Optimal Protein Intake in Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Sarcopenia: An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definition and Epidemiology of Sarcopenia in CKD
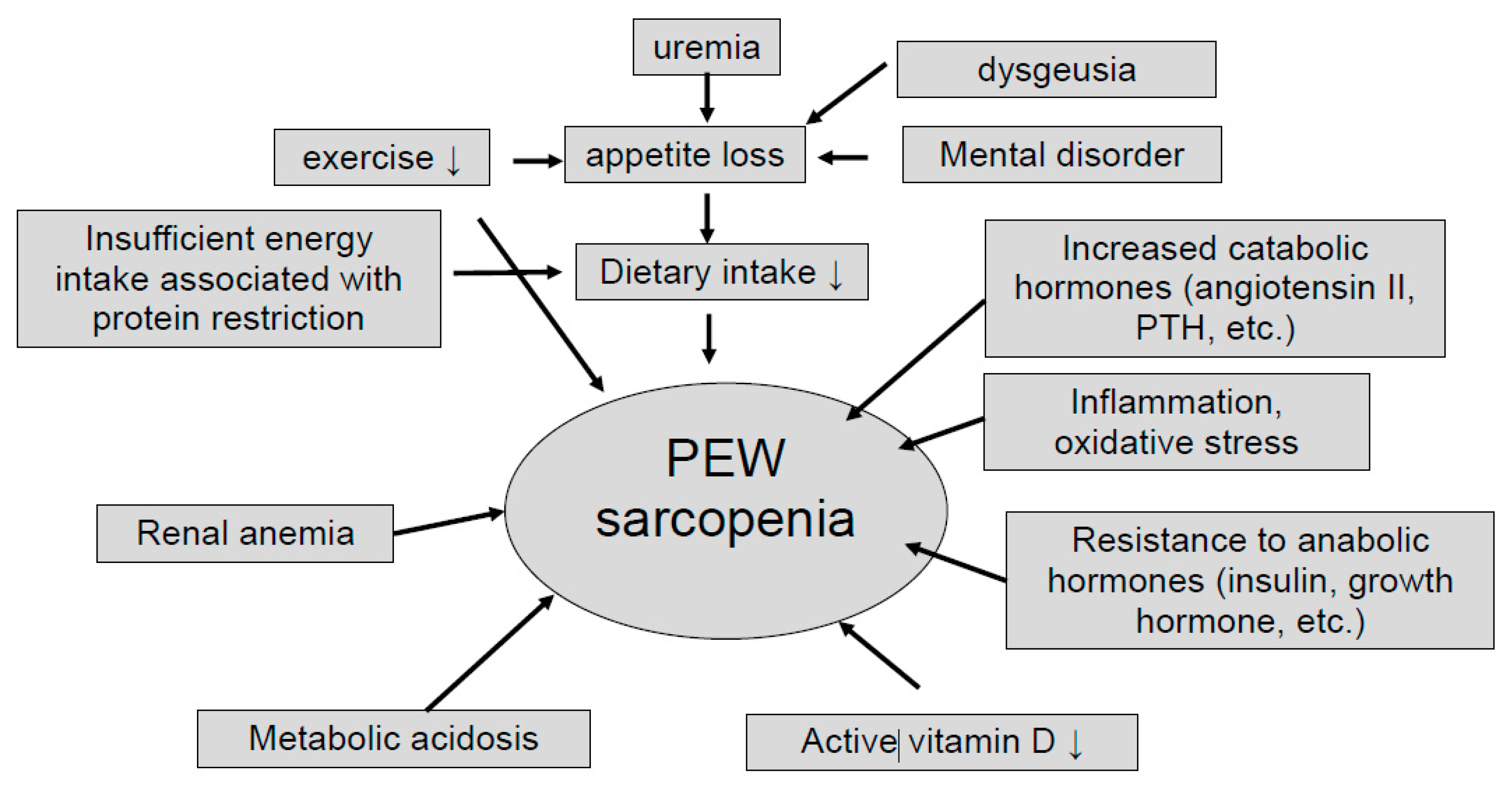
3. CKD with Sarcopenia and Protein Restriction
4. Effect of Increased Protein Intake for CKD Patients with Sarcopenia
5. Increased Protein Intake and Exercise for CKD Patients with Sarcopenia
6. Excessive Protein Intake in CKD Patients
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouque, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.; Cano, N.; Chauveau, P.; Cuppari, L.; Franch, H.; Guarnieri, G.; Ikizler, T.; Kaysen, G.; et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein–energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrero, J.J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Cuppari, L.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kaysen, G.; Mitch, W.E.; Price, S.R.; Wanner, C.; Wang, A.Y.; et al. Etiology of the Protein-Energy Wasting Syndrome in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Statement From the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM). J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moorthi, R.N.; Avin, K.G. Clinical relevance of sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2017, 26, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabatino, A.; Cuppari, L.; Stenvinkel, P.; Lindholm, B.; Avesani, C.M. Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease: What have we learned so far? J. Nephrol. 2020, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Greene, J.H.; Wingard, R.L.; Parker, R.A.; Hakim, R.M. Spontaneous dietary protein intake during progression of chronic renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1995, 6, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Duenhas, M.R.; Draibe, S.A.; Avesani, C.M.; Sesso, R.; Cuppari, L. Influence of renal function on spontaneous dietary intake and on nutritional status of chronic renal insufficiency patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajan, V.; Mitch, W.E. Ubiquitin, proteasomes and proteolytic mechanisms activated by kidney disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2008, 1782, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.-H.; Li, Y.; Du, J.; Mitch, W.E.; Rosenthal, N.; Delafontaine, P. Muscle-specific expression of IGF-1 blocks angiotensin II–induced skeletal muscle wasting. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onder, G.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Balkrishnan, R.; Fried, L.P.; Chaves, P.H.M.; Williamson, J.; Carter, C.; Di Bari, M.; Guralnik, J.M.; Pahor, M. Relation between use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and muscle strength and physical function in older women: An observational study. Lancet 2002, 359, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Lai, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-H.; Liou, H.-H.; Hsu, B.-G. Angiotensin II receptor blockade is associated with preserved muscle strength in chronic hemodialysis patients. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, I.; Moutabarrik, A.; Okada, N.; Kitamura, E.; Hayashi, A.; Syouji, T.; Namiki, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Zaid, D.; Tsubakihara, Y. Interleukin-8 in chronic renal failure and dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1994, 9, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Meuwese, C.L.; Carrero, J.J.; Stenvinkel, P. Recent Insights in Inflammation-Associated Wasting in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 171, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utaka, S.; Avesani, C.M.; Draibe, S.A.; Kamimura, M.A.; Andreoni, S.; Cuppari, L. Inflammation is associated with increased energy expenditure in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boirie, Y.; Broyer, M.; Gagnadoux, M.F.; Niaudet, P.; Bresson, J.