Skin Manifestations and Coeliac Disease in Paediatric Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dermatitis Herpetiformis
3. Psoriasis
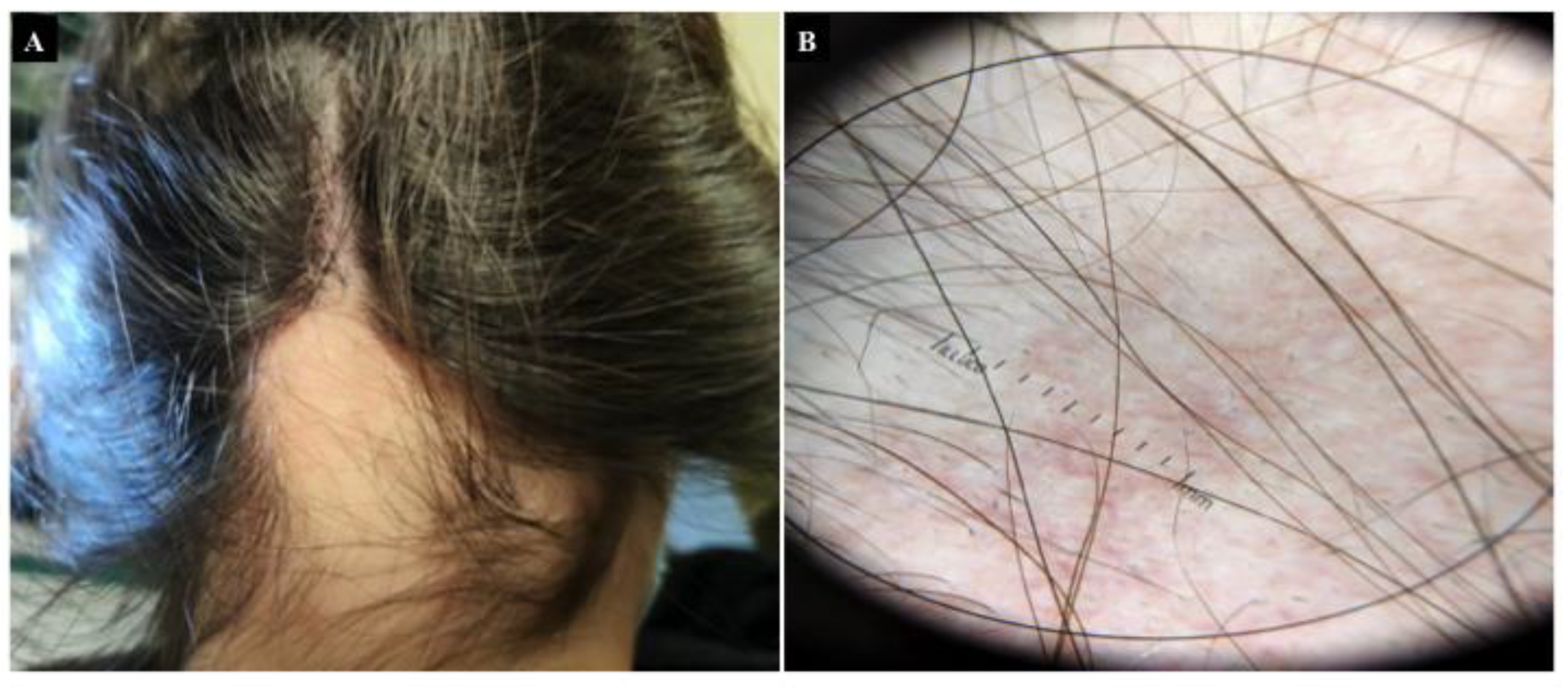
4. Alopecia Areata
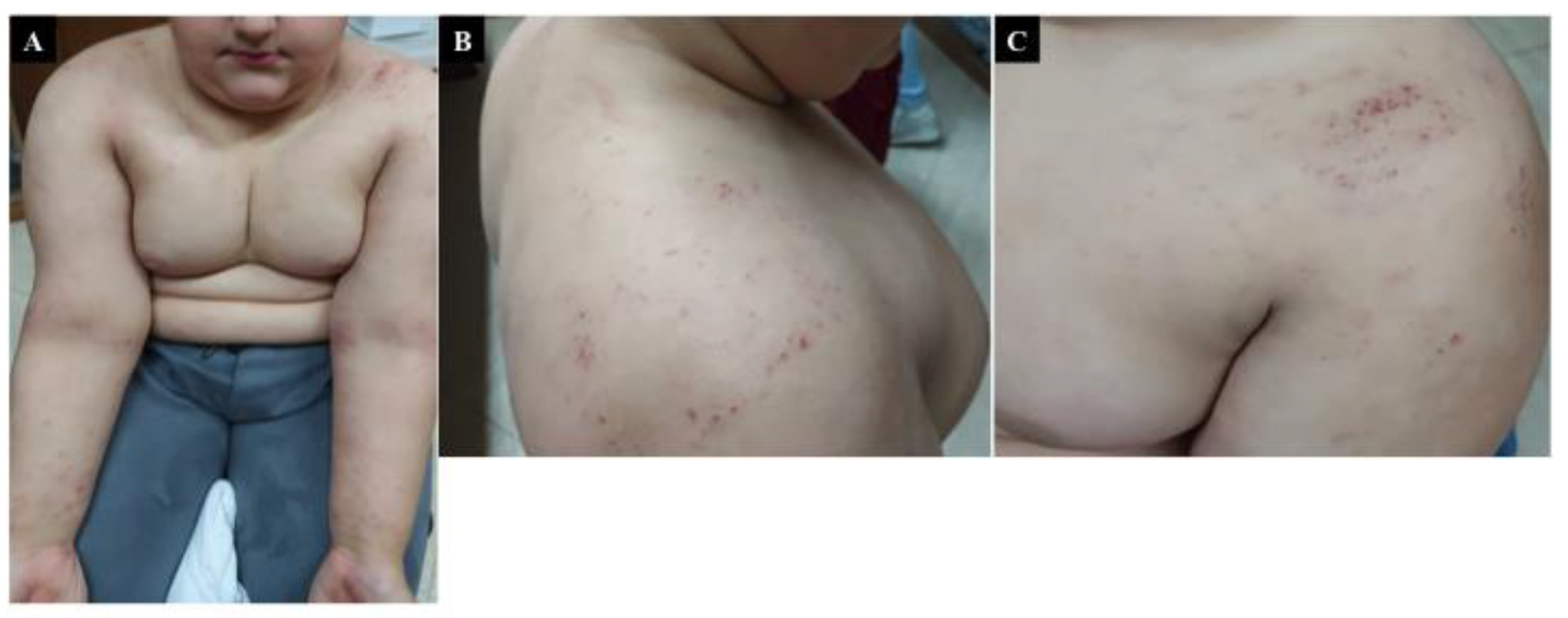
5. Chronic Urticaria
6. Atopic Dermatitis
7. Hereditary Angioneurotic Oedema
8. Other CD-Associated Skin Conditions
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lebwohl, B.; Rubio-Tapia, A. Epidemiology, presentation and diagnosis of coeliac disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.E.; Morrison-Rees, S.; Thapar, N.; Benninga, M.A.; Borrelli, O.; Broekaert, I.; Dolinsek, J.; Martin-de-Carpi, J.; Mas, E.; Miele, E.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis: The incidence and prevalence of paediatric coeliac disease across Europe. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, K.E.; Castiglione, D.A.; Butzner, J.D. The changing face of childhood celiac disease in North America: Impact of serological testing. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almallouhi, E.; King, K.S.; Patel, B.; Wi, C.; Juhn, Y.J.; Murray, J.A.; Absah, I. Increasing incidence and altered presentation in a population-based study of pediatric celiac disease in North America. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, A.; Magazzù, G.; Greco, L. Duration of exposure to gluten and risk for autoimmune disorders in patients with celiac disease. SIGEP Study Group for Autoimmune Disorders in Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, L.; Lahner, E.; Galli, G.; Esposito, G.; Carabotti, M.; Annibale, B. Risk Factors Associated with the Occurrence of Autoimmune Diseases in Adult Coeliac Patients. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 3049286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, P.H.; Cellier, C. Celiac disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, M.; Cortes, A.; van Heel, D.A.; Brown, M.A. Genetic insights into common pathways and complex relationships among immune-mediated diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, K.E.; Wijmenga, C. Coeliac disease and autoimmune disease-genetic overlap and screening. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Matthias, T. Adverse effects of gluten ingestion and advantages of gluten withdrawal in nonceliac autoimmune disease. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humbert, P.; Pelletier, F.; Dreno, B.; Puzenat, E.; Aubin, F. Gluten intolerance and skin diseases. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2006, 16, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lebwohl, B.; Söderling, J.; Roelstraete, B.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Green, P.H.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Risk of Skin Disorders in Patients with Celiac Disease: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görög, A.; Antiga, E.; Caproni, M.; Cianchini, G.; De, D.; Dmochowski, M.; Dolinsek, J.; Drenovska, K.; Feliciani, C.; Hervonen, K.; et al. S2k guidelines (consensus statement) for diagnosis and therapy of dermatitis herpetiformis initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1251–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, P.; Salmi, T.T.; Hervonen, K.; Kaukinen, K.; Reunala, T. Dermatitis herpetiformis: A cutaneous manifestation of coeliac disease. Ann. Med. 2017, 49, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, L.; Seah, P.P.; Riches, D.J.; Hoffbrand, A.V. Clearance of skin lesions in dermatitis herpetiformis after gluten withdrawal. Lancet 1973, 75, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunala, T.; Salo, O.P.; Tiilikainen, A.; Selroos, O.; Kuitunen, P. Family studies in dermatitis herpetiformis. Ann. Clin. Res. 1976, 8, 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, S.I.; Falchuk, Z.M.; Dahl, M.V.; Rogentine, G.N.; Strober, W. HL-A8: A genetic link between dermatitis herpetiformis and gluten-sensitive enteropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 1972, 51, 2977–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurkland, A.; Ingvarsson, G.; Falk, E.S.; Knutsen, I.; Sollid, L.M.; Thorsby, E. Dermatitis herpetiformis and celiac disease are both primarily associated with the HLA-DQ (alpha 1*0501, beta 1*02) or the HLA-DQ (alpha 1*03, beta 1*0302) heterodimers. Tissue Antigens 1997, 49, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemberg, D.; Day, A.S.; Bohane, T. Coeliac disease presenting as dermatitis herpetiformis in infancy. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2005, 41, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermacora, E.; Prampolini, L.; Tribbia, G.; Pezzoli, G.; Gelmetti, C.; Cucchi, G.; Tettamanti, A.; Giunta, A.; Gianotti, F. Long-term follow-up of dermatitis herpetiformis in children. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986, 15, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.B.; Tulloch, J.E.; Meyer, L.J.; Zone, J.J. The incidence and prevalence of dermatitis herpetiformis in Utah. Arch. Dermatol. 1992, 128, 1608–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, T.T.; Hervonen, K.; Kautiainen, H.; Collin, P.; Reunala, T. Prevalence and incidence of dermatitis herpetiformis: A 40-year prospective study from Finland. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.; Fleming, K.M.; Tata, L.J.; Card, T.R.; Crooks, C.J. Incidence and prevalence of celiac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis in the UK over two decades: Population-based study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reunala, T.; Lokki, J. Dermatitis herpetiformis in Finland. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1978, 58, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antiga, E.; Verdelli, A.; Calabrò, A.; Fabbri, P.; Caproni, M. Clinical and immunopathological features of 159 patients with dermatitis herpetiformis: An Italian experience. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 148, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reunala, T.; Hervonen, K.; Salmi, T. Dermatitis Herpetiformis: An Update on Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, T.W.; Bennion, S.D. Palmar purpura: An atypical presentation of childhood dermatitis herpetiformis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1994, 11, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpati, S.; Torok, E.; Kosnai, I. Discrete palmar and plantar symptoms in children with dermatitis herpetiformis Duhring. Cutis 1986, 37, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- López Aventín, D.; Ilzarbe, L.; Herrero-González, J.E. Recurrent digital petechiae and weight loss in a young adult. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, e10–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savilahti, E.; Reunala, T.; Mäki, M. Increase of lymphocytes bearing the gamma/delta T cell receptor in the jejunum of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. Gut 1992, 33, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansikka, E.; Hervonen, K.; Kaukinen, K.; Collin, P.; Huhtala, H.; Reunala, T.; Salmi, T. Prognosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis Patients with and without Villous Atrophy at Diagnosis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leffler, D.A.; Green, P.H.; Fasano, A. Extraintestinal manifestations of coeliac disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashtari, S.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Rostami, K.; Aghdaei, H.A.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Busani, L.; Tavirani, M.R.; Zali, M.R. Prevalence of gluten-related disorders in Asia-Pacific region: A systematic review. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2019, 28, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasternack, C.; Kaukinen, K.; Kurppa, K.; Mäki, M.; Collin, P.; Hervonen, K.; Reunala, T.; Huhtala, H.; Kekkonen, L.; Salmi, T. Gastrointestinal Symptoms Increase the Burden of Illness in Dermatitis Herpetiformis: A Prospective Study. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurppa, K.; Koskinen, O.; Collin, P.; Mäki, M.; Reunala, T.; Kaukinen, K. Changing phenotype of celiac disease after long-term gluten exposure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 47, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karell, K.; Korponay-Szabo, I.; Szalai, Z.; Holopainen, P.; Mustalahti, K.; Collin, P.; Mäki, M.; Partanen, J. Genetic dissection between coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis in sib pairs. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2002, 66, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolotin, D.; Petronic-Rosic, V. Dermatitis herpetiformis. Part II. Diagnosis, management, and prognosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 64, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietikko, M.; Hervonen, K.; Salmi, T.; Ilus, T.; Zone, J.J.; Kaukinen, K.; Reunala, T.; Lindfors, K. Disappearance of epidermal transglutaminase and IgA deposits from the papillary dermis of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis after a long-term gluten-free diet. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, e198–e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierard, J.; Whimster, I. The histological diagnosis of dermatitis herpetiformis, bullous pemphigoid and erythema multifore. Br. J. Dermatol. 1961, 73, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresler, S.C.; Granter, S.R. Utility of direct immunofluorescence testing for IgA in patients with high and low clinical suspicion for dermatitis herpetiformis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 144, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, B.; Hook, K. Bullous Diseases in Children: A Review of Clinical Features and Treatment Options. Paediatr. Drugs 2019, 21, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, W.; Laag, E.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Reunala, T.; Kárpáti, S.; Zágoni, T.; Riecken, E.O.; Schuppan, D. Antibodies to tissue transglutaminase as serologic markers in patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sárdy, M.; Kárpáti, S.; Merkl, B.; Paulsson, M.; Smyth, N. Epidermal transglutaminase (TGase 3) is the autoantigen of dermatitis herpetiformis. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.I.; Stiller, M.J. Dapsone and sulfones in dermatology: Overview and update. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehncke, W.H.; Schon, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachakonda, T.; Schupp, C.; Armstrong, A. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronckers, I.M.; Paller, A.S.; van Geel, M.J.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.; Seyger, M.M. Psoriasis in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Management and Comorbidities. Paediatr. Drugs 2015, 17, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tollefson, M.M.; Crowson, C.S.; McEvoy, M.T.; Maradit Kremers, H. Incidence of psoriasis in children: A population-based study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, B.; Jain, R.; Sandhu, K.; Kaur, I.; Handa, S. Epidemiology of childhood psoriasis: A study of 419 patients from northern India. Int. J. Dermatol. 2004, 43, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, M.; Coskun, B.K.; Saglam, H.; Ozcan, H.; Karincaoglu, Y. Psoriasis in childhood and adolescence: Evaluation of demographic and clinical features. Pediatr. Int. 2006, 48, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Paller, A.S.; Tom, W.L.; Sugarman, J.; Hebert, A.A.; Friedlander, S.F.; Siegfried, E.; Silverberg, N.; Cordoro, K.M. Pediatric psoriasis: Evolving perspectives. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2018, 35, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenfeld, S.; Dreiher, J.; Weitzman, D.; Cohen, A.D. Coeliac disease associated with psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojetti, V.; Aguilar Sanchez, J.; Guerriero, C.; Fossati, B.; Capizzi, R.; De Simone, C.; Migneco, A.; Amerio, P.; Gasbarrini, G.; Gasbarrini, A. High prevalence of celiac disease in psoriasis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 2574–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagui, N.; El Nabarawy, E.; Mahgoub, D.; Mashaly, H.M.; Saad, N.E.; El-Deeb, D.F. Estimation of (IgA) anti-gliadin, anti-endomysium and tissue transglutaminase in the serum of patients with psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 36, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, P.; Mathur, M. Association between psoriasis and celiac disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungprasert, P.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Kittanamongkolchai, W. Psoriasis and Risk of Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Indian J. Dermatol. 2017, 62, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Lindelöf, B.; Zingone, F.; Ciacci, C. Psoriasis in a nationwide cohort study of patients with celiac disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2010–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vos, R.; Boer, W.; Haas, F. Is there a relationship between psoriasis and coeliac disease? J. Intern. Med. 1995, 237, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, F.; Alizadeh, S.; Amiri, A.; Shakeri, R.; Robati, M.; Alimohamadi, S.M.; Abdi, H.; Malekzadeh, R. Psoriasis and Coeliac Disease; Is There Any Relationship? Acta Derm. Venereol. 