Ethanol Extract of Liriope platyphylla Root Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice via Regulation of Lipogenesis and Lipid Uptake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. LPE Preparation
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Serum Biochemical Analyses
2.4. Histological Staining and NAFLD Activity Score (NAS)
2.5. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Measurement of Hepatic Triglyceride from Liver Tissue and HepG2 Cells
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
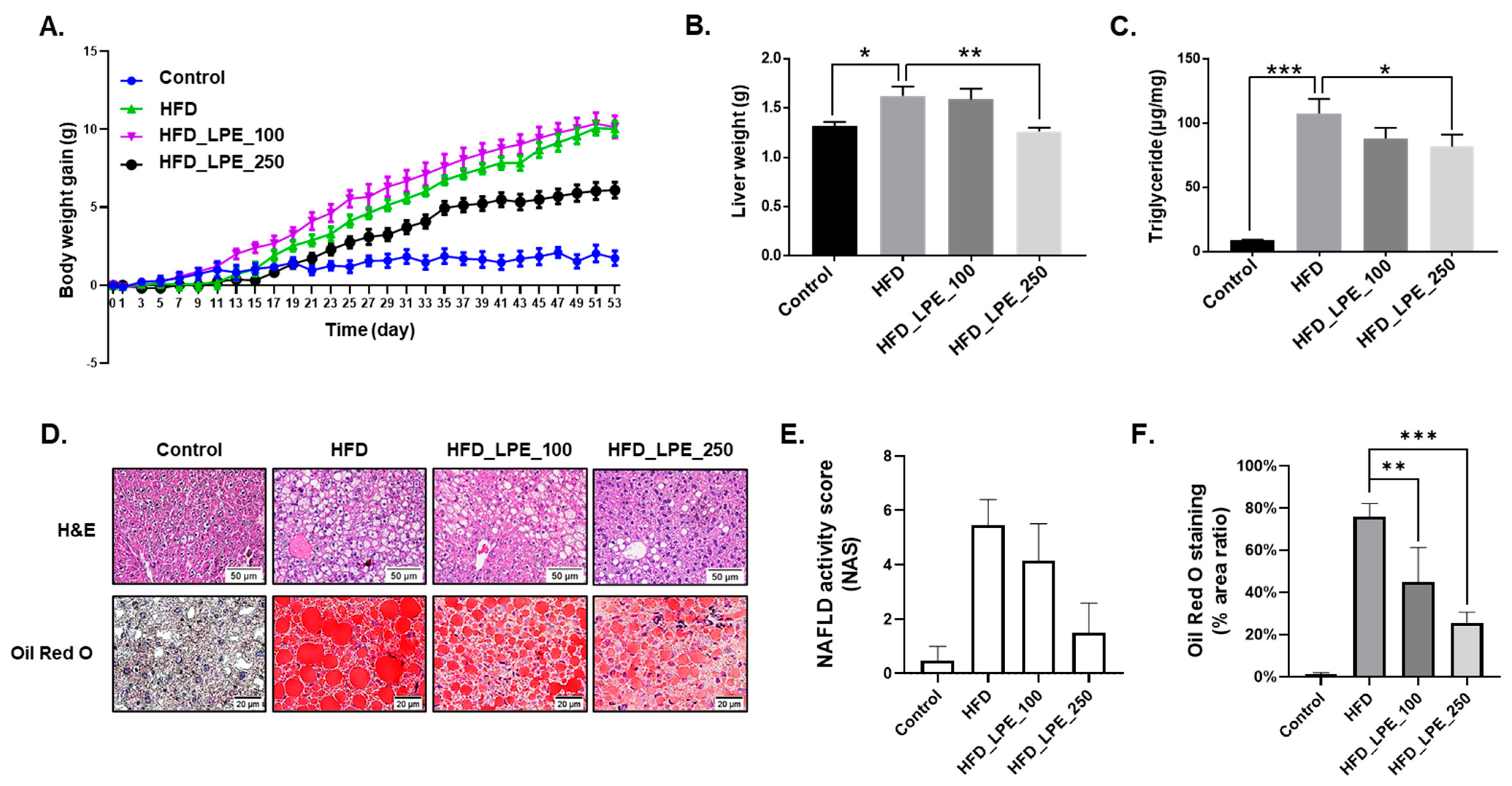
3.1. LPE Treatment Decreased Body Weight Gain and Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
3.2. LPE Treatment Improved Liver Injury and Serum Lipid Levels in HFD Mice
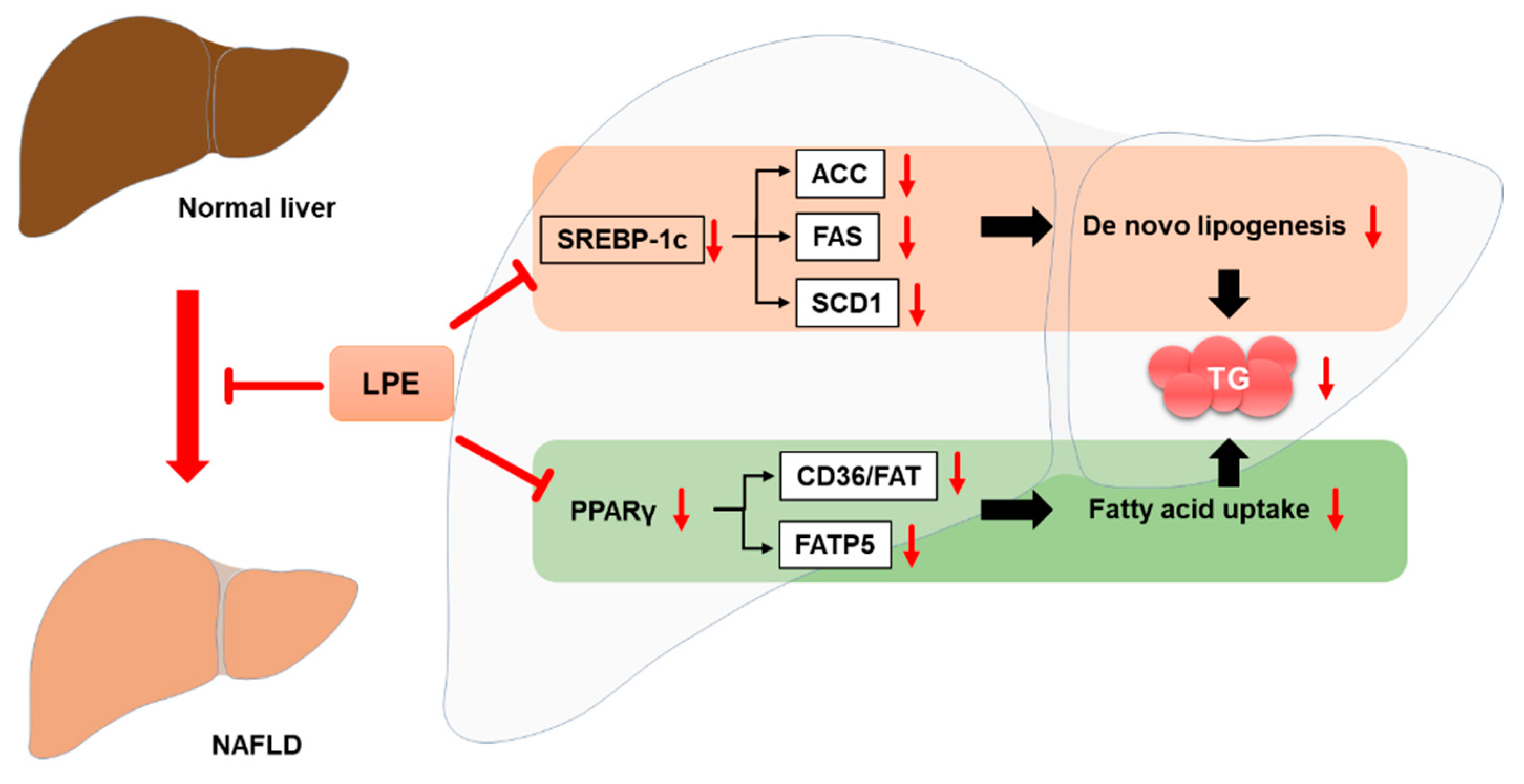
3.3. LPE Treatment Decreased the Expression of Proteins Involved in Lipogenesis in the Livers of HFD-Fed Mice
3.4. LPE Treatment Decreased the Expression of Proteins Involved in Fatty Acid Uptake in the Livers of HFD-Fed Mice
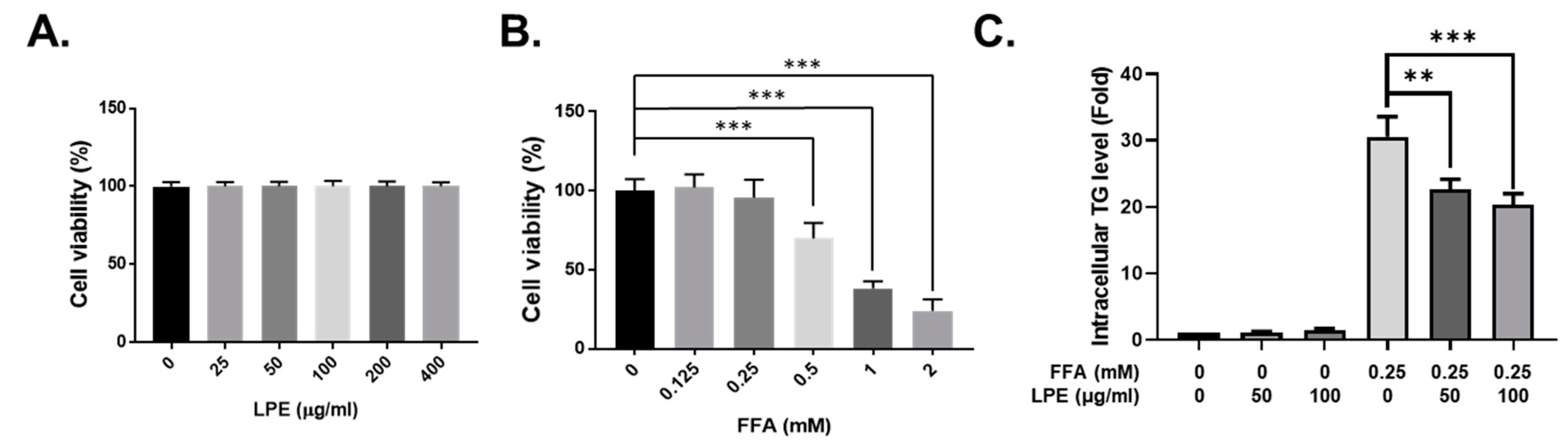
3.5. LPE Treatment Decreased TG Accumulation in FFA-Treated HepG2 Cells
3.6. LPE Treatment Decreased the Expression of Proteins Involved in Lipogenesis in FFA-Treated HepG2 Cells
3.7. LPE Treatment Decreased the Expression of Proteins Involved in Fatty Acid Uptake in FFA-Treated HepG2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.Q.; El-Serag, H.B.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of nafld-related hcc: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazel, Y.; Koenig, A.B.; Sayiner, M.; Goodman, Z.D.; Younossi, Z.M. Epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2016, 65, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of nafld development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappachan, J.M.; Babu, S.; Krishnan, B.; Ravindran, N.C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A clinical update. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.L.; Xie, L.Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, G.Q.; Grant, S.J.; Liu, J.P. Herbal medicines for fatty liver diseases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 8, CD009059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2019, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.; Younossi, Z.M. Treatment options for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2010, 3, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld). Metab. Clin. Exp. 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Allison, M.; Griffin, J.L.; Vidal-Puig, A. Fatty acid and glucose sensors in hepatic lipid metabolism: Implications in nafld. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 250–261. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, J.E.; Ramos-Roman, M.A.; Browning, J.D.; Parks, E.J. Increased de novo lipogenesis is a distinct characteristic of individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3313–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimano, H.; Horton, J.D.; Shimomura, I.; Hammer, R.E.