Bovine Milk-Derived Emulsifiers Increase Triglyceride Absorption in Newborn Formula-Fed Pigs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Lipolysis
2.2. Microstructure of Emulsions
2.3. Preparation of Emulsions for In Vivo Studies
2.4. In Vivo Lipid Digestibility of Complete Formulas (Study 1)
2.5. In Vivo Fat Absorption Kinetics of Pure Emulsions (Study 2)
2.6. In Vivo Lipid Absorption Kinetics from Complete Formulas (Study 3)
3. Statistics
4. Results
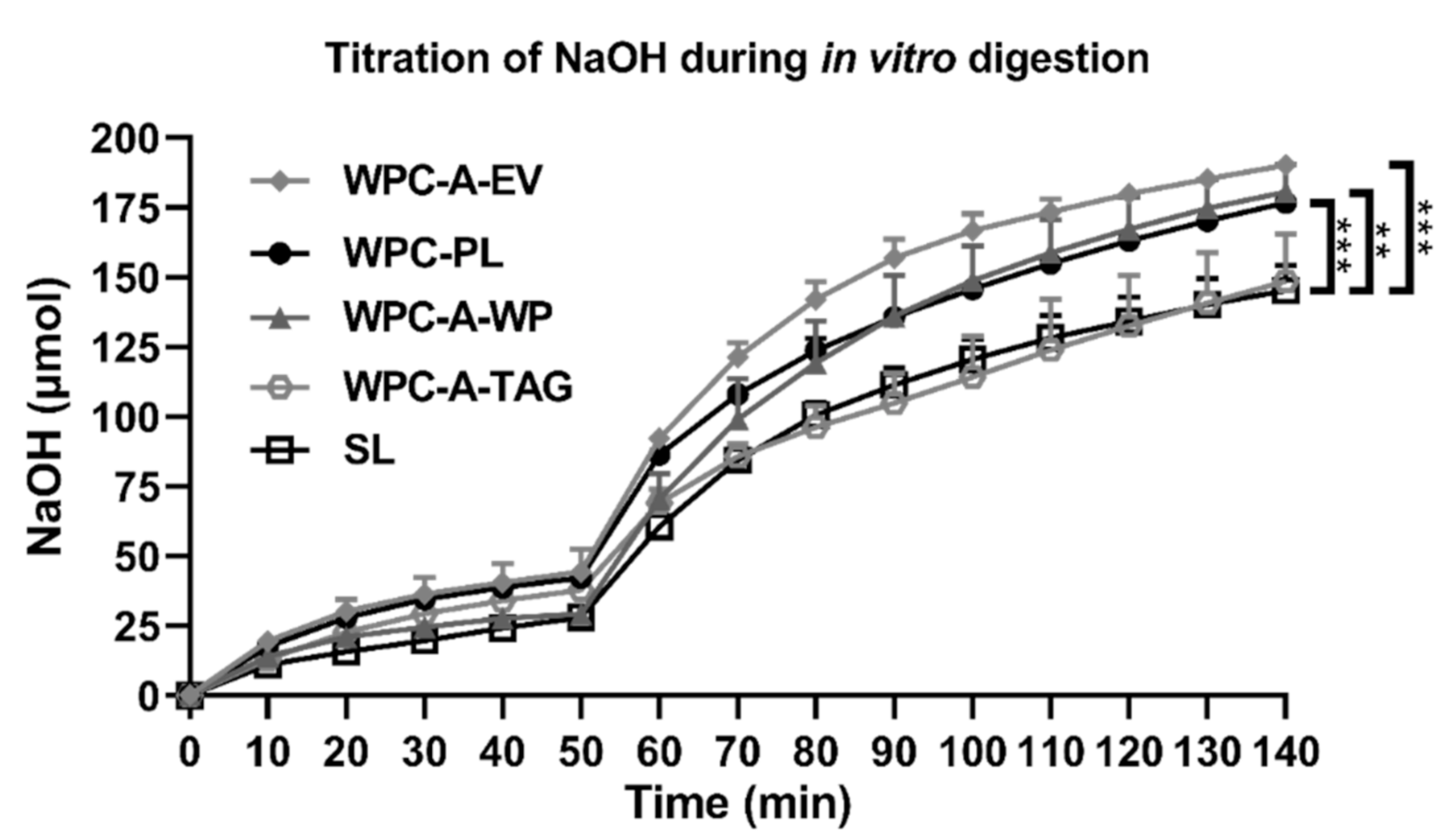
4.1. In Vitro Lipolysis
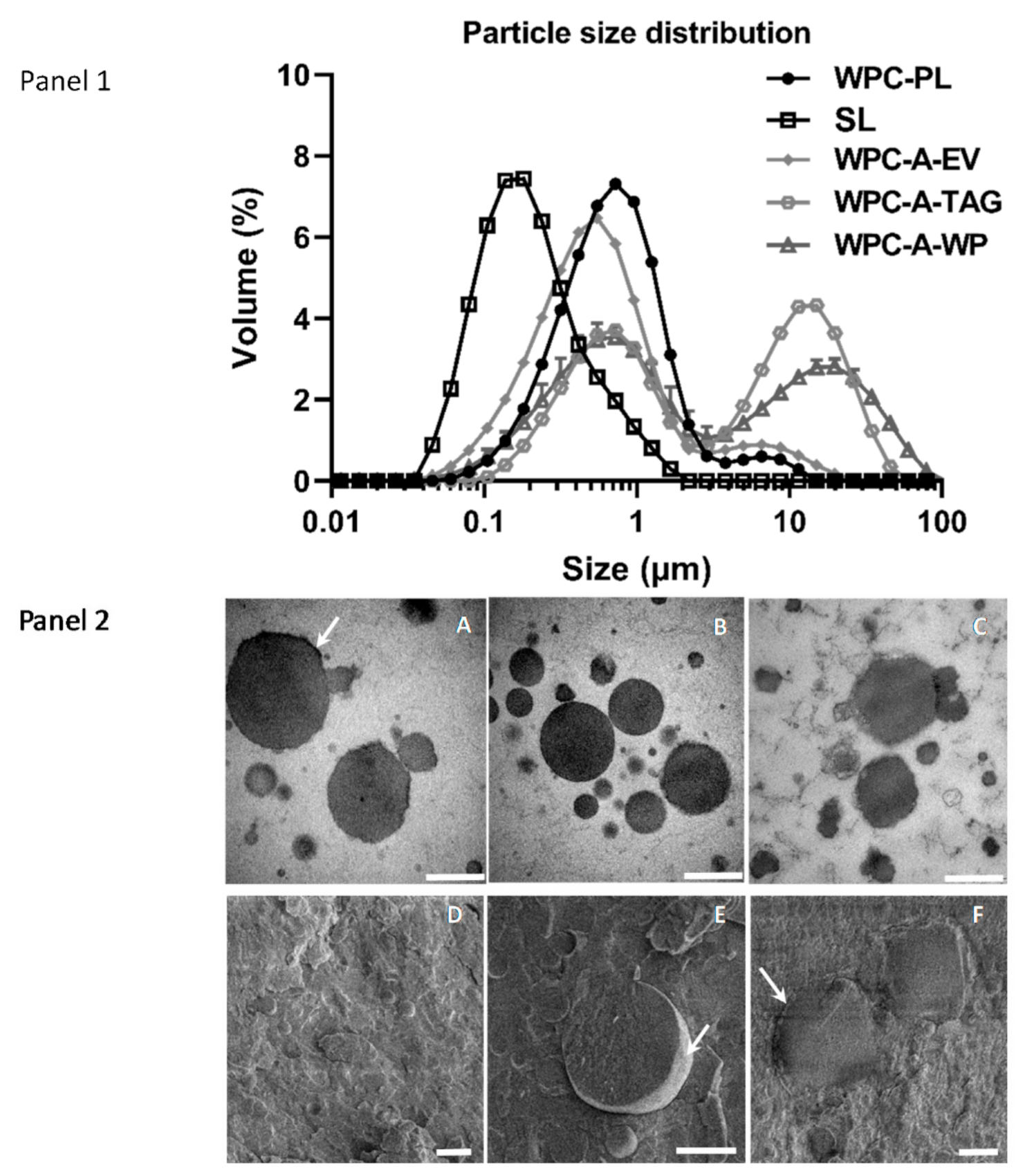
4.2. In Vitro Study 2—Microstructure of Emulsions
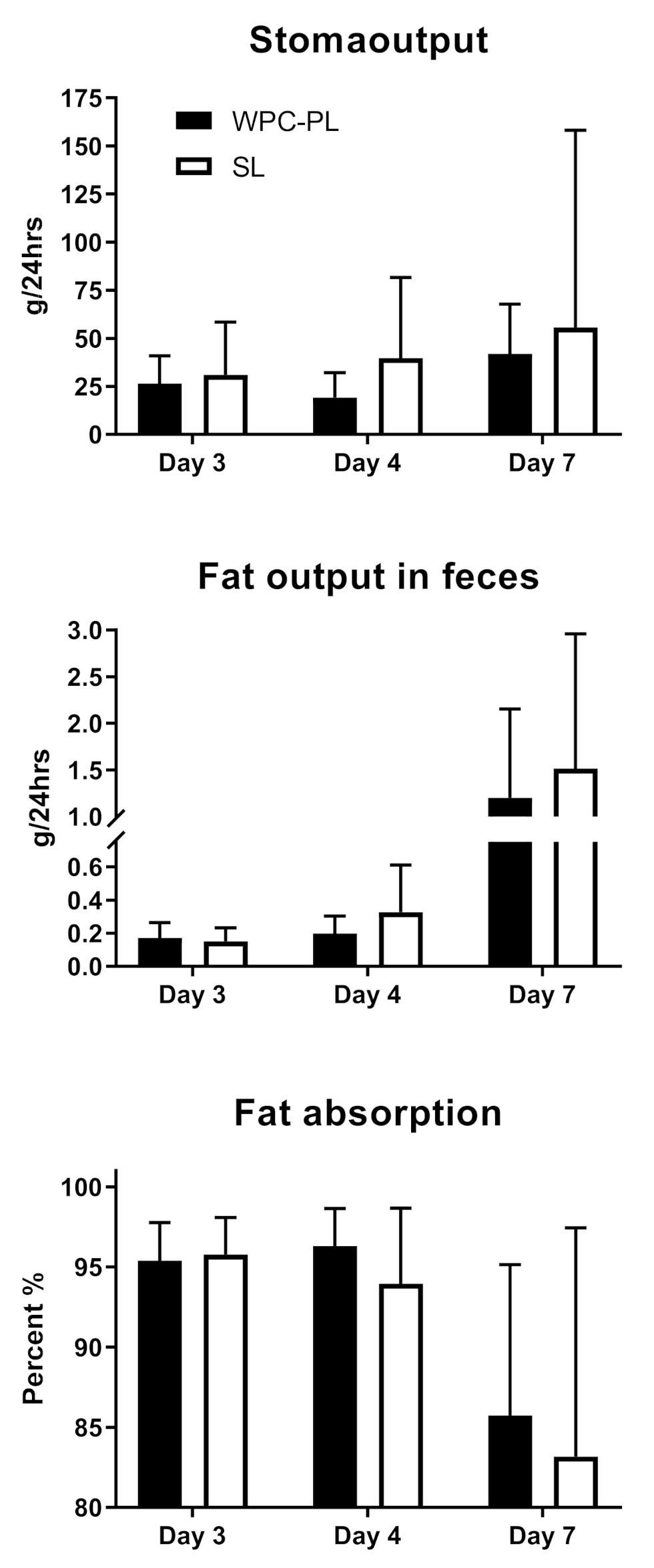
4.3. In Vivo Study 1—In Vivo Fat Digestibility of Complete Emulsions
4.4. In Vivo Study 2—In Vivo Fat Absorption Kinetics of Pure Emulsions
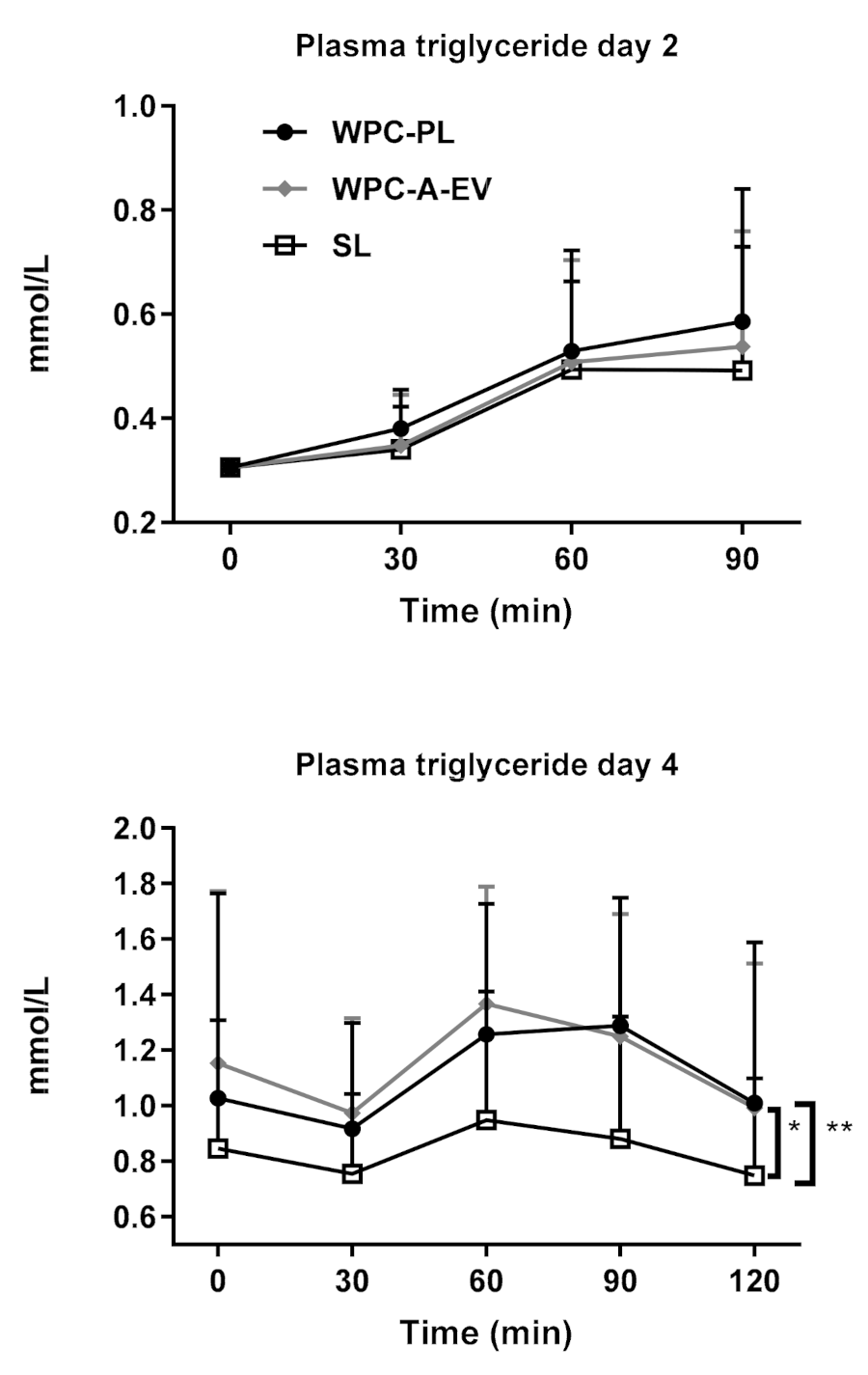
4.5. In Vivo Study 3—In Vivo Fat Absorption Kinetics from Complete Formulas
4.6. Gastric Fat Concentration and Lipase Activity—Related to In Vivo Study 3
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. The Optimal Duration of Exclusive Breastfeeding, Report of an Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- UNICEF. Infant and Young Child Feeding Data. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/nutrition/infant-and-young-child-feeding/ (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Simmons, L.E.; Rubens, C.E.; Darmstadt, G.L.; Gravett, M.G. Preventing preterm birth and neonatal mortality: Exploring the epidemiology, causes, and interventions. Semin. Perinatol. 2010, 34, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arslanoglu, S.; Corpeleijn, W.; Moro, G.; Braegger, C.; Campoy, C.; Colomb, V.; Decsi, T.; Domellof, M.; Fewtrell, M.; Hojsak, I.; et al. Donor human milk for preterm infants: Current evidence and research directions. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gdalevich, M.; Mimouni, D.; David, M.; Mimouni, M. Breast-feeding and the onset of atopic dermatitis in childhood: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, S.; Chung, M.; Raman, G.