Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Gut Microbiota Composition and Faecal Metabolome Related to Obesity Remission
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Faecal Metagenomic Analysis
2.4. Faecal Metabolomic Analysis
2.5. SCFAs Identification and Quantification
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Biochemical and Anthropometric Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Severe Obesity
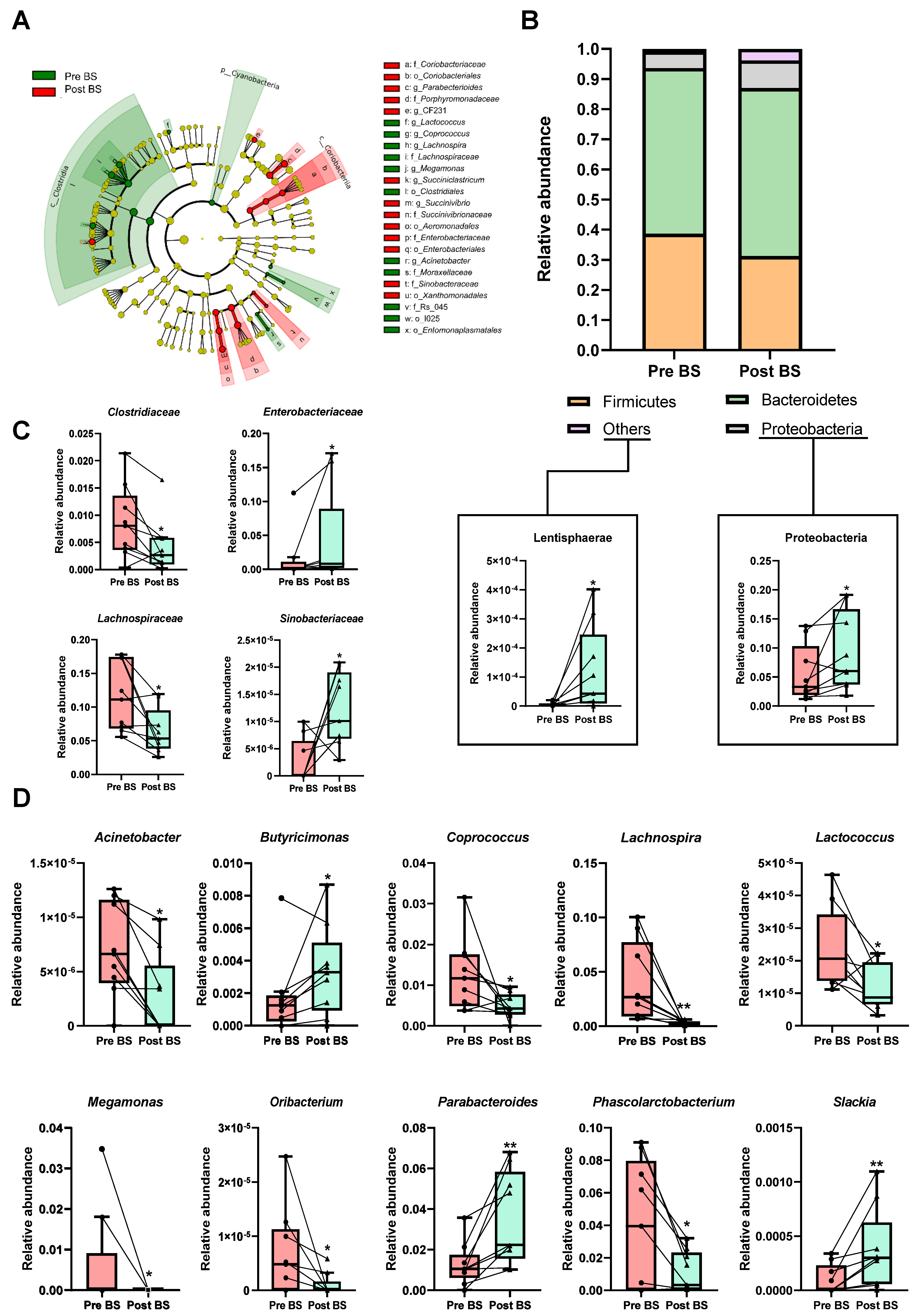
3.2. Differences in Faecal Microbiota Composition Associated to Bariatric Surgery
3.3. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Faecal Metabolomic Profile of Patients with Severe Obesity
3.4. SCFAs Faecal Profile before and after Bariatric Surgery of Patients with Severe Obesity
3.5. Correlations between Biochemical and Anthropometric Parameters, Gut Microbiota Composition and Metabolomic Profile of Patients with Severe Obesity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lorenzo, A.; Romano, L.; Di Renzo, L.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Cenname, G.; Gualtieri, P. Obesity: A preventable, treatable, but relapsing disease. Nutrition 2020, 71, 110615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, T.; Stigler, F.L.; Jeitler, K.; Horvath, K.; Siebenhofer, A. Management of overweight and obesity in primary care—A systematic overview of international evidence-based guidelines. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Nam, S.J.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.W.; Sohn, W.; Yoon, J.H.; Jung, S.H.; Hyun, Y.S.; et al. Comparative efficacy of bariatric surgery in the treatment of morbid obesity and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2180–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, A.; Ibarzabal, A.; Moizé, V.; Pané, A.; Andreu, A.; Molero, J.; de Hollanda, A.; Flores, L.; Ortega, E.; Lacy, A.; et al. Ten-year outcomes after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: An observational nonrandomized cohort study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arterburn, D.E.; Telem, D.A.; Kushner, R.F.; Courcoulas, A.P. Benefits and risks of bariatric surgery in adults: A review. JAMA 2020, 324, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Martinez, J.A. Diet, gut microbiota, and obesity: Links with host genetics and epigenetics and potential applications. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S17–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debédat, J.; Clément, K.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in human obesity: Impact of bariatric surgery. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaroli, V.; Karlsson, F.; Werling, M.; Ståhlman, M.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Olbers, T.; Fändriks, L.; Le Roux, C.W.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and vertical banded gastroplasty induce long-term changes on the human gut microbiome contributing to fat mass regulation. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Mueller, N.T.; Álvarez-Quintero, R.; Velásquez-Mejía, E.P.; Sierra, J.A.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Higher fecal short-chain fatty acid levels are associated with gut microbiome dysbiosis, obesity, hypertension and cardiometabolic disease risk factors. Nutrients 2019, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilg, H.; Zmora, N.; Adolph, T.E.; Elinav, E. The intestinal microbiota fuelling metabolic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Ianiro, G.; Laterza, L.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Ponziani, F.R.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Gut microbiota during dietary restrictions: New insights in non-communicable diseases. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbiano, S.; Suárez-Zamorano, N.; Chevalier, C.; Lazarević, V.; Kieser, S.; Rigo, D.; Leo, S.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Gaïa, N.; Maresca, M.; et al. Functional gut microbiota remodeling contributes to the caloric restriction-induced metabolic improvements. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 907–921.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heianza, Y.; Sun, D.; Smith, S.R.