Urinary Potassium Excretion, Fibroblast Growth Factor 23, and Incident Hypertension in the General Population-Based PREVEND Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Study Outcome
2.4. Laboratory Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Urinary Potassium Excretion and FGF23
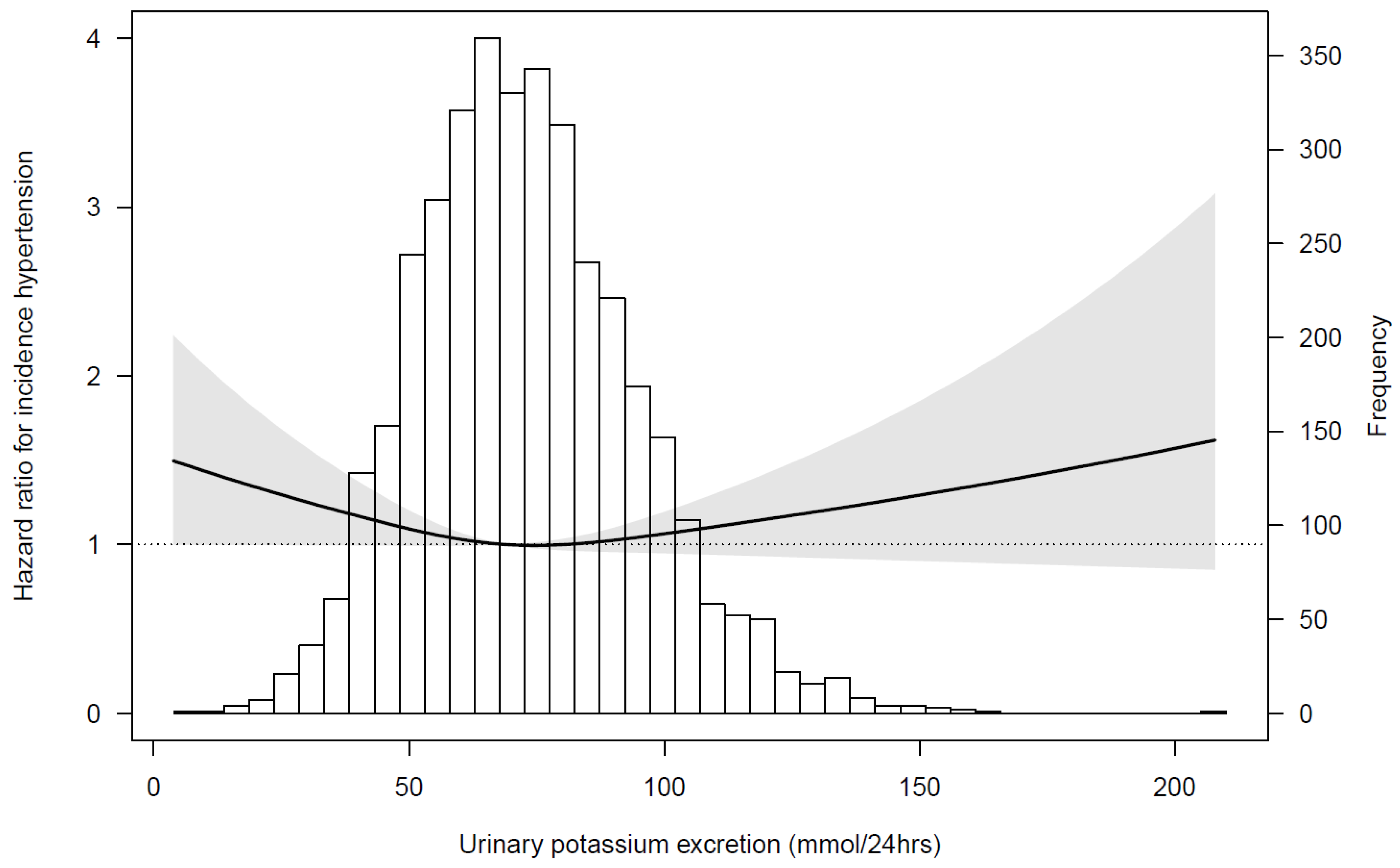
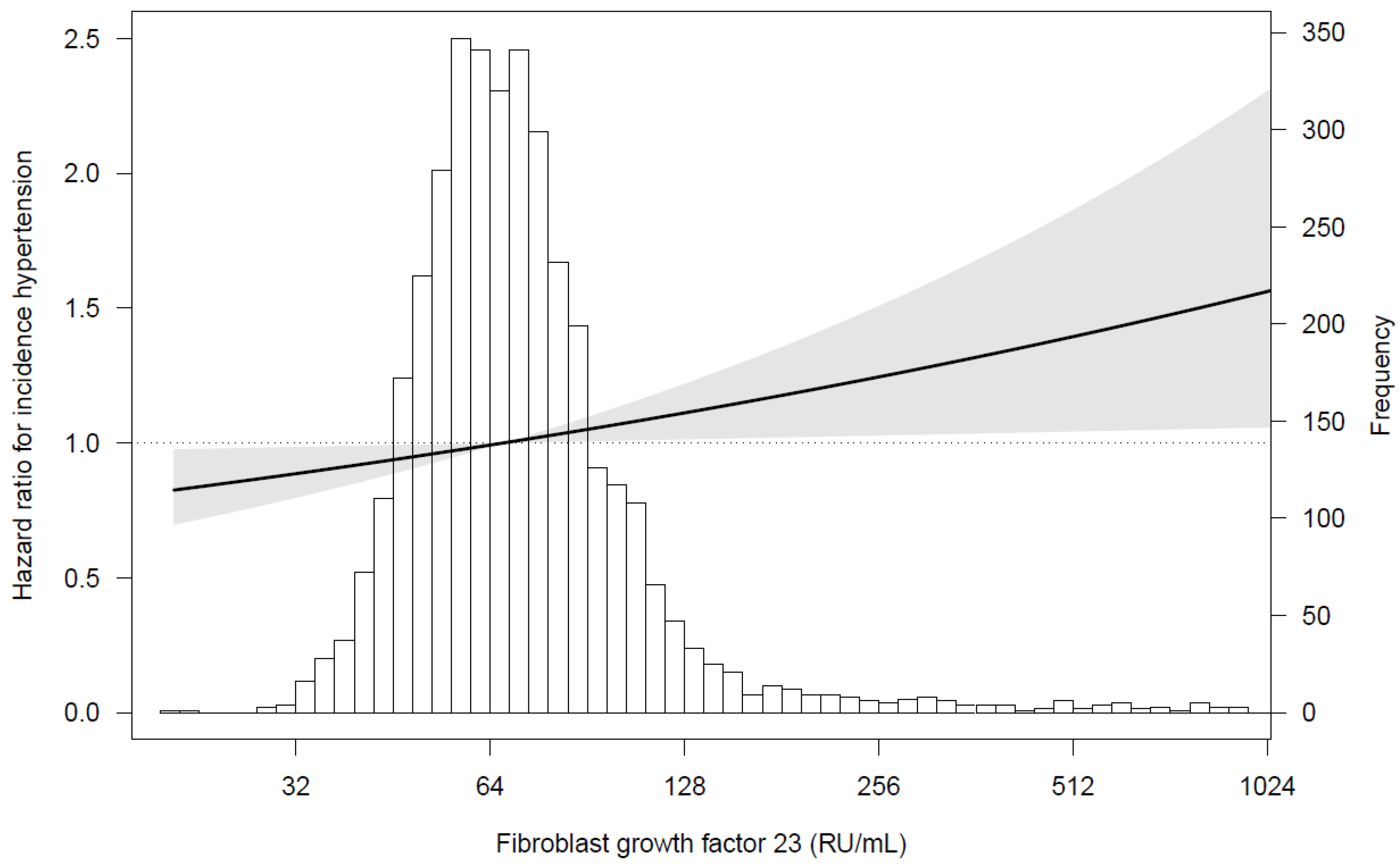
3.3. Urinary Potassium Excretion, FGF23, and Incident Hypertension
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordain, L.; Eaton, S.B.; Sebastian, A.; Mann, N.; Lindeberg, S.; Watkins, B.A.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Brand-Miller, J. Origins and evolution of the Western diet: Health implications for the 21st century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guideline: Potassium Intake for Adults and Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kieneker, L.M.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Mukamal, K.J.; De Boer, R.A.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Joosten, M.M. Urinary potassium excretion and risk of developing hypertension: The prevention of renal and vascular end-stage disease study. Hypertension 2014, 64, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Neiman, A.; Batis, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Popkin, B.M. Understanding the patterns and trends of sodium intake, potassium intake, and sodium to potassium ratio and their effect on hypertension in China. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cogswell, M.E.; Gillespie, C.; Fang, J.; Loustalot, F.; Dai, S.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Kuklina, E.V.; Hong, Y.; Merritt, R.; et al. Association between Usual Sodium and Potassium Intake and Blood Pressure and Hypertension among U.S. Adults: NHANES 2005–2010. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Violi, F.; D’Amico, R.; Vinceti, M. The effect of potassium supplementation on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 230, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorn, E.J.; Gritter, M.; Cuevas, C.A.; Fenton, R.A. Regulation of the renal nacl cotransporter and its role in potassium homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 321–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, P.; Bonjour, J.P.; Karlmark, B.; Stanton, B.; Kirk, R.G.; Duplinsky, T.; Giebisch, G. Influence of acute potassium loading on renal phosphate transport in the rat kidney. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 1983, 245, F601–F605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Hernandez, R.E.; Portale, A.A.; Colman, J.; Tatsuno, J.; Morris, R.C. Dietary potassium influences kidney maintenance of serum phosphorus concentration. Kidney Int. 1990, 37, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humalda, J.K.; Yeung, S.M.H.