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Isoform 1c of sterol regulatory element binding protein is less active than isoform 1a in livers of transgenic mice and in cultured cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Listenberger, L.L.; Han, X.; Lewis, S.E.; Cases, S.; Farese, R.V., Jr.; Ory, D.S.; Schaffer, J.E. Triglyceride accumulation protects against fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3077–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, S.H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Molecular mechanisms for the hepatic steatosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Guo, Z.; Johnson, C.M.; Hensrud, D.D.; Jensen, M.D. Splanchnic lipolysis in human obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Videla, L.A.; Pettinelli, P. Misregulation of ppar functioning and its pathogenic consequences associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in human obesity. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012, 107434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geisler, C.E.; Renquist, B.J. Hepatic lipid accumulation: Cause and consequence of dysregulated glucoregulatory hormones. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 234, R1–R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.H.; Wen, S.L.; Tong, H.; Wang, C.H.; Yang, W.J.; Tang, S.H.; Yan, Z.P.; Tai, Y.; Ye, C.; Liu, R.; et al. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 alleviates liver cirrhosis via improvement of the dysfunctional gut-liver axis in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G962–G972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hur, J.; Lee, P.; Kim, J.; Kim, A.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.Y. Induction of nerve growth factor by butanol fraction of liriope platyphylla in c6 and primary astrocyte cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.; Chae, K.; Jung, Y.S.; Rho, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Ha, J.; Yoon, K.H.; Kim, G.C.; Oh, K.S.; Shin, S.S.; et al. The korean traditional medicine gyeongshingangjeehwan inhibits obesity through the regulation of leptin and pparalpha action in oletf rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Wha, J.D.; Park, S. The insulin sensitizing effect of homoisoflavone-enriched fraction in liriope platyphylla wang et tang via pi3-kinase pathway. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 2653–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Lee, J.C.; Seo, Y.B.; Kook, Y.B. Liriopis tuber inhibit ova-induced airway inflammation and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in murine model of asthma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 101, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Hwang, I.S.; Choi, S.I.; Lee, H.