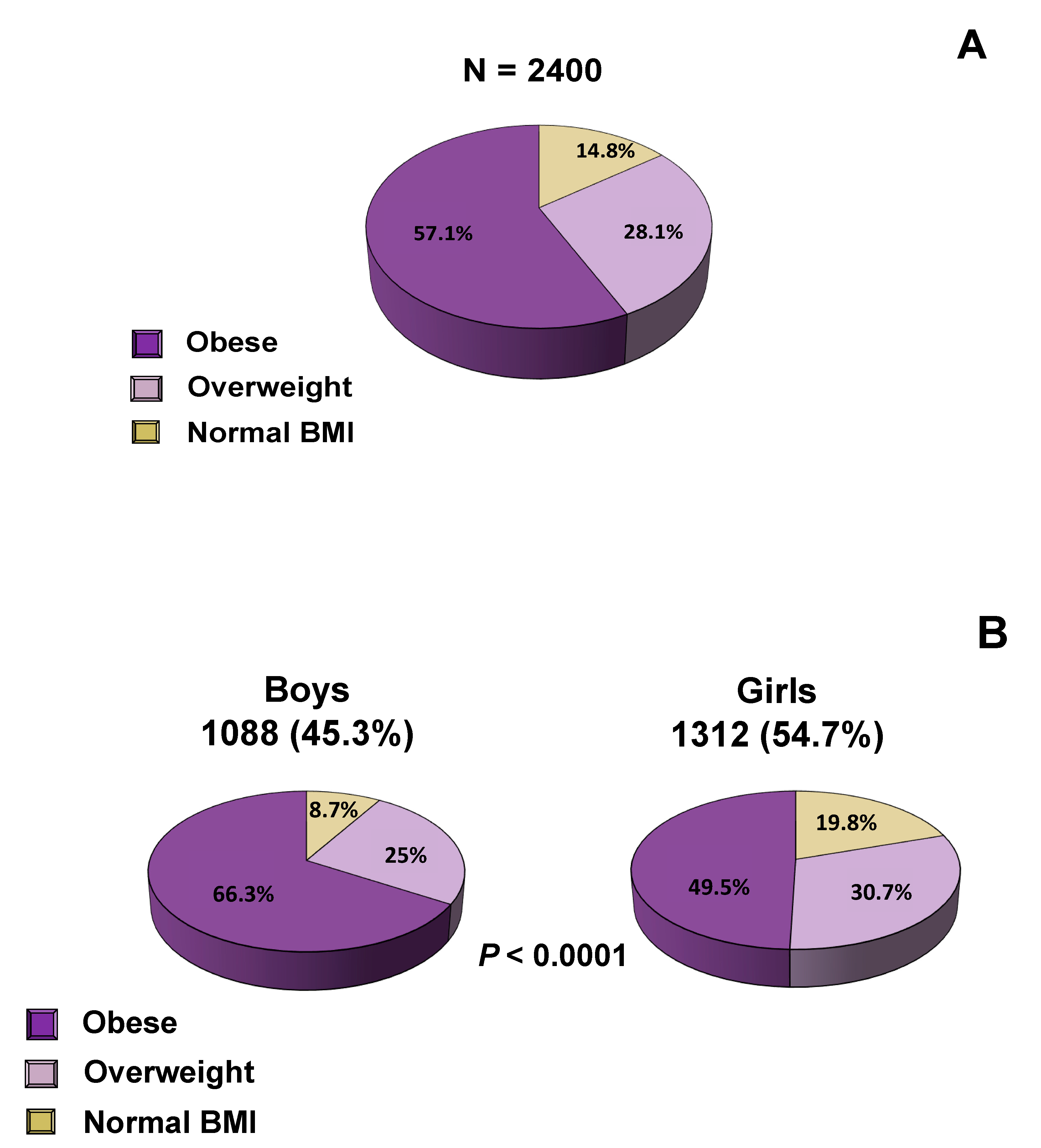
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight. Fact Sheet N°311. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Lobstein, T.; Jackson-Leach, R.; Moodie, M.L.; Hall, K.D.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Swinburn, B.A.; James, W.P.; Wang, Y.; McPherson, K. Child and adolescent obesity: Part of a bigger picture. Lancet 2015, 385, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Childhood Overweight and Obesity. 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/childhood/en/ (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Brug, J.; van Stralen, M.M.; Chinapaw, M.J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Lien, N.; Bere, E.; Singh, A.S.; Maes, L.; Moreno, L.; Jan, N.; et al. Differences in weight status and energy-balance related behaviours according to ethnic background among adolescents in seven countries in Europe: The ENERGY-project. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.; Oliveira, T.; Fernandes, R. Biochemistry of adipose tissue: An endocrine organ. Arch. Med Sci. AMS 2013, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Güngör, N.K. Overweight and obesity in children and adolescents. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2014, 6, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, M.; Martos, R.; Gascón, F.; Cañete, R.; Zafra, M.A.; Morales, R. Low-grade systemic inflammation, hypoadiponectinemia and a high concentration of leptin are present in very young obese children, and correlate with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2005, 31, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, A.C.; Perrin, E.M.; Moss, L.A.; Skelton, J.A. Cardiometabolic risks and severity of obesity in children and young adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerregaard, L.G.; Jensen, B.W.; Ängquist, L.; Osler, M.; Sørensen, T.I.A.; Baker, J.L. Change in overweight from childhood to early adulthood and risk of type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geserick, M.; Vogel, M.; Gausche, R.; Lipek, T.; Spielau, U.; Keller, E.; Pfäffle, R.; Kiess, W.; Körner, A. Acceleration of BMI in early childhood and risk of sustained obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.C.; Lawlor, D.A.; Kimm, S.Y.S. Childhood obesity. Lancet 2010, 375, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, R.; Sawers, C.; Thompson, F.; Manyika, J.; Woetzel, J.; Child, P.; McKenna, S.; Spatharou, A. Overcoming Obesity: An Initial Economic Analysis; McKinsey Global Institute: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014; pp. 1–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kassari, P.; Papaioannou, P.; Billiris, A.; Karanikas, H.; Eleftheriou, S.; Thireos, E.; Manios, Y.; Chrousos, G.P.; Charmandari, E. Electronic registry for the management of childhood obesity in Greece. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genitsaridi, S.M.; Giannios, C.; Karampatsou, S.; Papageorgiou, I.; Papadopoulos, G.; Farakla, I.; Koui, E.; Georgiou, A.; Romas, S.; Terzioglou, E.; et al. A comprehensive multidisciplinary management plan is effective in reducing the prevalence of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2020, 93, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragomalou, A.; Moschonis, G.; Manios, Y.; Kassari, P.; Ioakimidis, I.; Diou, C.; Stefanopoylos, L.; Lekka, E.; Maglaveras, N.; Delopoulos, A.; et al. Novel e-health applications for the management of cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents in Greece. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, J.M.; Ingwersen, L.A.; Moshfegh, A.J. Accuracy of dietary recall using the USDA five-step multiple-pass method in men: An observational validation study. J. Am. Diet Assoc. 2004, 104, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA. Choose My Plate, US Department of Agriculture. Available online: https://www.choosemyplate.gov/about-us (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- National Dietary Guidelines for Infants, Children and Adolescents. Ten Steps to Healthy Eating for Children and Adolescents. Available online: http://www.diatrofikoiodigoi.gr/?Page=summary-children (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Kumanyika, S.K. Environmental influences on childhood obesity: Ethnic and cultural influences in context. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; Ferranti, S.D.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Foramn, D.E.; et al. Guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: A report of the American College of cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 73, 3168–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, G.; De Simone, M.; Iughetti, L.; Rosato, T.; Iezzi, M.L.; Marinucci, M.C.; Cofini, V.; Croce, G.; Passacquale, G.; Necozione, S.; et al. Early activation of vascular endothelial cells and platelets in obese children. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 3145–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tounian, P.; Aggoun, Y.; Dubern, B.; Varille, V.; Guy-Grand, B.; Sidi, D.; Girardet, J.P.; Bonnet, D. Presence of increased stiffness of the common carotid artery and endothelial dysfunction in severely obese children: A prospective study. Lancet 2001, 358, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, J.S.; Kytö, V.; Juonala, M.; Viikari, J.S.A.; Nevalainen, J.; Kähönen, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Laitinen, T.; Tossavainen, P.; et al. Childhood risk factors and carotid atherosclerotic plaque in adulthood: The cardiovascular risk in young finns study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 293, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskinen, M.R.; Barter, P.J.; Ehnholm, C.; Sullivan, D.R.; Mann, K.; Simes, J.; Best, J.D.; Hamwood, S.; Keech, A.C.; FIELD Study Investigators. Ability of traditional lipid ratios and apolipoprotein ratios to predict cardiovascular risk in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Hou, D.