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Gijsbers, L.; Riphagen, I.J.; Hoorn, E.J.; Rotmans, J.I.; Vogt, L.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.L.; et al. Effects of Potassium or Sodium Supplementation on Mineral Homeostasis: A Controlled Dietary Intervention Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3246–e3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakova, T.; Wahl, P.; Vargas, G.S.; Gutiérrez, O.M.; Scialla, J.; Xie, H.; Appleby, D.; Nessel, L.; Bellovich, K.; Chen, J.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonston, D.; Wolf, M. FGF23 at the crossroads of phosphate, iron economy and erythropoiesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe-Johnson, A.L.; Alonso, A.; Selvin, E.; Bower, J.K.; Pankow, J.S.; Agarwal, S.K.; Lutsey, P.L. Serum fibroblast growth factor-23 and incident hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhabue, E.; Montag, S.; Reis, J.P.; Pool, L.R.; Mehta, R.; Yancy, C.W.; Zhao, L.; Wolf, M.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; et al. FGF23 (Fibroblast Growth Factor-23) and Incident Hypertension in Young and Middle-Aged Adults. Hypertension 2018, 72, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Borst, M.H.; Vervloet, M.G.; ter Wee, P.M.; Navis, G. Cross Talk Between the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Vitamin D-FGF-23-klotho in Chronic Kidney Disease: Figure 1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrukhova, O.; Slavic, S.; Smorodchenko, A.; Zeitz, U.; Shalhoub, V.; Lanske, B.; Pohl, E.E.; Erben, R.G. FGF23 regulates renal sodium handling and blood pressure. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 744–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercadal, L.; Metzger, M.; Haymann, J.P.; Thervet, E.; Boffa, J.-J.; Flamant, M.; Vrtovsnik, F.; Gauci, C.; Froissart, M.; Stengel, B. A 3-Marker Index Improves the Identification of Iron Disorders in CKD Anaemia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84144. [Google Scholar]
- Kroot, J.J.C.; Laarakkers, C.M.M.; Geurts-Moespot, A.J.; Grebenchtchikov, N.; Pickkers, P.; van Ede, A.E.; Peters, H.P.E.; van Dongen-Lases, E.; Wetzels, J.F.M.; Sweep, F.C.G.J.; et al. Immunochemical and Mass-Spectrometry–Based Serum Hepcidin Assays for Iron Metabolism Disorders. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inker, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Tighiouart, H.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Feldman, H.I.; Greene, T.; Kusek, J.W.; Manzi, J.; Van Lente, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Estimating glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine and cystatin C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; White, I.R.; Carlin, J.B.; Spratt, M.; Royston, P.; Kenward, M.G.; Wood, A.M.; Carpenter, J.R. Multiple imputation for missing data in epidemiological and clinical research: Potential and pitfalls. BMJ 2009, 338, b2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, O.; Zhou, X.