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Changes in gut microbiota-related metabolites and longterm successful weight loss in response to weight-loss diets: The POUNDS lost trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; Jorquera, F.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Functional interactions between gut microbiota transplantation, quercetin, and high-fat diet determine non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development in germ-free mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babraham Bioinformatics. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pẽa, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Desantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnsen, L.G.; Skou, P.B.; Khakimov, B.; Bro, R. Gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry data processing made easy. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1503, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Prifti, E.; Belda, E.; Ichou, F.; Kayser, B.D.; Dao, M.C.; Verger, E.O.; Hedjazi, L.; Bouillot, J.L.; Chevallier, J.M.; et al. Major microbiota dysbiosis in severe obesity: Fate after bariatric surgery. Gut 2019, 68, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros Pomar, M.D.; Vilarrasa García, N.; Rubio Herrera, M.Á.; Barahona, M.J.; Bueno, M.; Caixàs, A.; Calañas Continente, A.; Ciudin, A.; Cordido, F.; de Hollanda, A.; et al. The SEEN comprehensive clinical survey of adult obesity: Executive summary. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2021, 68, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, T.C.; Simmons, E.B.; Webb, K.; Burns, J.L.; Kushner, R.F. Trends in weight regain following Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1474–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulas, S.G.; Stefanou, C.K.; Stefanou, S.K.; Tepelenis, K.; Zikos, N.; Tepetes, K.; Kapsoritakis, A. Gut microbiota in patients with morbid obesity before and after bariatric surgery: A ten-year review study (2009–2019). Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.P.; Liu, C.Q.; Qi, L.; Sheng, Y.; Zou, D.J. Modulation of the gut microbiome: A systematic review of the effect of bariatric surgery. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijten, J.C.H.B.M.; Vugts, G.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Luyer, M.D.P. The importance of the microbiome in bariatric surgery: A systematic review. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oduro-Donkor, D.; Turner, M.C.; Farnaud, S.; Renshaw, D.; Kyrou, I.; Hanson, P.; Hattersley, J.; Weickert, M.O.; Menon, V.; Randeva, H.S.; et al. Modification of fecal microbiota as a mediator of effective weight loss and metabolic benefits following bariatric surgery. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 15, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Shu, X.O.; Howard, E.F.; Long, J.; English, W.J.; Flynn, C.R. Fecal metagenomics and metabolomics reveal gut microbial changes after bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2020, 16, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Caixàs, A.; Ahlers, M.; Patel, K.; Gao, Z.; Dutia, R.; Blaser, M.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Laferrère, B. Longitudinal changes of microbiome composition and microbial metabolomics after surgical weight loss in individuals with obesity. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crovesy, L.; Masterson, D.; Lopes Rosado, E. Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobârcă, D.; Cătoi, A.F.; Copăescu, C.; Miere, D.; Crișan, G. Bariatric surgery in obesity: Effects on gut microbiota and micronutrient status. Nutrients 2020, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paganelli, F.L.; Luyer, M.; Hazelbag, C.M.; Uh, H.W.; Rogers, M.R.C.; Adriaans, D.; Berbers, R.M.; Hendrickx, A.P.A.; Viveen, M.C.; Groot, J.A.; et al. Roux-Y Gastric Bypass and sleeve gastrectomy directly change gut microbiota composition independent of surgery type. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alcoholado, L.; Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Gómez-Pérez, A.M.; García-Fuentes, E.; Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno-Indias, I. Gut microbiota adaptation after weight loss by Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy bariatric surgeries. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.V.; Ashrafian, H.; Bueter, M.; Kinross, J.; Sands, C.; Le Roux, C.W.; Bloom, S.R.; Darzi, A.; Athanasiou, T.; Marchesi, J.R.; et al. Metabolic surgery profoundly influences gut microbial—Host metabolic cross-talk. Gut 2011, 60, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; DiBaise, J.K.; Zuccolo, A.; Kudrna, D.; Braidotti, M.; Yu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.; Crowell, M.D.; Wing, R.; Rittmann, B.E.; et al. Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patrone, V.; Vajana, E.; Minuti, A.; Callegari, M.L.; Federico, A.; Loguercio, C.; Dallio, M.; Tolone, S.; Docimo, L.; Morelli, L. Postoperative changes in fecal bacterial communities and fermentation products in obese patients undergoing bilio-intestinal bypass. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seganfredo, F.; Blume, C.; Moehlecke, M.; Giongo, A.; Casagrande, D.; Spolidoro, J.; Padoin, A.; Schaan, B.; Mottin, C. Weight-loss interventions and gut microbiota changes in overweight and obese patients: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 832–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, Z.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice is associated with the indigenous opportunistic bacteria on the interior of Peyer’s patches. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 55, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Moreno-Indias, I.; de Hollanda, A.; Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Vidal, J.; Tinahones, F.J. Gut microbiota specific signatures are related to the successful rate of bariatric surgery. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 942–952. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, S.L.; Santos, A.; Magro, D.O.; Cazzo, E.; Assalin, H.B.; Guadagnini, D.; Vieira, F.T.; Dutra, E.S.; Saad, M.J.A.; Ito, M.K. Gut microbiota modifications and weight regain in morbidly obese women after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 4958–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Li, M.; Yu, M.; Ping, F.; Zheng, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, X. Vildagliptin increases butyrate-producing bacteria in the gut of diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, C.E.; Aardema, N.D.J.; Bunnell, M.L.; Larson, D.P.; Aguilar, S.S.; Bergeson, J.R.; Malysheva, O.V.; Caudill, M.A.; Lefevre, M. Effect of choline forms and gut microbiota composition on trimethylamine-n-oxide response in healthy men. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Jiang, F.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Shen, X.; Wei, P. Alteration of the gut microbiota associated with childhood obesity by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Carrillo, S.; Ciordia, S.; Rojo, D.; Zubeldia-Varela, E.; Méndez-García, C.; Martínez-Martínez, M.; Barbas, C.; Ruiz-Ruiz, S.; Moya, A.; Garriga, M.; et al. A body weight loss- and health-promoting gut microbiota is established after bariatric surgery in individuals with severe obesity. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Kitahama, S.; Yamashita, T.; Hirono, Y.; Tabata, T.; Saito, Y.; Shinohara, R.; Nakashima, H.; Emoto, T.; Hirota, Y.; et al. Metabolic alterations in plasma after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narath, S.H.; Mautner, S.I.; Svehlikova, E.; Schultes, B.; Pieber, T.R.; Sinner, F.M.; Gander, E.; Libiseller, G.; Schimek, M.G.; Sourij, H.; et al. An untargeted metabolomics approach to characterize short-term and long-term metabolic changes after bariatric surgery. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gralka, E.; Luchinat, C.; Tenori, L.; Ernst, B.; Thurnheer, M.; Schultes, B. Metabolomic fingerprint of severe obesity is dynamically affected by bariatric surgery in a procedure-dependent manner. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, Z.E.; DiBaise, J.K.; Dautel, S.E.; Isern, N.G.; Kim, Y.M.; Hoyt, D.W.; Schepmoes, A.A.; Brewer, H.M.; Weitz, K.K.; Metz, T.O.; et al. Temporospatial shifts in the human gut microbiome and metabolome after gastric bypass surgery. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mediani, A.; Abas, F.; Maulidiani, M.; Khatib, A.; Tan, C.P.; Ismail, I.S.; Shaari, K.; Ismail, A.; Lajis, N.H. Metabolic and biochemical changes in streptozotocin induced obese-diabetic rats treated with Phyllanthus niruri extract. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 128, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T.I.B.; Geloneze, B.; Pareja, J.C.; Calixto, A.R.; Ferreira, M.M.C.; Marsaioli, A.J. Omics prospective monitoring of bariatric surgery: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass outcomes using mixed-meal tolerance test and time-resolved 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Omi. A J. Integr. Biol. 2016, 20, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes, T.I.B.; Geloneze, B.; Pareja, J.C.; Calixto, A.R.; Ferreira, M.M.C.; Marsaioli, A.J. Blood metabolome changes before and after bariatric surgery: A 1H NMR-based clinical investigation. Omi. A J. Integr. Biol. 2015, 19, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Tulipani, S.; Marco-Ramell, A.; Miñarro, A.; Jáuregui, O.; Sanchez-Pla, A.; Ramos-Molina, B.; Tinahones, F.J.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Metabotypes of response to bariatric surgery independent of the magnitude of weight loss. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijayatunga, N.N.; Sams, V.G.; Dawson, J.A.; Mancini, M.L.; Mancini, G.J.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery alters serum metabolites and fatty acids in patients with morbid obesity. Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasubuchi, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Hiramatsu, T.; Ichimura, A.; Kimura, I. Dietary gut microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, and host metabolic regulation. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2839–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quiroga, R.; Nistal, E.; Estébanez, B.; Porras, D.; Juárez-Fernández, M.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; de Paz, J.A.; González-Gallego, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; et al. Exercise training modulates the gut microbiota profile and impairs inflammatory signaling pathways in obese children. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajo-Pescador, S.; Porras, D.; Garcia-Mediavilla, M.V.; Martinez-Florez, S.; Juarez-Fernandez, M.; Cuevas, M.J.; Mauriz, J.L.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Sanchez-Campos, S. Beneficial effects of exercise on gut microbiota functionality and barrier integrity, and gut-liver crosstalk in an in vivo model of early obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. DMM Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.N.; Yao, Y.; Ju, S.Y. Short chain fatty acids and fecal microbiota abundance in humans with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liou, A.P.; Paziuk, M.; Luevano, J.M.; Machineni, S.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Kaplan, L.M. Conserved shifts in the gut microbiota due to gastric bypass reduce host weight and adiposity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 178ra41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayengbam, S.; Lambert, J.E.; Parnell, J.A.; Tunnicliffe, J.M.; Nicolucci, A.C.; Han, J.; Sturzenegger, T.; Shearer, J.; Mickiewicz, B.; Vogel, H.J.; et al. Impact of dietary fiber supplementation on modulating microbiota–host–metabolic axes in obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 64, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Fernández, M.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Román-Sagüillo, S.; González-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Aging, gut microbiota and metabolic diseases: Management through physical exercise and nutritional interventions. Nutrients 2021, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoum, I.J.; Stein, H.K.; Merrifield, B.F.; Kaplan, L.M. Capacity for physical activity predicts weight loss after roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obesity 2009, 17, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabesh, M.R.; Maleklou, F.; Ejtehadi, F.; Alizadeh, Z. Nutrition, physical activity, and prescription of supplements in pre- and post-bariatric surgery patients: A practical guideline. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 3385–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Pre BS | Post BS | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric parameters | |||