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, H.; Mi, J. Independent influences of excessive body weight and elevated blood pressure from childhood on left ventricular geometric remodeling in adulthood. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 243, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-C.; Sun, D.; Cen, R.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Fernandez-Alonso, C.; Chen, W.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S. Impact of long-term burden of excessive adiposity and elevated blood pressure from childhood on adulthood left ventricular remodeling patterns: The bogalusa heart study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1580–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forsythe, L.K.; Wallace, J.M.W.; Livingstone, M.B. Obesity and inflammation: The effects of weight loss. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2008, 21, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, C.; Couture, P.; Desroches, S.; Lamarche, B. Effect of the mediterranean diet with and without weight loss on markers of inflammation in men with metabolic syndrome. Obesity 2013, 21, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcicki, J.M.; Heyman, M.B. Let’s Move—Childhood obesity prevention from pregnancy and infancy onward. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1457–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Min, J.; Khuri, J.; Li, M. A systematic examination of the association between parental and child obesity across countries. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 15, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, V.; Jacobsson, J.A.; Fredriksson, R.; Danielsson, P.; Sobko, T.; Schiöth, H.B.; Marcus, C. Associations between severity of obesity in childhood and adolescence, obesity onset and parental BMI: A longitudinal cohort study. Int. J. Obes. Lond. 2011, 35, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Suzuki, M. Parental obesity and overweight affect the body-fat accumulation in the offspring: The possible effect of a high-fat diet through epigenetic inheritance. Obes. Rev. 2006, 7, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lim, I.Y.; Wu, Y.; Teh, A.L.; Chen, L.; Aris, I.M.; Soh, S.E.; Tint, M.T.; MacIsaac, J.L.; Morin, A.M.; et al. Developmental pathways to adiposity begin before birth are influenced by genotype, prenatal environment and epigenome. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dick, K.J.; Nelson, C.P.; Tsaprouni, L.; Sandling, J.K.; Ssi, D.A.; Wahl, S.; Meduri, E.; Morange, P.-E.; Gagnon, F.; Grallert, H.; et al. DNA methylation and body-mass index: A genome-wide analysis. Lancet 2014, 383, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapuano, K.M.; Zieselman, A.L.; Kelley, W.M.; Sargent, J.D.; Heatherton, T.F.; Gilbert-Diamond, D. Genetic risk for obesity predicts nucleus accumbens size and responsivity to real-world food cues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Obesity | Overweight | Normal-BMI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 10.10 ± 0.09 | 10.20 ± 0.11 | 9.80 ± 0.16 | 0.147 |
