Treatment with a Probiotic Mixture Containing Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis BB12 and Enterococcus faecium L3 for the Prevention of Allergic Rhinitis Symptoms in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants and Design
- nasal obstruction (stuffy nose),
- rhinorrhea (runny nose),
- sneezing, and
- nasal itching.
2.2. Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebert, C.S., Jr.; Pillsbury, H.C., 3rd. Epidemiology of allergy. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 44, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykewicz, M.S.; Hamilos, D.L. Rhinitis and sinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S103–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sifuro, M.M.; Suppa, M.; Ginaldi, L. New prospective in food allergy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mastrorilli, C.; Caffarelli, C.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K. Food allergy and atopic dermatitis: Prediction, progression and prevention. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 28, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocchi, A.; Pawankar, R.; Cuello-Garcia, C.; Ahn, K.; Al-Hammadi, S.; Agarwal, A.; Beyer, K.; Burks, W.; Canonica, G.W.; Ebisawa, M.; et al. World Allergy Organization-McMaster University Guidelines for Allergic Disease Prevention (GLAD-P): Probiotics. World Allergy Organ J. 2015, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bousquet, J.; Khaltaev, N.; Cruz, A.A.; Denburg, J.; Fokkens, W.J.; Togias, A.; Zuberbier, T.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Canonica, G.W.; van Weel, C.; et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA (2) LEN and AllerGen). Allergy 2008, 63 (Suppl. S86), 8–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zicari, A.M.; De Castro, G.; Leonardi, L.; Duse, M. Update on rhinitis and rhinosinusitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhong, P.; Li, G.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, Y. Application of probiotics in adjuvant treatment of infant allergic rhinitis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón, M.A.; Penagos, M.; Sheikh, A.; Canonica, G.W.; Durham, S.R. Sublingual immunotherapy for treating allergic conjunctivitis: Cochrane Database Systematic review and meta-ananlysis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, K.; Rogala, B.; Chugh, K.; Paraskakis, E.; Pampura, A.; Boev, R. Safety considerations in the management of allergic diseases: Focus on antihistamines. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2012, 28, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawankar, R.; Canonica, G.; Holgate, S.; Lockey, R.; Blaiss, M. (Eds.) World Allergy Organization (WAO) White Book on Allergy: Update 2013; World Allergy Organization: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fioramonti, J.; Theodorou, V.; Bueno, L. Probiotics: What are they? What are their effects on gut physiology? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003, 17, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrowska, B.; Bierła, J.B.; Zakrzewska, M.; Klukowski, M.; Maciorkowska, E. The relationship between the infant gut microbiota and allergy. The role of Bifidobacterium breve and prebiotic oligosaccharides in the activation of anti-allergic mechanisms in early life. Nutrients 2020, 12, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Pierro, F.; Basile, I.; Danza, M.L.; Venturelli, L.; Contini, R.; Risso, P.; Colombo, M. Use of probiotic mixture containing Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis BB12 and Enterococcus faecium L3 in atopic children. Minerva Pediatr. 