Circulating Adiponectin and Its Association with Metabolic Traits and Type 2 Diabetes: Gene-Diet Interactions Focusing on Selected Gene Variants and at the Genome-Wide Level in High-Cardiovascular Risk Mediterranean Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Baseline Anthropometric, Clinical, Biochemical and Lifestyle Variables
2.3. Biochemical Determinations and Plasma Adiponectin Measures
2.4. DNA Isolation and Genotyping
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. General Associations and Candidate Gene Analysis
2.5.2. GWASs Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Associations between Plasma Adiponectin and Fasting Glucose, Plasma Lipids, Adiposity Variables and Type 2 Diabetes
3.3. Association between the Pre-Selected ADIPOQ SNPs and Plasma Adiponectin Concentrations. Interactions with Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet
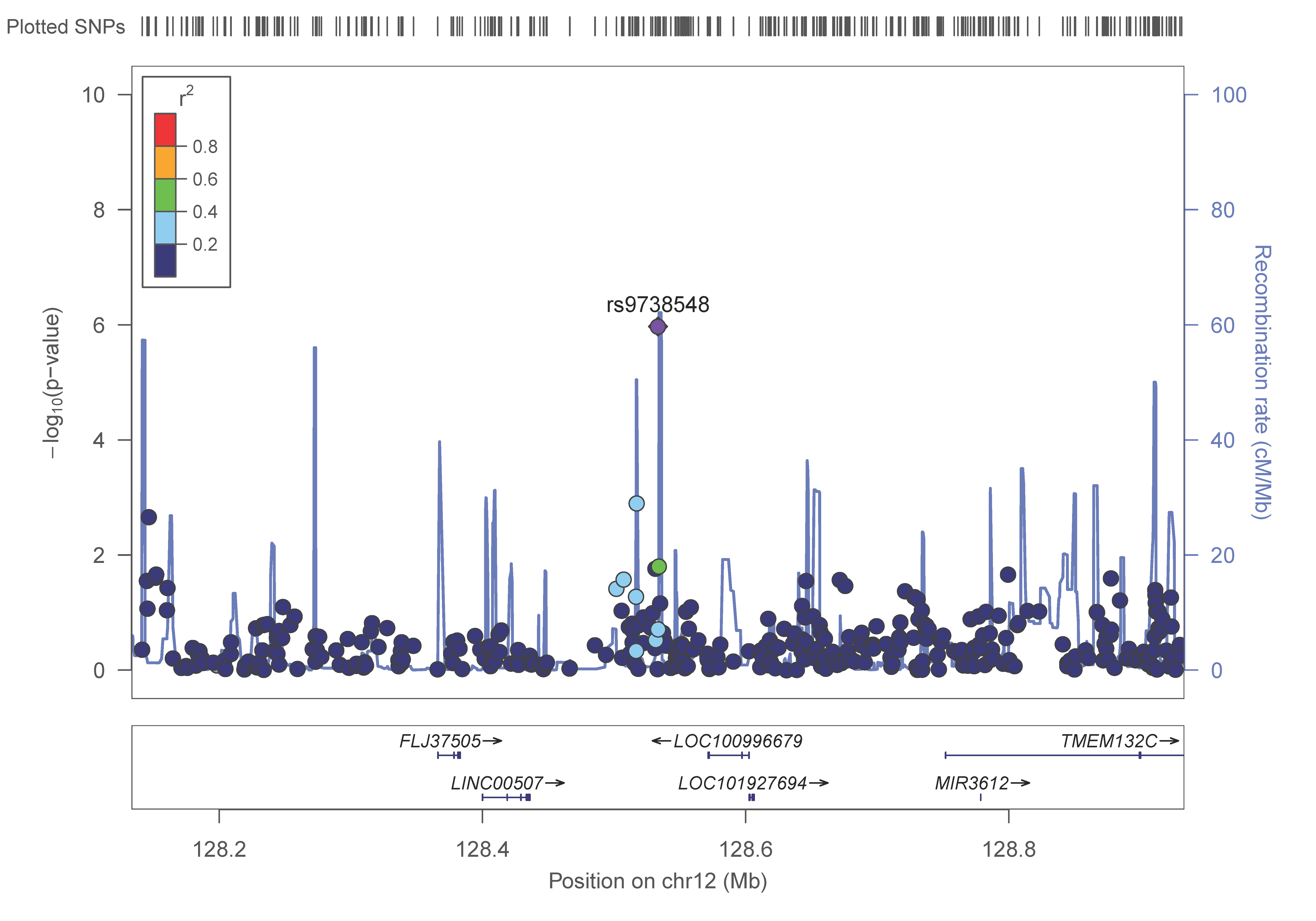
3.4. GWAS for Plasma Adiponectin Concentrations in the Whole Population
3.5. ADIPOQ and CDH13 Genes and Plasma Adiponectin Concentrations in the GWAS
3.6. Stratified GWASs for Plasma Adiponectin
3.6.1. Analysis per Sex
3.6.2. Analysis per Diabetes Status
3.7. Gene–Mediterranean Diet Interactions for Adiponectin Concentrations at the Genome-Wide Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsao, T.-S.; Lodish, H.F.; Fruebis, J. ACRP30, a new hormone controlling fat and glucose metabolism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 440, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, M.E.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin—Journey from an adipocyte secretory protein to biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 257, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Kihara, S.; Shimomura, I. Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuzawa, Y. The metabolic syndrome and adipocytokines. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2917–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pischon, T.; Girman, C.J.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Rifai, N.; Hu, F.B.; Rimm, E.B. Plasma adiponectin levels and risk of myocardial infarction in men. JAMA 2004, 291, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: Adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 1999, 100, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyrou, I.; Tsantarlioti, O.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Tsigos, C.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Chrysohoou, C.; Skoumas, I.; Tousoulis, D.; Stefanadis, C.; Pitsavos, C.; et al. Adiponectin circulating levels and 10-year (2002–2012) cardiovascular disease incidence: The ATTICA study. Endocrine 2017, 58, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Mo, X.; Hao, Y.; Huang, J.; Lu, X.; Cao, J.; Gu, D. Adiponectin levels and risk of coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 345, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Li, W.; Guo, R.; Yang, J.-G.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, M.-Y.; Peng, Y.-G.; Wang, Z.-W. Serum total adiponectin level and the risk of cardiovascular disease in general population: A meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witberg, G.; Ayers, C.R.; Turer, A.T.; Lev, E.; Kornowski, R.; de Lemos, J.; Neeland, I.J. Relation of adiponectin to all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and major adverse cardiovascular events (from the Dallas Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, W.-J.; Qiu, H.-C.; Liu, Y.-K.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, J. Elevated levels of adiponectin associated with major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events and mortality risk in ischemic stroke. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.D. Adiponectin: Role in physiology and pathophysiology. Int. J. Prev Med. 2020, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francischetti, E.A.; Dezonne, R.S.; Pereira, C.M.; de Moraes Martins, C.J.; Celoria, B.M.J.; de Oliveira, P.A.C.; de Abreu, V.G. Insights into the controversial aspects of adiponectin in cardiometabolic disorders. Horm. Metab. Res. 2020, 52, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted physiological roles of adiponectin in inflammation and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohashi, K.; Yuasa, D.; Shibata, R.; Murohara, T.; Ouchi, N. Adiponectin as a target in obesity-related inflammatory state. Endocr. Metab. Immune. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 15, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Ouchi, N.; Matsuzawa, Y. Anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic properties of adiponectin. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2137–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un Nisa, K.; Reza, M.I. Key relevance of epigenetic programming of adiponectin gene in pathogenesis of metabolic disorders. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargnoli, J.L.; Fung, T.T.; Olenczuk, D.M.; Chamberland, J.P.; Hu, F.B.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adherence to healthy eating patterns is associated with higher circulating total and high-molecular-weight adiponectin and lower resistin concentrations in women from the Nurses’ Health Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzoros, C.S.; Williams, C.J.; Manson, J.E.; Meigs, J.B.; Hu, F.B. Adherence to the mediterranean dietary pattern is positively associated with plasma adiponectin concentrations in diabetic women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, V.; Azadbakht, L. Specific dietary patterns and concentrations of adiponectin. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Baden, M.Y.; Satija, A.; Hu, F.B.; Huang, T. Change in plant-based diet quality is associated with changes in plasma adiposity-associated biomarker concentrations in women. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, V.; Larijani, B.; Azadbakht, L. Is coffee and green tea consumption related to serum levels of adiponectin and leptin? Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmiran, P.; Hosseini, S.; Hosseinpour-Niazi, S.; Azizi, F. Legume consumption increase adiponectin concentrations among type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized crossover clinical trial. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2019, 66, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, J.; Jabakhanji, A.; Biemann, R.; Mai, K.; Abraham, K.; Weikert, C. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the associations of vegan and vegetarian diets with inflammatory biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavian, S.P.; Rahimlou, M.; Saneei, P.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effects of dairy products consumption on inflammatory biomarkers among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. CardioVasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comuzzie, A.G.; Funahashi, T.; Sonnenberg, G.; Martin, L.J.; Jacob, H.J.; Black, A.E.; Maas, D.; Takahashi, M.; Kihara, S.; Tanaka, S.; et al. The genetic basis of plasma variation in adiponectin, a global endophenotype for obesity and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackevics, V.; Heid, I.M.; Wagner, S.A.; Cip, P.; Doppelmayr, H.; Lejnieks, A.; Gohlke, H.; Ladurner, G.; Illig, T.; Iglseder, B.; et al. The adiponectin gene is associated with adiponectin levels but not with characteristics of the insulin resistance syndrome in healthy Caucasians. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 14, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitfeld, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Kovacs, P. Genetics of adiponectin. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero, M.E.; Cai, G.; Göring, H.H.H.; Diego, V.; Cole, S.A.; Bacino, C.A.; Butte, N.F.; Comuzzie, A.G. Linkage analysis of circulating levels of adiponectin in Hispanic children. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Alokail, M.S.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Yakout, S.M.; Sabico, S.B.; Gibson, G.C.; Chrousos, G.P.; Kumar, S. Parent-offspring transmission of adipocytokine levels and their associations with metabolic traits. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, E.; Liang, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crimmins, N.A.; Martin, L.J. Polymorphisms in adiponectin receptor genes ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2 and insulin resistance. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, S.H.; Sull, J.W.; Lee, J.-E.; Shin, C.; Park, J.; Kimm, H.; Cho, E.-Y.; Shin, E.