| Weight (Kg) | 62.78 ± 0.65 | 49.41 ± 0.54 | 38.79 ± 0.73 | <0.0001 |
| Height (cm) | 144.47 ± 0.52 | 143.43 ± 0.58 | 139.03 ± 0.94 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.70 ± 0.14 | 23.40 ± 0.09 | 19.31 ± 0.16 | <0.0001 |
| Waist/Hip ratio | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | <0.0001 |
| Waist/Height | 0.61 ± 0.003 | 0.55 ± 0.003 | 0.51 ± 0.005 | <0.0001 |
| SBP | 114 ± 0.39 | 110 ± 0.45 | 105 ± 0.62 | <0.0001 |
| DBP | 67 ± 0.32 | 66 ± 0.75 | 63 ± 0.50 | <0.0001 |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Pubertal status | ||||
| Prepubertal | 732 (57.1) | 367 (28.6) | 183 (14.3) | 0.829 |
| Pubertal | 599 (57) | 294 (27.9) | 159 (15.1) | |
| Mother’s BMI | ||||
| Normal BMI | 300 (41.7) | 249 (34.6) | 170 (23.6) | <0.0001 |
| Overweight | 331 (61) | 142 (26.2) | 70 (12.9) | |
| Obesity | 367 (69.4) | 109 (20.6) | 53 (10) | |
| Father’s BMI | ||||
| Normal BMI | 147 (41.2) | 124 (34.7) | 86 (24.1) | <0.0001 |
| Overweight | 388 (53.2) | 228 (31.3) | 113 (15.5) | |
| Obesity | 455 (65.8) | 149 (21.5) | 88 (12.7) |
| Obesity | Overweight | Normal-BMI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 11.20 ± 0.16 | 10.96 ± 0.14 | 11.18 ± 0.20 | 0.345 |
| Weight (Kg) | 68 ± 1.15 | 53.60 ± 0.77 | 45 ± 0.85 | <0.0001 |
| Height (cm) | 150.47 ± 0.87 | 149.11 ± 0.80 | 147 ± 1.04 | 0.008 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.87 ± 0.24 | 23.53 ± 0.12 | 20.37 ± 0.17 | <0.0001 |
| Waist/Hip ratio | 0.93 ± 0.005 | 0.91 ± 0.005 | 0.86 ± 0.007 | <0.0001 |
| Waist/Height | 0.60 ± 0.004 | 0.53 ± 0.003 | 0.49 ± 0.005 | <0.0001 |
| SBP | 115 ± 0.79 | 111 ± 0.66 | 107 ± 0.85 | <0.0001 |
| DBP | 69 ± 0.62 | 67 ± 0.59 | 65 ± 0.69 | <0.0001 |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Pubertal status | ||||
| Prepubertal | 107 (42.3) | 103 (40.7) | 43 (17) | 0.043 |
| Pubertal | 165 (38.6) | 155 (36.2) | 108 (25.2) | |
| Mother’s BMI | ||||
| Normal BMI | 88 (29.6) | 118 (39.7) | 91 (30.6) | <0.0001 |
| Overweight | 95 (42.2) | 84 (37.3) | 46 (20.4) | |
| Obesity | 136 (53.8) | 89 (35.2) | 28 (11.1) | |
| Father’s BMI | ||||
| Normal BMI | 41 (27.3) | 59 (39.3) | 50 (33.3) | <0.0001 |
| Overweight | 117 (37) | 126 (39.9) | 73 (23.1) | |
| Obesity | 157 (52.3) | 104 (34.7) | 39 (13) |
| Obesity | Overweight | Normal-BMI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 80.20 ± 0.28 | 78.72 ± 0.34 | 79.11 ± 0.43 | 0.003 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 157.11 ± 0.81 | 158.45 ± 1.17 | 159.71 ± 1.53 | 0.290 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 82.38 ± 1.28 | 73.99 ± 1.77 | 64.35 ± 1.79 | <0.0001 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 50.05 ± 0.36 | 53.67 ± 0.53 | 59.51 ± 0.87 | <0.0001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 91.76 ± 0.72 | 90.96 ± 1.04 | 87.60 ± 1.32 | 0.015 |
| ApoA1 (mg/dL) | 138.86 ± 0.62 | 142.86 ± 0.89 | 149.76 ± 1.33 | <0.0001 |