2018, 70, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, F.; Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Lugli, G.A.; Bernasconi, S.; Margolles, A.; Di Pierro, F.; Van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. The infant gut microbiome as a microbial organ influencing host well-being. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2020, 46, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, F.; Peano, C.; Pass, D.A.; Foroni, E.; Severgnini, M.; Claesson, M.J.; Kerr, C.; Hourihane, J.; Murray, D.; Fuligni, F.; et al. Diversity of Bifidobacteria within the Infant Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milani, C.; Hevia, A.; Foroni, E.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; Sanchez, B.; Martín, R.; Gueimonde, M.; Van Sinderen, D.; et al. Assessing the Fecal Microbiota: An Optimized Ion Torrent 16S rRNA Gene-Based Analysis Protocol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.C.; Manges, A.R.; Finlay, B.B.; Prendergast, A.J. The Human Microbiome and Child Growth—First 1000 Days and Beyond. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Putignani, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Petrucca, A.; Vernocchi, P.; Dallapiccola, B. The human gut microbiota: A dynamic interplay with the host from birth to senescence settled during childhood. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 76, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, A.; Yoo, J.Y.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Morgan, K.H.; Groer, M. The Association between Early-Life Gut Microbiota and Long-Term Health and Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, K.E.; Sitarik, A.R.; Havstad, S.; Lin, D.L.; LeVan, S.; Fadrosh, D.; Panzer, A.R.; LaMere, B.; Rackaityte, E.; Lukacs, N.W.; et al. Neonatal gut microbiota associates with childhood multisensitized atopy and T cell differentiation. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Björkstén, B.; Sepp, E.; Julge, K.; Voor, T.; Mikelsaar, M. Allergy development and the intestinal microflora during the first year of life. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanishi, S.; Pawankar, R. Current advances on the microbiome and role of probiotics in upper airways disease. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 20, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gi-Campos, M.; Gill, A. Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, L.; Delgado, S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A. Bifidobacteria and Their Molecular Communication with the Immune System. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hevia, A.; Milani, C.; López, P.; Donado, C.D.; Cuervo, A.; González, S.; Suárez, P.L.; Turroni, F.; Gueimonde, M.; Ventura, M.; et al. Allergic Patients with Long-Term Asthma Display Low Levels of Bifidobacterium adolescentis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skiavo, L.A.L.; Gonchar, N.V.; Fedorova, M.S.; Suvorov, A.N. Dynamics of contamination and persistence of Clostridium difficile in intestinal microbiota in newborn infants during antibiotic therapy and use of probiotic strain enterococcus faecium L3. Antibiot. Khimioter. 2013, 58, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jungersen, M.; Wind, A.; Johansen, E.; Christensen, J.E.; Stuer-Lauridsen, B.; Eskesen, D. The science behind the probiotic strains Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. Lactis BB-12®. Microorganisms 2014, 2, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzanica, F.; Urbani, E.; Atac, M.; Scottà, G.; Luciano, K.; Bulgheroni, C.; De Cristofaro, V.; Gera, R.; Schindler, A.; Ottaviani, F. Reliability and validity of the Italian nose obstruction symptom evaluation (I-NOSE) scale. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2013, 270, 3087–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brożek, J.L.; Bousquet, J.; Agache, I.; Agarwal, A.; Bachert, C.; Bosnic-Anticevich, S.