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Lau, J. A summary of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s evidence report on breastfeeding in developed countries. Breastfeed. Med. 2009, 4 (Suppl. 1), S17–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowning, R.; Radmacher, P.; Lewis, S.; Serke, L.; Pettit, N.; Adamkin, D.H. A retrospective analysis of the effect of human milk on prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis and postnatal growth. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, V.; Sandoz, L.; Garcia-Rodenas, C.L. Importance of the regiospecific distribution of long-chain saturated fatty acids on gut comfort, fat and calcium absorption in infants. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essential Fatty Acids 2017, 121, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Johnstone, B.M.; Remley, D.T. Breast-feeding and cognitive development: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta, B.L.; Loret de Mola, C.; Victora, C.G. Breastfeeding and intelligence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.S.; Aboud, F.; Mironova, E.; Vanilovich, I.; Platt, R.W.; Matush, L.; Igumnov, S.; Fombonne, E.; Bogdanovich, N.; Ducruet, T.; et al. Breastfeeding and child cognitive development: New evidence from a large randomized trial. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 65, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, C.G.; Horta, B.L.; Loret de Mola, C.; Quevedo, L.; Pinheiro, R.T.; Gigante, D.P.; Goncalves, H.; Barros, F.C. Association between breastfeeding and intelligence, educational attainment, and income at 30 years of age: A prospective birth cohort study from Brazil. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e199–e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kafouri, S.; Kramer, M.; Leonard, G.; Perron, M.; Pike, B.; Richer, L.; Toro, R.; Veillette, S.; Pausova, Z.; Paus, T. Breastfeeding and brain structure in adolescence. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, C.I.; Kiliaan, A.J. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA) from genesis to senescence: The influence of LCPUFA on neural development, aging, and neurodegeneration. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 53, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, E.C.; Farquharson, J.; Logan, R.W.; Howatson, A.G.; Patrick, W.J.; Weaver, L.T.; Cockburn, F. Infant cerebellar gray and white matter fatty acids in relation to age and diet. Lipids 1999, 34, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrides, M.; Neumann, M.A.; Byard, R.W.; Simmer, K.; Gibson, R.A. Fatty acid composition of brain, retina, and erythrocytes in breast- and formula-fed infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuringer, M.; Connor, W.E.; Lin, D.S.; Barstad, L.; Luck, S. Biochemical and functional effects of prenatal and postnatal omega 3 fatty acid deficiency on retina and brain in rhesus monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4021–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delplanque, B.; Gibson, R.; Koletzko, B.; Lapillonne, A.; Strandvik, B. Lipid Quality in Infant Nutrition: Current Knowledge and Future Opportunities. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qawasmi, A.; Landeros-Weisenberger, A.; Leckman, J.F.; Bloch, M.H. Meta-analysis of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation of formula and infant cognition. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smithers, L.G.; Collins, C.T.; Simmonds, L.A.; Gibson, R.A.; McPhee, A.; Makrides, M. Feeding preterm infants milk with a higher dose of docosahexaenoic acid than that used in current practice does not influence language or behavior in early childhood: A follow-up study of a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, S.; Hernell, O. Lipid digestion and absorption in early life: An update. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, J.E.; Clandinin, M.T.; Kearney-Volpe, C.; Reichman, B.; Swyer, P.W. Fatty acid balance studies in premature infants fed human milk or formula: Effect of calcium supplementation. J. Pediatr. 1986, 108, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Hamosh, M.; Mehta, N.R.; Angelus, P.A.; Philpott, J.R.; Henderson, T.R.; Dwyer, N.K.; Lairon, D.; Hamosh, P. Effect of human milk or formula on gastric function and fat digestion in the premature infant. Pediatr.Res. 1996, 40, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koletzko, B. Human Milk Lipids. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69 (Suppl. 2), 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Padhi, E.; Hasegawa, Y.; Larke, J.; Parenti, M.; Wang, A.; Hernell, O.; Lonnerdal, B.; Slupsky, C. Compositional Dynamics of the Milk Fat Globule and Its Role in Infant Development. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernell, O.; Timby, N.; Domellof, M.; Lonnerdal, B. Clinical Benefits of Milk Fat Globule Membranes for Infants and Children. J. Pediatr. 2016, 173, S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, A.K.; Hindmarsh, J.P.; Haisman, D.; Rades, T.; Singh, H. Comparison of the structure and properties of liposomes prepared from milk fat globule membrane and soy phospholipids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3704–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zempleni, J.; Aguilar-Lozano, A.; Sadri, M.; Sukreet, S.; Manca, S.; Wu, D.; Zhou, F.; Mutai, E. Biological Activities of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Cargos from Bovine and Human Milk in Humans and Implications for Infants. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallier, S.; Vocking, K.; Post, J.A.; Van De Heijning, B.; Acton, D.; Van Der Beek, E.M.; Van Baalen, T. A novel infant milk formula concept: Mimicking the human milk fat globule structure. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathiassen, J.H.; Nejrup, R.G.; Frøkiær, H.; Nilsson, Å.; Ohlsson, L.; Hellgren, L.I. Emulsifying triglycerides with dairy phospholipids instead of soy lecithin modulates gut lipase activity. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1522–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerup, C.; Ebbesen, M.F.; Geng, X.; Madsen, S.F.; Berthelsen, R.; Müllertz, A. Effects of recombinant human gastric lipase and pancreatin during in vitro pediatric gastro-intestinal digestion. Food Funct. 2021. submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Timby, N.; Domellof, E.; Hernell, O.; Lonnerdal, B.; Domellof, M. Neurodevelopment, nutrition, and growth until 12 mo of age in infants fed a low-energy, low-protein formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGrath, J.C.; Drummond, G.B.; McLachlan, E.M.; Kilkenny, C.; Wainwright, C.L. Guidelines for reporting experiments involving animals: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharm. 2010, 160, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sangild, P.T.; Thymann, T.; Schmidt, M.; Stoll, B.; Burrin, D.G.; Buddington, R.K. Invited review: The preterm pig as a model in pediatric gastroenterology. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4713–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeppesen, P.B.; Hoy, C.E.; Mortensen, P.B. Differences in essential fatty acid requirements by enteral and parenteral routes of administration in patients with fat malabsorption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreau, H.; Gargouri, Y.; Lecat, D.; Junien, J.L.; Verger, R. Purification, characterization and kinetic properties of the rabbit gastric lipase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 960, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton, A.; Sebban-Kreuzer, C.; Rouvellac, S.; Lopez, C.; Crenon, I. Individual and combined action of pancreatic lipase and pancreatic lipase-related proteins 1 and 2 on native versus homogenized milk fat globules. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 1592–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunsholt, L.; Thymann, T.; Qvist, N.; Sigalet, D.; Husby, S.; Sangild, P.T. Prematurity Reduces Functional Adaptation to Intestinal Resection in Piglets. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billeaud, C.; Puccio, G.; Saliba, E.; Guillois, B.; Vaysse, C.; Pecquet, S.; Steenhout, P. Safety and tolerance evaluation of milk fat globule membrane-enriched infant formulas: A randomized controlled multicenter non-inferiority trial in healthy term infants. Clin. Med. Insights Pediatr. 2014, 8, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Christensen, B.; Heckmann, A.B.; Stenlund, H.; Lonnerdal, B.; Hernell, O. Feeding Infants Formula With Probiotics or Milk Fat Globule Membrane: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timby, N.; Hernell, O.; Vaarala, O.; Melin, M.; Lonnerdal, B.; Domellof, M. Infections in infants fed formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grip, T.; Dyrlund, T.S.; Ahonen, L.; Domellof, M.; Hernell, O.; Hyotylainen, T.; Knip, M.; Lonnerdal, B.; Oresic, M.; Timby, N. Serum, plasma and erythrocyte membrane lipidomes in infants fed formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurnida, D.A.; Rowan, A.M.; Idjradinata, P.; Muchtadi, D.; Sekarwana, N. Association of complex lipids containing gangliosides with cognitive development of 6-month-old infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, A.D.; Sangild, P.T.; Munch, S.L.; van der Beek, E.M.; Renes, I.B.; Ginneken, C.; Greisen, G.O.; Thymann, T. Delayed growth, motor function and learning in preterm pigs during early postnatal life. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R481–R492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| WPC-PL | WPC-A-TAG | WPC-A-EV | WPC-A-WP | SL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent of total: | |||||
| Proteins | 72.7 | 53 | 76 | 89.3 | N/A |
| Neutral fat | 17.8 | 41 | 18 | 1.87 | N/A |
| Phospholipids (PL) | 7.1 | 12.4 | 8.9 | 0.75 | 43.3 |
| Percent of PL: | |||||
| PC | 27.4 | 26 | 27.3 | 28 | 31.2 |
| PE | 29 | 29 | 28 | 28 | 16.6 |
