Cord Blood Manganese Concentrations in Relation to Birth Outcomes and Childhood Physical Growth: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Umbilical-Cord Blood Mn Analysis
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. Mn Concentrations in Cord Blood
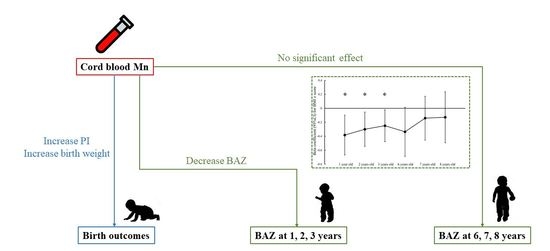
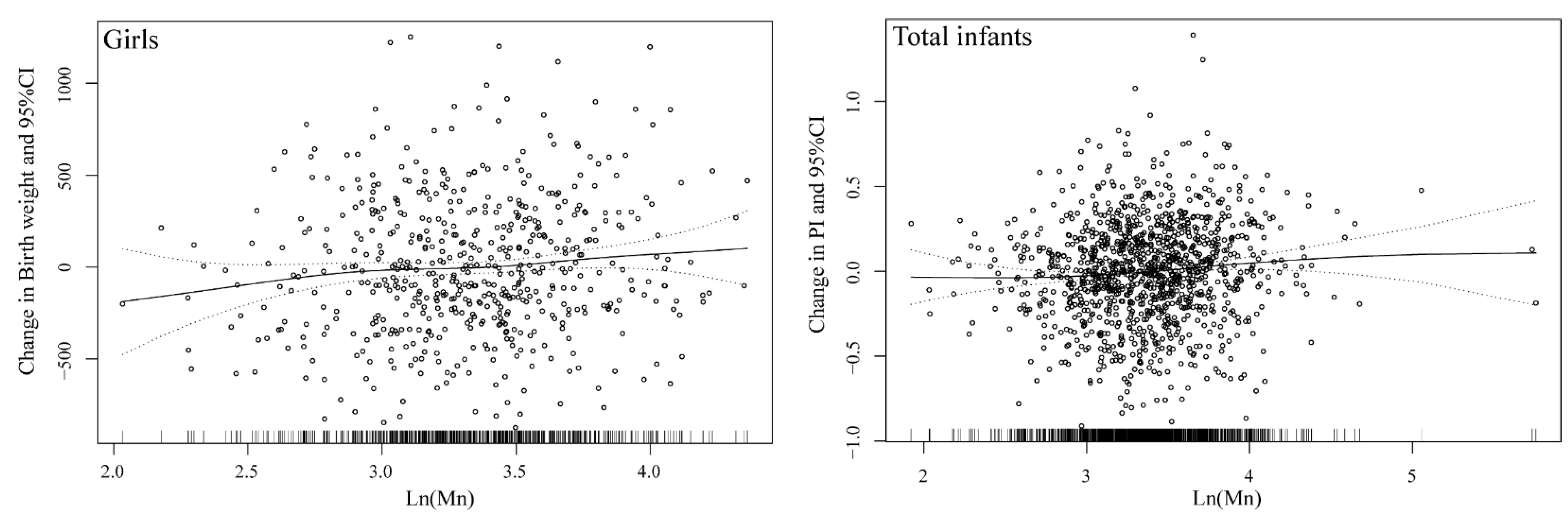
3.3. Cord-Blood Mn Concentration and Birth Outcomes
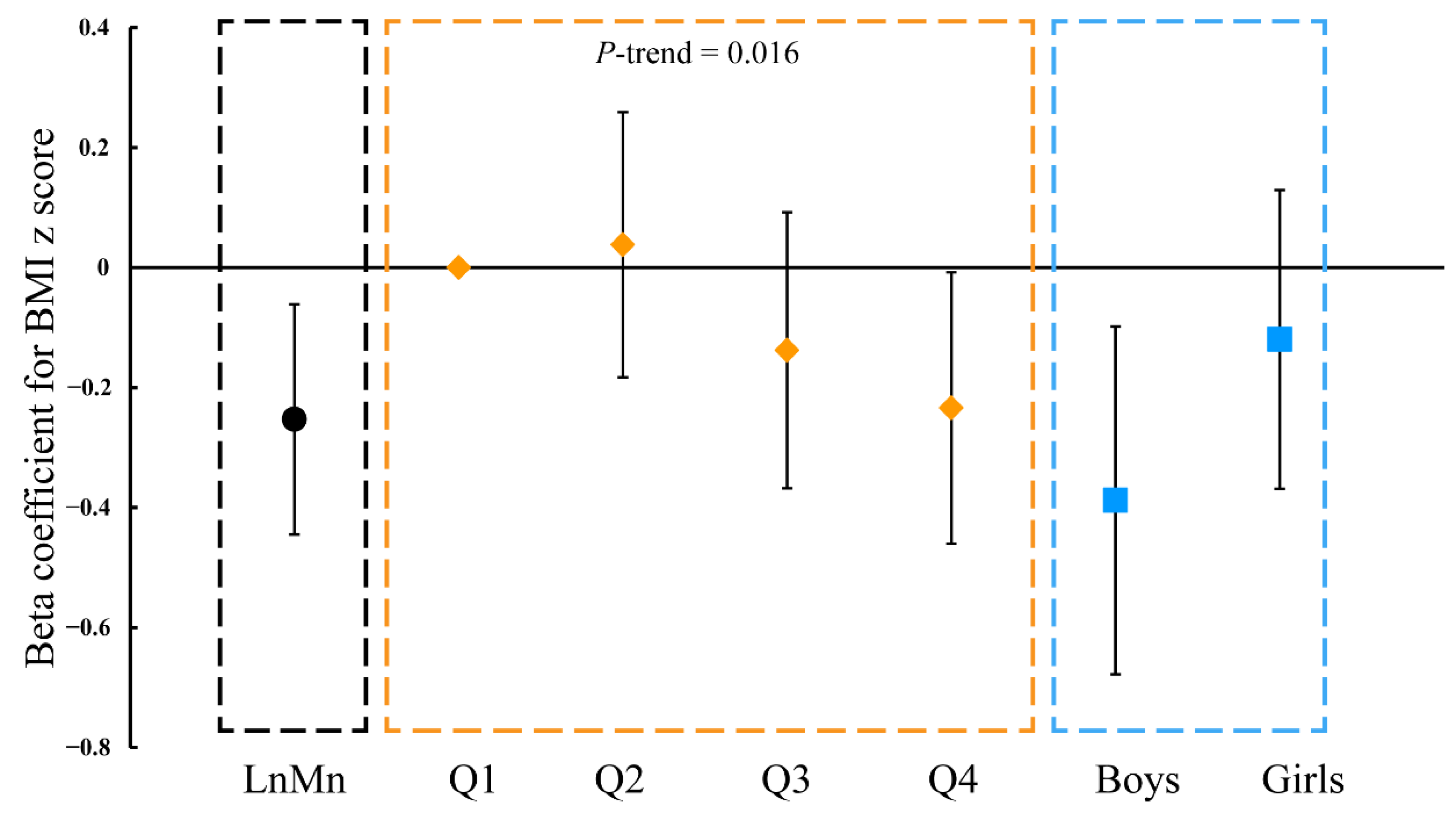
3.4. Cord-Blood Mn Level and BMI of Children Aged 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, and 8 Years Old
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nadaska, G.; Lesny, J.; Michalik, I. Environmental aspect of manganese chemistry. Hung. Electron. J. Sci. HEJ. 2012, 1–16. Available online: http://heja.szif.hu/ENV/ENV-100702-A/env100702a.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Boudissa, S.M.; Lambert, J.; Müller, C.; Kennedy, G.; Gareau, L.; Zayed, J. Manganese concentrations in the soil and air in the vicinity of a closed manganese alloy production plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 361, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aelion, C.M.; Davis, H.T.; McDermott, S.; Lawson, A.B. Metal concentrations in rural topsoil in South Carolina: Potential for human health impact. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aschner, J.L.; Aschner, M. Nutritional aspects of manganese homeostasis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harischandra, D.S.; Ghaisas, S.; Zenitsky, G.; Jin, H.; Kanthasamy, A.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity: New Insights into the Triad of Protein Misfolding, Mitochondrial Impairment, and Neuroinflammation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Claus Henn, B.; Bellinger, D.C.; Hopkins, M.R.; Coull, B.A.; Ettinger, A.S.; Jim, R.; Hatley, E.; Christiani, D.C.; Wright, R.O. Maternal and Cord Blood Manganese Concentrations and Early Childhood Neurodevelopment among Residents near a Mining-Impacted Superfund Site. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 67020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, E.J.; Frisbie, S.H.; Roudeau, S.; Carmona, A.; Ortega, R. How much manganese is safe for infants? A review of the scientific basis of intake guidelines and regulations relevant to the manganese content of infant formulas. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 65, 126710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez, L.; García-Vicent, C.; López, J.; Torró, M.I.; Lurbe, E. Assessment of ten trace elements in umbilical cord blood and maternal blood: Association with birth weight. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mora, A.M.; van Wendel De Joode, B.; Mergler, D.; Córdoba, L.; Cano, C.; Quesada, R.; Smith, D.R.; Menezes-Filho, J.A.; Eskenazi, B. Maternal blood and hair manganese concentrations, fetal growth, and length of gestation in the ISA cohort in Costa Rica. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, J.; Cheong, H.; Ha, E.; Ha, M.; Kim, Y.; Hong, Y.; Park, H.; Chang, N. Maternal blood manganese level and birth weight: A MOCEH birth cohort study. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, M.; Nong, A.; Clewell, H.J.; Taylor, M.D.; Dorman, D.C.; Andersen, M.E. Evaluating Placental Transfer and Tissue Concentrations of Manganese in the Pregnant Rat and Fetuses after Inhalation Exposures with a PBPK Model. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 112, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oulhote, Y.; Mergler, D.; Bouchard, M.F. Sex- and age-differences in blood manganese levels in the U.S. general population: National health and nutrition examination survey 2011–2012. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andiarena, A.; Irizar, A.; Molinuevo, A.; Urbieta, N.; Babarro, I.; Subiza-Pérez, M.; Santa-Marina, L.; Ibarluzea, J.; Lertxundi, A. Prenatal Manganese Exposure and Long-Term Neuropsychological Development at 4 Years of Age in a Population-Based Birth Cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Cha, C.; Lv, X.; Liu, J.; He, J.; Pang, Q.; Meng, L.; Kuang, H.; Fan, R. Association between 10 urinary heavy metal exposure and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder for children. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31233–31242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Qin, Q.; Ye, K.; Wu, W.; Huo, X. Heavy metal exposure has adverse effects on the growth and development of preschool children. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2019, 41, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, M.; Rossipal, E.; Micetic-Turk, D. Trace element transfer from the mother to the newborn—Investigations on triplets of colostrum, maternal and umbilical cord sera. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Zhuang, T.; Shi, J.; Liang, Y.; Song, M. Heavy metals in maternal and cord blood in Beijing and their efficiency of placental transfer. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ding, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Shi, R.; Huang, H.; Tian, Y. Manganese concentrations in maternal–infant blood and birth weight. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6170–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Piao, F.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Kitamura, F.; Yokoyama, K. Manganese concentrations in maternal and umbilical cord blood: Related to birth size and environmental factors. Eur. J. Public Health. 2014, 24, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Wu, C.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, B.; Xia, W.; Peng, Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, M.; Liu, S.; Buka, S.L.; et al. Critical Windows for Associations between Manganese Exposure during Pregnancy and Size at Birth: A Longitudinal Cohort Study in Wuhan, China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 127006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freire, C.; Amaya, E.; Gil, F.; Murcia, M.; LLop, S.; Casas, M.; Vrijheid, M.; Lertxundi, A.; Irizar, A.; Fernández-Tardón, G.; et al. Placental metal concentrations and birth outcomes: The Environment and Childhood (INMA) project. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Zheng, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, G.; Feng, C.; Zhou, Z. Urinary pyrethroid metabolites among pregnant women in an agricultural area of the Province of Jiangsu, China. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Qi, X.; Lv, S.