The Insight into Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Insulin-Like Growth-Factor-Binding Proteins and Metabolic Profile in Pediatric Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Anthropometric Evaluation
2.3. Protocol of the Study
2.4. Biochemical Tests
- IGF1—Labor Diagnostika Nord GmbH & Co.KG, Germany,
- IGF2—Mediagnost, Reultingen, Germany,
- IGFBP1, IGFBP2, IGFBP3, IGFBP6—Mediagnost, Reultingen, Germany,
- IGFBP4, IGFBP7—FineTest, Wuhan, China.
2.5. Microarray Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Concentration of IGF Proteins
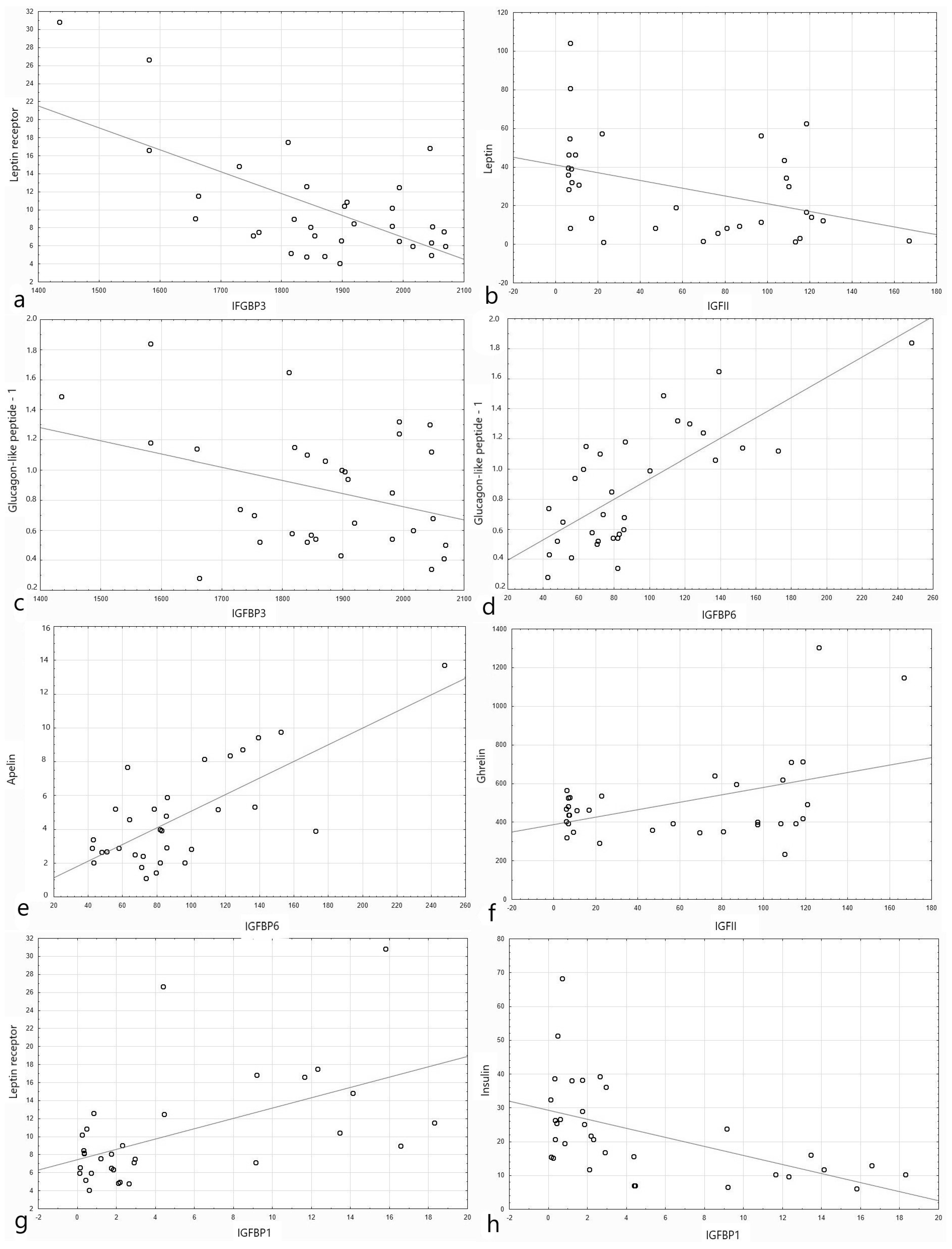
3.2. IGF Proteins Concentration and Other Metabolic Parameters
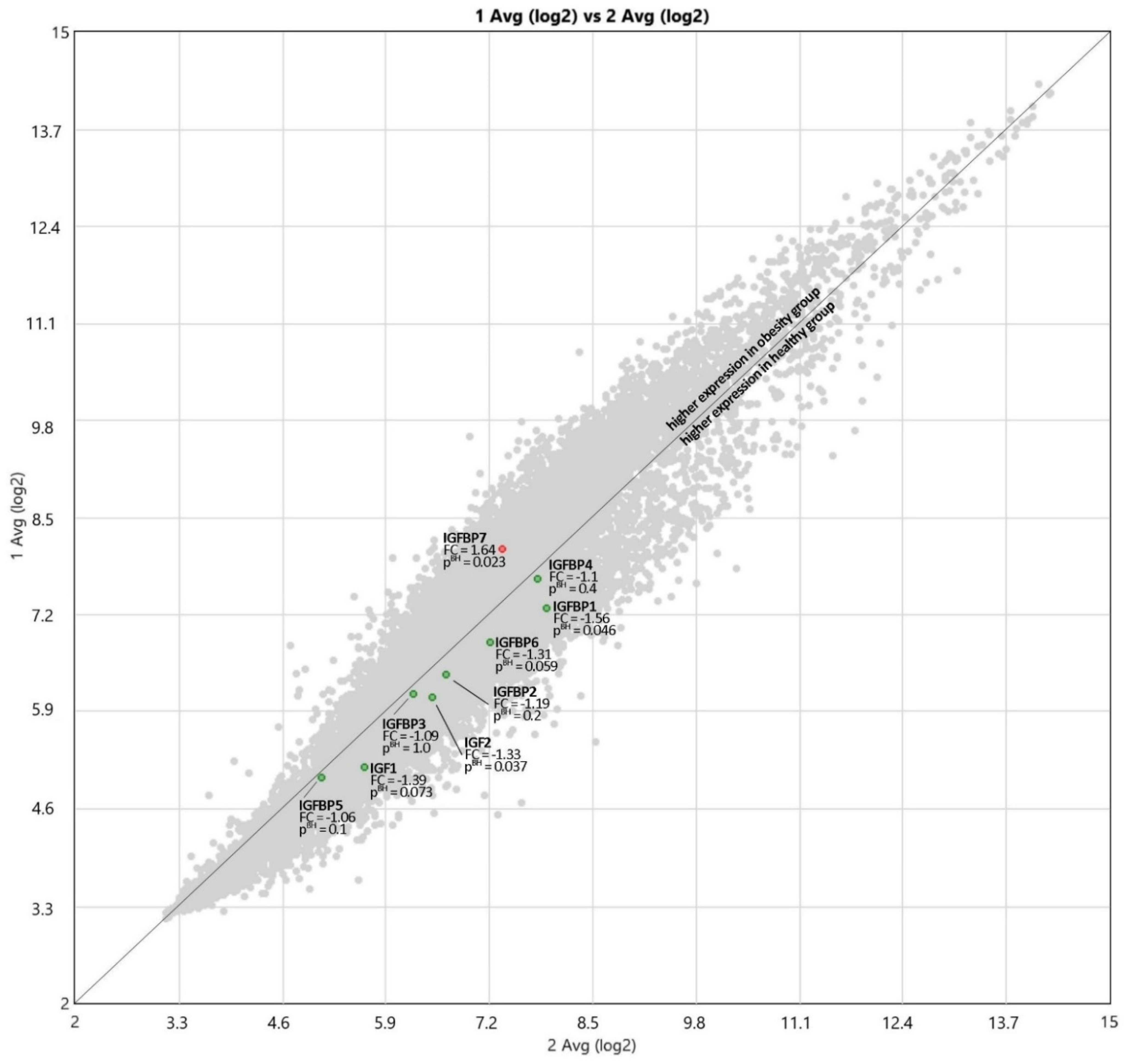
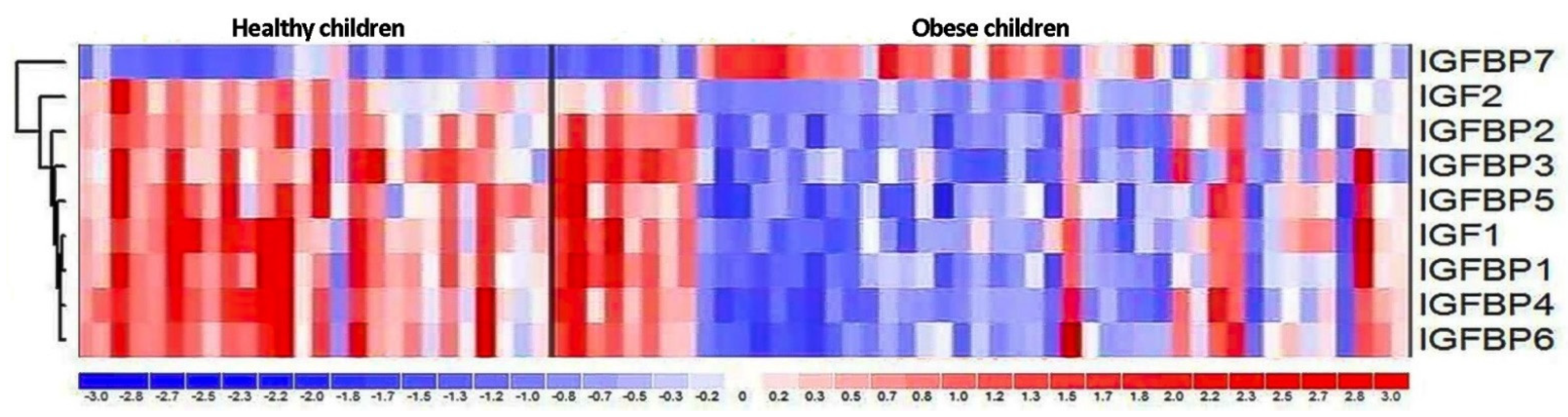
3.3. Expression of IGF Proteins’ Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. Concentration of IGF-Axis Proteins
4.2. IGF Proteins Concentration and Other Metabolic Parameters
4.3. Expression of IGF Proteins’ Genes
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Kolb, R.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Zhang, W. Obesity and cancer: Inflammation bridges the two. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Gucalp, A.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Hudis, C.A. Obesity and Cancer Mechanisms: Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bideci, A.; Cinaz, P.; Hasanoglu, A.; Elbeg, S. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in obese children. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 10, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, A.L.; Joe, J.R.; Young, R.S.; Winter, W.E. Emerging epidemic of type 2 diabetes in youth. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Fisch, G.; Teague, B.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Banyas, B.; Allen, K.; Savoye, M.; Rieger, V.; Taksali, S.; Barbetta, G.; et al. Prevalence of Impaired Glucose Tolerance among Children and Adolescents with Marked Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, K.E.; Kaplan, L.M. Obesity and liver disease. The epidemic of the twenty-first century. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, R.S. Childhood Obesity and Self-Esteem. Pediatrics 2000, 105, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slyper, A.H. The pediatric obesity epidemic: Causes and controversies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2540–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Controlling the Global Obesity Epidemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/controlling-the-global-obesity-epidemic (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Falorni, A.; Bini, V.; Cabiati, G.; Papi, F.; Arzano, S.; Celi, F.; Sanasi, M. Serum levels of type I procollagen C-terminal propeptide, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), and IGF binding protein-3 in obese children and adolescents: Relationship to gender, pubertal development, growth, insulin, and nutritional status. Metabolism 1997, 46, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Qi, J.; Li, G. Low insulin-like growth factor 1 is associated with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and metabolic syndrome in Chinese nondiabetic obese children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczówka, P.; Wieczorek, A.; Czogała, M.; Książek, T.; Szewczyk, K.; Balwierz, W. The role of N-Myc gene amplification in neuroblastoma childhood tumour—Single-centre experience. Współczesna Onkol. 2018, 22, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, T.; Ackerman, S.E.; Shen, L.; Engleman, E. Role of innate and adaptive immunity in obesity-associated metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitadamo, P.; Zenzeri, L.; Mozzillo, E.; Giorgio, V.; Rocco, A.; Franzese, A.; Nardone, G.; Staiano, A. Plasma dosage of ghrelin, IGF-1, GLP- 1 and leptin related to gastric emptying and esophageal pH-impedance in children with obesity. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, N.; Jørgensen, T.; Juul, A.; Spielhagen, C.; Nauck, M.; Wallaschofski, H.; Linneberg, A. Insulin-like Growth Factor I and Anthropometric Parameters in a Danish Population. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2012, 120, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.M.; Maravall, F.J.; Gómez, N.; Navarro, M.Á.; Casamitjana, R.; Soler, J. The IGF-I system component concentrations that decrease with ageing are lower in obesity in relationship to body mass index and body fat. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2004, 14, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, N.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Heptulla, R.; Maggs, D.; Grozman, A.; Sherwin, R.S.; Caprio, S. The Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Regulation in Adolescent Obesity1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frystyk, J.; Vestbo, E.; Skjærbaek, C.; Mogensen, C.E.; Ørskov, H. Free insulin-like growth factors in human obesity. Metabolism 1995, 44, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frystyk, J.; Skjærbæk, C.; Vestbo, E.; Fisker, S.; Ørskov, H. Circulating levels of free insulin-like growth factors in obese subjects: The impact of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 1999, 15, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kim, H.-S.; Kang, J.; Kim, D.; Chung, C. Serum Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-I, Free IGF-I, IGF Binding Protein (IGFBP)-l, IGFBP-3 and Insulin in Obese Children. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 12, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryman, D.E.; Glad, C.A.M.; List, E.O.; Johannsson, G. The GH/IGF-1 axis in obesity: Pathophysiology and therapeutic considerations. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreitschmann-Andermahr, I.; Suarez, P.; Jennings, R.; Evers, N.; Brabant, G. GH/IGF-I Regulation in Obesity—Mechanisms and Practical Consequences in Children and Adults. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2010, 73, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, S.R.; Rosa, J.S.; Minh, T.D.C.; Pontello, A.M.; Flores, R.L.; Barnett, M.; Galassetti, P.R. Dose-dependent relationship between severity of pediatric obesity and blunting of the growth hormone response to exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marcovecchio, M.L.; Chiarelli, F. Obesity and Growth during Childhood and Puberty. World Rev. Nutr. Diet 2013, 106, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadakia, R.; Josefson, J. The Relationship of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 to Fetal Growth and Adiposity. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2016, 85, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfares, M.N.; Perks, C.M.; Hamilton-Shield, J.P.; Holly, J.M.P. Insulin-like growth factor-II in adipocyte regulation: Depot-specific actions suggest a potential role limiting excess visceral adiposity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E1098–E1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, N.J.; Slater, T.A.; Matthews, C.J.; Wheatcroft, S.B. The insulin like growth factor and binding protein family: Novel therapeutic targets in obesity & diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2019, 19, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, M.E.; Smerieri, A.; Montanini, L.; Predieri, B.; Iughetti, L.; Valenzise, M.; De Luca, F.; Vigone, M.C.; Weber, G.; Maghnie, M.; et al. Interactions among pro-inflammatory cytokines, IGF system and thyroid function in pre-pubertal obese subjects. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2013, 27, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Kamoda, T.; Saitoh, H.; Inudoh, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Matsui, A. The serum levels of proinsulin and their relationship with IGFBP-1 in obese children. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2006, 8, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoda, T.; Saitoh, H.; Nakahara, S.; Inudoh, M.; Hirano, T.; Matsui, A. The phosphorylation status of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in prepubertal obese children. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 141, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Travers, S.H.; Labarta, J.I.; Gargosky, S.E.; Rosenfeld, R.G.; Jeffers, B.W.; Eckel, R.H. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-I Levels Are Strongly Associated with Insulin Sensitivity and Obesity in Early Pubertal Children1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.M.; Park, H.K.; Yang, S.; Kim, E.Y.; Chung, S.C.; Hwang, I.T. Association between insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 levels and cardiovascular risk factors in Korean children. Endocrinol. J. 2012, 59, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranke, M.B. Insulin-like growth factor binding-protein-3 (IGFBP-3). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, T.; Panteliadou, A.; De Sousa, G.; Andler, W. Insulin-like Growth Factor-I, Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 and Growth in Obese Children Before and After Reduction of Overweight. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 22, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ounis, O.; Elloumi, M.; Zouhal, H.; Makni, E.; Denguezli, M.; Amri, M.; Lac, G.; Tabka, Z. Effect of Individualized Exercise Training Combined with Diet Restriction on Inflammatory Markers and IGF-1/IGFBP-3 in Obese Children. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 56, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, A.; Dalgaard, P.; Blum, W.F.; Bang, P.; Hall, K.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Müller, J.; Skakkebaek, N.E. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in healthy infants, children, and adolescents: The relation to IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-1, IGFBP-2, age, sex, body mass index, and pubertal maturation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 2534–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boney, C.M.; Moats-Staats, B.M.; Stiles, A.D.; D’Ercole, A.J. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding proteins during adipogenesis. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Zahid, A.A.; Phillips, L.; Delafontaine, P. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-4 Expression Is Decreased by Angiotensin II and Thrombin in Rat Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ning, Y.; Schuller, A.G.P.; Conover, C.A.; Pintar, J.E. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein-4 Is Both a Positive and Negative Regulator of IGF Activity in Vivo. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Smith, E.P.; Kuroda, H.; Banach, W.; Chernausek, S.D.; Fagin, J.A. Targeted Expression of a Protease-resistant IGFBP-4 Mutant in Smooth Muscle of Transgenic Mice Results in IGFBP-4 Stabilization and Smooth Muscle Hypotrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21285–21290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakoshi, N.; Qin, X.; Kasukawa, Y.; Richman, C.; Srivastava, A.K.; Baylink, D.J.; Mohan, S. Systemic Administration of Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF)-Binding Protein-4 (IGFBP-4) Increases Bone Formation Parameters in Mice by Increasing IGF Bioavailability via an IGFBP-4 Protease-Dependent Mechanism. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, L.A.; Hsieh, S.; Sakano, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Perdue, J.F.; Rechler, M.M. Binding of Mutants of Human Insulin-like Growth Factor I1 to Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins 1-6. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 9246–9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, L.A. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-6: The “Forgotten” Binding Protein? Horm. Metab. Res. 1999, 31, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Nagalla, S.R.; Oh, Y.; Wilson, E.; Roberts, C.