A High-Sodium Diet Modulates the Immune Response of Food Allergy in a Murine Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Ethics Statement
2.2. Antigen Preparation
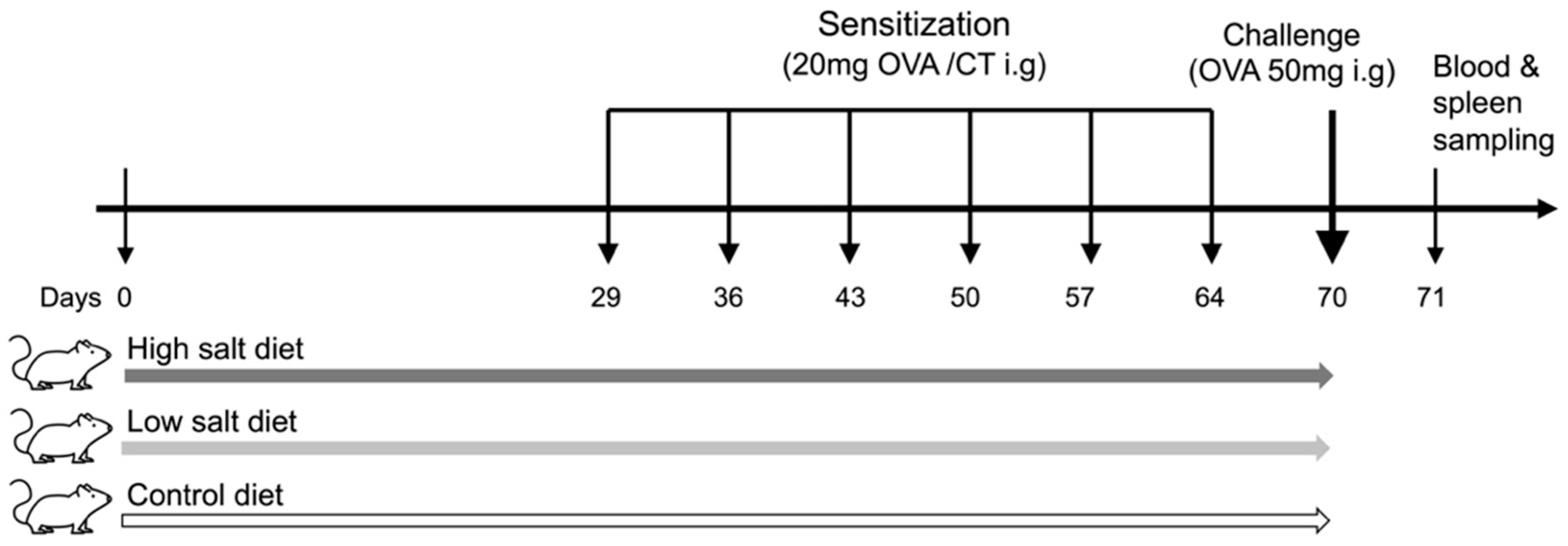
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Measurement of OVA-Specific Immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgG1, and IgG2a Antibodies
2.5. Measurement of OVA-Specific IgE Antibody
2.6. Analysis of Cytokine Production in OVA-Stimulated Spleen Cells
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HSD Induces High Levels of OVA-Specific Serum IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, and IgE in Mice
3.2. High IL-4 and Low IL-10 Production in Splenocytes of Mice Maintained on HSD
3.3. HSD Causes No Change in the Serum Levels of Sodium and Chloride
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afsar, B.; Kuwabara, M.; Ortiz, A.; Yerlikaya, A.; Siriopol, D.; Covic, A.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, B.; Johnson, R.J.; Kanbay, M. Salt intake and immunity. Hypertension 2018, 72, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinewietfeld, M.; Manzel, A.; Titze, J.; Kvakan, H.; Yosef, N.; Linker, R.A.; Muller, D.N.; Hafler, D.A. Sodium chloride drives autoimmune disease by the induction of pathogenic TH 17 cells. Nature 2013, 496, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Yosef, N.; Thalhamer, T.; Zhu, C.; Xiao, S.; Kishi, Y.; Regev, A.; Kuchroo, V.K. Induction of pathogenic TH 17 cells by inducible salt-sensing kinase SGK1. Nature 2013, 496, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharif, K.; Amital, H.; Shoenfeld, Y. The role of dietary sodium in autoimmune diseases: The salty truth. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lopes, J.E.; Chong, M.M.; Ivanov, I.I.; Min, R.; Victora, G.D.; Shen, Y.; Du, J.; Rubtsov, Y.P.; Rudensky, A.Y. TGF-β-induced Foxp3 inhibits TH 17 cell differentiation by antagonizing RORγt function. Nature 2008, 453, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, A.L.; Kitz, A.; Wu, C.; Lowther, D.E.; Rodriguez, D.M.; Vudattu, N.; Deng, S.; Herold, K.C.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Kleinewietfeld, M. Sodium chloride inhibits the suppressive function of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4212–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akdis, M.; Verhagen, J.; Taylor, A.; Karamloo, F.; Karagiannidis, C.; Crameri, R.; Thunberg, S.; Deniz, G.; Valenta, R.; Fiebig, H. Immune responses in healthy and allergic individuals are characterized by a fine balance between allergen-specific T regulatory 1 and T helper 2 cells. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, C.A. Therapies for allergic inflammation: Refining strategies to induce tolerance. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.N.; Burton, O.T.; Wise, P.; Charbonnier, L.-M.; Georgiev, P.; Oettgen, H.C.; Rachid, R.; Chatila, T.A. Regulatory T cell reprogramming toward a Th2-cell-like lineage impairs oral tolerance and promotes food allergy. Immunity 2015, 42, 512–523. [Google Scholar]