2010, 90, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, K.; Nair, R.; Ike, R.; Hiremagalore, R.; Elder, J.; Ellis, C. Prevalence of Antigliadin Antibodies in Patients with Psoriasis is Not Elevated Compared with Controls. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 8, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, C.; Degl’innocenti, D.; Caproni, M.; Fabbri, P. Is the search for serum antibodies to gliadin, endomysium and tissue transglutaminase meaningful in psoriatic patients? Relationship between the pathogenesis of psoriasis and coeliac disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 147, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Sonkar, G.K.; Singh, S. Celiac disease-associated antibodies in patients with psoriasis and correlation with HLA Cw6. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2010, 24, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Nguyen, T.U.; Poon, K.Y.; Herrinton, L.J. The association of psoriasis with autoimmune diseases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assa, A.; Frenkel-Nir, Y.; Tzur, D.; Katz, L.H.; Shamir, R. Large population study shows that adolescents with celiac disease have an increased risk of multiple autoimmune and nonautoimmune comorbidities. Acta Paediatr. 2017, 106, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Epstein, A.J.; Skup, M.; Zueger, P.; Garg, V.; Panaccione, R. Risk of Developing Additional Immune-Mediated Manifestations: A Retrospective Matched Cohort Study. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osier, E.; Wang, A.S.; Tollefson, M.M.; Cordoro, K.M.; Daniels, S.R.; Eichenfield, A.; Gelfand, J.M.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Kimball, A.B.; Lebwohl, M.; et al. Pediatric Psoriasis Comorbidity Screening Guidelines. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaëlsson, G.; Gerdén, B.; Hagforsen, E.; Nilsson, B.; Pihl-Lundin, I.; Kraaz, W.; Hjelmquist, G.; Lööf, L. Psoriasis patients with antibodies to gliadin can be improved by a gluten-free diet. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 142, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolchak, N.A.; Tetarnikova, M.K.; Theodoropoulou, M.S.; Michalopoulou, A.P.; Theodoropoulos, D.S. Prevalence of antigliadin IgA antibodies in psoriasis vulgaris and response of seropositive patients to a gluten-free diet. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2018, 11, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bastiani, R.; Gabrielli, M.; Lora, L.; Napoli, L.; Tosetti, C.; Pirrotta, E.; Ubaldi, E.; Bertolusso, L.; Zamparella, M.; De Polo, M.; et al. Association between coeliac disease and psoriasis: Italian primary care multicentre study. Dermatology 2015, 230, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addolorato, G.; Parente, A.; de Lorenzi, G.; D’angelo Di Paola, M.E.; Abenavoli, L.; Leggio, L.; Capristo, E.; De Simone, C.; Rotoli, M.; Rapaccini, G.L.; et al. Rapid regression of psoriasis in a coeliac patient after gluten-free diet. A case report and review of the literature. Digestion 2003, 68, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, O.N.; Khavkin, A.I. Coeliac disease and psoriasis combination in 5-year-old child. Eksp. Klin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 8, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.H.; Gwillim, E.; Patel, K.R.; Hua, T.; Rastogi, S.; Ibler, E.; Silverberg, J.I. Epidemiology of alopecia areata, ophiasis, totalis, and universalis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhar, A.; Etzioni, A.; Paus, R. Alopecia areata. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strazzulla, L.; Wang, E.H.C.; Avila, L.; Lo Sicco, K.; Brinster, N.; Christiano, A.M.; Shapiro, J. Alopecia areata: Disease characteristics, clinical evaluation, and new perspectives on pathogenesis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.A.; Gupta, A.K.; Watteel, G.N. Stress and alopecia areata: A psychodermatologic study. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1997, 77, 296–298. [Google Scholar]