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Canonica, G.W.; Casale, T.; Chavannes, N.H.; et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines—2016 revision. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, M.G.; Witsell, D.L.; Smith, T.L.; Weaver, E.M.; Yueh, B.; Hannley, M.T. Development and Validation of the Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation (NOSE) Scale. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.K.; Soliman, M.; Steacy, L.; Boulay, M.-È.; Boulet, L.-P.; Keith, P.K.; Vliagoftis, H.; Waserman, S.; Neighbour, H. The Allergic Rhinitis—Clinical Investigator Collaborative (AR-CIC): Nasal allergen challenge protocol optimization for studying AR pathophysiology and evaluating novel therapies. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Chen, C.-J.; Chen, L.-K.; Wen, S.-H.; Jan, R.-H. Effect of probiotics on allergic rhinitis in Df, Dp or dust-sensitive children: A randomized double blind controlled trial. Indian Pediatr. 2013, 50, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Li, A.; Yu, L.; Qin, G. The role of probiotics in prevention and treatment for patients with allergic rhinitis: A systematic review. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuello-Garcia, C.A.; Brożek, J.L.; Fiocchi, A.; Pawankar, R.; Yepes-Nuñez, J.J.; Terracciano, L.; Gandhi, S.; Agarwal, A.; Zhang, Y.; Schünemann, H.J. Probiotics for the prevention of allergy. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, M.M.; Indolfi, C.; Capasso, M.; Maiello, N.; Decimo, F.; Ciprandi, G. Bifidobacterium mixture (B longum BB536, B infantis M-63, B breve M-16V) treatment in children with seasonal allergic rhinitis and intermittent asthma. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| ALLERGEN | % |
|---|---|
| PARIETARIA | 0.85 |
| DPT, DPF, GRASS POLLEN | 13.68 |
| OLEA, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| DPT, DPF, PARIETARIA, GRASS POLLEN | 7.70 |
| DPT, DPF, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 2.60 |
| DPT, DPF | 17.95 |
| DPT, DPF, PARIETARIA, OLEA, CYNODON, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 2.60 |
| DPT, DPF, PARIETARIA, OLEA, GRASS POLLEN | 4.27 |
| GRASS POLLEN | 5.13 |
| LOLIUM | 1.71 |
| DPT, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 3.42 |
| DPT, DPF, ALTERNARIA | 1.71 |
| DPT, DPF, PARIETARIA, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| DPT, DPF, PARIETARIA, CYNODON, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 1.71 |
| LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 4.27 |
| OLEA | 0.85 |
| ALTERNARIA | 0.85 |
| CYNODON, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 1.71 |
| DPT, DPF, OLEA | 3.42 |
| OLEA, GRASS POLLEN | 1.71 |
| PARIETARIA, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| OLEA, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| DPT | 0.85 |
| CYNODON, LOLIUM | 1.71 |
| ALTERNARIA, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| PARIETARIA, LOLIUM | 0.85 |
| DPT, DPF, LOLIUM | 0.85 |
| DPF, DPT, OLEA, GRASS POLLEN | 3.42 |
| DPF, DPT, ALTERNARIA, GRASS POLLEN | 2.60 |
| DPT, DPF, PARIETARIA | 1.71 |
| DPT, DPF, PARIETARIA, ALTERNARIA | 0.85 |
| DPT, DPF, OLEA, CYNODON, LOLIUM | 0.85 |
| PARIETARIA, OLEA, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| PARIETARIA, OLEA, CYNODON, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| PARIETARIA, OLEA, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| OLEA, CYNODON, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| LOLIUM, ALTERNARIA, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| DPF, DPT, OLEA, ALTERNARIA, GRASS POLLEN | 2.60 |
| DPT, DPF, CYNODON, LOLIUM, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| DPT, DPF, CYNODON, GRASS POLLEN | 0.85 |