-S.; Yun, J.E.; Park, J.W.; et al. Adiponectin concentrations: A genome-wide association study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heid, I.M.; Henneman, P.; Hicks, A.; Coassin, S.; Winkler, T.; Aulchenko, Y.S.; Fuchsberger, C.; Song, K.; Hivert, M.-F.; Waterworth, D.M.; et al. Clear detection of ADIPOQ locus as the major gene for plasma adiponectin: Results of genome-wide association analyses including 4659 European individuals. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morisaki, H.; Yamanaka, I.; Iwai, N.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kokubo, Y.; Okamura, T.; Okayama, A.; Morisaki, T. CDH13 gene coding T-cadherin influences variations in plasma adiponectin levels in the Japanese population. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Chen, P.; Igase, M.; Kawamoto, R.; Kim, M.K.; Kohara, K.; Lee, J.; Miki, T.; Ong, R.T.-H.; et al. Genetic variation in CDH13 is associated with lower plasma adiponectin levels but greater adiponectin sensitivity in East Asian populations. Diabetes 2013, 62, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.-M.; Lin, T.-H.; Chen, J.-W.; Leu, H.-B.; Yang, H.-C.; Ho, H.-Y.; Ting, C.-T.; Sheu, S.-H.; Tsai, W.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; et al. A genome-wide association study reveals a quantitative trait locus of adiponectin on CDH13 that predicts cardiometabolic outcomes. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lange, E.M.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Kuzawa, C.W.; McDade, T.W.; Qin, L.; Curocichin, G.; Borja, J.B.; Lange, L.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study for adiponectin levels in Filipino women identifies CDH13 and a novel uncommon haplotype at KNG1-ADIPOQ. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4955–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, H.; Tabara, Y.; Nakatochi, M.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Park, E.J.; Wen, W.; Adair, L.S.; Borja, J.B.; et al. A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for adiponectin levels in east Asians identifies a novel locus near WDR11-FGFR2. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dastani, Z.; Hivert, M.-F.; Timpson, N.; Perry, J.R.B.; Yuan, X.; Scott, R.A.; Henneman, P.; Heid, I.M.; Kizer, J.R.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; et al. Novel loci for adiponectin levels and their influence on type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits: A multi-ethnic meta-analysis of 45,891 individuals. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, J.B.; Waterworth, D.; O’Rahilly, S.; Hivert, M.-F.; Loos, R.J.F.; Perry, J.R.B.; Tanaka, T.; Timpson, N.J.; Semple, R.K.; Soranzo, N.; et al. A genome-wide association study reveals variants in ARL15 that influence adiponectin levels. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen-Torvik, L.J.; Pankow, J.S.; Peacock, J.M.; Borecki, I.B.; Hixson, J.E.; Tsai, M.Y.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Arnett, D.K. Suggestion for linkage of chromosome 1p35.2 and 3q28 to plasma adiponectin concentrations in the GOLDN study. BMC Med. Genet. 2009, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spracklen, C.N.; Iyengar, A.K.; Vadlamudi, S.; Raulerson, C.K.; Jackson, A.U.; Brotman, S.M.; Wu, Y.; Cannon, M.E.; Davis, J.P.; Crain, A.T.; et al. Adiponectin GWAS loci harboring extensive allelic heterogeneity exhibit distinct molecular consequences. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslibekyan, S.; An, P.; Frazier-Wood, A.C.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Irvin, M.R.; Straka, R.J.; Tiwari, H.K.; Tsai, M.Y.; Hopkins, P.N.; Borecki, I.B.; et al. Preliminary evidence of genetic determinants of adiponectin response to fenofibrate in the genetics of lipid lowering drugs and diet network. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyriakou, T.; Collins, L.J.; Spencer-Jones, N.J.; Malcolm, C.; Wang, X.; Snieder, H.; Swaminathan, R.; Burling, K.A.; Hart, D.J.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Adiponectin gene ADIPOQ SNP associations with serum adiponectin in two female populations and effects of SNPs on promoter activity. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 53, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Chu, Z.; Miao, J.; Zhou, H. Meta-analysis of the association between adiponectin SNP 45, SNP 276, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melistas, L.