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, T.; Lu, D.; Feng, C.; Chang, X.; et al. Prenatal exposure to mixture of heavy metals, pesticides and phenols and IQ in children at 7 years of age: The SMBCS study. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Qi, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, T.; Xiao, H.; Li, W.; Lu, D.; Feng, C.; et al. Early-life carbamate exposure and intelligence quotient of seven-year-old children. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wu, C.; Chang, X.; Qi, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Z. Adverse Associations of both Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Organophosphorous Pesticides with Infant Neurodevelopment in an Agricultural Area of Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Qi, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Chang, X.; Zhou, Z. Adverse associations between maternal and neonatal cadmium exposure and birth outcomes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, H.; Qi, X.; Wu, C.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Sex-Specific Differences in Cognitive Abilities Associated with Childhood Cadmium and Manganese Exposures in School-Age Children: A Prospective Cohort Study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Lv, S.; Lu, D.; Feng, C.; Qi, X.; Liang, W.; Chang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, G.; et al. Associations of prenatal exposure to five chlorophenols with adverse birth outcomes. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmann, E.; Reiss, I.; Misselwitz, B.; Gortner, L. Ponderal index for discrimination between symmetric and asymmetric growth restriction: Percentiles for neonates from 30 weeks to 43 weeks of gestation. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2006, 19, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, R.S.; Kumbartski, M.; Harth, V.; Brüning, T.; Käfferlein, H.U. Partition of metals in the maternal/fetal unit and lead-associated decreases of fetal iron and manganese: An observational biomonitoring approach. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbuckle, T.E.; Liang, C.L.; Morisset, A.S.; Fisher, M.; Weiler, H.; Cirtiu, C.M.; Legrand, M.; Davis, K.; Ettinger, A.S.; Fraser, W.D. Maternal and fetal exposure to cadmium, lead, manganese and mercury: The MIREC study. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kupsco, A.; Sanchez-Guerra, M.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Brennan, K.J.M.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G.; Svensson, K.; Schnaas, L.; Pantic, I.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; Baccarelli, A.A.; et al. Prenatal manganese and cord blood mitochondrial DNA copy number: Effect modification by maternal anemic status. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohaudomchok, W.; Lin, X.; Herrick, R.F.; Fang, S.C.; Cavallari, J.M.; Christiani, D.C.; Weisskopf, M.G. Toenail, blood, and urine as biomarkers of manganese exposure. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 53, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neal, S.L.; Zheng, W. Manganese Toxicity upon Overexposure: A Decade in Review. Curr. Environ. Health. Rep. 2015, 2, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milne, D.B.; Sims, R.L.; Ralston, N.V. Manganese content of the cellular components of blood. Clin. Chem. 1990, 36, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley-Martin, J.; Dodds, L.