| ApoB (mg/dL) | 75.93 ± 0.53 | 73.69 ± 0.77 | 71.52 ± 0.88 | <0.0001 |
| Lp(a) (mg/dL) | 17.46 ± 0.68 | 17.02 ± 0.97 | 17.98 ± 1.42 | 0.874 |
| IGF-I (ng/mL) | 301.87 ± 5.10 | 306.64 ± 7.1 | 305.73 ± 10.66 | 0.517 |
| IGFBP-3 (μg/mL) | 5.09 ± 0.03 | 5.01 ± 0.04 | 4.82 ± 0.07 | 0.001 |
| Insulin (μUI/mL) | 17.39 ± 0.32 | 12.50 ± 0.29 | 9.45 ± 0.34 | <0.0001 |
| HbA1C (%) | 5.26 ± 0.01 | 5.21 ± 0.01 | 5.18 ± 0.01 | <0.0001 |
| Obesity | Overweight | Normal-BMI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol (≥200 mg/dL) | 213.98 ± 1.72 | 218.54 ± 3.15 | 218.63 ± 3.76 | 0.297 |
| LDL (≥130 mg/dL) | 146.66 ± 2.34 | 146.47 ± 3.45 | 141.31 ± 4.26 | 0.598 |
| ApoB (≥110 mg/dL) | 124.69 ± 2.08 | 129.94 ± 4.87 | 117 ± 5.13 | 0.400 |
| Triglycerides | ||||
| 0–9 age (≥100 mg/dL) | 133.95 ± 4.30 | 146.62 ± 8.87 | 123.29 ± 8.11 | 0.496 |
| 10–19age (≥30 mg/dL) | 176.60 ± 5.73 | 180.55 ± 12.96 | 159.67 ± 14.82 | 0.152 |
| HDL (<40 mg/dL) | 35.04 ± 0.25 | 35.53 ± 0.43 | 34.23 ± 0.96 | 0.340 |
| ApoA1 (<115 mg/dL) | 104.93 ± 0.88 | 107.49 ± 0.98 | 105.07 ± 2.24 | 0.241 |
| Lp(a) (>30 mg/dL) | 57.23 ± 1.71 | 61.21 ± 2.74 | 61.97 ± 3.77 | 0.327 |
| Initial Assessment (Mean ± SEM) | Annual Assessment (Mean ± SEM) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 80.11 ± 0.36 | 80.54 ± 0.10 | 0.269 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 158.57 ± 1.21 | 157.36 ± 1.38 | 0.056 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 82.36 ± 1.81 | 81.07 ± 1.84 | 0.657 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 50.23 ± 0.53 | 53.28 ± 0.60 | <0.0001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 92.39 ± 1.05 | 89.37 ± 1.14 | <0.0001 |
| ApoA1 (mg/dL) | 140.55 ± 0.96 | 141.60 ± 1.03 | 0.163 |
| ApoB (mg/dL) | 75.59 ± 0.91 | 73.48 ± 0.78 | <0.0001 |
| Lp(a) (mg/dL) | 16.45 ± 0.99 | 15.29 ± 1.05 | 0.031 |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 20,705.41 ± 1203.62 | 23,115.45 ± 1239.64 | 0.008 |
| Insulin (μUI/mL) | 17.52 ± 0.50 | 16.53 ± 0.42 | 0.321 |
| HbA1C (%) | 5.28 ± 0.01 | 5.24 ± 0.01 | <0.0001 |
| Initial Assessment (Mean ± SEM) | Annual Assessment (Mean ± SEM) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 78.05 ± 0.51 | 80.55 ± 0.50 | <0.0001 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 157.96 ± 1.76 | 156.91 ± 1.87 | 0.442 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 73.49 ± 2.64 | 74.63 ± 2.68 | 0.258 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 54.94 ± 3.16 | 55.79 ± 0.85 | <0.0001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 90.52 ± 1.55 | 87.50 ± 1.87 | <0.0001 |
| ApoA1 (mg/dL) | 140.72 ± 1.40 | 143.15 ± 1.35 | 0.087 |
| ApoB (mg/dL) | 73.61 ± 1.23 | 71.19 ± 1.11 | 0.042 |
| Lp(a) (mg/dL) | 14.55 ± 1.26 | 14.18 ± 1.38 | 0.026 |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 24,436.87 ± 1865.23 | 29,474.32 ± 2110.22 | 0.004 |
| Insulin (μUI/mL) | 12.08 ± 0.40 | 13.14 ± 0.46 | 0.006 |
| HbA1C (%) | 5.23 ± 0.01 | 5.21 ± 0.02 | 0.018 |