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Kontogianni, M.; Antonopoulou, S.; Ordovas, J.M.; Yiannakouris, N. Association of the +45T>G and +276G>T polymorphisms in the adiponectin gene with insulin resistance in nondiabetic Greek women. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hivert, M.-F.; Manning, A.K.; McAteer, J.B.; Florez, J.C.; Dupuis, J.; Fox, C.S.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Meigs, J.B. Common variants in the adiponectin gene (ADIPOQ) associated with plasma adiponectin levels, type 2 diabetes, and diabetes-related quantitative traits: The Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes 2008, 57, 3353–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasseur, F.; Meyre, D.; Froguel, P. Adiponectin, type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: Lessons from human genetic studies. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2006, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, A.; Crepostnaia, D.; Maniou, Z.; Lewis, F.J.; Hall, W.L.; Sanders, T.A.B.; O’Dell, S.D. MARINA study team adiponectin gene variant interacts with fish oil supplementation to influence serum adiponectin in older individuals. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AlSaleh, A.; Sanders, T.A.B.; O’Dell, S.D. Effect of interaction between PPARG, PPARA and ADIPOQ gene variants and dietary fatty acids on plasma lipid profile and adiponectin concentration in a large intervention study. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2012, 71, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ntalla, I.; Dedoussis, G.; Yannakoulia, M.; Smart, M.C.; Louizou, E.; Sakka, S.D.; Papoutsakis, C.; Talmud, P.J. ADIPOQ gene polymorphism Rs1501299 interacts with fibre intake to affect adiponectin concentration in children: The Gene-Diet ATTICA Investigation on childhood obesity. Eur. J. Nutr. 2009, 48, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Primo, D.; de Luis, D.A. The effect of single-nucleotide polymorphisms at the ADIPOQ gene locus Rs1501299 on metabolic parameters after 9 months of a high-protein/low-carbohydrate versus a standard hypocaloric diet. Nutrition 2019, 65, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, D.; Coltell, O.; Macian, F.; Ordovás, J.M. Advances in understanding the molecular basis of the mediterranean diet effect. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Azorín, C.; Coltell, O.; Asensio, E.M.; Sorlí, J.V.; González, J.I.; Portolés, O.; Saiz, C.; Estruch, R.; Ramírez-Sabio, J.B.; Pérez-Fidalgo, A.; et al. Candidate gene and genome-wide association studies for circulating leptin levels reveal population and sex-specific associations in high cardiovascular risk Mediterranean subjects. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M.; Babio, N.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ibarrola-Jurado, N.; Basora, J.; Estruch, R.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with the Mediterranean diet: Results of the PREDIMED-reus nutrition intervention randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Azorín, C.; Sorlí, J.V.; Asensio, E.M.; Coltell, O.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.-I.; Arós, F.; Lapetra, J.; Serra-Majem, L.; et al. Associations of the FTO Rs9939609 and the MC4R Rs17782313 polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes are modulated by diet, being higher when adherence to the Mediterranean diet pattern is low. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corella, D.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Sorlí, J.V.; Covas, M.I.; Carrasco, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Arós, F.; Lapetra, J.; Serra-Majem, L.; et al. Statistical and biological gene-lifestyle interactions of MC4R and FTO with diet and physical activity on obesity: New effects on alcohol consumption. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schröder, H.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.; Ros, E.; Salaverría, I.; Fiol, M.; et al. A short screener is valid for assessing Mediterranean diet adherence among older Spanish men and women. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.-K.; Yuan, X.-C.; Sun, J.; Liu, D.