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Ettinger, A.S.; Shapiro, G.D.; Fisher, M.; Monnier, P.; Morisset, A.; Fraser, W.D.; Bouchard, M.F. Maternal and cord blood manganese (Mn) levels and birth weight: The MIREC birth cohort study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina, T.; Domingo, J.; Llobet, J.; Corbella, J. Effect of day of exposure on the developmental toxicity of manganese in mice. Vet. Hum. Hum. Toxicol. 1996, 38, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Cao, L.; Yu, X. Elevated cord serum manganese level is associated with a neonatal high ponderal index. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erikson, K.M.; Dorman, D.C.; Fitsanakis, V.; Lash, L.H.; Aschner, M. Alterations of oxidative stress biomarkers due to in utero and neonatal exposures of airborne manganese. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2006, 111, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duhig, K.; Chappell, L.C.; Shennan, A.H. Oxidative stress in pregnancy and reproduction. Obstet. Med. 2016, 9, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.L.; Oken, E.; Hivert, M.; Rifas-Shiman, S.; Lin, P.D.; Colicino, E.; Wright, R.O.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Claus Henn, B.G.; Gold, D.R.; et al. Early pregnancy exposure to metal mixture and birth outcomes—A prospective study in Project Viva. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Núñez, Z.; Ashrap, P.; Barrett, E.S.; Watkins, D.J.; Cathey, A.L.; Vélez-Vega, C.M.; Rosario, Z.; Cordero, J.F.; Alshawabkeh, A.; Meeker, J.D. Association of biomarkers of exposure to metals and metalloids with maternal hormones in pregnant women from Puerto Rico. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupsco, A.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G.; Cantoral, A.; Schnaas, L.; Pantic, I.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Svensson, K.; Bellinger, D.C.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Baccarelli, A.A.; et al. Modification of the effects of prenatal manganese exposure on child neurodevelopment by maternal anemia and iron deficiency. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 88, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundaram, P.; Avulakunta, I.D. Human Growth and Development; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Durán, C.; Cassorla, F. Trace minerals in human growth and development. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 12, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bu, J. Relationship between Selected Serum Metallic Elements and Obesity in Children and Adolescent in the U.S. Nutrients 2017, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajee, N.; Sobngwi, E.; Macnab, A.; Daar, A.S. The Developmental Origins of Health and Disease and Sustainable Development Goals: Mapping the way forward. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2018, 9, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toftlund, L.H.; Halken, S.; Agertoft, L.; Zachariassen, G. Catch-Up Growth, Rapid Weight Growth, and Continuous Growth from Birth to 6 Years of Age in Very-Preterm-Born Children. Neonatology 2018, 114, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treinen, K.A.; Gray, T.J.; Blazak, W.F. Developmental toxicity of mangafodipir trisodium and manganese chloride in Sprague-Dawley rats. Teratology 1995, 52, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, D.J.; Domingo, J.; Llobet, J.M.; Keen, C.L. Maternal and developmental toxicity of manganese in the mouse. Toxicol. Lett. 1993, 69, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.L.; Spears, J.W.; Lloyd, K.E.; Whisnant, C.S. Feeding a Low Manganese Diet to Heifers During Gestation Impairs Fetal Growth and Development. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4305–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarale, P.; Daiwile, A.; Sivanesan, S.D.; Stöger, R.; Bafana, A.; Naoghare, P.; Parmar, D.; Chakrabarti, T.; Krishnamurthi, K. Manganese exposure: Linking down-regulation of miRNA−7 and miRNA−433 with α-synuclein overexpression and risk of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 46, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, C.; Ensunsa, J.L.; Watson, M.H.; Baly, D.; Donovan, S.; Monaco, M.; Clegg, M. Nutritional aspects of manganese from experimental studies. Neurotoxicology 1999, 20, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, M.; Lubiński, J. Serum Microelements in Early Pregnancy and their Risk of Large-for-Gestational Age Birth Weight. Nutrients 2020, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | Pregnancy (n = 1179) | 1 Year Old (n = 567) | 2 Years Old (n = 358) | 3 Years Old (n = 409) | 6 Years Old (n = 421) | 7 Years Old (n = 388) | 8 Years Old (n = 374) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal age (years) | ||||||||
| <35 | 1072 (90.9) | 507 (89.4) | 323 (90.2) | 374 (91.4) | 370 (87.9) | 344 (88.7) | 332 (88.8) | |
| ≥35 | 107 (9.1) | 60 (10.6) | 35 (9.8) | 35 (8.6) | 51 (12.1) | 44 (11.3) | 42 (11.2) | 0.461 |
| Gestational age (weeks) | ||||||||
| <37 | 9 (0.8) | 3 (0.5) | 2 (0.6) | 2 (0.5) | 4 (1.0) | 3 (0.8) | 2 (0.5) | |
| ≥37 | 1170 (99.2) | 564 (99.5) | 356 (99.4) | 407 (99.5) | 417 (99.0) | 385 (99.2) | 372 (99.5) | 0.975 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||||
| <18.5 | 149 (12.6) | 74 (13.1) | 52 (14.5) | 53 (12.9) | 43 (10.2) | 41 (10.6) | 42 (11.2) | |
| 18.5–23.9 | 842 (71.4) | 405 (71.4) | 248 (69.3) | 287 (70.2) | 294 (69.8) | 269 (69.3) | 254 (67.9) | |
| ≥24 | 188 (16.0) | 88 (15.5) | 58 (16.2) | 69 (16.9) | 84 (20.0) | 78 (20.1) | 78 (20.9) | 0.288 |
| Maternal education | ||||||||
| <High school (9 years) | 753 (63.9) | 388 (68.4) | 252 (70.4) | 284 (69.4) | 302 (71.7) | 272 (70.1) | 272 (72.7) | |
| ≥High school (9 years) | 426 (36.1) | 179 (31.6) | 106 (29.6) | 125 (30.6) | 119 (28.3) | 116 (29.9) | 102 (27.3) | 0.006 |
| Neonatal sex | ||||||||
| Boys | 619 (52.5) | 296 (52.2) | 194 (54.2) | 202 (49.4) | 227 (53.9) | 216 (55.7) | 203 (54.3) | |
| Girls | 560 (47.5) | 271 (47.8) | 164 (45.8) | 207 (50.6) | 194 (46.1) | 172 (44.3) | 171 (45.7) | 0.663 |
| Parity | ||||||||
| 0 | 613 (52.0) | 293 (51.7) | 196 (54.7) | 224 (54.8) | 225 (53.4) | 212 (54.6) | 192 (51.3) | |
| ≥1 | 566 (48.0) | 274 (48.3) | 162 (45.3) | 185 (45.2) | 196 (46.4) | 176 (45.4) | 182 (48.7) | 0.848 |
| Birth Weight (kg) | Birth Length (cm) | Head Circumference (cm) | Ponderal Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95% CI) | p | β (95% CI) | p | β (95% CI) | p | β (95% CI) | p | |