| PI | 7.2 | 5.5 | 5.6 | 5.3 | 26.2 |
| PS-Na | 6 | 10.6 | 9.8 | 9.3 | 0.6 |
| SM | 30.2 | 26.9 | 27.5 | 24 | 0 |
| Other | 0.2 | 2 | 1.8 | 5.4 | 25.4 |
| Final Assay Composition | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound 1 | Simulated Gastric Digestion, mM | Simulated Intestinal Digestion, mM |
| NaCl | 10.4 | 51.8 |
| Tris | 2.0 | 2.2 |
| Maleic acid | 2.0 | 2.2 |
| CaCl2 | 10.1 | 5.9 |
| Sodium taurocholate | 0.0 | 0.5 |
| Phospholipid | 0.0 | 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bach Korsholm Knudsen, K.; Heerup, C.; Røngaard Stange Jensen, T.; Geng, X.; Drachmann, N.; Nordby, P.; Bekker Jeppesen, P.; Ifaoui, I.; Müllertz, A.; Torp Sangild, P.; et al. Bovine Milk-Derived Emulsifiers Increase Triglyceride Absorption in Newborn Formula-Fed Pigs. Nutrients 2021, 13, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020410
Bach Korsholm Knudsen K, Heerup C, Røngaard Stange Jensen T, Geng X, Drachmann N, Nordby P, Bekker Jeppesen P, Ifaoui I, Müllertz A, Torp Sangild P, et al. Bovine Milk-Derived Emulsifiers Increase Triglyceride Absorption in Newborn Formula-Fed Pigs. Nutrients. 2021; 13(2):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020410
Chicago/Turabian StyleBach Korsholm Knudsen, Kristine, Christine Heerup, Tine Røngaard Stange Jensen, Xiaolu Geng, Nikolaj Drachmann, Pernille Nordby, Palle Bekker Jeppesen, Inge Ifaoui, Anette Müllertz, Per Torp Sangild, and et al. 2021. "Bovine Milk-Derived Emulsifiers Increase Triglyceride Absorption in Newborn Formula-Fed Pigs" Nutrients 13, no. 2: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020410
APA StyleBach Korsholm Knudsen, K., Heerup, C., Røngaard Stange Jensen, T., Geng, X., Drachmann, N., Nordby, P., Bekker Jeppesen, P., Ifaoui, I., Müllertz, A., Torp Sangild, P., Stampe Ostenfeld, M., & Thymann, T. (2021). Bovine Milk-Derived Emulsifiers Increase Triglyceride Absorption in Newborn Formula-Fed Pigs. Nutrients, 13(2), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020410