| Score | Clinical Significance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Absence of symptoms | |||||||
| 1 | Symptoms of mild severity | |||||||
| 2 | Symptoms of moderate severity | |||||||
| 3 | Symptoms of severe severity | |||||||
| Score | NASAL SYMPTOM Severity (S)/Duration (D) | |||||||
| Stuffy nose S D | Runny nose S D | Sneezing S D | Nasal Itching S D | |||||
| 0 | ||||||||
| 1 | ||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||
| Before Treatment | After Treatment | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention group (group A) | 14.07 | 5.43 | 2.2 × 1016 |
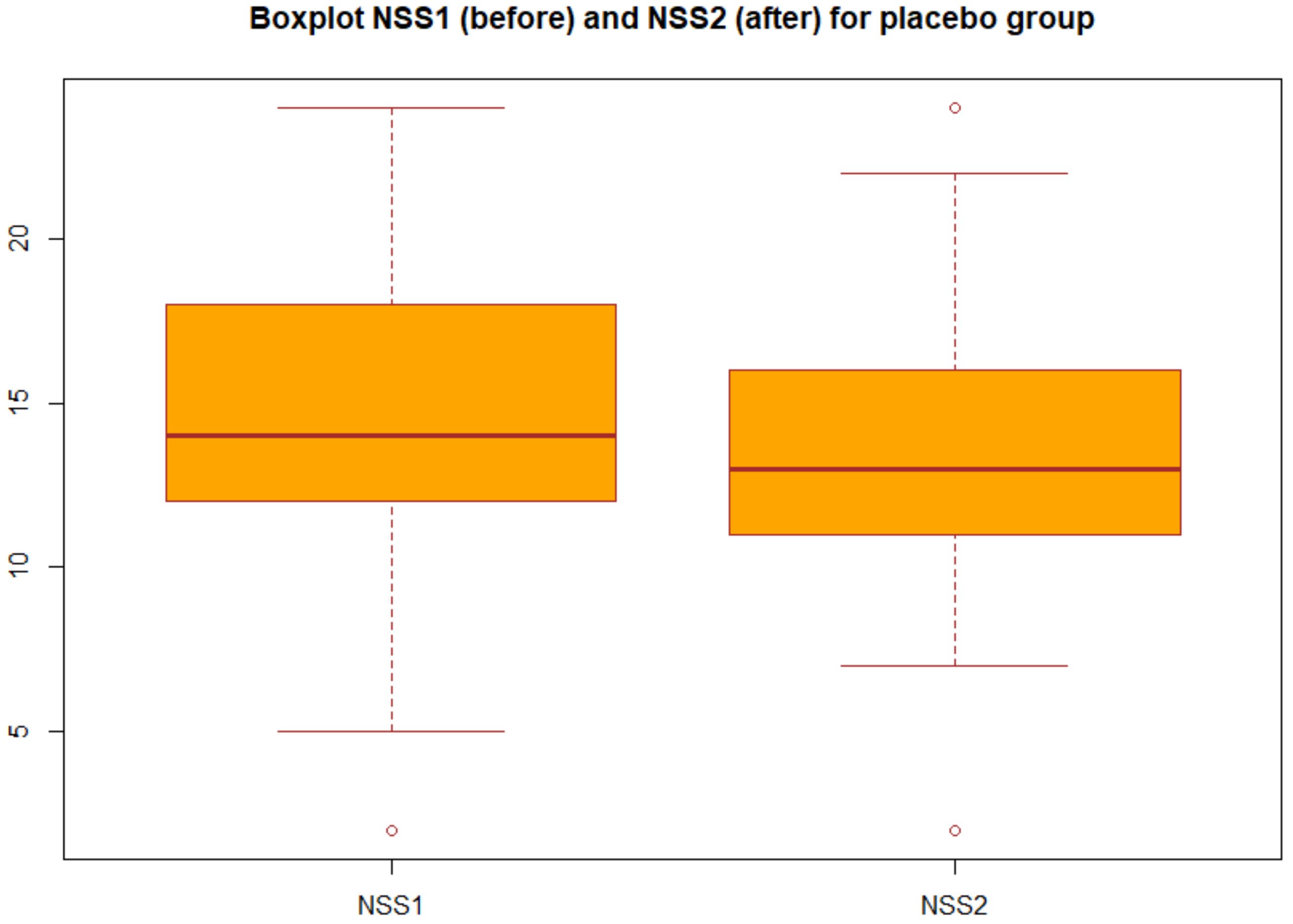
| Placebo group(group B) | 14.51 | 13.60 | 0.52 |
| Drugs | Before Treatment | After Treatment | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines (oral) | 67 (57%) | 7 (6%) | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Corticosteroids (local) | 88 (75%) | 32 (27%) | 2.229 × 10−13 |
| Both | 48 (41%) | 0 (0%) | 1.5 × 10−15 |
| Drugs | Before Treatment | After Treatment | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines (oral) | 66 (78%) | 74 (87%) | 0.16 |
| Corticosteroids (local) | 71 (84%) | 51 (60%) | 8.2 × 10−04 |
| Both | 54 (64%) | 40 (40%) | 0.04 |
| Probiotic (n. 117) | Placebo (n. 86) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 10.5 ± 3.1 | 8.8 ± 3.5 |
| Sex (M/F) | 73/44 | 49/36 |
| Rhinitis | 55 (47.0%) | 37 (43.02%) |
| Asthma + Rhinitis | 50 (42.7%) | 39 (45.34%) |
| Asthma + dermatitis | 1 (0.9%) | 1 (1.17%) |
| Rhinitis + dermatitis | 6 (5.1%) | 6 (6.97%) |
| Rhinitis + asthma + dermatitis | 5 (4.3%) | 3 (3.49%) |
| SPT_DPT | 88 (75.2%) | 48 (62.3%) |
| SPT_DPF | 86 (73.5%) | 47 (61.0%) |
| SPT_Parietary | 29 (24.8%) | 10 (13%) |
| SPT_Olea | 29 (24.8%) | 26 (33.8%) |
| SPT_Cynodon | 15 (12.8%) | 14 (18.2%) |
| SPT_Lolium | 26 (22.2%) | 18 (23.4%) |
| SPT_Grass pollen | 76 (65.0%) | 38 (49.4%) |
| SPT_Alternaria | 12 (10.0%) | 8 (10.4%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anania, C.; Di Marino, V.P.; Olivero, F.; De Canditiis, D.; Brindisi, G.; Iannilli, F.; De Castro, G.; Zicari, A.M.; Duse, M. Treatment with a Probiotic Mixture Containing Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis BB12 and Enterococcus faecium L3 for the Prevention of Allergic Rhinitis Symptoms in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041315
Anania C, Di Marino VP, Olivero F, De Canditiis D, Brindisi G, Iannilli F, De Castro G, Zicari AM, Duse M. Treatment with a Probiotic Mixture Containing Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis BB12 and Enterococcus faecium L3 for the Prevention of Allergic Rhinitis Symptoms in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2021; 13(4):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041315
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnania, Caterina, Vincenza Patrizia Di Marino, Francesca Olivero, Daniela De Canditiis, Giulia Brindisi, Federico Iannilli, Giovanna De Castro, Anna Maria Zicari, and Marzia Duse. 2021. "Treatment with a Probiotic Mixture Containing Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis BB12 and Enterococcus faecium L3 for the Prevention of Allergic Rhinitis Symptoms in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 13, no. 4: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041315
APA StyleAnania, C., Di Marino, V. P., Olivero, F., De Canditiis, D., Brindisi, G., Iannilli, F., De Castro, G., Zicari, A. M., & Duse, M. (2021). Treatment with a Probiotic Mixture Containing Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis BB12 and Enterococcus faecium L3 for the Prevention of Allergic Rhinitis Symptoms in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 13(4), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041315