| All newborns a | ||||||||
| Ln (Mn) | 0.044 (−0.012, 0.100) | 0.124 | −0.190 (−0.508, 0.128) | 0.242 | 0.105 (−0.093, 0.303) | 0.299 | 0.065 (0.021, 0.109) | 0.004 |
| Q1 | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| Q2 | 0.033 (−0.031, 0.096) | 0.316 | 0.059 (−0.301, 0.420) | 0.748 | 0.097 (−0.125, 0.320) | 0.391 | 0.032 (−0.018, 0.081) | 0.209 |
| Q3 | 0.035 (−0.029, 0.098) | 0.283 | −0.031 (−0.391, 0.329) | 0.865 | 0.012 (−0.211, 0.236) | 0.914 | 0.042 (−0.008, 0.091) | 0.101 |
| Q4 | 0.067 (0.003, 0.131) | 0.041 | −0.160 (−0.522, 0.202) | 0.385 | 0.193 (−0.031, 0.418) | 0.091 | 0.082 (0.032, 0.132) | 0.001 |
| p-trend | 0.051 | 0.331 | 0.172 | 0.002 | ||||
| Boys b | ||||||||
| Ln (Mn) | 0.005 (−0.073, 0.083) | 0.899 | −0.378 (−0.804, 0.047) | 0.082 | 0.104 (−0.183, 0.392) | 0.477 | 0.052 (−0.005, 0.110) | 0.073 |
| Q1 | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| Q2 | 0.050 (−0.047, 0.146) | 0.312 | 0.143 (−0.381, 0.667) | 0.592 | 0.173 (−0.178, 0.524) | 0.334 | 0.023 (−0.048, 0.093) | 0.528 |
| Q3 | 0.056 (−0.039, 0.151) | 0.245 | 0.194 (0.323, 0.710) | 0.462 | 0.090 (−0.258, 0.438) | 0.611 | 0.002 (−0.068, 0.071) | 0.962 |
| Q4 | 0.054 (−0.039, 0.147) | 0.256 | −0.287 (−0.792, 0.219) | 0.266 | 0.285 (−0.056, 0.626) | 0.102 | 0.078 (0.010, 0.146) | 0.024 |
| p-trend | 0.288 | 0.260 | 0.159 | 0.043 | ||||
| Girls b | ||||||||
| Ln (Mn) | 0.090 (0.010, 0.170) | 0.027 | 0.043 (−0.435, 0.521) | 0.861 | 0.109 (−0.158, 0.376) | 0.424 | 0.079 (0.011, 0.146) | 0.022 |
| Q1 | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| Q2 | 0.012 (−0.072, 0.095) | 0.784 | −0.035 (−0.531, 0.461) | 0.889 | 0.027 (−0.248, 0.302) | 0.848 | 0.035 (−0.035, 0.976) | 0.323 |
| Q3 | 0.011 (−0.073, 0.096) | 0.792 | −0.281 (−0.782, 0.221) | 0.273 | −0.038 (−0.317, 0.241) | 0.788 | 0.081 (0.011, 0.152) | 0.024 |
| Q4 | 0.085 (−0.003, 0.172) | 0.059 | 0.019 (−0.503, 0.542) | 0.943 | 0.096 (−0.193, 0.385) | 0.516 | 0.080 (0.006, 0.153) | 0.034 |
| p-trend | 0.089 | 0.755 | 0.665 | 0.013 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, P.; Jiang, S.; Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Z. Cord Blood Manganese Concentrations in Relation to Birth Outcomes and Childhood Physical Growth: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124304
Dai Y, Zhang J, Qi X, Wang Z, Zheng M, Liu P, Jiang S, Guo J, Wu C, Zhou Z. Cord Blood Manganese Concentrations in Relation to Birth Outcomes and Childhood Physical Growth: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124304
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Yiming, Jiming Zhang, Xiaojuan Qi, Zheng Wang, Minglan Zheng, Ping Liu, Shuai Jiang, Jianqiu Guo, Chunhua Wu, and Zhijun Zhou. 2021. "Cord Blood Manganese Concentrations in Relation to Birth Outcomes and Childhood Physical Growth: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124304
APA StyleDai, Y., Zhang, J., Qi, X., Wang, Z., Zheng, M., Liu, P., Jiang, S., Guo, J., Wu, C., & Zhou, Z. (2021). Cord Blood Manganese Concentrations in Relation to Birth Outcomes and Childhood Physical Growth: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study. Nutrients, 13(12), 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124304