| Weight (kg) | 124.98 ± 6.33 | 85.78 ± 5.81 *** | 1 × 10−6 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 45.46 ± 2.05 | 31.09 ± 1.81 *** | 4 × 10−6 |
| Body fat (%) | 50.75 ± 1.03 | 36.54 ± 2.91 ** | 0.003 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 130.63 ± 4.54 | 111.71 ± 7.05 | 0.059 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 131.13 ± 8.83 | 102.17 ± 8.26 ** | 0.008 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm) | 133.63 ± 3.23 | 118 ± 6.77 | 0.064 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm) | 87.38 ± 2.52 | 86.86 ± 5.82 | 0.966 |
| Biochemical parameters | |||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 91 ± 3.08 | 83 ± 2.49 ** | 0.009 |
| Insulin (mUI/mL) | 21.46 ± 3.12 | 7.08 ± 1.05 ** | 0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 4.34 ± 0.59 | 1.45 ± 0.21 ** | 0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.76 ± 0.13 | 5.19 ± 0.15 ** | 0.009 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 175.75 ± 6.39 | 161.88 ± 14.84 | 0.427 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 105.5 ± 6.65 | 80.38 ± 11.35 | 0.120 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 51.50 ± 3.01 | 66.5 ± 4.07 ** | 0.004 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 93.75 ± 13.67 | 73.38 ± 11.95 | 0.247 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.68 ± 0.42 | 4.37 ± 0.34 * | 0.033 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 30.75 ± 2.70 | 31.75 ± 2.66 | 0.584 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.72 ± 0.03 | 0.72 ± 0.07 | 0.933 |
| AST (U/L) | 19.38 ± 1.44 | 14.88 ± 1.11 * | 0.013 |
| ALT (U/L) | 25.75 ± 3.60 | 20.75 ± 8.29 | 0.476 |
| GGT (U/L) | 31.38 ± 6.42 | 16.5 ± 4.57 | 0.059 |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) | 27.25 ± 2.96 | 52.25 ± 10.58 | 0.063 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 19.63 ± 10.98 | 2.71 ± 1.37 * | 0.017 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juárez-Fernández, M.; Román-Sagüillo, S.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Linares, P.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Urioste-Fondo, A.; Álvarez-Cuenllas, B.; González-Gallego, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; et al. Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Gut Microbiota Composition and Faecal Metabolome Related to Obesity Remission. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082519
Juárez-Fernández M, Román-Sagüillo S, Porras D, García-Mediavilla MV, Linares P, Ballesteros-Pomar MD, Urioste-Fondo A, Álvarez-Cuenllas B, González-Gallego J, Sánchez-Campos S, et al. Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Gut Microbiota Composition and Faecal Metabolome Related to Obesity Remission. Nutrients. 2021; 13(8):2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082519
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuárez-Fernández, María, Sara Román-Sagüillo, David Porras, María Victoria García-Mediavilla, Pedro Linares, María Dolores Ballesteros-Pomar, Ana Urioste-Fondo, Begoña Álvarez-Cuenllas, Javier González-Gallego, Sonia Sánchez-Campos, and et al. 2021. "Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Gut Microbiota Composition and Faecal Metabolome Related to Obesity Remission" Nutrients 13, no. 8: 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082519
APA StyleJuárez-Fernández, M., Román-Sagüillo, S., Porras, D., García-Mediavilla, M. V., Linares, P., Ballesteros-Pomar, M. D., Urioste-Fondo, A., Álvarez-Cuenllas, B., González-Gallego, J., Sánchez-Campos, S., Jorquera, F., & Nistal, E. (2021). Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Gut Microbiota Composition and Faecal Metabolome Related to Obesity Remission. Nutrients, 13(8), 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082519