-H. Multiple imputation: Review of theory, implementation and software. Stat. Med. 2007, 26, 3057–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckberg, K.; Kramer, H.; Wolf, M.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.; Tayo, B.; Luke, A.; Cooper, R. Impact of westernization on fibroblast growth factor 23 levels among individuals of African ancestry. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vervloet, M.G.; Van Ittersum, F.J.; Büttler, R.M.; Heijboer, A.C.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Ter Wee, P.M. Effects of dietary phosphate and calcium intake on fibroblast growth factor-23. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, J.; Chonchol, M.; Levi, M. Renal Control of Calcium, Phosphate, and Magnesium Homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erben, R.G. Physiological Actions of Fibroblast Growth Factor-23. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tønnesen, R.; Hovind, P.H.; Jensen, L.T.; Schwarz, P. Determinants of vitamin D status in young adults: Influence of lifestyle, sociodemographic and anthropometric factors. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, V.; Martin, A.; Isakova, T.; Spaulding, C.; Qi, L.; Ramirez, V.; Zumbrennen-Bullough, K.B.; Sun, C.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Babitt, J.L.; et al. Inflammation and functional iron deficiency regulate fibroblast growth factor 23 production. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushinsky, D.A.; Riordon, D.R.; Chan, J.S.; Krieger, N.S. Decreased potassium stimulates bone resorption. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, F774–F780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Kawai, M.; Miyagawa, K.; Ohata, Y.; Tachikawa, K.; Kinoshita, S.; Nishino, J.; Ozono, K.; Michigami, T. Interleukin-1-induced acute bone resorption facilitates the secretion of fibroblast growth factor 23 into the circulation. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2015, 33, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritter, M.; Rotmans, J.I.; Hoorn, E.J. Role of Dietary K + in Natriuresis, Blood Pressure Reduction, Cardiovascular Protection, and Renoprotection. Hypertension 2019, 73, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoro, R.; Ni, P.; Noonan, M.L.; White, K.E. Osteocytic FGF23 and Its Kidney Function. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco, R.F.V.; Takayama, L.; Pereira, R.M.R.; Moyses, R.M.A.; Elias, R.M. Effects of diuretics furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide on CKD-MBD: A prospective randomized study. Bone Rep. 2021, 14, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coruzzi, P.; Brambilla, L.; Brambilla, V.; Gualerzi, M.; Rossi, M.; Parati, G.; Di Rienzo, M.; Tadonio, J.; Novarini, A. Potassium Depletion and Salt Sensitivity in Essential Hypertension. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2857–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Wu, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Tian, M.; Huang, L.; Li, Z.; et al. Effect of Salt Substitution on Cardiovascular Events and Death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, M.; Ando, K.; Onozato, M.L.; Tojo, A.; Yoshikawa, M.; Ogita, T.; Fujita, T. Protective effect of dietary potassium against vascular injury in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 2008, 51, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanch, N.; Clifton, P.M.; Keogh, J.B. A systematic review of vascular and endothelial function: Effects of fruit, vegetable and potassium intake. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Byon, C.H.; Yang, Y.; Bradley, W.E.; Dell’Italia, L.J.; Sanders, P.W.; Agarwal, A.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y. Dietary potassium regulates vascular calcification and arterial stiffness. JCI Insight 2017, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-C.; Wu, H.-Y.; Peng, Y.-S.; Hsu, S.-P.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yang, J.-Y.; Ko, M.-J.; Pai, M.-F.; Tu, Y.-K.; et al. Effects of lower versus higher phosphate diets on fibroblast growth factor-23 levels in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Iorio, B.; Di Micco, L.; Torraca, S.; Sirico, M.L.; Russo, L.; Pota, A.; Mirenghi, F.; Russo, D. Acute Effects of Very-Low-Protein Diet on FGF23 Levels: A Randomized Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.; Rios, R.; Pineda, C.; Lopez, I.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Rodriguez, M.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Raya, A.I. Direct regulation of fibroblast growth factor 23 by energy intake through mTOR. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthi, A.; Donovan, K.; Haynes, R.; Wheeler, D.C.; Baigent, C.; Rooney, C.M.; Landray, M.J.; Moe, S.M.; Yang, J.; Holland, L.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and Risks of Cardiovascular and Noncardiovascular Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritter, M.; Vogt, L.; Yeung, S.M.H.; Wouda, R.D.; Ramakers, C.R.B.; de Borst, M.H.; Rotmans, J.I.; Hoorn, E.J. Rationale and Design of a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Assessing the Renoprotective Effects of Potassium Supplementation in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephron 2018, 140, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engberink, R.H.O.; van den Born, B.-J.H.; Peters-Sengers, H.; Vogt, L. Estimation of potassium intake: Single versus repeated measurements and the associated cardiorenal risk. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviv, A.; Hollenberg, N.K.; Weder, A. Urinary Potassium Excretion and Sodium Sensitivity in Blacks. Hypertension 2004, 43, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sex-Specific Tertiles of Total Urinary Potassium Excretion, mmol/24-h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | p-Trend * | |
