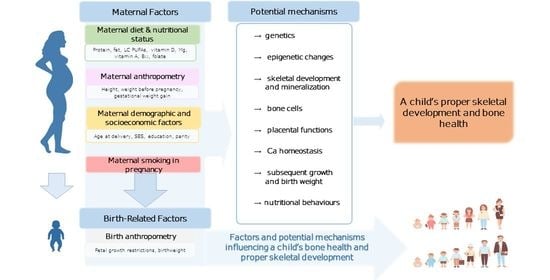
Maternal Diet, Nutritional Status, and Birth-Related Factors Influencing Offspring’s Bone Mineral Density: A Narrative Review of Observational, Cohort, and Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Share and Cite
Masztalerz-Kozubek, D.; Zielinska-Pukos, M.A.; Hamulka, J. Maternal Diet, Nutritional Status, and Birth-Related Factors Influencing Offspring’s Bone Mineral Density: A Narrative Review of Observational, Cohort, and Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072302
Masztalerz-Kozubek D, Zielinska-Pukos MA, Hamulka J. Maternal Diet, Nutritional Status, and Birth-Related Factors Influencing Offspring’s Bone Mineral Density: A Narrative Review of Observational, Cohort, and Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2021; 13(7):2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072302
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasztalerz-Kozubek, Daria, Monika A. Zielinska-Pukos, and Jadwiga Hamulka. 2021. "Maternal Diet, Nutritional Status, and Birth-Related Factors Influencing Offspring’s Bone Mineral Density: A Narrative Review of Observational, Cohort, and Randomized Controlled Trials" Nutrients 13, no. 7: 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072302
APA StyleMasztalerz-Kozubek, D., Zielinska-Pukos, M. A., & Hamulka, J. (2021). Maternal Diet, Nutritional Status, and Birth-Related Factors Influencing Offspring’s Bone Mineral Density: A Narrative Review of Observational, Cohort, and Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 13(7), 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072302