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Identification of a family of low-affinity insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs): Characterization of connective tissue growth factor as a member of the IGFBP superfamily. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12981–12986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjortebjerg, R. IGFBP-4 and PAPP-A in normal physiology and disease. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2018, 41, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, L.A. 40 years of IGF1: IGF-binding proteins. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T11–T28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, R.C.; Ricco, R.G.; Queluz, M.C.; de Paula, M.T.S.; Atique, P.V.; Custódio, R.J.; Filho, H.T.; Liberatori, R.D.R.; Martinelli, C.E. IGF-1R mRNA expression is increased in obese children. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2018, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekaran, I.R.; Yao, S.; Wang, C.C.; Bansal, P.S.; Alewood, P.F.; Forbes, B.E.; Wallace, J.C.; Bach, L.A.; Norton, R.S. The N-Terminal Subdomain of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein 6. Structure and Interaction with IGFs. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorof, J.; Daniels, S. Obesity hypertension in children: A problem of epidemic proportions. Hypertension 2002, 40, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faienza, M.F.; Santoro, N.; Lauciello, R.; Calabrò, R.; Giordani, L.; Di Salvo, G.; Ventura, A.; Delvecchio, M.; Perrone, L.; Del Giudice, E.M.; et al. IGF2 Gene Variants and Risk of Hypertension in Obese Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Association study of IGFBP1 and IGFBP3 polymorphisms with hypertension and cardio-cerebral vascular diseases in a Chinese Han population. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77836–77845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xargay-Torrent, S.; Dorado-Ceballos, E.; Benavides-Boixader, A.; Lizárraga-Mollinedo, E.; Mas-Parés, B.; Montesinos-Costa, M.; De Zegher, F.; Ibanez, L.; Bassols, J.; López-Bermejo, A. Circulating IGF-1 Independently Predicts Blood Pressure in Children with Higher Calcium-Phosphorus Product Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e610–e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, M.S.; Heald, A.H.; Gibson, M.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dunger, P.D.; Wareham, N.J. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and development of glucose intolerance: A prospective observational study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpathak, S.N.; He, M.; Sun, Q.; Kaplan, R.C.; Muzumdar, R.; Rohan, T.E.; Gunter, M.J.; Pollak, M.; Kim, M.; Pessin, J.E.; et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Axis and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Women. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.W.; Harcourt, B.E.; Kao, K.-T.; Alexander, E.J.; Russo, V.C.; Werther, G.A.; Sabin, M.A. Serum IGFBP-2 levels are associated with reduced insulin sensitivity in obese children. Clin. Obes. 2018, 8, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalitin, S.; Phillip, M. Role of obesity and leptin in the pubertal process and pubertal growth—A review. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra-Reynoso, L.D.R.; Pisarchyk, L.; Pérez-Luque, E.L.; Garay-Sevilla, M.E.; Malacara, J.M. Whole-Body and Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Obese Children. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, H.F.; Frystyk, J.; Efendic, S.; Brismar, K.; Thorell, A. Analyses of IGFBP2 DNA methylation and mRNA expression in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2019, 45, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, A.G.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F.; Carreira, M.C. Leptin, Obesity, and Leptin Resistance: Where Are We 25 Years Later? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaab, M.; Kausch, H.; Klammt, J.; Nowicki, M.; Anderegg, U.; Gebhardt, R.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J.; Thiery, J.; Kratzsch, J. Novel Regulatory Mechanisms for Generation of the Soluble Leptin Receptor: Implications for Leptin Action. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinaz, P.; Bideci, A.; Çamurdan, M.O.; Gilven, A.; Gönen, S. Leptin and Soluble Leptin Receptor Levels in Obese Children in Fasting and Satiety States. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 18, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önnerfält, J.; Erlanson-Albertsson, C.; Montelius, C.; Thorngren-Jerneck, K. Obese children aged 4–6 displayed decreased fasting and postprandial ghrelin levels in response to a test meal. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Castro, P.; Pena, L.; Cordido, F. Ghrelin in Obesity, Physiological and Pharmacological Considerations. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinehr, T.; De Sousa, G.; Roth, C.L. Obestatin and ghrelin levels in obese children and adolescents before and after reduction of overweight. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 68, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.; Rizi, E.P.; Shabeer, M.; Chhay, V.; Mok, S.F.; Loh, T.P.; Magkos, F.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Tai, E.S.; Khoo, C.M.; et al. Metabolic gene expression profile in circulating mononuclear cells reflects obesity-associated metabolic inflexibility. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melián, E.; González, B.; Ajo, R.; González, N.; Sánchez Franco, F. Tissue-specific response of IGF-I mRNA expression to obesity-associated GH decline in the male Zucker fatty rat. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 160, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Son, J.L. Muscle IGF-1 Regulation in Humans with Obesity. Bachelor’s Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rajwani, A.; Ezzat, V.; Smith, J.; Yuldasheva, N.Y.; Duncan, E.R.; Gage, M.; Cubbon, R.M.; Kahn, M.B.; Imrie, H.; Abbas, A.; et al. Increasing Circulating IGFBP1 Levels Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Promotes Nitric Oxide Production, Lowers Blood Pressure, and Protects Against Atherosclerosis. Diabetes 2012, 61, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, H.; Kamoda, T.; Nakahara, S.; Hirano, T.; Nakamura, N. Serum concentrations of insulin, insulin-like growth factor(IGF)-I, IGF binding protein (IGFBP)-1 and -3 and growth hormone binding protein in obese children: Fasting IGFBP-1 is suppressed in normoinsulinaemic obese children. Clin. Endocrinol. 1998, 48, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballerini, M.G.; Ropelato, M.G.; Domené, H.M.; Pennisi, P.; Heinrich, J.J.; Jasper, H.G. Differential Impact of Simple Childhood Obesity on the Components of the Growth Hormone-Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-IGF Binding Proteins Axis. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 17, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Baseline Characteristic | Obesity Group (n = 28) | Control Group (n = 34) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boys/girls n (%) | 12/16 (42.9%/57.1%) | 13/21 (38.2%/61.8%) | 0.574 |
| Age (years) | 13.4 ± 3.8 | 12.0 ± 3.5 | 0.207 |
| Height (cm) | 168.89 ± 15.42 | 152.1 ± 20.2 | 0.090 |
| Weight (kg) | 86.5 ± 26.9 | 46.05 ± 17.85 | <0.001 |
| BMI (percentile) | 99.6 ± 0.86 | 61.87 ± 28.6 | 0.002 |
| BMI Z-score | 2.30 ± 0.27 | 0.05 ± 0.89 | <0.001 |
| Blood pressure (average systolic) | 125 ± 9.61 | 110 ± 9.82 | <0.001 |
| Blood pressure (average diastolic) | 77 ± 6.76 | 66 ± 8.75 | <0.001 |
| HOMA | 5.2 ± 3.8 | 2.3 ± 1.5 | 0.13 |
| Baseline Characteristic | Obesity Group (n = 28) | Control Group (n = 34) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose T0 (mmol/L) | 4.52 ± 0.74 | 4.65 ± 0.46 | 0.479 |
| Glucose T60 (mmol/L) | 6.64 ± 1.65 | 6.96 ± 1.8 | 0.529 |