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Goo, J.S.; Lee, H.S.; Son, H.J.; Jang, M.J.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Aqueous extract of liriope platyphylla, a traditional chinese medicine, significantly inhibits abdominal fat accumulation and improves glucose regulation in oletf type ii diabetes model rats. Lab. Anim. Res. 2012, 28, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, E.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, M.H.; Seo, Y.W.; Lee, J.I.; Jun, H.S. Polyphenol-rich fraction of brown alga ecklonia cava collected from gijang, korea, reduces obesity and glucose levels in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. Ecam 2012, 2012, 418912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-H.; Niu, M.-W.; Gong, S.-H.; Wu, G.-Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, F.-Z.; Wei, G.-Q.; He, Z.-K.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, P. Intestinal epithelial chemokine (c-c motif) ligand 7 overexpression protects against high fat diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis in mice. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Huo, T.-I.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Tsai, J.-C.; Liao, J.-W.; Lee, M.-S.; Qin, X.-M.; Hsieh, M.-T.; Pao, L.-H.; Peng, W.-H. Gallic acid ameliorated impaired glucose and lipid homeostasis in high fat diet-induced nafld mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larter, C.Z.; Yeh, M.M.; Van Rooyen, D.M.; Brooling, J.; Ghatora, K.; Farrell, G.C. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist, wy 14,643, improves metabolic indices, steatosis and ballooning in diabetic mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-J.; Lee, K.; Song, J.-H.; Chei, S.; Lee, B.-Y. Ishige okamurae extract suppresses obesity and hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, S.-S.; Zhang, N.-Y.; Zhou, F.-C.; He, X.; Wang, H.-Y.; Li, L.-Z.; Zheng, X.; Dong, Y.-J.; Luo, R.; Li, B.; et al. Dendrobium officinale regulates fatty acid metabolism to ameliorate liver lipid accumulation in nafld mice. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 6689727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Lechon, M.J.; Donato, M.T.; Martinez-Romero, A.; Jimenez, N.; Castell, J.V.; O’Connor, J.E. A human hepatocellular in vitro model to investigate steatosis. Chem. -Biol. Interact. 2007, 165, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhan, Y.-T. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease cirrhosis: A review of its epidemiology, risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnosis, management, and prognosis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 2784537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Scorletti, E.; Mosca, A.; Alisi, A.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Complications, morbidity and mortality of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2020, 111, 154170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, J.F.