Weight Gain Associated with COVID-19 Lockdown in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Quality and Risk of Bias Assessments
2.4. Outcomes and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
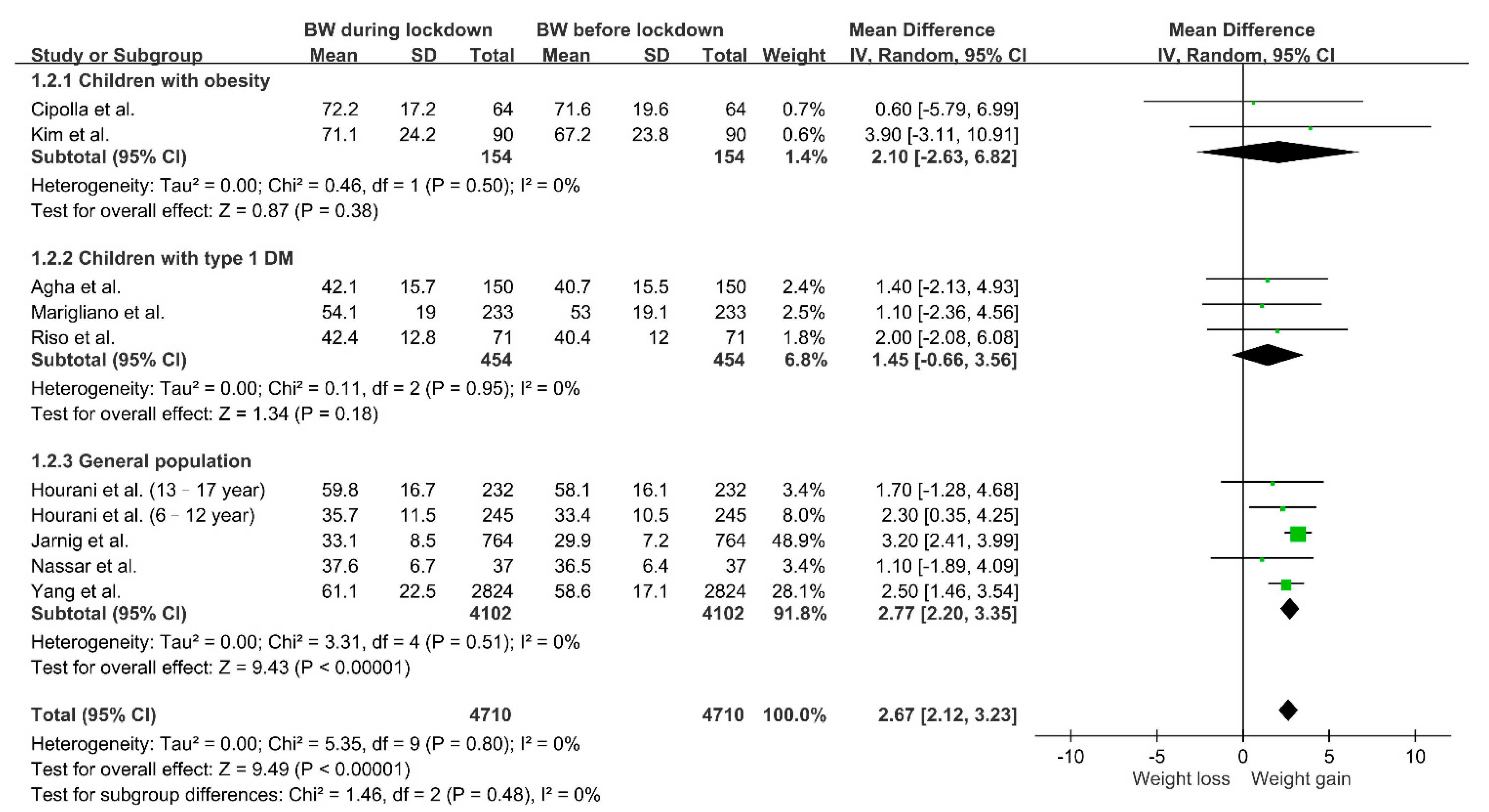
3.3. Changes in Body Weight during Lockdown
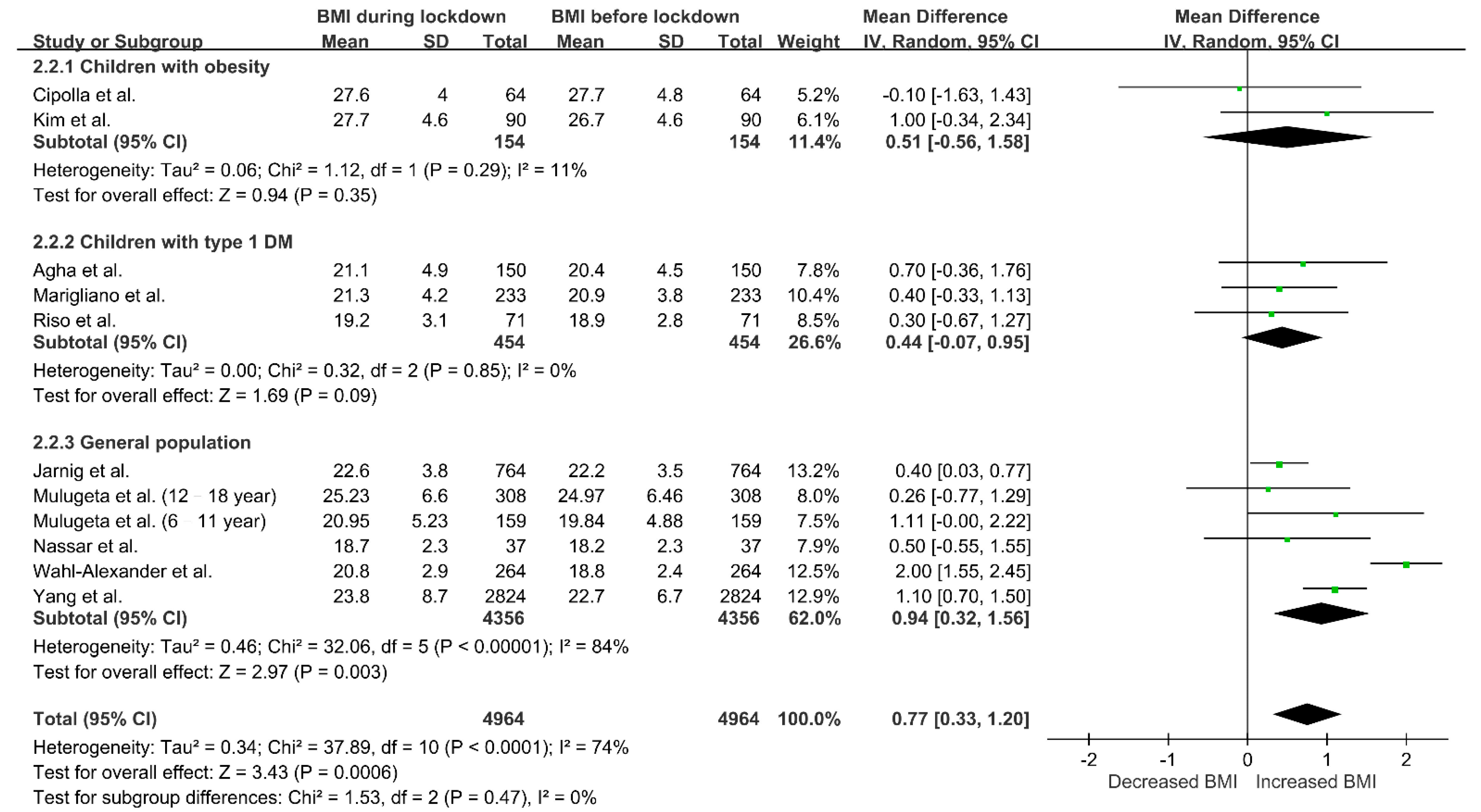
3.4. Changes in BMI during Lockdown
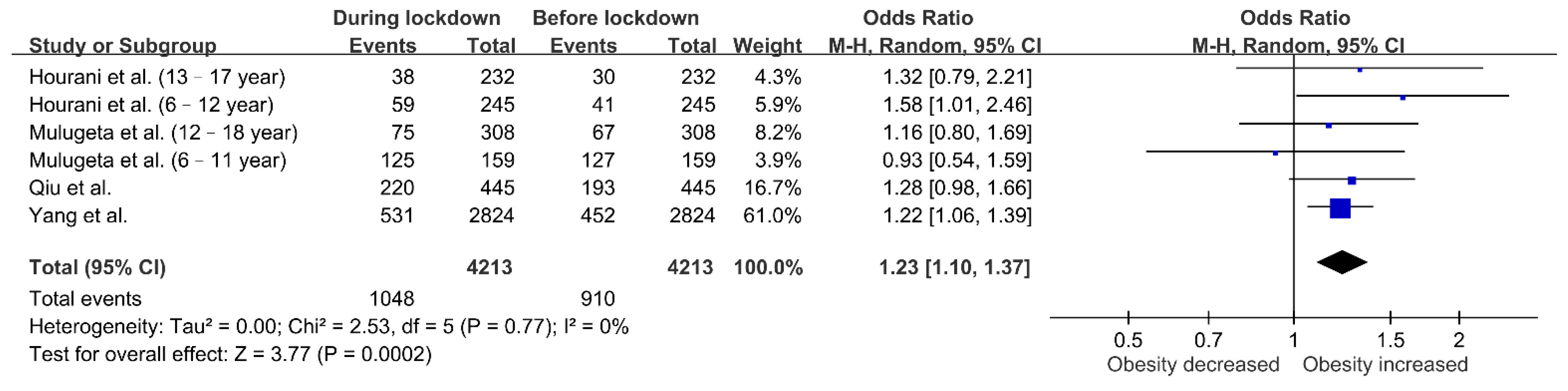
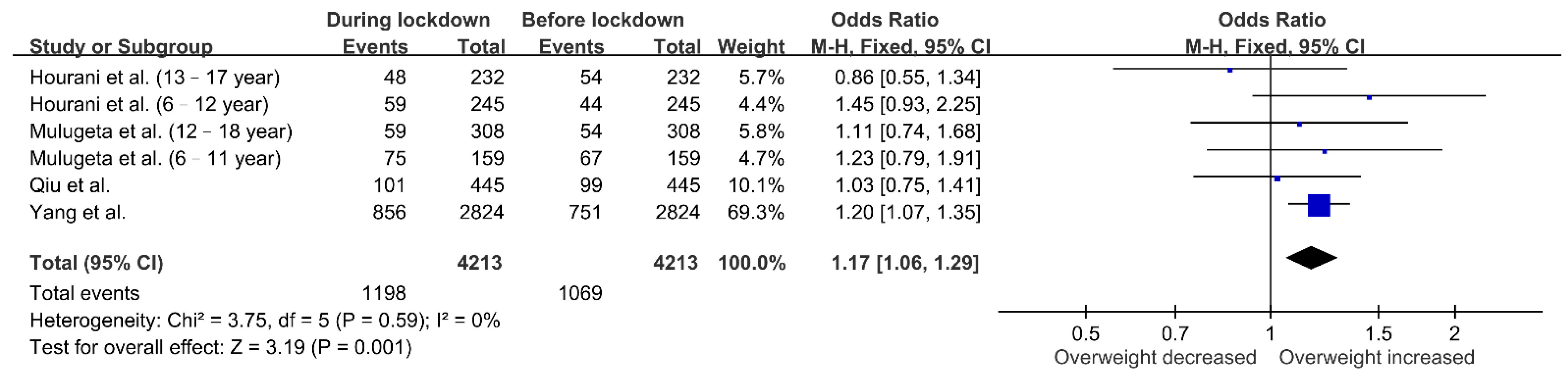
3.5. Changes in BMI Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pietrobelli, A.; Pecoraro, L.; Ferruzzi, A.; Heo, M.; Faith, M.; Zoller, T.; Antoniazzi, F.; Piacentini, G.; Fearnbach, S.N.; Heymsfield, S.B. Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown on Lifestyle Behaviors in Children with Obesity Living in Verona, Italy: A Longitudinal Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2020, 28, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsos, O.; Perperidi, M.; Georgiou, C.; Chouliaras, G. Lifestyle Changes and Determinants of Children’s and Adolescents’ Body Weight Increase during the First COVID-19 Lockdown in Greece: The COV-EAT Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morres, I.D.; Galanis, E.; Hatzigeorgiadis, A.; Androutsos, O.; Theodorakis, Y. Physical Activity, Sedentariness, Eating Behaviour and Well-Being during a COVID-19 Lockdown Period in Greek Adolescents. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakaloudi, D.R.; Barazzoni, R.; Bischoff, S.C.; Breda, J.; Wickramasinghe, K.; Chourdakis, M. Impact of the first COVID-19 lockdown on body weight: A combined systematic review and a meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Santo, S.G.; Franchini, F.; Filiputti, B.; Martone, A.; Sannino, S. The effects of COVID-19 and quarantine measures on the lifestyles and mental health of people over 60 at increased risk of dementia. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 578628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.H.; Wu, J.L.; Chang, L.Y. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic challenges of pediatric COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 119, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.A.; Saliba, V.; Lopez Bernal, J.; Ramsay, M.E.; Ladhani, S.N. SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission in educational settings: A prospective, cross-sectional analysis of infection clusters and outbreaks in England. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Dozier, M.; He, Y.; Kirolos, A.; Theodoratou, E.; UNCOVER. The role of children in transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A rapid review. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 011101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, J.; Ekinci, A.; Krehl, H.; Meincke, M.; Finci, I.; Klein, J.; Geisel, B.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Eichner, M.; Brockmann, S. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in children aged 0 to 19 years in childcare facilities and schools after their reopening in May 2020, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, P.K.; Gupta, J.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Kumar, R.; Meena, A.K.; Madaan, P.; Sharawat, I.K.; Gulati, S. Psychological and behavioral impact of lockdown and quarantine measures for COVID-19 pandemic on children, adolescents and caregivers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67, fmaa122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Agha, A.E.; Alharbi, R.S.; Almohammadi, O.A.; Yousef, S.Y.; Sulimani, A.E.; Alaama, R.A. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic control in children and adolescents. Saudi Med. J. 2021, 42, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, C.; Curatola, A.; Ferretti, S.; Giugno, G.; Condemi, C.; Delogu, A.B.; Birritella, L.; Lazzareschi, I. Eating habits and lifestyle in children with obesity during the COVID19 lockdown: A survey in an Italian center. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hourani, H.; Alkhatib, B.; Abdullah, M. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Body Weight, Eating Habits, and Physical Activity of Jordanian Children and Adolescents. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarnig, G.; Jaunig, J.; van Poppel, M.N.M. Association of COVID-19 Mitigation Measures With Changes in Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Mass Index Among Children Aged 7 to 10 Years in Austria. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2121675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Kwon, Y.; Choe, Y.H.; Kim, M.J. COVID-19-related school closing aggravate obesity and glucose intolerance in pediatric patients with obesity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigliano, M.; Maffeis, C. Glycemic control of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes improved after COVID-19 lockdown in Italy. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulugeta, W.; Hoque, L. Impact of the COVID-19 lockdown on weight status and associated factors for obesity among children in Massachusetts. Obes. Med. 2021, 22, 100325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.F.; Allam, M.F.; Shata, M.O. Effect of COVID-19 Lockdown on Young Egyptian Soccer Players. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2021, 8, 2333794X211012980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, N.; He, H.; Qiao, L.; Ding, Y.; Ji, S.; Guo, X.; Luo, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, Y.; Pang, H.; et al. Sex differences in changes in BMI and blood pressure in Chinese school-aged children during the COVID-19 quarantine. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2021, 45, 2132–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Riso, D.; Bertini, S.; Spaggiari, S.; Olivieri, F.; Zaffani, S.; Comerlati, L.; Marigliano, M.; Piona, C.; Maffeis, C. Short-Term Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown in Italian Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: The Role of Separation Anxiety. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl-Alexander, Z.; Camic, C.L. Impact of COVID-19 on School-Aged Male and Female Health-Related Fitness Markers. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 33, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Guo, B.; Ao, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Jia, P. Obesity and activity patterns before and during COVID-19 lockdown among youths in China. Clin. Obes. 2020, 10, e12416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, L.; Yu, W.; Yu, B.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, S. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on activity patterns and weight status among youths in China: The COVID-19 Impact on Lifestyle Change Survey (COINLICS). Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, B.P.; Kelly, M.K.; Powell, M.; Bouchelle, Z.; Mayne, S.L.; Fiks, A.G. COVID-19 and Changes in Child Obesity. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e2021050123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piercy, K.L.; Troiano, R.P.; Ballard, R.M.; Carlson, S.A.; Fulton, J.E.; Galuska, D.A.; George, S.M.; Olson, R.D. The physical activity guidelines for Americans. JAMA 2018, 320, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.P.; Johnston, C.A.; Woehler, D. Changes in weight over the school year and summer vacation: Results of a 5-year longitudinal study. J. Sch. Health 2013, 83, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franckle, R.; Adler, R.; Davison, K. Accelerated weight gain among children during summer versus school year and related racial/ethnic disparities: A systematic review. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2014, 11, E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, P.; Liu, L.; Xie, X.; Yuan, C.; Chen, H.; Guo, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, S. Impacts of COVID-19 lockdown on diet patterns among youths in China: The COVID-19 Impact on Lifestyle Change Survey (COINLICS). Appetite 2020, 158, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Holzapfel, C.; Schneider, U.; Hauner, H. Lifestyle and Body Weight Consequences of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Children: Increasing Disparity. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 77, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Roso, M.B.; de Carvalho Padilha, P.; Mantilla-Escalante, D.C.; Ulloa, N.; Brun, P.; Acevedo-Correa, D.; Arantes Ferreira Peres, W.; Martorell, M.; Aires, M.T.; de Oliveira Cardoso, L.; et al. COVID-19 Confinement and Changes of Adolescent’s Dietary Trends in Italy, Spain, Chile, Colombia and Brazil. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, L.; McDowell, M.; Bar-Or, O. Relationship between summer vacation weight gain and lack of success in a pediatric weight control program. Eat. Behav. 2005, 6, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Study Period | Country | Lockdown Duration in Study | Case Number | Population | Age (Mean ± SD or Range) (Year) | Male % | Method of Body Weight Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agha et al. (2021) [11] | April 2020 to June 2020 | Saudi Arabia | 3 months | 150 | Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus | 12.5 ± 4.6 | 28% | Direct measurement |
| Cipolla et al. (2021) [12] | June 2020 | Italy | 3 months | 64 | Children with obesity or overweight | 13.9 ± 2.4 | 40.6% | Telephone interview assessing self-reported BW |
| Hourani et al. (2021) [13] | June 2020 | Jordan | 4 months | 477 | Healthy children | 6–17 year | 48.4% | Online questionnaire assessing self-reported BW |