| Initial Assessment (Mean ± SEM) | Annual Assessment (Mean ± SEM) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 78.15 ± 0.73 | 79.06 ± 0.63 | 0.052 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 161.45 ± 2.66 | 158.11 ± 2.66 | 0.020 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 67.23 ± 3.15 | 69.27 ± 3.88 | 0.918 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 57.89 ± 1.32 | 60.68 ± 1.49 | 0.002 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 90.04 ± 2.26 | 83.76 ± 2.22 | <0.0001 |
| ApoA1 (mg/dL) | 148.97 ± 2.02 | 147.79 ± 2.12 | 0.575 |
| ApoB (mg/dL) | 71.13 ± 1.42 | 69.43 ± 1.50 | 0.167 |
| Lp(a) (mg/dL) | 14.71 ± 1.89 | 15.90 ± 2.10 | 0.042 |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 18,555.65 ± 2867.98 | 27,270.78 ± 3133.59 | 0.002 |
| Insulin (μUI/mL) | 12.08 ± 0.40 | 13.14 ± 0.46 | 0.006 |
| HbA1C (%) | 5.23 ± 0.01 | 5.21 ± 0.02 | 0.018 |
| Initial Assessment | Annual Assessment | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol (≥200mg/dL) | 221.23 ± 3.01 | 202.06 ± 4.22 | <0.0001 |
| LDL (≥130mg/dL) | 142.33 ± 2 | 122.17 ± 3.02 | <0.0001 |
| ApoB (≥110 mg/dL) | 130.16 ± 3.17 | 97.87 ± 4.61 | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides | |||
| 0–9 age (≥100 mg/dL) | 130.60 ± 4.83 | 100.79 ± 5.70 | <0.0001 |
| 10–19 age (≥130 mg/dL) | 174.68 ± 5.68 | 125.34 ± 7.77 | <0.0001 |
| HDL (<40 mg/dL) | 35.39 ± 0.30 | 41.61 ± 0.74 | <0.0001 |
| ApoA1 (<115 mg/dL) | 95.36 ± 7.70 | 99.36 ± 1.59 | 0.629 |
| Lp(a) (>30 mg/dL) | 58.77 ± 2.09 | 57.68 ± 2.90 | 0.113 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tragomalou, A.; Moschonis, G.; Kassari, P.; Papageorgiou, I.; Genitsaridi, S.-M.; Karampatsou, S.; Manios, Y.; Charmandari, E. A National e-Health Program for the Prevention and Management of Overweight and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence in Greece. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092858
Tragomalou A, Moschonis G, Kassari P, Papageorgiou I, Genitsaridi S-M, Karampatsou S, Manios Y, Charmandari E. A National e-Health Program for the Prevention and Management of Overweight and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence in Greece. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092858
Chicago/Turabian StyleTragomalou, Athanasia, George Moschonis, Penio Kassari, Ifigeneia Papageorgiou, Sofia-Maria Genitsaridi, Sofia Karampatsou, Yannis Manios, and Evangelia Charmandari. 2020. "A National e-Health Program for the Prevention and Management of Overweight and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence in Greece" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092858
APA StyleTragomalou, A., Moschonis, G., Kassari, P., Papageorgiou, I., Genitsaridi, S.-M., Karampatsou, S., Manios, Y., & Charmandari, E. (2020). A National e-Health Program for the Prevention and Management of Overweight and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence in Greece. Nutrients, 12(9), 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092858