-H. Adiponectin single nucleotide polymorphisms and serum levels are relevant to prognosis of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhages. Am. J. Ther. 2017, 24, e308–e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, S.D. Qqman: An R package for visualizing GWAS results using Q-Q and Manhattan plots. Bioinformatics 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Umićević Mirkov, M.; de Leeuw, C.A.; van den Heuvel, M.P.; Posthuma, D. Genetic mapping of cell type specificity for complex traits. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruim, R.J.; Welch, R.P.; Sanna, S.; Teslovich, T.M.; Chines, P.S.; Gliedt, T.P.; Boehnke, M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Willer, C.J. LocusZoom: Regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2336–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, M.; Raffler, J.; Pfeufer, A.; Suhre, K.; Kastenmüller, G. SNiPA: An interactive, genetic variant-centered annotation browser. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1334–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Huang, K. PARP-1 suppresses adiponectin expression through Poly(ADP-Ribosyl)Ation of PPAR gamma in cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 81, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erener, S.; Hesse, M.; Kostadinova, R.; Hottiger, M.O. Poly(ADP-Ribose)Polymerase-1 (PARP1) controls adipogenic gene expression and adipocyte function. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devalaraja-Narashimha, K.; Padanilam, B.J. PARP1 deficiency exacerbates diet-induced obesity in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 205, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Llorens, S.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Talebi, M.; Shakibaei, M.; Samarghandian, S. An overview of the role of adipokines in cardiometabolic diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shin, H.J.; Ding, E.L.; van Dam, R.M. Adiponectin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2009, 302, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snijder, M.B.; Heine, R.J.; Seidell, J.C.; Bouter, L.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Nijpels, G.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Shimomura, I.; Dekker, J.M. Associations of adiponectin levels with incident impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes in older men and women: The Hoorn study. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2498–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, R.-W.; Kunutsor, S.K.; Chowdhury, R.; Yuan, J.-M.; Koh, W.-P.; Pan, A. Plasma adiponectin levels and type 2 diabetes risk: A nested case-control study in a Chinese population and an updated meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial effects of adiponectin on glucose and lipid metabolism and atherosclerotic progression: Mechanisms and perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Lowe, G.D.O.; Rumley, A.; Cherry, L.; Whincup, P.H.; Sattar, N. Adipokines and risk of type 2 diabetes in older men. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hivert, M.-F.; Sullivan, L.M.; Shrader, P.; Fox, C.S.; Nathan, D.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Kowall, B.; Herder, C.; Meisinger, C.; et al. Insulin resistance influences the association of adiponectin levels with diabetes incidence in two population-based cohorts: The cooperative health research in the region of Augsburg (KORA) S4/F4 study and the Framingham offspring study. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hivert, M.-F.; Sullivan, L.M.; Fox, C.S.; Nathan, D.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Meigs, J.B. Associations of adiponectin, resistin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3165–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; Prins, J.; Venkatesh, B. Clinical review: Adiponectin biology and its role in inflammation and critical illness. Crit. Care 2011, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi-Mamaeghani, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Arefhosseini, S.R.; Fallah, P.; Bazi, Z. Adiponectin as a potential biomarker of vascular disease. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straub, L.G.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic messengers: Adiponectin. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Patel, K.P.; Teng, A.K.; Berens, A.J.; Lachance, J. Genetic disease risks can be misestimated across global populations. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, A.R.; Kanai, M.; Kamatani, Y.; Okada, Y.; Neale, B.M.; Daly, M.J. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltell, O.; Asensio, E.M.; Sorlí, J.V.; Barragán, R.; Fernández-Carrión, R.; Portolés, O.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Martínez-LaCruz, R.; González, J.I.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) on bilirubin concentrations in subjects with metabolic syndrome: Sex-specific GWAS analysis and gene-diet interactions in a Mediterranean population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coltell, O.; Sorlí, J.V.; Asensio, E.M.; Fernández-Carrión, R.; Barragán, R.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Estruch, R.; González, J.I.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Lamon-Fava, S.; et al. Association between taste perception and adiposity in overweight or obese older subjects with metabolic syndrome and identification of novel taste-related genes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1709–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltell, O.; Sorlí, J.V.; Asensio, E.M.; Barragán, R.; González, J.I.; Giménez-Alba, I.M.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; Estruch, R.; Ramírez-Sabio, J.B.; Pascual, E.C.; et al. Genome-wide association study for serum Omega-3 and Omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Exploratory analysis of the sex-specific effects and dietary modulation in Mediterranean subjects with metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabangin, M.E.; Woo, J.G.; Martin, L.J. The effect of minor allele frequency on the likelihood of obtaining false positives. BMC Proc. 2009, 3 (Suppl. 7), S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.; Fang, K.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J. Network-based analysis of schizophrenia genome-wide association data to detect the joint. Functional association signals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Sun, Y.; Dai, J.; Su, B. Transcriptomic landscape of von economo neurons in human anterior cingulate cortex revealed by microdissected-cell RNA sequencing. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, L. Identification of key genes and pathways in calcific aortic valve disease by bioinformatics analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 5417–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Jin-Cheng, G.; Jue, Z.; Quan-Fu, M.; Bin, Y.; Xu-Feng, W. Protein-coding genes, long non-coding RNAs combined with microRNAs as a novel clinical multi-dimension transcriptome signature to predict prognosis in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 72847–72859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Tong, C.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M.; Zhao, X. Identification and characterization of differentially expressed exosomal microRNAs in bovine milk infected with Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowroozpoor, A.; Gutterman, D.; Safdar, B. Is microvascular dysfunction a systemic disorder with common biomarkers found in the heart, brain, and kidneys?—A scoping review. Microvasc. Res. 2021, 134, 104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolajević-Starčević, J.; Pleskovič, A.; Santl Letonja, M.; Jenko Pražnikar, Z.; Petrovič, D. Polymorphisms +45T>G and +276G>T of the adiponectin gene does not affect plasma adiponectin level and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Int. Angiol. 2014, 33, 434–440. [Google Scholar]
- Palit, S.P.; Patel, R.; Jadeja, S.D.; Rathwa, N.; Mahajan, A.; Ramachandran, A.V.; Dhar, M.K.; Sharma, S.; Begum, R. A Genetic analysis identifies a haplotype at adiponectin locus: Association with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Total (n = 954) | Men (n = 348) | Women (n = 606) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 67.0 ± 0.2 | 66.2 ± 0.4 | 67.4 ± 0.2 | 0.007 |