- Abbring, S.; Wolf, J.; Ayechu-Muruzabal, V.; Diks, M.A.P.; Alhamwe, B.A.; Alhamdan, F.; Harb, H.; Renz, H.; Garn, H.; Garssen, J.; et al. Raw Cow’s Milk Reduces Allergic Symptoms in a Murine Model for Food Allergy-A Potential Role For Epigenetic Modifications. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alashkar Alhamwe, B.; Meulenbroek, L.; Veening-Griffioen, D.H.; Wehkamp, T.M.D.; Alhamdan, F.; Miethe, S.; Harb, H.; Hogenkamp, A.; Knippels, L.M.J.; Pogge von Strandmann, E.; et al. Decreased Histone Acetylation Levels at Th1 and Regulatory Loci after Induction of Food Allergy. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3193. [Google Scholar]
- Wilck, N.; Balogh, A.; Markó, L.; Bartolomaeus, H.; Müller, D.N. The role of sodium in modulating immune cell function. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 546–558. [Google Scholar]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy: A review and update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Osborne, N.J.; Koplin, J.J.; Martin, P.E.; Gurrin, L.C.; Lowe, A.J.; Matheson, M.C.; Ponsonby, A.-L.; Wake, M.; Tang, M.L.; Dharmage, S.C. Prevalence of challenge-proven IgE-mediated food allergy using population-based sampling and predetermined challenge criteria in infants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 668–676.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, V.; Macia, L.; Dombrowicz, D. The impact of diet on asthma and allergic diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2015, 15, 308–322. [Google Scholar]
- Acevedo, N.; Alashkar Alhamwe, B.; Caraballo, L.; Ding, M.; Ferrante, A.; Garn, H.; Garssen, J.; Hii, C.S.; Irvine, J.; Llinas-Caballero, K.; et al. Perinatal and Early-Life Nutrition, Epigenetics, and Allergy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Esch, B.; Porbahaie, M.; Abbring, S.; Garssen, J.; Potaczek, D.P.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; van Neerven, R.J.J. The Impact of Milk and Its Components on Epigenetic Programming of Immune Function in Early Life and Beyond: Implications for Allergy and Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-F.; Wang, C.-C.; Wu, T.-C.; Chu, C.-H.; Peng, H.-J. Effect of sublingual administration with a native or denatured protein allergen and adjuvant CpG oligodeoxynucleotides or cholera toxin on systemic TH2 immune responses and mucosal immunity in mice. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007, 99, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.-H.; Chen, C.-S.; Lin, J.-Y. Dietary perilla oil lowers serum lipids and ovalbumin-specific IgG1, but increases total IgE levels in ovalbumin-challenged mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, E.; Do, S.G.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, M.B.; Min, K.Y.; Koo, J.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Polysaccharide isolated from Aloe vera gel suppresses ovalbumin-induced food allergy through inhibition of Th2 immunity in mice. Biomed Pharm. 2018, 101, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Bihouée, T.; Bouchaud, G.; Chesné, J.; Lair, D.; Rolland-Debord, C.; Braza, F.; Cheminant, M.-A.; Aubert, P.; Mahay, G.; Sagan, C. Food allergy enhances allergic asthma in mice. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, A.; Schliep, A.; Jörg, S.; Haghikia, A.; Gold, R.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Müller, D.N.; Linker, R.A. Impact of combined sodium chloride and saturated long-chain fatty acid challenge on the differentiation of T helper cells in neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthias, J.; Maul, J.; Noster, R.; Meinl, H.; Chao, Y.