| Men | <66 | 66–85 | >85 | |
| Women | <55 | 55–72 | >72 | |
| Urinary potassium excretion, (mmol/24 h) | 47 (10) | 68 (8) | 93 (16) | |
| Men, n (%) | 647 (46) | 648 (47) | 648 (46) | |
| Age, (year) | 50 (11) | 50 (10) | 49 (10) | <0.001 |
| BMI, (kg/m2) | 25.0 (22.8–27.6) | 25.2 (23.0–27.8) | 25.5 (23.5–28.3) | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure, (mmHg) | 117 (109–126) | 117 (109–127) | 117 (110–127) | 0.36 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, (mmHg) | 70 (65–76) | 70 (65–75) | 70 (65–76) | 0.70 |
| Lipid lowering drugs, n (%) | 53 (4) | 39 (3) | 37 (3) | 0.24 |
| Antidiabetic drugs, n (%) | 15 (1) | 19 (2) | 20 (2) | 0.58 |
| Smoking status | 0.007 | |||
| Never, n (%) | 386 (28) | 449 (32) | 455 (33) | |
| Former or current, n (%) | 1008 (72) | 942 (68) | 938 (67) | |
| Alcohol consumption, yes (%) | 999 (72) | 1095 (78) | 1140 (82) | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular disease, yes (%) | 55 (5) | 56 (6) | 72 (8) | 0.15 |
| Diabetes, yes (%) | 43 (3) | 39 (3) | 36 (3) | 0.74 |
| eGFR (CKD-epi), (mL/min·1.73 m2) | 97 (14) | 97 (13) | 97 (13) | 0.33 |
| Plasma albumin, (g/L) | 44 (4) | 44 (5) | 44 (6) | 0.43 |
| Plasma potassium, (mmol/L) | 4.2 (0.3) | 4.2 (0.3) | 4.2 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| Plasma sodium, (mmol/L) | 141 (2) | 141 (2) | 141 (2) | 0.17 |
| High sensitive CRP, (mg/L) | 1.23 (0.59–2.85) | 1.07 (0.50–2.47) | 1.02 (0.48–2.22) | <0.001 |
| Plasma phosphate, (mmol/L) | 1.02 (0.25) | 1.05 (0.53) | 1.02 (0.32) | 0.07 |
| Plasma PTH, (pmol/L) | 4.8 (4.0–5.8) | 4.7 (3.9–5.7) | 4.7 (3.9–5.5) | 0.08 |
| Plasma vitamin D3, 25-OH, (nmol/L) | 55.1 (38.7–74.9) | 57.8 (40.8–77.2) | 58.6 (42.8–77.7) | 0.001 |
| Plasma fibroblast growth factor 23 (RU/mL) | 70 (56–87) | 68 (56–84) | 66 (55–81) | 0.001 |
| Plasma calcium, (mmol/L) | 2.29 (0.12) | 2.29 (0.12) | 2.29 (0.10) | 0.66 |
| Plasma corrected calcium, (mmol/L) | 2.22 (0.15) | 2.21 (0.17) | 2.21 (0.15) | 0.68 |
| Iron, (umol/L) | 16 (6) | 16 (6) | 16 (6) | 0.62 |
| Ferritin, (μg/L) | 86 (41–157) | 79 (39–144) | 79 (38–149) | 0.29 |
| Transferrin saturation, (%) | 25 (10) | 25 (9) | 25 (9) | 0.75 |
| Urinary sodium excretion, (mmol/24 h) | 112 (88–146) | 139 (110–173) | 160 (131–198) | <0.001 |
| Urinary phosphate excretion, (mmol/24 h) | 21 (17–27) | 25 (20–32) | 30 (23–37) | <0.001 |
| TMP/GFR | 0.97 (0.80–1.18) | 1.01 (0.82–1.22) | 1.03 (0.83–1.24) | <0.001 |
| Urinary creatinine excretion, (mmol/24 h) | 11 (3) | 12 (3) | 14 (3) | <0.001 |