-L. Alterations of protein metabolism by metabolic acidosis in children with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pickering, W.P.; Price, S.R.; Bircher, G.; Marinovic, A.C.; Mitch, W.E.; Walls, J. Nutrition in CAPD: Serum bicarbonate and the ubiquitin-proteasome system in muscle. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frangos, E.; Trombetti, A.; Graf, C.E.; Lachat, V.; Samaras, N.; Vischer, U.M.; Zekry, D.; Rizzoli, R.; Herrmann, F.R. Malnutrition in very old hospitalized patients: A new etiologic factor of anemia? J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Deeg, D.J.H.; Lips, P. Low Vitamin D and High Parathyroid Hormone Levels as Determinants of Loss of Muscle Strength and Muscle Mass (Sarcopenia): The Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5766–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Hiraki, K.; Otobe, Y.; Izawa, K.P.; Sakurada, T.; Shibagaki, Y. Relationship between Serum Vitamin D and Leg Strength in Older Adults with Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.; Mukai, H.; Lindholm, B.; Heimbürger, O.; Barany, P.; Stenvinkel, P.; Qureshi, A.R. Clinical global assessment of nutritional status as predictor of mortality in chronic kidney disease patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houston, D.K.; Nicklas, B.J.; Ding, J.; Harris, T.B.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Newman, A.B.; Lee, J.S.; Sahyoun, N.R.; Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; et al. Dietary protein intake is associated with lean mass change in older, community-dwelling adults: The Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.-P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuttle, C.S.; Thang, L.A.; Maier, A.B. Markers of inflammation and their association with muscle strength and mass: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehle, S.; Krapf, R. Effects of acidogenic diet forms on musculoskeletal function. J. Nephrol. 2010, 23, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Tajar, A.; Lee, D.M.; Pye, S.R.; O’Connell, M.D.L.; Ravindrarajah, R.; Gielen, E.; Boonen, S.; Vanderschueren, D.; Pendleton, N.; Finn, J.D.; et al. The association of frailty with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and parathyroid hormone levels in older European men. Age Ageing 2013, 42, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, S.; Naito, S.; Iimori, S.; Takahashi, D.; Zeniya, M.; Sato, H.; Nomura, N.; Sohara, E.; Okado, T.; Uchida, S.; et al. Loop diuretics are associated with greater risk of sarcopenia in patients with non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandai, S.; Furukawa, S.; Kodaka, M.; Hata, Y.; Mori, T.; Nomura, N.; Ando, F.; Mori, Y.; Takahashi, D.; Yoshizaki, Y.; et al. Loop diuretics affect skeletal myoblast differentiation and exercise-induced muscle hypertrophy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.-K.; Liu, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.-Y.; Hsu, P.-S.; Krairit, O.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.P.; Teo, K.K.; Rangarajan, S.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Avezum, A.; Orlandini, A.; Seron, P.; Ahmed, S.H.; Rosengren, A.; Kelishadi, R.; et al. Prognostic value of grip strength: Findings from the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study. Lancet 2015, 386, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Hwang, H.-J. Relationship between Stage of Chronic Kidney Disease and Sarcopenia in Korean Aged 40 Years and Older Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES IV-2, 3, and V-1, 2), 2008–2011. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, R.A.; Cordeiro, A.C.; Avesani, C.M.; Carrero, J.J.; Lindholm, B.; Amparo, F.C.; Amodeo, C.; Cuppari, L.; Kamimura, M.A. Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease on conservative therapy: Prevalence and association with mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, H.; Gong, D.; Jia, F.; Xu, B.; Liu, Z. Sarcopenia in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: Incidence rate, risk factors and its effect on survival risk. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, R.N.; Wang, C.; Ishani, A.; Collins, A.J.; Murray, A.M. Kidney Function and Sarcopenia in the United States General Population: NHANES III. Am. J. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshanravan, B.; Patel, K.V.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; De Boer, I.H.; O’Hare, A.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Himmelfarb, J.; Kestenbaum, B. Creatinine Clearance, Walking Speed, and Muscle Atrophy: A Cohort Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinkeler, S.J.; Kwakernaak, A.J.; Bakker, S.J.; Shahinfar, S.; Esmatjes, E.; De Zeeuw, D.; Navis, G.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Creatinine Excretion Rate and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, S.; Taniguchi, M.; Tokumoto, M.; Yoshitomi, R.; Yoshida, H.; Tatsumoto, N.; Hirakata, H.; Fujimi, S.; Kitazono, T.; Tsuruya, K. Modified Creatinine Index and the Risk of Bone Fracture in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: The Q-Cohort Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hare, A.M.; Choi, A.I.; Bertenthal, D.; Bacchetti, P.; Garg, A.X.; Kaufman, J.S.; Walter, L.C.; Mehta, K.M.; Steinman, M.A.; Allon, M.; et al. Age Affects Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-Based Recommendations for Optimal Dietary Protein Intake in Older People: A Position Paper From the PROT-AGE Study Group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciaruso, B.; Pota, A.; Pisani, A.; Torraca, S.; Annecchini, R.; Lombardi, P.; Capuano, A.; Nazzaro, P.; Bellizzi, V.; Sabbatini, M. Metabolic effects of two low protein diets in chronic kidney disease stage 4–5—A randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 23, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mircescu, G.; Gârneaţă, L.; Stancu, S.H.; Căpuşă, C. Effects of a Supplemented Hypoproteic Diet in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Su, X.; Xu, B.; Qiao, X.; Wang, L. Effect of diet protein restriction on progression of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nicola, L.; Provenzano, M.; Chiodini, P.; Borrelli, S.; Russo, L.; Bellasi, A.; Santoro, D.; Conte, G.; Minutolo, R. Epidemiology of low-proteinuric chronic kidney disease in renal clinics. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, Y.; Kimura, T.; Nagasawa, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Yasuda, K.; Sasaki, K.; Kitamura, H.; Imai, E.; Rakugi, H.; Isaka, Y.; et al. Impact of Age and Overt Proteinuria on Outcomes of Stage 3 to 5 Chronic Kidney Disease in a Referred Cohort. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inaguma, D.; For The Chronic Kidney Disease Japan Cohort Study Group; Imai, E.; Takeuchi, A.; Ohashi, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Nitta, K.; Akizawa, T.; Matsuo, S.; Makino, H.; et al. Risk factors for CKD progression in Japanese patients: Findings from the Chronic Kidney Disease Japan Cohort (CKD-JAC) study. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2017, 21, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coresh, J.; Turin, T.C.; Matsushita, K.; Sang, Y.; Ballew, S.H.; Appel, L.J.; Arima, H.; Chadban, S.J.; Cirillo, M.; Djurdjev, O.; et al. Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate and Subsequent Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease and Mortality. JAMA 2014, 311, 2518–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Coresh, J.; Ballew, S.H.; Woodward, M.; Levin, A.; Naimark, D.M.J.; Nally, J.; Rothenbacher, D.; Stengel, B.; Iseki, K.; et al. Past Decline Versus Current eGFR and Subsequent ESRD Risk. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 27, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rughooputh, M.S.; Zeng, R.; Yao, Y. Protein Diet Restriction Slows Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in Non-Diabetic and in Type 1 Diabetic Patients, but Not in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Using Glomerular Filtration Rate as a Surrogate. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bauer, J.M.; Verlaan, S.; Bautmans, I.; Brandt, K.; Donini, L.M.; Maggio, M.; McMurdo, M.E.; Mets, T.; Seal, C.; Wijers, S.L.; et al. Effects of a Vitamin D and Leucine-Enriched Whey Protein Nutritional Supplement on Measures of Sarcopenia in Older Adults, the PROVIDE Study: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, J.T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Landi, F.; Hickson, M.; Zamboni, M.; Pereira, S.L.; Hustead, D.S.; Mustad, V.A. Impacts of High-Protein Oral Nutritional Supplements Among Malnourished Men and Women with Sarcopenia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tieland, M.; van de Rest, O.; Dirks, M.L.; van der Zwaluw, N.; Mensink, M.; van Loon, L.J.; de Groot, L.C. Protein Supplementation Improves Physical Performance in Frail Elderly People: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2012, 13, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yamada, M.; Kim, H.; Harada, A.; Arai, H. Interventions for Treating Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 553.e1–553.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.P.; Burris, D.D.; Lucas, F.L.; Crocker, G.A.; Wasserman, J.C. Effects of a Renal Rehabilitation Exercise Program in Patients with CKD: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, E.L.; Greening, N.J.; Viana, J.L.; Aulakh, J.; Bodicoat, D.H.; Barratt, J.; Feehally, J.; Smith, A.C. Progressive Resistance Exercise Training in CKD: A Feasibility Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castaneda, C.; Gordon, P.L.; Parker, R.C.; Uhlin, K.L.; Roubenoff, R.; Levey, A.S. Resistance training to reduce the malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome of chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, C.; Gordon, P.L.; Uhlin, K.L.; Levey, A.S.; Kehayias, J.J.; Dwyer, J.T.; Fielding, R.A.; Roubenoff, R.; Singh, M.F. Resistance Training To Counteract the Catabolism of a Low-Protein Diet in Patients with Chronic Renal Insufficiency. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, E.L.; Gould, D.W.; Wilkinson, T.J.; Xenophontos, S.; Clarke, A.L.; Vogt, B.P.; Viana, J.L.; Smith, A.C. Twelve-week combined resistance and aerobic training confers greater benefits than aerobic training alone in nondialysis CKD. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2018, 314, F1188–F1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denic, A.; Mathew, J.; Lerman, L.O.; Lieske, J.C.; Larson, J.J.; Alexander, M.P.; Poggio, E.; Glassock, R.J.; Rule, A.D. Single-Nephron Glomerular Filtration Rate in Healthy Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2349–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommos, M.S.; Glassock, R.J.; Rule, A.D. Structural and Functional Changes in Human Kidneys with Healthy Aging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2838–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walrand, S.; Short, K.R.; Bigelow, M.L.; Sweatt, A.J.; Hutson, S.M.; Nair, K.S. Functional impact of high protein intake on healthy elderly people. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2008, 295, E921–E928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haring, B.; Selvin, E.; Liang, M.