-Y.; Gerstenberg, H.; Jeschke, F.; Gasparoni, G.; Welle, A.; Walter, J. Sodium chloride is an ionic checkpoint for human TH2 cells and shapes the atopic skin microenvironment. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau0683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KIM, J.; OHSAWA, M. Oral tolerance to ovalbumin in mice as a model for detecting modulators of the immunologic tolerance to a specific antigen. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dearman, R.; Kimber, I. Animal models of protein allergenicity: Potential benefits, pitfalls and challenges. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wijk, F.; Wehrens, E.; Nierkens, S.; Boon, L.; Kasran, A.; Pieters, R.; Knippels, L. CD4+ CD25+ T cells regulate the intensity of hypersensitivity responses to peanut, but are not decisive in the induction of oral sensitization. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Umetsu, D.T.; Akbari, O.; DeKruyff, R.H.; Shearer, W.T.; Rosenwasser, L.J.; Bochner, B.S. Regulatory T cells control the development of allergic disease and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.N.; Wilck, N.; Haase, S.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Linker, R.A. Sodium in the microenvironment regulates immune responses and tissue homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, D.P.; Marshall, J.S.; Perdue, M.H.; Liang, H. Production of IgE antibody and allergic sensitization of intestinal and peripheral tissues after oral immunization with protein Ag and cholera toxin. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gärdby, E.; Lycke, N.Y. CD19-deficient mice exhibit poor responsiveness to oral immunization despite evidence of unaltered total IgA levels, germinal centers and IgA-isotype switching in Peyer’s patches. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdic, D.; Smith, R.; Donachie, A.; Kjerrulf, M.; Hörnquist, E.; Mowat, A.; Lycke, N. The mucosal adjuvant effects of cholera toxin and immune-stimulating complexes differ in their requirement for IL-12, indicating different pathways of action. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski, C.E. Regulation of T Cell Responses by Ionic Salt Signals. Cells 2021, 10, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin, K.; Müller, D.N.; Jantsch, J.; Kurts, C. Sodium and its manifold impact on our immune system. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbs, A.L.; Liu, B.; Rogers, T.D.; Sartor, R.B.; Miao, E.A. Dietary salt exacerbates experimental colitis. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Li, S.-K.; Huang, C.-K.; Huang, C.-F. A High-Sodium Diet Modulates the Immune Response of Food Allergy in a Murine Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113684
Liu Z, Li S-K, Huang C-K, Huang C-F. A High-Sodium Diet Modulates the Immune Response of Food Allergy in a Murine Model. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113684
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zheying, Shih-Kuan Li, Chih-Kang Huang, and Ching-Feng Huang. 2021. "A High-Sodium Diet Modulates the Immune Response of Food Allergy in a Murine Model" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113684
APA StyleLiu, Z., Li, S.-K., Huang, C.-K., & Huang, C.-F. (2021). A High-Sodium Diet Modulates the Immune Response of Food Allergy in a Murine Model. Nutrients, 13(11), 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113684