| Glucose T120 (mmol/L) | 5.43 ± 1.59 | 5.67 ± 1.25 | 0.581 |
| Insulin T0 (µIU/L) | 25.82 ± 13.72 | 10.6 ± 4.6 | <0.001 |
| Insulin T60 (µIU/L) | 162.16 ± 94.44 | 63.26 ± 39.77 | <0.001 |
| Insulin T120 (µIU/L) | 113.42 ± 77.85 | 45.41 ± 24.91 | <0.001 |
| Adiponectin T0 (µg/mL) | 2.79 ± 1.54 | 4.04 ± 2.19 | 0.037 |
| Adiponectin T60 (µg/mL) | 2.76 ± 1.78 | 4.29 ± 2.21 | 0.026 |
| Adiponectin T120 (µg/mL) | 2.62 ± 1.65 | 4.05 ± 2.11 | 0.011 |
| Apelin T0 (pg/mL) | 1.76 ± 0.79 | 4.32 ± 1.74 | <0.001 |
| Apelin T60 (pg/mL) | 1.63 ± 0.83 | 4.15 ± 1.95 | <0.001 |
| Apelin T120 (pg/mL) | 1.77 ± 1.06 | 4.04 ± 1.92 | <0.001 |
| Cholecystokinin T0 (nmol/L) | 1.5 ± 1.06 | 3.9 ± 1.5 | <0.001 |
| Cholecystokinin T60 (nmol/L) | 1.42 ± 0.87 | 3.46 ± 1.25 | <0.001 |
| Cholecystokinin T120 (nmol/L) | 1.44 ± 0.92 | 3.87 ± 1.08 | <0.001 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21 T0 (ng/mL) | 169.65 ± 92.06 | 87.89 ± 48.17 | <0.001 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21T60 (ng/mL) | 137.08 ± 70.6 | 77.18 ± 41.9 | 0.003 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21T120 (ng/mL) | 194.84 ± 106.79 | 83.41 ± 46.05 | <0.001 |
| Ghrelin T0 (pg/mL) | 475.51 ± 197.06 | 753.18 ± 261.2 | <0.001 |
| Ghrelin T60 (pg/mL) | 444.87 ± 118.33 | 629.75 ± 207.15 | <0.001 |
| Ghrelin T120 (pg/mL) | 450.66 ± 135.7 | 632.45 ± 203.07 | <0.001 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T0 (nmol/dL) | 0.74 ± 0.29 | 1.35 ± 0.36 | <0.001 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T60 (nmol/dL) | 0.67 ± 0.25 | 1.26 ± 0.33 | <0.001 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T120 (nmol/dL) | 0.68 ± 0.26 | 1.3 ± 0.38 | <0.001 |
| Leptin T0 (ng/dL) | 34.84 ± 24.01 | 4.75 ± 4.52 | <0.001 |
| Leptin T60 (ng/dL) | 34.93 ± 24.97 | 4.35 ± 4.7 | <0.001 |
| Leptin T120 (ng/dL) | 30.94 ± 21.11 | 3.73 ± 3.68 | <0.001 |
| Leptin receptor T0 (µg/L) | 8.21 ± 3.12 | 15.59 ± 6.49 | <0.001 |
| Leptin receptor T60 (µg/L) | 8.4 ± 3.28 | 15.62 ± 6.78 | <0.001 |
| Leptin receptor T120 (µg/L) | 8.47 ± 3.16 | 15.41 ± 6.23 | <0.001 |
| Resistin T0 (ng/mL) | 3.65 ± 2 | 4.1 ± 1.18 | 0.0596 |
| Resistin T60 (ng/mL) | 3.5 ± 1.69 | 4.16 ± 1.05 | 0.023 |
| Resistin T120 (ng/mL) | 3.23 ± 1.25 | 3.85 ± 0.9 | 0.012 |
| Visfatin T0 (ng/mL) | 8.47 ± 6.9 | 17.49 ± 5.77 | <0.001 |
| Visfatin T60 (ng/mL) | 8.66 ± 6.6 | 14.9 ± 3.44 | <0.001 |
| Visfatin T120 (ng/mL) | 8.64 ± 5.77 | 12.95 ± 4.18 | 0.006 |
| Parameters | Obese Children (ng/mL) | Healthy Control (ng/mL) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IGF1 | 299 ± 112.9 | 231 ± 122.6 | 0.216 |
| IGF2 | 51.95 ± 47.43 | 107 ± 43.86 | 0.06 |
| IGFBP1 | 4.386 ± 5.66 | 7.85 ± 9.32 | 0.049 |
| IGFBP2 | 75.62 ± 38.69 | 143.82 ± 124.387 | 0.021 |
| IGFBP3 | 1896.46 ± 126.19 | 1763.88 ± 201.74 | 0.06 |
| IGFBP4 | 54.1 ± 75.29 | 27.09 ± 19.17 | 0.02 |
| IGFBP6 | 78.09 ± 28.45 | 151.9 ± 65.13 | 0.008 |
| IGFBP7 | 42.25 ± 33.9 | 67.84 ± 48.47 | 0.06 |
| IGF1 | IGF2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Spearman’s Correlation r | p Value | Spearman’s Correlation r | p Value |
| BMI percentile | 0.239 | 0.22 | −0.25 | 0.15 |
| Blood pressure | 0.089 | 0.689 | −0.132 | 0.46 |
| Insulin T0 | 0.179 | 0.37 | −0.16 | 0.375 |
| Insulin T60 | 0.249 | 0.219 | −0.153 | 0.4 |
| Insulin T120 | 0.283 | 0.152 | −0.01 | 0.584 |
| Adiponectin T0 | −0.228 | 0.273 | 0.169 | 0.365 |
| Adiponectin T60 | −0.455 | 0.033 | 0.053 | 0.08 |
| Adiponectin T120 | −0.344 | 0.099 | 0.073 | 0.7 |
| Apelin T0 | 0.124 | 0.547 | 0.388 | 0.028 |
| Apelin T60 | 0.117 | 0.568 | 0.433 | 0.013 |
| Apelin T120 | 0.213 | 0.3 | 0.374 | 0.035 |
| Cholecystokinin T0 | 0.025 | 0.9 | 0.363 | 0.038 |
| Cholecystokinin T60 | 0.16 | 0.423 | 0.49 | 0.004 |
| Cholecystokinin T120 | 0.078 | 0.7 | 0.517 | 0.002 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21 T0 | −0.3 | 0.1 | −0.27 | 0.128 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21 T60 | −0.29 | 0.14 | −0.254 | 0.154 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21 T120 | −0.257 | 0.2 | −0.128 | 0.479 |
