Effects of Elaidic Acid on HDL Cholesterol Uptake Capacity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Preparation of the apoB-Depleted Serum
2.3. Clinical Variables
2.4. CUC Assay
2.5. Measurement of Elaidic Acid Incorporated into HDL Phospholipids
2.6. Preparation of rHDL
2.7. CUC Assay for rHDL
2.8. Fluorescence-Based Assay for LCAT Activity
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
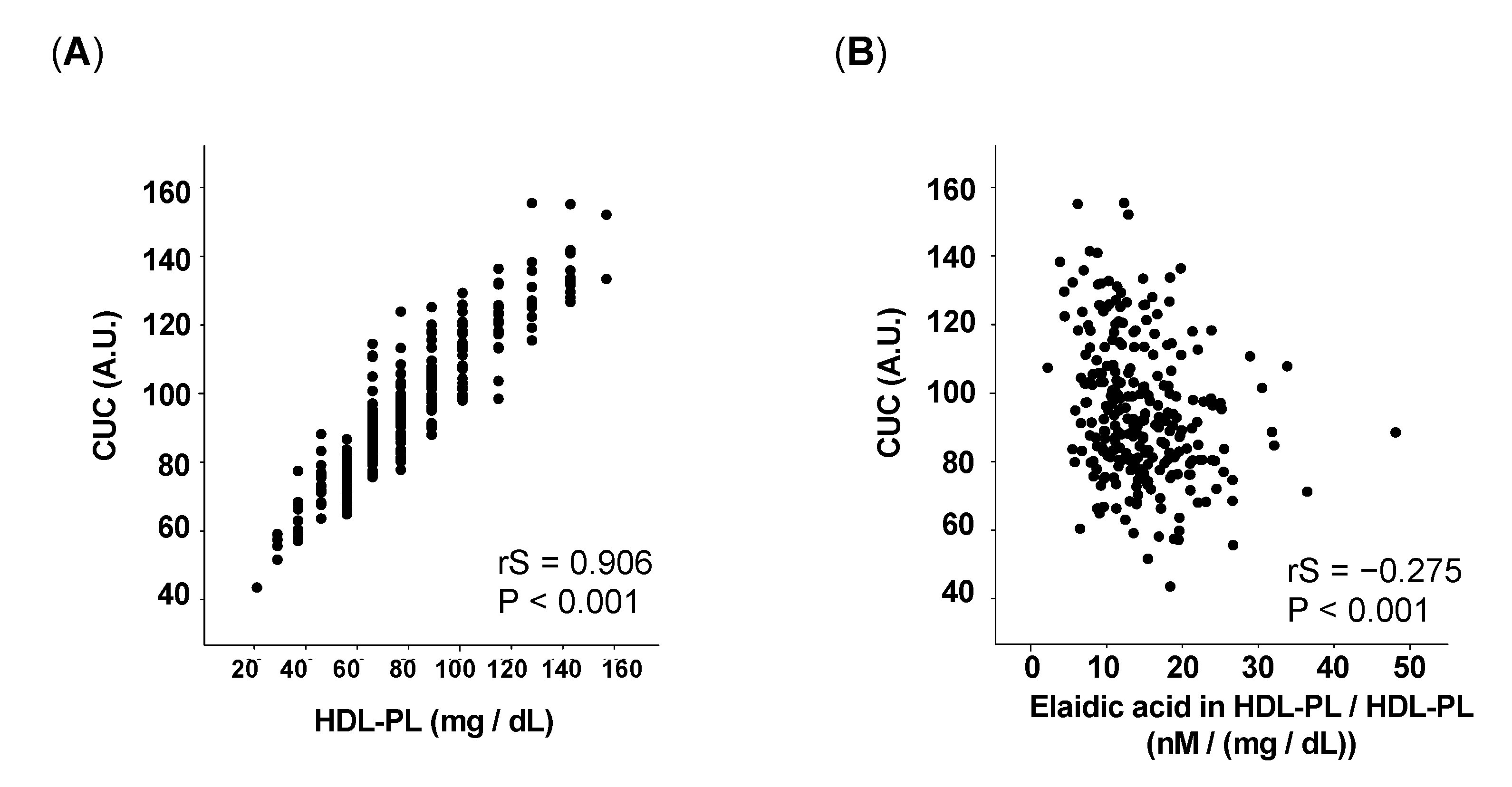
3.2. The Proportion of Elaidic Acid in HDL-PL Inversely Correlates with CUC
3.3. LCAT-Dependent Enhancement of CUC Is Suppressed in rHDL Containing Elaidic Acid-PC
3.4. LCAT-Dependent Cholesterol Esterification Is Suppressed in rHDL Containing Elaidic Acid-PC
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Supplemental Methods
Appendix A.1. Generation of Mouse Monoclonal Antibody 8E10 and P1A5
Appendix A.2. Synthesis of Biotin-PEG7-Cholesterol
References
- Khera, A.V.; Cuchel, M.; De La Llera-Moya, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Burke, M.F.; Jafri, K.; French, B.C.; Phillips, J.A.; Mucksavage, M.L.; Wilensky, R.L.; et al. Cholesterol Efflux Capacity, High-Density Lipoprotein Function, and Atherosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohatgi, A.; Khera, A.; Berry, J.D.; Givens, E.G.; Ayers, C.R.; Wedin, K.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Rader, D.R.; De Lemos, J.A.; et al. HDL Cholesterol Efflux Capacity and Incident Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleheen, D.; Scott, R.; Javad, S.; Zhao, W.; Rodrigues, A.; Picataggi, A.; Lukmanova, D.; Mucksavage, M.L.; Luben, R.; Billheimer, J.; et al. Association of HDL cholesterol efflux capacity with incident coronary heart disease events: A prospective case-control study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anastasius, M.; Kockx, M.; Jessup, W.; Sullivan, D.; Rye, K.-A.; Kritharides, L. Cholesterol efflux capacity: An introduction for clinicians. Am. Heart J. 2016, 180, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothblat, G.H.; de la Llera-Moya, M.; Atger, V.; Kellner-Weibel, G.; Williams, D.L.; Phillips, M.C. Cell cholesterol efflux: Integration of old and new observations provides new insights. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Toh, R.; Murakami, K.; Kiriyama, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Miwa, K.; Kubo, T.; Irino, Y.; Mori, K.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Cholesterol Uptake Capacity: A New Measure of HDL Functionality for Coronary Risk Assessment. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2017, 2, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toh, R. Assessment of HDL Cholesterol Removal Capacity: Toward Clinical Application. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2019, 26, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agnani, G.; Marcel, Y.L. Cholesterol efflux from fibroblasts to discoidal lipoproteins with apolipoprotein A-I (LpA-I) increases with particle size but cholesterol transfer from LpA-I to lipoproteins decreases with size. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2643–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.S.; Lund-Katz, S.; Johnson, W.J.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Palgunachari, M.N.; Segrest, J.P.; Rothblat, G.H.; Phil-lips, M.C. The Influence of Apolipoprotein Structure on the Efflux of Cellular Free Cholesterol to High Density Lipopro-tein. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 22975–22982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.; Gillotte, K.L.; Lund-Katz, S.; Johnson, W.J.; Rothblat, G.H.; Phillips, M.C. The Effect of High Density Lipoprotein Phospholipid Acyl Chain Composition on the Efflux of Cellular Free Cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5882–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, N.; Ishida, T.; Nagao, M.; Mori, T.; Monguchi, T.; Sasaki, M.; Mori, K.; Kondo, K.; Nakajima, H.; Honjo, T.; et al. Administration of high dose eicosapentaenoic acid enhances anti-inflammatory properties of high-density lipoprotein in Japanese patients with dyslipidemia. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Irino, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Tsuda, S.; Mori, T.; Nagao, M.; Oshita, T.; Mori, K.; Hara, T.; Toh, R.; et al. Eicosapentaenoic Acid-Enriched High-Density Lipoproteins Exhibit Anti-Atherogenic Properties. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, K.; Ishida, T.; Yasuda, T.; Hasokawa, M.; Monguchi, T.; Sasaki, M.; Kondo, K.; Nakajima, H.; Shinohara, M.; Shinke, T.; et al. Serum Trans-Fatty Acid Concentration Is Elevated in Young Patients With Coronary Artery Disease in Japan. Circ. J. 2015, 79, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshita, T.; Toh, R.; Shinohara, M.; Mori, K.; Irino, Y.; Nagao, M.; Hara, T.; Otake, H.; Ishida, T.; Hirata, K.-I. Elevated Serum Elaidic Acid Predicts Risk of Repeat Revascularization After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Japan. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Aro, A.; Willett, W.C. Health effects of trans-fatty acids: Experimental and observational evidence. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, S5–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willett, W.; Stampfer, M.; Manson, J.; Colditz, G.; Speizer, F.; Rosner, B.; Hennekens, C.; Sampson, L. Intake of trans fatty acids and risk of coronary heart disease among women. Lancet 1993, 341, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Katan, M.B.; Ascherio, A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C. Trans Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidgren, H.M.; Louheranta, A.M.; Ågren, J.J.; Schwab, U.S.; Uusitupa, M.I.J. Divergent incorporation of dietary trans fatty acids in different serum lipid fractions. Lipids 1998, 33, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, C.; Feller, S.E.; Ward, J.A.; Shaikh, S.R.; Zerouga, M.; Stillwell, W. Comparison of Cis and Trans Fatty Acid Containing Phosphatidylcholines on Membrane Properties†. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 6344–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontush, A.; Lhomme, M.; Chapman, M.J. Unraveling the complexities of the HDL lipidome. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2950–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, W.; Heink, A.; Sexmith, H.; Melchior, J.T.; Gordon, S.M.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Woollett, L.; Barr, J.R.; Jones, J.; Toth, C.; et al. The effects of apolipoprotein B depletion on HDL subspecies composition and function. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavigiolio, G.; Shao, B.; Geier, E.G.; Ren, G.; Heinecke, J.W.; Oda, M.N. The Interplay between Size, Morphology, Stability, and Functionality of High-Density Lipoprotein Subclasses. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 4770–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, T.; Sakurai, A.; Vaisman, B.L.; Nishida, T.; Neufeld, E.B.; Demosky, S.J.; Sampson, M.L.; Shamburek, R.D.; Freeman, L.A.; Remaley, A.T. Development of a novel fluorescent activity assay for lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 55, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, T.; Sasaki, J.; Ishibashi, S.; Birou, S.; Daida, H.; Dohi, S.; Egusa, G.; Hiro, T.; Hirobe, K.; Iida, M.; et al. Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis. Executive Summary of the Japan Atherosclerosis Society (JAS) Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases in Japan―2012 Version. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2014, 21, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousset, X.; Vaisman, B.; Amar, M.; Sethi, A.A.; Remaley, A.T. Lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase—From biochemistry to role in cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2009, 16, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, E.J.; Anthanont, P.; Asztalos, B.F. High-density lipoprotein metabolism, composition, function, and deficiency. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2014, 25, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorci-Thomas, M.G.; Bhat, S.; Thomas, M.J. Activation of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase by HDL ApoA-I central helices. Clin. Lipidol. 2009, 4, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czarnecka, H.; Yokoyama, S. Regulation of Cellular Cholesterol Efflux by Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase Reaction through Nonspecific Lipid Exchange. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamburek, R.D.; Bakker-Arkema, R.; Shamburek, A.M.; Freeman, L.A.; Amar, M.J.; Auerbach, B.; Krause, B.R.; Homan, R.; Adelman, S.J.; Collins, H.L.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of ACP-501, a Recombinant Human Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase, in a Phase 1 Single-Dose Escalation Study. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khovidhunkit, W.; Shigenaga, J.K.; Moser, A.H.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Cholesterol Efflux by Acute-Phase High Den-sity Lipoprotein: Role of Lecithin: Cholesterol Acyltransferase. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, O.; Goren, R.; Stein, Y. Removal of cholesterol from fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells in culture in the presence and absence of cholesterol esterification in the medium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Lipids Lipid Metab. 1978, 529, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, E.; Bellini, F.; Stoudt, G.; Hemperly, S.; Rothblat, G. Influence of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase on cholesterol metabolism in hepatoma cells and hepatocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Lipids Lipid Metab. 1980, 617, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecka, H.; Yokoyama, S. Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction on cellular lipid released by free apolipoprotein-mediated efflux. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 4385–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lands, W.E.; Merkl, I. Metabolism of Glycerolipids. III. Reactivity of Various Acyl Esters of Coenzyme A With Al-pha’-Acylglycerophosphorylcholine, and Positional Specificities in Lecithin Synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuuchi, H.; O’Brien, J.S. Positional distribution of fatty acids in glycerophosphatides of bovine gray matter. J. Lipid Res. 1968, 9, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, M.M.; Tiberti, M.L.; Pagnotta, S.; Barelli, H.; Gautier, R.; Antonny, B. Acyl chain asymmetry and polyunsaturation of brain phospholipids facilitate membrane vesiculation without leakage. eLife 2018, 7, e34394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, N.; Paul, J.-L.; Atger, V.; Cogny, A.; Soni, T.; de la Llera-Moya, M.; Rothblat, G.; Moatti, N. HDL Phospholipid Content and Composition as a Major Factor Determining Cholesterol Efflux Capacity From Fu5AH Cells to Human Serum. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997, 17, 2685–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Oram, J.F.; Asztalos, B.F.; Vaughan, A.M.; Lund-Katz, S.; Adorni, M.P.; Phillips, M.C.; Rothblat, G.H. Effects of acceptor composition and mechanism of ABCG1-mediated cellular free cholesterol efflux. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L. There Are Three Common Types of Membrane Lipids. In Biochemistry, 5th ed.; WH Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.E. Dietary trans fatty acids: Review of recent human studies and food industry responses. Lipids 2006, 41, 967–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthei, K.A.; Patra, D.; Wilson, C.J.; Fawaz, M.V.; Piersimoni, L.; Shenkar, J.C.; Yuan, W.; Andrews, P.; Engen, J.R.; Schwendeman, A.; et al. Structural analysis of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase bound to high density lipoprotein particles. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, M.; Delawary, M.; Sakurai, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakao, N.; Tsuru, H.; Fukushima, Y.; Honzumi, S.; Moriyama, S.; Wada, N.; et al. Novel LCAT (Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase) Activator DS-8190a Prevents the Progression of Plaque Accumulation in Atherosclerosis Models. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 41, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Aulak, K.; Huang, Y.; Wagner, M.; Gerstenecker, G.; Topbas, C.; Gogonea, V.; DiDonato, A.J.; Tang, W.H.W.; Mehl, R.A.; et al. Site-specific Nitration of Apolipoprotein A-I at Tyrosine 166 Is Both Abundant within Human Atherosclerotic Plaque and Dysfunctional. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10276–10292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Variables | n = 264 |
|---|---|
| Age | 70.8 ± 9.3 |
| Male, n (%) | 210 (79.5) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 204 (77.3) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 221 (83.7) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 119 (45.1) |
| Smoking history, n (%) | 180 (68.4) |
| Statin, n (%) | 233 (88.2) |
| Laboratory data | |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.4 ± 1.0 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 128.8 ± 71.2 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 146.8 ± 31.2 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 82.1 ± 26.3 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 46.1 ± 12.6 |
| CUC (A.U.) | 94.8 ± 20.5 |
| ApoA1 (mg/dL) | 118.0 ± 19.3 |
| HDL-PL (mg/dL) | 78.0 ± 26.6 |
| HDL-TG (mg/dL) | 13.6 ± 6.6 |
| Elaidic acid in HDL-PL (μM) | 1.1 ± 0.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iino, T.; Toh, R.; Nagao, M.; Shinohara, M.; Harada, A.; Murakami, K.; Irino, Y.; Nishimori, M.; Yoshikawa, S.; Seto, Y.; et al. Effects of Elaidic Acid on HDL Cholesterol Uptake Capacity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093112
Iino T, Toh R, Nagao M, Shinohara M, Harada A, Murakami K, Irino Y, Nishimori M, Yoshikawa S, Seto Y, et al. Effects of Elaidic Acid on HDL Cholesterol Uptake Capacity. Nutrients. 2021; 13(9):3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093112
Chicago/Turabian StyleIino, Takuya, Ryuji Toh, Manabu Nagao, Masakazu Shinohara, Amane Harada, Katsuhiro Murakami, Yasuhiro Irino, Makoto Nishimori, Sachiko Yoshikawa, Yutaro Seto, and et al. 2021. "Effects of Elaidic Acid on HDL Cholesterol Uptake Capacity" Nutrients 13, no. 9: 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093112
APA StyleIino, T., Toh, R., Nagao, M., Shinohara, M., Harada, A., Murakami, K., Irino, Y., Nishimori, M., Yoshikawa, S., Seto, Y., Ishida, T., & Hirata, K.-i. (2021). Effects of Elaidic Acid on HDL Cholesterol Uptake Capacity. Nutrients, 13(9), 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093112