| Weight (kg) | 76.3 ± 0.4 | 81.5 ± 0.6 | 73.4 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.3 ± 0.1 | 29.6 ± 0.2 | 30.7 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 102.5 ± 0.4 | 104.2 ± 0.6 | 101.5 ± 0.5 | 0.001 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 146.8 ± 0.7 | 148.3 ± 1.1 | 145.9 ± 0.9 | 0.086 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 81.9 ± 0.3 | 82.6 ± 0.6 | 81.4 ± 0.4 | 0.099 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 207.7 ± 1.3 | 199.7 ± 2.0 | 212.3 ± 1.6 | <0.001 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 129.1 ± 1.2 | 124.5 ± 1.9 | 131.6 ± 1.5 | 0.004 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 52.5 ± 0.4 | 47.9 ± 0.6 | 55.1 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides 1 (mg/dL) | 131.5 ± 2.3 | 136.6 ± 3.7 | 128.6 ± 2.8 | 0.051 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 120.4 ± 1.3 | 128.3 ± 2.2 | 115.8 ± 1.5 | <0.001 |
| Plasma adiponectin 2 (µg/mL) | 10.4 ± 0.2 | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 11.9 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| Physical activity (MET-min/day) | 166 ± 6 | 216 ± 12 | 137 ± 5 | <0.001 |
| Adherence to MedDiet (P14) 3 | 8.0 ± 2.8 | 7.9 ± 2.8 | 8.1 ± 2.7 | 0.130 |
| High adherence MedDiet 4 | 476 (50.0) | 177 (51.0) | 299 (49.4) | 0.637 |
| Current smokers: n, % | 116 (12.2) | 88 (25.3) | 28 (4.6) | <0.001 |
| Type 2 diabetes: n, % | 450 (47.2) | 197 (56.6) | 253 (41.7) | <0.001 |
| Obesity: n, % | 478 (50.1) | 151 (43.4) | 327 (54.0) | 0.002 |
| Trait 1 | Total Adiponectin (µg/mL) | Men Adiponectin (µg/mL) | Women Adiponectin (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | r2 | −0.261 | −0.109 | −0.271 |
| p3 | 3.48 × 10−16 | 0.043 | 1.42 × 10−11 | |
| Tryglicerides (mg/dL) | r2 | −0.276 | −0.169 | −0.340 |
| p3 | 4.72 × 10−18 | 1.59 × 10−3 | 8.17 × 10−18 | |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | r2 | 0.391 | 0.292 | 0.342 |
| p3 | 5.59 × 10−36 | 3.03 × 10−8 | 5.00 × 10−18 | |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | r2 | 0.109 | 0.084 | 0.077 |
| p3 | 8.52 × 10−4 | 0.122 | 0.059 | |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | r2 | 0.029 | 0.068 | −0.075 |
| p3 | 0.367 | 0.209 | 0.064 | |
| Waist circumference (cm) | r2 | −0.090 | 0.032 | −0.093 |
| p3 | 0.006 | 0.559 | 0.024 |
| Total | Men | Women | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adiponectin | OR 3 and 95% CI | p5 | OR 3 and 95% CI | p5 | OR 3 and 95% CI | p5 |
| Dichotomous variable 1 | ||||||
| Model 1 2 | 0.65 (0.49–0.84) | 0.001 | 0.77 (0.50–1.19) | 0.239 | 0.59 (0.42–0.82) | 0.002 |
| Model 2 3 | 0.61 (0.46–0.79) | 2.80 × 10−4 | 0.68 (0.43–1.06) | 0.090 | 0.57 (0.41–0.81) | 0.001 |
| Model 3 4 | 0.61 (0.46–0.80) | 4.40 × 10−4 | 0.67 (0.42–1.07) | 0.093 | 0.59 (0.42–0.85) | 0.004 |
| Continuous variable 6 | ||||||
| Model 1 2 | 0.46 (0.35–0.59) | 3.00 × 10−9 | 0.69 (0.48–1.09) | 0.097 | 0.42 (0.29–0.59) | 1.01 × 10−6 |
| Model 2 3 | 0.47 (0.35–0.62) | 1.41 × 10−7 | 0.64 (0.39–1.03) | 0.065 | 0.40 (0.28–0.57) | 6.40 × 10−7 |
| Model 3 4 | 0.47 (0.35–0.63) | 3.03 × 10−7 | 0.64 (0.39–1.03) | 0.066 | 0.42 (0.29–0.61) | 3.10 × 10−5 |
| Pre-Selected ADIPOQ Candidate SNPs | Genotypes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 Mean ± SE | 12 Mean ± SE | 22 Mean ± SE | p1 | p2 | p-Int3 MedDiet | |
| −11391 G > A (rs17300539) 4 | 10.09 ± 0.20 | 11.45 ± 0.47 | 13.45 ± 1.00 | 4.80 × 10−4 | 7.20 × 10−5 | 0.559 |
| +45T > G (rs2241766) in exon 2 5 | 10.41 ± 0.22 | 10.37 ± 0.36 | 11.40 ± 0.89 | 0.436 | 0.808 | 0.072 |
| +276G > T (rs1501299) in intron 2 6 | 10.33 ± 0.25 | 10.26 ± 0.30 | 12.02 ± 0.69 | 0.091 | 0.047 | 0.795 |
| rs17366568 (G > A) 7 | 10.49 ± 0.20 | 10.39 ± 0.46 | 8.57 ± 1.39 | 0.271 | 0.257 | 0.525 |
| Chr | SNP | BP | Beta | p | Alleles | MAF | Strand | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | rs9738548 | 128533430 | 0.141 | 1.07 × 10−6 | T | 0.137 | + | intergenic |
| 13 | rs396318 | 56590135 | 0.247 | 3.03 × 10−6 | G | 0.129 | + | intergenic |
| 4 | rs17613848 | 23485012 | −0.123 | 3.72 × 10−6 | A | 0.135 | + | LOC105374524 |
| 16 | rs12149200 | 678430 | 0.184 | 4.43 × 10−6 | T | 0.020 | + | RAB40C |
| 4 | rs998888 | 160494830 | 0.215 | 8.02 × 10−6 | T | 0.097 | - | LOC107986324 |
| 11 | rs11024603 | 18306399 | 0.129 | 8.77 × 10−6 | A | 0.228 | + | HPS5 |
| 1 | rs6698721 | 185849364 | 0.446 | 1.00 × 10−5 | A | 0.176 | + | HMCN1 |
| 16 | rs11647294 | 77917661 | 0.098 | 1.01 × 10−5 | T | 0.401 | + | VAT1L |
| 21 | rs2850066 | 37338018 | −0.119 | 1.02 × 10−5 | G | 0.273 | + | LOC101928269 |