| Urinary albumin excretion, (mg/24 h) | 10.5 (7.8–16.7) | 11.7 (8.7–17.3) | 12.5 (9.4–20.6) | <0.001 |
| Urinary albumin-to creatinine ratio, (mg/mmol) | 0.66 (0.48–1.06) | 0.64 (0.48–0.99) | 0.64 (0.48–1.04) | 0.70 |
| Difference per Unit Standardized Variable in Urinary Potassium Excretion with FGF23 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Model | Standardized Beta | p-Value |
| 1 | −0.04 | 0.02 |
| 2 | −0.04 | 0.05 |
| 3 | −0.04 | 0.02 |
| 4 | −0.06 | 0.002 |
| 5 | −0.04 | 0.02 |
| Sex-Specific Tertiles of Urinary Potassium Excretion Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | |
| Men | <66 mmol/24 h | 66–85 mmol/24 h | >85 mmol/24 h |
| Women | <55 mmol/24 h | 55–72 mmol/24 h | >72 mmol/24 h |
| Model 1 | 1.20 (1.03–1.39) * | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.08 (0.93–1.26) |
| Model 2 | 1.19 (1.02–1.38) * | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.09 (0.94–1.26) |
| Model 3 | 1.19 (1.02–1.38) * | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.09 (0.94–1.26) |
| Sex-Specific Tertiles of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | |
| Men | <58 RU/mL | 58–73 RU/mL | ≥73 RU/mL |
| Women | <61 RU/mL | 61–82 RU/mL | ≥82 RU/mL |
| Model 1 | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.02 (0.88–1.19) | 1.19 (1.03–1.38) * |
| Model 2 | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.00 (0.86–1.16) | 1.17 (1.01–1.36) * |
| Model 3 | 1.0 (ref.) | 1.00 (0.86–1.17) | 1.17 (1.01–1.37) * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeung, S.M.H.; Hoorn, E.J.; Rotmans, J.I.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Vogt, L.; de Borst, M.H. Urinary Potassium Excretion, Fibroblast Growth Factor 23, and Incident Hypertension in the General Population-Based PREVEND Cohort. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124532
Yeung SMH, Hoorn EJ, Rotmans JI, Gansevoort RT, Bakker SJL, Vogt L, de Borst MH. Urinary Potassium Excretion, Fibroblast Growth Factor 23, and Incident Hypertension in the General Population-Based PREVEND Cohort. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124532
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeung, Stanley M. H., Ewout J. Hoorn, Joris I. Rotmans, Ron T. Gansevoort, Stephan J. L. Bakker, Liffert Vogt, and Martin H. de Borst. 2021. "Urinary Potassium Excretion, Fibroblast Growth Factor 23, and Incident Hypertension in the General Population-Based PREVEND Cohort" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124532
APA StyleYeung, S. M. H., Hoorn, E. J., Rotmans, J. I., Gansevoort, R. T., Bakker, S. J. L., Vogt, L., & de Borst, M. H. (2021). Urinary Potassium Excretion, Fibroblast Growth Factor 23, and Incident Hypertension in the General Population-Based PREVEND Cohort. Nutrients, 13(12), 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124532