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Nagao, K.; Yanagita, T.; Xue, C.H. Dietary saponins of sea cucumber alleviate orotic acid-induced fatty liver in rats via pparalpha and srebp-1c signaling. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghazadeh, S.; Amini, R.; Yazdanparast, R.; Ghaffari, S.H. Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of silybum marianum in treatment of experimental steatohepatitis. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. Off. J. Ges. Fur Toxikol. Pathol. 2011, 63, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.P.; Ji, G. Natural products on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, B. Joint effect of hepatic steatosis and alanine aminotransferase within the normal range on incident ischemic heart disease: A prospective study in koreans. Clin. Interv. Aging 2021, 16, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirichaiwetchakoon, K.; Lowe, G.M.; Kupittayanant, S.; Churproong, S.; Eumkeb, G. Pluchea indica (L.) less. Tea ameliorates hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and obesity in high fat diet-fed mice. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. Ecam 2020, 2020, 8746137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, K.; van Gorp, P.J.; Bieghs, V.; Gijbels, M.J.; Duimel, H.; Lutjohann, D.; Kerksiek, A.; van Kruchten, R.; Maeda, N.; Staels, B.; et al. Dietary cholesterol, rather than liver steatosis, leads to hepatic inflammation in hyperlipidemic mouse models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2008, 48, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.; Gu, M.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhou, Z. Extracts of pomelo peels prevent high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in c57bl/6 mice through activating the pparalpha and glut4 pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77915. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.J.; Yang, Z.; Grinchuk, V.; Smith, A.; Qin, B.; Lu, N.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Wynn, T.A.; et al. Il-25 or il-17e protects against high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in mice dependent upon il-13 activation of stat6. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urtasun, R.; Diaz-Gomez, J.; Arana, M.; Pajares, M.J.; Oneca, M.; Torre, P.; Jimenez, M.; Munilla, G.; Barajas, M.; Encio, I. A combination of apple vinegar drink with bacillus coagulans ameliorates high fat diet-induced body weight gain, insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doege, H.; Stahl, A. Protein-mediated fatty acid uptake: Novel insights from in vivo models. Physiology 2006, 21, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosui, A.; Tatsumi, T.; Hikita, H.; Saito, Y.; Hiramatsu, N.; Tsujii, M.; Hennighausen, L.; Takehara, T. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 plays a crucial role in hepatic lipid metabolism through regulation of cd36 expression. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2017, 47, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedfar, F.; Sung, M.M.; Aparicio-Vergara, M.; Kloosterhuis, N.J.; Miquilena-Colina, M.E.; Vargas-Castrillón, J.; Febbraio, M.; Jacobs, R.L.; de Bruin, A.; Vinciguerra, M.; et al. Increased hepatic cd36 expression with age is associated with enhanced susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aging 2014, 6, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mun, J.; Kim, S.; Yoon, H.G.; You, Y.; Kim, O.K.; Choi, K.C.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Jun, W. Water extract of Curcuma longa L. Ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, C.M.; Stahl, A. Slc27 fatty acid transport proteins. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janani, C.; Ranjitha Kumari, B.D. Ppar gamma gene—A review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2015, 9, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardwick, J.P.; Osei-Hyiaman, D.; Wiland, H.; Abdelmegeed, M.A.; Song, B.J. Ppar/rxr regulation of fatty acid metabolism and fatty acid omega-hydroxylase (cyp4) isozymes: Implications for prevention of lipotoxicity in fatty liver disease. PPAR Res. 2009, 2009, 952734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, M.; Kang, C.; Lee, H.-J. Effect of bombyx mori on the liver protection of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on in vitro and in vivo models. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, T.; Nakade, Y.; Ibusuki, M.; Kitano, R.; Yamauchi, T.; Kimoto, S.; Inoue, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Ito, K.; et al. Conophylline inhibits high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, T.N.H.; Choi, H.-J.; Jun, H.-S. Ethanol Extract of Liriope platyphylla Root Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice via Regulation of Lipogenesis and Lipid Uptake. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103338
Le TNH, Choi H-J, Jun H-S. Ethanol Extract of Liriope platyphylla Root Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice via Regulation of Lipogenesis and Lipid Uptake. Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103338
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Trang Nu Huyen, Ho-Jung Choi, and Hee-Sook Jun. 2021. "Ethanol Extract of Liriope platyphylla Root Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice via Regulation of Lipogenesis and Lipid Uptake" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103338
APA StyleLe, T. N. H., Choi, H.-J., & Jun, H.-S. (2021). Ethanol Extract of Liriope platyphylla Root Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice via Regulation of Lipogenesis and Lipid Uptake. Nutrients, 13(10), 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103338