| Ghrelin T0 | −0.164 | 0.415 | 0.446 | 0.009 |
| Ghrelin T60 | 0.042 | 0.836 | 0.44 | 0.01 |
| Ghrelin T120 | −0.327 | 0.513 | 0.459 | 0.007 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T0 | 0.117 | 0.569 | 0.366 | 0.04 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T60 | 0.043 | 0.83 | 0.429 | 0.013 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T120 | 0.058 | 0.773 | 0.5 | 0.002 |
| Leptin T0 | 0.222 | 0.265 | −0.4 | 0.02 |
| Leptin T60 | 0.283 | 0.153 | −0.45 | 0.008 |
| Leptin T120 | 0.197 | 0.3 | −0.45 | 0.007 |
| Leptin receptor T0 | −0.348 | 0.08 | 0.169 | 0.35 |
| Leptin receptor T60 | −0.338 | 0.08 | 0.127 | 0.483 |
| Leptin receptor T120 | −0.34 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.645 |
| Resistin T0 | 0.21 | 0.3 | 0.227 | 0.212 |
| Resistin T60 | 0.354 | 0.07 | 0.092 | 0.6 |
| Resistin T120 | 0.085 | 0.672 | 0.234 | 0.189 |
| Visfatin T0 | −0.047 | 0.829 | 0.243 | 0.17 |
| Visfatin T60 | −0.066 | 0.749 | 0.28 | 0.12 |
| Visfatin T120 | −0.13 | 0.524 | 0.07 | 0.7 |
| IGFBP1 | IGFBP2 | IGFBP3 | IGFBP4 | IGFBP6 | IGFBP7 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Spearman’s Correlation r | p Value | Spearman’s Correlation r | p Value | Spearman’s Correlation r | p Value | Spearman’s Correlation r | p Value | Spearman’s Correlation r | p Value | Spearman’s Correlation r | p Value |
| BMI percentile | −0.34 | 0.051 | −0.22 | 0.14 | 0.415 | 0.015 | 0.073 | 0.68 | −0.417 | 0.014 | −0.077 | 0.667 |
| Blood pressure | −0.502 | 0.003 | −0.39 | 0.006 | 0.39 | 0.02 | 0.217 | 0.219 | −0.212 | 0.228 | 0.116 | 0.515 |
| Insulin T0 | −0.54 | 0.001 | −0.343 | 0.02 | 0.4 | 0.02 | 0.022 | 0.905 | −0.4 | 0.022 | −0.186 | 0.299 |
| Insulin T60 | −0.493 | 0.004 | −0.37 | 0.011 | 0.475 | 0.006 | 0.2 | 0.272 | −0.33 | 0.06 | −0.026 | 0.888 |
| Insulin T120 | −0.409 | 0.018 | −0.3 | 0.02 | 0.367 | 0.036 | 0.256 | 0.15 | −0.135 | 0.455 | 0.023 | 0.9 |
| Adiponectin T0 | 0.194 | 0.295 | 0.076 | 0.62 | −0.307 | 0.093 | −0.186 | 0.315 | 0.206 | 0.266 | −0.112 | 0.553 |
| Adiponectin T60 | 0.157 | 0.424 | 0.076 | 0.617 | −0.198 | 0.314 | −0.224 | 0.25 | 0.163 | 0.407 | −0.129 | 0.514 |
| Adiponectin T120 | 0.144 | 0.449 | 0.04 | 0.743 | −0.208 | 0.27 | −0.188 | 0.319 | 0.173 | 0.36 | −0.138 | 0.466 |
| Apelin T0 | 0.193 | 0.3 | 0.122 | 0.286 | −0.333 | 0.06 | 0.175 | 0.337 | 0.73 | <0.001 | 0.356 | 0.046 |
| Apelin T60 | 0.287 | 0.112 | 0.08 | 0.47 | −0.363 | 0.04 | 0.085 | 0.64 | 0.636 | 0.00009 | 0.266 | 0.14 |
| Apelin T120 | 0.23 | 0.207 | 0.087 | 0.45 | −0.288 | 0.1 | 0.099 | 0.589 | 0.624 | 0.0001 | 0.253 | 0.16 |
| Cholecystokinin T0 | 0.259 | 0.145 | 0.086 | 0.566 | −0.459 | 0.007 | −0.119 | 0.51 | 0.677 | 0.00001 | 0.304 | 0.3 |
| Cholecystokinin T60 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.136 | 0.364 | −0.278 | 0.117 | −0.148 | 0.41 | 0.737 | <0.001 | 0.163 | 0.365 |
| Cholecystokinin T120 | 0.217 | 0.2 | 0.066 | 0.659 | −0.358 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.956 | 0.653 | 0.00004 | 0.2 | 0.238 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21 T0 | −0.2 | 0.266 | −0.257 | 0.08 | 0.166 | 0.357 | 0.199 | 0.268 | −0.474 | 0.005 | 0.16 | 0.37 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21 T60 | −0.14 | 0.4 | −0.27 | 0.066 | 0.234 | 0.195 | 0.203 | 0.258 | −0.416 | 0.016 | 0.167 | 0.354 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 21 T120 | −0.05 | 0.777 | −0.268 | 0.068 | 0.206 | 0.25 | 0.126 | 0.486 | −0.349 | 0.046 | 0.11 | 0.54 |
| Ghrelin T0 | 0.36 | 0.037 | 0.345 | 0.017 | −0.14 | 0.426 | −0.309 | 0.08 | 0.108 | 0.55 | −0.126 | 0.486 |
| Ghrelin T60 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0.343 | 0.018 | 0.05 | 0.778 | −0.355 | 0.04 | 0.223 | 0.2 | −0.222 | 0.215 |