- Messenger, A.G.; McKillop, J.; Farrant, P.; McDonagh, A.J.; Sladden, M. British Association of Dermatologists’ guidelines for the management of alopecia areata 2012. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, K.H.; Muller, S.A.; Suman, V.J.; Moshell, A.N.; Melton, L.J., 3rd. Incidence of alopecia areata in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1975 through 1989. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1995, 70, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzuncakmak, T.K.; Engin, B.; Serdaroglu, S.; Tuzun, Y. Demographic and Clinical Features of 1641 Patients with Alopecia Areata, Alopecia Totalis, and Alopecia Universalis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Skin. Appendage Disord. 2021, 7, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waard-van der Spek, F.B.; Oranje, A.P.; De Raeymaecker, D.M.; Peereboom-Wynia, J.D. Juvenile versus maturity-onset alopecia areata--a comparative retrospective clinical study. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1989, 14, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelidze, K.; Lipner, S.R. Nail changes in alopecia areata: An update and review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifah, A.; Alsantali, A.; Wang, E.; McElwee, K.J.; Shapiro, J. Alopecia areata update: Part I. Clinical picture, histopathology, and pathogenesis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Dai, Z.; Jabbari, A.; Cerise, J.E.; Higgins, C.A.; Gong, W.; de Jong, A.; Harel, S.; DeStefano, G.M.; Rothman, L.; et al. Alopecia areata is driven by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and is reversed by JAK inhibition. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ertekin, V.; Selimoglu, M.A.; Altinkaynak, S. Celiac disease in childhood: Evaluation of 140 patients. Eurasian J. Med. 2009, 41, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guariso, G.; Conte, S.; Presotto, F.; Basso, D.; Brotto, F.; Visonà Dalla Pozza, L.; Pedini, B.; Betterle, C. Clinical, subclinical and potential autoimmune diseases in an Italian population of children with coeliac disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, G.R.; Andreani, M.L.; Venturo, N.; Bernardi, M.; Tosti, A.; Gasbarrini, G. Celiac disease and alopecia areata: Report of a new association. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volta, U.; Bardazzi, F.; Zauli, D.; DeFranceschi, L.; Tosti, A.; Molinaro, N.; Ghetti, S.; Tetta, C.; Grassi, A.; Bianchi, F.B. Serological screening for coeliac disease in vitiligo and alopecia areata. Br. J. Dermatol. 1997, 136, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Panjehpour, T.; Naeini, F.F.; Hosseini, S.M.; Nilforoushzadeh, M.A.; Matin, M. The Frequency Distribution of Celiac Autoantibodies in Alopecia Areata. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.T.; Romero, K.; Almohanna, H.M.; Griggs, J.; Ahmed, A.; Tosti, A. The Role of Diet as an Adjuvant Treatment in Scarring and Nonscarring Alopecia. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020, 6, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, M.; Viola, F.; Grillo, R.; Franchin, L.; Lo Russo, L.; Lucarelli, S.; Frediani, T.; Mazzilli, M.C.; Cardi, E. Alopecia and coeliac disease: Report of two patients showing response to gluten-free diet. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1998, 23, 236–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessatou, S.; Kostaki, M.; Karpathios, T. Coeliac disease and alopecia areata in childhood. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2003, 39, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardella, M.T.; Marino, R.; Barbareschi, M.; Bianchi, F.; Faglia, G.; Bianchi, P. Alopecia areata and coeliac disease: No effect of a gluten-free diet on hair growth. Dermatology 2000, 200, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondavalli, P.; Quadri, G.; Parodi, A.; Rebora, A. Failure of gluten-free diet in celiac disease associated alopecia areata. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1998, 78, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radonjic-Hoesli, S.; Hofmeier, K.S.; Micaletto, S.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; Bircher, A.; Simon, D. Urticaria and Angioedema: An Update on Classification and Pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 54, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuberbier, T.; Aberer, W.; Asero, R.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Abdul Latiff, A.H.; Baker, D.; Ballmer-Weber, B.; Bernstein, J.A.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Brzoza, Z.; et al. The EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF/WAO Guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis, and management of urticaria: The 2013 revision and update. Allergy 2014, 69, 868–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, L.M.; Bernstein, J.A. Guideline of chronic urticaria beyond. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2016, 8, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Donnell, B.; Lawlor, F.; Simpson, J.; Morgan, M.; Greaves, M. The impact of chronic urticaria on the quality of life. Br. J. Dermatol. 1997, 136, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauteke, M.; De Clerck, L.; Stevens, W. Chronic urticaria associated with coeliac disease. Lancet 1987, 329, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminiti, L.; Passalacqua, G.; Magazzu, G.; Comisi, F.; Vita, D.; Barberio, G.; Sferlazzas, C.; Pajno, G.B. Chronic urticaria and associated coeliac disease in children: A case-control study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 16, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Lindelöf, B.; Rashtak, S.; Rubio-Tapia, A.; Murray, J.A. Does urticaria risk increase in patients with celiac disease? A large population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2013, 23, 6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.; Dalal, I.; Bujanover, Y. Celiac disease associated with familial chronic urticaria and thyroid autoimmunity in a child. Pediatrics 1999, 104, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abenavoli, L.; Proietti, L.; Leggio, L.; Ferrulli, A.; Vonghia, L.; Capizzi, R.; Rotoli, M.; Amerio, P.L.; Gasbarrini, G.; Addolorato, G. Cutaneous manifestations in celiac disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peroni, D.G.; Paiola, G.; Tenero, L.; Fornaro, M.; Bodini, A.; Pollini, F.; Piacentini, G.L. Chronic urticaria and celiac disease: A case report. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2010, 27, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolkhir, P.; Borzova, E.; Grattan, C.; Asero, R.; Pogorelov, D.; Maurer, M. Autoimmune comorbidity in chronic spontaneous urticaria: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, M.W. Chronic idiophatic urticaria. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 4, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutten, S. Atopic dermatitis: Global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann. Nutr. Metabl. 2015, 66, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darlenski, R.; Kazandjieva, J.; Hristakieva, E.; Fluhr, J.W. Atopic dermatitis as a systemic disease. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M. From atopic dermatitis to asthma: The atopic march. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 105, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidesang, I.; Saunes, M.; Storrø, O.; Øien, T.; Holmen, T.L.; Johnsen, R.; Henriksen, A.H. Atopic dermatitis among 2-year olds; high prevalence, but predominantly mild disease--the PACT study, Norway. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2008, 25, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruin Weller, M.S.; Knulst, A.C.; Meijer, Y.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M.; Pasmans, S.G.M. Evaluation of the child with atopic dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narla, S.; Silverberg, J.I. Association between atopic dermatitis and autoimmune disorders in US adults and children: A cross-sectional study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkasalo, M.; Tiilikainen, A.; Kuitunen, P.; Savilahti, E.; Backman, A. HLA antigens and atopy in children with coeliac disease. Gut 1983, 24, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greco, L.; De Seta, L.; D’Adamo, G.; Baldassarre, C.; Mayer, M.; Siani, P.; Lojodice, D. Atopy and coeliac disease: Bias or true relation? Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1990, 79, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ress, K.; Annus, T.; Putnik, U.; Luts, K.; Uibo, R.; Uibo, O. Celiac disease in children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalom, G.; Kridin, K.; Raviv, K.O.; Freud, T.; Comaneshter, D.; Friedland, R.; Cohen, A.D.; Ben-Amitai, D. Atopic Dermatitis and Celiac Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study of 116,816 Patients. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, S.; Jokelainen, J.; Timonen, M.; Tasanen, K.; Huilaja, L. Atopic Dermatitis Is Associated with Dermatitis Herpetiformis and Celiac Disease in Children. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 191–193.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.; Cicardi, M.; Bork, K.; Zuraw, B.; Frank, M.; Ritchie, B.; Farkas, H.; Varga, L.; Zingale, L.C.; Binkley, K.; et al. Hereditary angiodema: A current state-of-the-art review, VII: Canadian Hungarian 2007 International Consensus Algorithm for the Diagnosis, Therapy, and Management of Hereditary Angioedema. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 100, S30–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, H.; Visy, B.; Fekete, B.; Karádi, I.; Kovács, J.B.; Kovács, I.B.; Kalmár, L.; Tordai, A.; Varga, L. Association of celiac disease and hereditary angioneurotic edema. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2682–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csuka, D.; Kelemen, Z.; Czaller, I.; Molnár, K.; Füst, G.; Varga, L.; Rajczy, K.; Szabó, Z.; Miklós, K.; Bors, A.; et al. Association of celiac disease and hereditary angioedema due to C1-inhibitor deficiency. Screening patients with hereditary angioedema for celiac disease: Is it worth the effort? Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 23, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Similä, S.; Kokkonen, J.; Kallioinen, M. Cutaneous vasculitis as a manifestation of coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1982, 71, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, Y.; Şahin, S.; Adrovic, A.; Kutlu, T.; Çokuğras, F.Ç.; Barut, K.; Erkan, T.; Kasapçopur, Ö. Serological screening for celiac disease in children with systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 6, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.C.; Fasano, S.; Isenberg, D.A. Autoimmune gastrointestinal complications in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Case series and literature review. Lupus 2016, 25, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crişcov, G.I.; Stana, A.B.; Ioniue, I.K.; Alexoae, M.M.; Moraru, E. Coexistence of celiac disease and systemic lupus erythematosus in a 6-year-old girl-case report. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi 2015, 119, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hadjivassilious, M.; Sanders, D.S.; Grünewald, R.A.; Akil, M. Gluten sensitivity masquerading as systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 1501–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ergül, B.; Koçak, E.; Köklü, S. Behcet disease and celiac disease: To screen or not? Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 2591–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buderus, S.; Wagner, N.; Lentze, M.J. Concurrence of celiac disease and juvenile dermatomyositis: Result of a specific immunogenetic susceptibility? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1997, 25, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, K.; Torma, K.; Siklós, K.; Csanády, K.; Korponay-Szabó, I.; Szalai, Z. Juvenile dermatomyositis and celiac disease. A rare association. Eur. J. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2006, 16, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Abenavoli, L.; Dastoli, S.; Bennardo, L.; Boccuto, L.; Passante, M.; Silvestri, M.; Proietti, I.; Potenza, C.; Luzza, F.; Nisticò, S.P. The Skin in Celiac Disease Patients: The Other Side of the Coin. Medicina 2019, 55, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zone, J.J. Skin manifestations of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, S87–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartyik, K.; Várkonyi, A.; Kirschner, A.; Endreffy, E.; Túri, S.; Karg, E. Erythema nodosum in association with celiac disease. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2004, 21, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, S.O.; Franco, C.; Santos, P.; Amaral, R. Skin and coeliac disease, a lot to think about: A case series. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr2017222797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncone, R.; Discepolo, V. Celiac disease and autoimmunity. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, S9–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnemann, S.; Uibel, C.; Budig, P.; Mäurer, M. Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) in a patient with celiac disease. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nenna, R.; D’Eufemia, P.; Celli, M.; Mennini, M.; Petrarca, L.; Zambrano, A.; Montuori, M.; La Pietra, M.; Bonamico, M. Celiac disease and lamellar ichthyosis. Case study analysis and review of the literature. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2011, 19, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howard, G.; Horev, A.; Samueli, B.; Yerushalmi, B. Morphea as Part of the Dermatological Manifestation of Celiac Disease: Case Presentation and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2021, 13, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolfson, H.; McQueen, A.; Stephen, M. Erythroderma in a child with coeliac disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 1974, 90, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelander, H.E. Leiner’s disease followed by the celiac syndrome; a case report. J. Pediatr. 1946, 28, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.H.; Díez, S.G.; Aizpún, L.T.; Oliva, N.P. Antigliadin antibodies associated with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2002, 19, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkert, F.; Sornsakrin, M.; Krebs-Schmitt, D.; Ganschow, R. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis may cause elevated gliadin antibodies. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 1685–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Beissert, S.; Metze, D.; Luger, T.A.; Bonsmann, G. Lipodystrophia centrifugalis abdominalis infantilis in a 4-year-old Caucasian girl: Association with partial IgA deficiency and autoantibodies. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999, 140, 1161–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, S.; Tuna Kırsaçlıoğlu, C.; Şaylı, T.R. Celiac disease and hematological abnormalities in children with recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, G.; Di Liberto, C.; Carroccio, A.; Compilato, D.; Iacono, G.; Procaccini, M.; Di Fede, G.; Lo Muzio, L.; Craxi, A.; Catassi, C.; et al. Coeliac disease: Oral ulcer prevalence, assessment of risk and association with gluten-free diet in children. Dig. Liver Dis. 2008, 40, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Sirka, C.S.; Das, R.R.; Nanda, D. Secondary acrodermatitis enteropathica-like lesions in a child with newly diagnosed coeliac disease. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2016, 36, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macho, V.M.P.; Coelho, A.S.; Veloso, E.; Silva, D.M.; de Andrade, D.J.C. Oral Manifestations in Pediatric Patients with Coeliac Disease—A Review Article. Open Dent. J. 2017, 11, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Author (Year) | Type of Study | Skin Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Buderus, S. [125] (1997) Molnár, K. [126] (2006) | Case reports Case reports | Dermatomyositis |
| Abenavoli, L. [127] (2019); Zone, J.J. [128] (2005) Bartyik, K. [129] (2004) | Review Review Case report | Erythema nodosum |
| Vaz, S.O. [130] (2018) | Case report | Linear IgA bullous dermatosis |
| Troncone, R. [131] (2014) | Review | pityriasis lichenoides |
| Nunnemann, S. [132] (2020) | Case report | Porphyria |
| Nenna, R. [133] (2011) | Case study | Ichthyosis |
| Howard, G. [134] (2021) | Case report | Morphea |
| Woolfson, H. [135] (1974) Thelander, H.E. [136] (1946) | Case report Case report | Erythroderma |
| Garcia, Y.H. [137] (2002) Brinkert, F. [138] (2009) | Case Report Case report | chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis |
| Müller, S. [139] (1999) | Case report | lypodistrophia centrifugalis abdominalis infantilis |
| Yılmaz, S. [140] (2020) Campisi, G. [141] (2008) | Case report Observational study | Stomatous aphtosis |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Persechino, F.; Galli, G.; Persechino, S.; Valitutti, F.; Zenzeri, L.; Mauro, A.; Corleto, V.D.; Parisi, P.; Ziparo, C.; Evangelisti, M.; et al. Skin Manifestations and Coeliac Disease in Paediatric Population. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103611
Persechino F, Galli G, Persechino S, Valitutti F, Zenzeri L, Mauro A, Corleto VD, Parisi P, Ziparo C, Evangelisti M, et al. Skin Manifestations and Coeliac Disease in Paediatric Population. Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103611
Chicago/Turabian StylePersechino, Flavia, Gloria Galli, Severino Persechino, Francesco Valitutti, Letizia Zenzeri, Angela Mauro, Vito Domenico Corleto, Pasquale Parisi, Chiara Ziparo, Melania Evangelisti, and et al. 2021. "Skin Manifestations and Coeliac Disease in Paediatric Population" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103611
APA StylePersechino, F., Galli, G., Persechino, S., Valitutti, F., Zenzeri, L., Mauro, A., Corleto, V. D., Parisi, P., Ziparo, C., Evangelisti, M., Quatrale, G., & Di Nardo, G. (2021). Skin Manifestations and Coeliac Disease in Paediatric Population. Nutrients, 13(10), 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103611