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E.; Petruski-Ivleva, N.; Steffen, L.M.; Rebholz, C.M. Dietary Protein Sources and Risk for Incident Chronic Kidney Disease: Results From the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2017, 27, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbesma, N.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Jansen, D.F.; Stolk, R.P.; De Zeeuw, D.; De Jong, P.E.; Gansevoort, R.T.; for The PREVEND Study Group. High Protein Intake Associates with Cardiovascular Events but not with Loss of Renal Function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knight, E.L.; Stampfer, M.J.; Hankinson, S.E.; Spiegelman, D.; Curhan, G.C. The Impact of Protein Intake on Renal Function Decline in Women with Normal Renal Function or Mild Renal Insufficiency. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Alonso, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Corella, D.; Estruch, R.; Fitó, M.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. High dietary protein intake is associated with an increased body weight and total death risk. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klahr, S.; Levey, A.S.; Beck, G.J.; Caggiula, A.W.; Hunsicker, L.; Kusek, J.W.; Striker, G. The Effects of Dietary Protein Restriction and Blood-Pressure Control on the Progression of Chronic Renal Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Greene, T.; Beck, G.J.; Caggiula, A.W.; Kusek, J.W.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Klahr, S. Dietary protein restriction and the progression of chronic renal disease: What have all of the results of the MDRD study shown? Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study group. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 2426–2439. [Google Scholar]
- Meloni, C.; Tatangelo, P.; Cipriani, S.; Rossi, V.; Suraci, C.; Tozzo, C.; Rossini, B.; Cecilia, A.; Di Franco, D.; Straccialano, E.; et al. Adequate protein dietary restriction in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with chronic renal failure. J. Ren. Nutr. 2004, 14, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, M.; Yuan, W.L.; Haymann, J.-P.; Flamant, M.; Houillier, P.; Thervet, E.; Boffa, J.-J.; Vrtovsnik, F.; Froissart, M.; Bankir, L.; et al. Association of a Low-Protein Diet with Slower Progression of CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhee, C.M.; Ahmadi, S.-F.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Low-protein diet for conservative management of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. J. Cachex Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 9, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciaruso, B.; Pota, A.; Bellizzi, V.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Di Micco, L.; Minutolo, R.; Pisani, A.; Sabbatini, M.; Ravani, P. Effect of a Low Moderate-Protein Diet on Progression of CKD: Follow-up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isaka, Y. Optimal Protein Intake in Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Sarcopenia: An Overview. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041205
Isaka Y. Optimal Protein Intake in Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Sarcopenia: An Overview. Nutrients. 2021; 13(4):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041205
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsaka, Yoshitaka. 2021. "Optimal Protein Intake in Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Sarcopenia: An Overview" Nutrients 13, no. 4: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041205
APA StyleIsaka, Y. (2021). Optimal Protein Intake in Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Sarcopenia: An Overview. Nutrients, 13(4), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041205