| Jarnig et al. (2021) [14] | September 2019 to June 2020 | Austria | 4 months | 764 | Healthy children | 9 ± 0.7 | 49.9% | Direct measurement |
| Kim et al. (2021) [15] | December 2019 to May 2020 | Korea | 3 months | 90 | Children with obesity | 12.2 ± 3.4 | 77.8% | Direct measurement |
| Marigliano et al. (2021) [16] | January 2020 to June 2020 | Italy | 2 months | 233 | Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus | 13.9 ± 4.4 | 55.7% | Direct measurement |
| Mulugeta et al. (2021) [17] | March 2020 to May 2020 | USA | 3 months | 701 | Healthy children | 2–18 year | 44.2% | Direct measurement |
| Nassar et al. (2021) [18] | March 2020 to July 2020 | Egypt | 5 months | 37 | Soccer players under at home self-training | 10.8 ± 0.46 | 100% | Direct measurement |
| Qiu et al. (2021) [19] | October 2019 to May 2020 | China | 5 months | 445 | Healthy children | 8.7–11 year | 58.4% | Direct measurement |
| Riso et al. (2021) [20] | January 2020 to June 2020 | Italy | 2 months | 73 | Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus | 10.8 ± 2.3 | 54.9% | Direct measurement |
| Wahl-Alexander et al. (2021) [21] | August 2019 to July 2020 | USA | 4 months | 264 | Healthy third- through eighth-grade students attending summer camp | 9.6 year | 49.6% | Direct measurement |
| Yang et al. (2020) [22] | December 2019 to February 2020 | China | 1 month | 2824 | High school students | 17.5 ± 1.2 | 24.0% | Online questionnaire assessing self-reported BW |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hsu, W.-Y.; Chou, Y.; Chang, Y.-H. Weight Gain Associated with COVID-19 Lockdown in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103668
Chang T-H, Chen Y-C, Chen W-Y, Chen C-Y, Hsu W-Y, Chou Y, Chang Y-H. Weight Gain Associated with COVID-19 Lockdown in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103668
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Tu-Hsuan, Yu-Chin Chen, Wei-Yu Chen, Chun-Yu Chen, Wei-Yun Hsu, Yun Chou, and Yi-Hsin Chang. 2021. "Weight Gain Associated with COVID-19 Lockdown in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103668
APA StyleChang, T. -H., Chen, Y. -C., Chen, W. -Y., Chen, C. -Y., Hsu, W. -Y., Chou, Y., & Chang, Y. -H. (2021). Weight Gain Associated with COVID-19 Lockdown in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 13(10), 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103668