| 16 | rs4785550 | 48864323 | 0.183 | 1.05 × 10−5 | T | 0.227 | + | intergenic |
| A: Non-Diabetic Subjects | ||||||||
| Chr | SNP | BP | Beta | p | Alleles | MAF | Strand | Gene |
| 21 | rs2850066 | 37338018 | −0.189 | 3.51 × 10−8 | G | 0.273 | + | LOC101928269 |
| 21 | rs2835220 | 37367098 | −0.157 | 3.18 × 10−7 | C | 0.283 | + | LOC101928269 |
| 6 | rs1283468 | 70038147 | 0.200 | 4.52 × 10−7 | A | 0.180 | + | ADGRB3 |
| 14 | rs12887387 | 90196183 | 0.232 | 1.71 × 10−6 | T | 0.162 | + | intergenic |
| 14 | rs2146971 | 90173453 | 0.198 | 2.11 × 10−6 | T | 0.161 | - | intergenic |
| 11 | rs11024603 | 18306399 | 0.184 | 2.36 × 10−6 | A | 0.228 | + | HPS5 |
| B: Diabetic Subjects | ||||||||
| Chr | SNP | BP | Beta | p | Alleles | MAF | Strand | Gene |
| 22 | rs5992838 | 18264831 | −0.147 | 7.73 × 10−6 | G | 0.411 | + | intergenic |
| 10 | rs11239763 | 43262368 | −0.161 | 1.07 × 10−5 | C | 0.393 | + | LOC105378269 |
| 9 | rs1779307 | 91449366 | 0.144 | 1.09 × 10−5 | C | 0.356 | + | intergenic |
| 10 | rs11239766 | 43264591 | −0.161 | 1.35 × 10−5 | G | 0.386 | + | LOC105378269 |
| 2 | rs2290130 | 232263127 | 0.168 | 1.35 × 10−5 | A | 0.233 | - | B3GNT7 |
| 3 | rs7616406 | 12862257 | 0.152 | 1.49 × 10−5 | G | 0.446 | + | CAND2 |
| Chr | SNP | Beta 1 | Beta 2 | p-Interaction 1 | Alleles | MAF | Strand | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | rs17249128 | −0.125 | 0.123 | 2.53 × 10−7 | G | 0.466 | + | LOC101927334 |
| 4 | rs828154 | 0.077 | −0.191 | 9.74 × 10−7 | G | 0.485 | − | intergenic |
| 3 | rs326251 | 0.131 | −0.097 | 4.20 × 10−6 | C | 0.333 | − | intergenic |
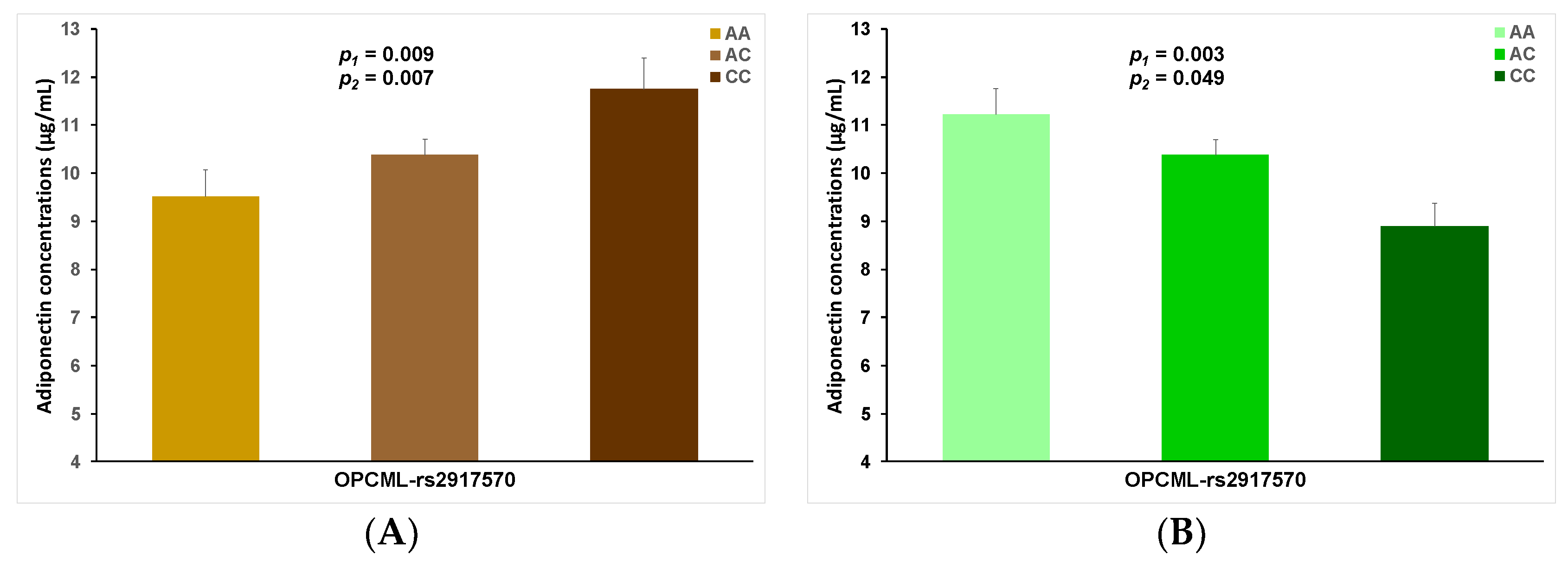
| 11 | rs2917570 | 0.113 | −0.118 | 5.12 × 10−6 | T | 0.497 | + | OPCML |
| 4 | rs13111850 | 0.334 | −0.130 | 6.42 × 10−6 | C | 0.033 | + | intergenic |
| 2 | rs6433691 | 0.197 | −0.162 | 6.45 × 10−6 | A | 0.241 | + | PDE11A |
| 4 | rs10019416 | −0.093 | 0.175 | 7.46 × 10−6 | A | 0.258 | + | SLIT2 |
| 11 | rs3016384 | 0.118 | −0.109 | 8.05 × 10−6 | T | 0.491 | − | OPCML |
| 2 | rs3770019 | 0.206 | −0.156 | 1.09 × 10−5 | C | 0.141 | + | PDE11A |
| 8 | rs13280216 | 0.174 | −0.100 | 1.16 × 10−5 | A | 0.267 | + | intergenic |
| 2 | rs9677333 | 0.203 | −0.156 | 1.31 × 10−5 | C | 0.139 | + | PDE11A |
| 4 | rs10023405 | −0.119 | 0.112 | 1.39 × 10−5 | G | 0.210 | + | KIAA1211 |
| 10 | rs912745 | −0.148 | 0.211 | 1.44 × 10−5 | T | 0.092 | + | LOC102724627 |
| 1 | rs3219110 | 0.061 | −0.146 | 1.51 × 10−5 | C | 0.319 | − | PARP1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coltell, O.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Sorlí, J.V.; Portolés, O.; Asensio, E.M.; Saiz, C.; Barragán, R.; Estruch, R.; Corella, D. Circulating Adiponectin and Its Association with Metabolic Traits and Type 2 Diabetes: Gene-Diet Interactions Focusing on Selected Gene Variants and at the Genome-Wide Level in High-Cardiovascular Risk Mediterranean Subjects. Nutrients 2021, 13, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020541
Coltell O, Ortega-Azorín C, Sorlí JV, Portolés O, Asensio EM, Saiz C, Barragán R, Estruch R, Corella D. Circulating Adiponectin and Its Association with Metabolic Traits and Type 2 Diabetes: Gene-Diet Interactions Focusing on Selected Gene Variants and at the Genome-Wide Level in High-Cardiovascular Risk Mediterranean Subjects. Nutrients. 2021; 13(2):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020541
Chicago/Turabian StyleColtell, Oscar, Carolina Ortega-Azorín, Jose V. Sorlí, Olga Portolés, Eva M. Asensio, Carmen Saiz, Rocío Barragán, Ramon Estruch, and Dolores Corella. 2021. "Circulating Adiponectin and Its Association with Metabolic Traits and Type 2 Diabetes: Gene-Diet Interactions Focusing on Selected Gene Variants and at the Genome-Wide Level in High-Cardiovascular Risk Mediterranean Subjects" Nutrients 13, no. 2: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020541
APA StyleColtell, O., Ortega-Azorín, C., Sorlí, J. V., Portolés, O., Asensio, E. M., Saiz, C., Barragán, R., Estruch, R., & Corella, D. (2021). Circulating Adiponectin and Its Association with Metabolic Traits and Type 2 Diabetes: Gene-Diet Interactions Focusing on Selected Gene Variants and at the Genome-Wide Level in High-Cardiovascular Risk Mediterranean Subjects. Nutrients, 13(2), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020541