| Ghrelin T120 | 0.29 | 0.1 | 0.364 | 0.012 | −0.009 | 0.96 | −0.294 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.219 | −0.166 | 0.355 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T0 | 0.282 | 0.118 | −0.032 | 0.84 | −0.35 | 0.049 | −0.02 | 0.909 | 0.745 | <0.001 | 0.259 | 0.15 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T60 | 0.299 | 0.09 | 0.087 | 0.56 | −0.3 | 0.026 | 0.05 | 0.785 | 0.677 | 0.00002 | 0.319 | 0.07 |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 T120 | 0.234 | 0.182 | 0.048 | 0.748 | −0.372 | 0.033 | 0.137 | 0.448 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 0.374 | 0.032 |
| Leptin T0 | −0.409 | 0.018 | −0.326 | 0.025 | 0.17 | 0.343 | 0.029 | 0.873 | −0.286 | 0.1 | −0.025 | 0.89 |
| Leptin T60 | −0.407 | 0.019 | −0.334 | 0.022 | 0.178 | 0.32 | −0.0002 | 0.999 | −0.287 | 0.1 | −0.08 | 0.647 |
| Leptin T120 | −0.421 | 0.015 | −0.328 | 0.025 | 0.156 | 0.386 | −0.009 | 0.96 | −0.3 | 0.078 | −0.065 | 0.72 |
| Leptin receptor T0 | 0.543 | 0.001 | 0.44 | 0.002 | −0.634 | 0.001 | −0.12 | 0.513 | 0.439 | 0.012 | −0.165 | 0.367 |
| Leptin receptor T60 | 0.524 | 0.002 | 0.427 | 0.003 | −0.604 | 0.002 | −0.147 | 0.4 | 0.444 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.427 |
| Leptin receptor T120 | 0.518 | 0.002 | 0.455 | 0.002 | −0.564 | 0.006 | −0.157 | 0.38 | 0.454 | 0.008 | 0.12 | 0.502 |
| Resistin T0 | 0.132 | 0.47 | −0.055 | 0.716 | −0.25 | 0.166 | −0.078 | 0.67 | 0.148 | 0.419 | 0.087 | 0.635 |
| Resistin T60 | 0.1 | 0.579 | 0.157 | 0.29 | −0.34 | 0.052 | −0.193 | 0.283 | 0.243 | 0.172 | 0.007 | 0.969 |
| Resistin T120 | 0.42 | 0.015 | 0.108 | 0.469 | −0.44 | 0.01 | −0.29 | 0.1 | 0.237 | 0.184 | −0.01 | 0.957 |
| Visfatin T0 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 0.27 | 0.06 | −0.26 | 0.14 | 0.384 | 0.03 | 0.568 | 0.0006 | 0.46 | 0.007 |
| Visfatin T60 | 0.08 | 0.652 | 0.143 | 0.344 | −0.2 | 0.24 | 0.493 | 0.004 | 0.353 | 0.047 | 0.502 | 0.003 |
| Visfatin T120 | 0.248 | 0.17 | 0.094 | 0.536 | −0.407 | 0.02 | 0.294 | 0.1 | 0.336 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 0.017 |
| Gene | Obese Children | Healthy Control | Fold Change | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGF1 | 5.15 | 5.63 | −1.39 | 0.073 |
| IGF2 | 6.09 | 6.49 | −1.33 | 0.037 |
| IGFBP1 | 7.28 | 7.91 | −1.56 | 0.046 |
| IGFBP2 | 6.4 | 6.65 | −1.19 | 0.2 |
| IGFBP3 | 6.12 | 6.25 | −1.09 | 1.0 |
| IGFBP4 | 7.68 | 7.81 | −1.1 | 0.4 |
| IGFBP5 | 5.01 | 5.1 | −1.06 | 0.1 |
| IGFBP6 | 6.83 | 7.22 | −1.31 | 0.059 |
| IGFBP7 | 8.08 | 7.37 | 1.64 | 0.023 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czogała, W.; Strojny, W.; Tomasik, P.; Multanowski, M.B.; Wójcik, M.; Miklusiak, K.; Krzysztofik, E.; Wróbel, A.; Miklusiak, K.; Skoczeń, S. The Insight into Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Insulin-Like Growth-Factor-Binding Proteins and Metabolic Profile in Pediatric Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072432
Czogała W, Strojny W, Tomasik P, Multanowski MB, Wójcik M, Miklusiak K, Krzysztofik E, Wróbel A, Miklusiak K, Skoczeń S. The Insight into Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Insulin-Like Growth-Factor-Binding Proteins and Metabolic Profile in Pediatric Obesity. Nutrients. 2021; 13(7):2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072432
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzogała, Wojciech, Wojciech Strojny, Przemysław Tomasik, Mirosław Bik Multanowski, Małgorzata Wójcik, Klaudia Miklusiak, Emil Krzysztofik, Albert Wróbel, Karol Miklusiak, and Szymon Skoczeń. 2021. "The Insight into Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Insulin-Like Growth-Factor-Binding Proteins and Metabolic Profile in Pediatric Obesity" Nutrients 13, no. 7: 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072432
APA StyleCzogała, W., Strojny, W., Tomasik, P., Multanowski, M. B., Wójcik, M., Miklusiak, K., Krzysztofik, E., Wróbel, A., Miklusiak, K., & Skoczeń, S. (2021). The Insight into Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Insulin-Like Growth-Factor-Binding Proteins and Metabolic Profile in Pediatric Obesity. Nutrients, 13(7), 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072432






