Nutritional Status According to the GLIM Criteria in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: Association with Prognosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Nutritional Screening and Assessment
2.3. Other Clinical and Analytical Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
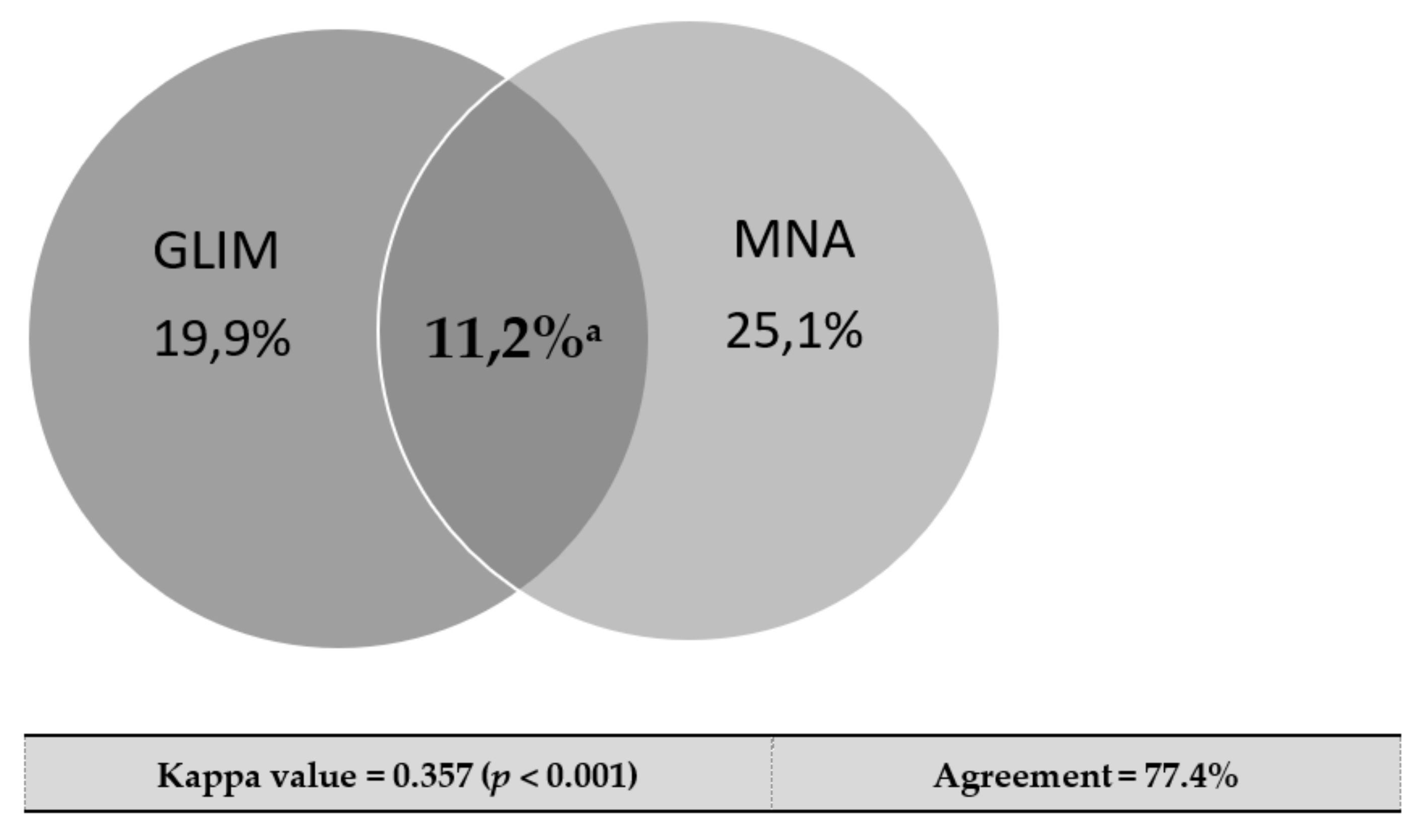
3.1. Patient’s Characteristics and Nutritional Assessment
3.2. Nutritional Assessment and Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonilla-Palomas, J.L.; Gámez-López, A.L.; Anguita-Sánchez, M.P.; Castillo-Domínguez, J.C.; García-Fuertes, D.; Crespin-Crespin, M.; López-Granados, A.; Suárez de Lezo, J. Impact of malnutrition on long-term mortality in hospitalized patients with heart failure. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2011, 64, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohashi, K.; Morisawa, T.; Kosugi, M.; Endoh, I.; Kusama, Y.; Atarashi, H.; Shimizu, W. Nutritional status is associated with inflammation and predicts a poor outcome in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 713–727. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauti, A.K.; Ochiai, M.E.; Bifulco, P.S.; de Araújo, M.A.; Alonso, R.R.; Ribeiro, R.H.; Pereira-Barretto, A.C. Subjective global assessment of nutritional status in cardiac patients. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2006, 87, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gastelurrutia, P.; Lupón, J.; de Antonio, M.; Zamora, E.; Domingo, M.; Urrutia, A.; Altimir, S.; Coll, R.; Díez, C.; Bayes-Genis, A. Body mass index, body fat, and nutritional status of patients with heart failure: The PLICA study. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastelurrutia, P.; Lupón, J.; Domingo, M.; Ribas, N.; Noguero, M.; Martinez, C.; Cortes, M.; Bayes-Genis, A. Usefulness of body mass index to characterize nutritional status in patients with heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 108, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, H.; Luo, X.; Li, J. Prediction of all-cause mortality with malnutrition assessed by controlling nutritional status score in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kootaka, Y.; Kamiya, K.; Hamazaki, N.; Nozaki, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yamashita, M.; Maekawa, E.; Reed, J.L.; Yamaoka-Tojo, M.; et al. The GLIM criteria for defining malnutrition can predict physical function and prognosis in patients with cardiovascular disease. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 40, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquín, C.; Puig, R.; Gastelurrutia, P.; Lupón, J.; de Antonio, M.; Domingo, M.; Moliner, P.; Zamora, E.; Martin, M.; Alonso, N.; et al. Mini nutritional assessment is a better predictor of mortality than subjective global assessment in heart failure out-patients. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2740–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickstein, K.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Filippatos, G.; McMurray, J.J.; Ponikowski, P.; Poole-Wilson, P.A.; Strömberg, A.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Atar, D.; Hoes, A.W.; et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). Eur. Heart J. 2008, 10, 933–989. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, E.; Lupón, J.; Vila, J.; Urrutia, A.; de Antonio, M.; Sanz, H.; Grau, M.; Ara, J.; Bayés-Genís, A. Estimated glomerular filtration rate and prognosis in heart failure: Value of the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study-4, Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration, and Cockroft-Gault formulas. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gastelurrutia, P.; Lupón, J.; de Antonio, M.; Urrutia, A.; Díez, C.; Coll, R.; Altimir, S.; Bayes-Genis, A. Statins in heart failure: The paradox between large randomized clinical trials and real life. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubenstein, L.Z.; Harker, J.O.; Salvà, A.; Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B. Screening for undernutrition in geriatric practice developing the short-form mini-nutritional assessment (MNA-SF). J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M366–M372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B.; Garry, P.J. Assessing the nutritional status of the elderly: The Mini Nutritional Assessment as part of the geriatric evaluation. Nutr. Rev. 1996, 54, S59–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alastrué, A.; Rull, M.; Camps, I.; Ginesta, C.; Melus, M.R.S. Nuevas normas y consejos en la valoración de los parámetros en nuestra población:Índice adiposo-muscular,índices ponderales y tablas de percentiles de los datos antropométricos útiles en una valoración nutricional. Med. Clin. 1988, 91, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Fess, E. Grip Strength. In Clinical Assessment Recommendations, 2nd ed.; Casanova, J.S., Ed.; American Society of Hand Therapists: Chicago, IL, USA, 1992; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Torralvo, F.J.S.; Porras, N.; Fernández, J.A.; Torres, F.G.; Tapia, M.J.; Lima, F.; Soriguer, F.; Gonzalo, M.; Martínez, G.R.; Olveira, G. Normative reference values for hand grip dynamometry in Spain. Association with lean mass. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D. Functional evaluation: The Barthel Index. Maryland State Med. J. 1965, 14, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kondrup, J.; Johansen, N.; Plum, L.M.; Bak, L.; Larsen, I.H.; Martinsen, A.; Andersen, J.R.; Baernthsen, H.; Bunch, E.; Lauesen, N. Incidence of nutritional risk and causes of inadequate nutritional care in hospitals. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 21, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.-P.; Guo, Z.-Q.; Xu, H.-X.; Yuan, K.-T.; Yu, M.; Braga, M.; Cederholm, T.; et al. The GLIM criteria as an effective tool for nutrition assessment and survival prediction in older adult cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 40, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla Palomas, J.L.; Gámez López, A.L.; Moreno Conde, M.; López Ibáñez, M.C.; Castellano García, P.; Ráez Ruiz, C.J.; Ruíz Quirós, R.; Ramiro Ortega, E. Impact of malnutrition on long-term mortality in outpatients with chronic heartFailure. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, J.P.; Keller, H.; Gramlich, L.; Jeejeebhoy, K.N.; Laporte, M.; Duerksen, D.R. GLIM criteria has fair sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing malnutrition when using SGA as comparator. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2771–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czapla, M.; Juárez-Vela, R.; Łokieć, K.; Karniej, P. The Association between Nutritional Status and In-Hospital Mortality among Patients with Heart Failure—A Result of the Retrospective Nutritional Status Heart Study 2 (NSHS2). Nutrients 2021, 14, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kałużna-Oleksy, M.; Krysztofiak, H.; Migaj, J.; Wleklik, M.; Dudek, M.; Uchmanowicz, I.; Lesiak, M.; Straburzyńska-Migaj, E. Relationship between Nutritional Status and Clinical and Biochemical Parameters in Hospitalized Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction, with 1-year Follow-Up. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla-Palomas, J.L.; Gámez-López, A.L.; Castillo-Domínguez, J.C.; Moreno-Conde, M.; Ibáñez, M.C.L.; Expósito, R.A.; Ortega, E.R.; Anguita-Sánchez, M.P.; Villar-Ráez, A. Nutritional intervention in malnourished hospitalized patients with heart failure. Arch. Med. Res. 2016, 47, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Total | Dead | Survivors | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 151 | N = 48 | N = 103 | ||
| Age (y) | 68.6 ± 10.9 | 75.6 ±8.7 | 65.4 ± 10.4 | <0.001 |
| Male (%) | 72.2 | 70.8 | 72.8 | ns |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.8 ± 5 | 27.1 ± 4.7 | 28.2 ± 5.2 | ns |
| NT-pro BNP (pg/mL) | 706.5 | 1830 | 448.5 | <0.001 |
| (245.2–1832.5) | (823–3500) | (150.7–1097.5) | ||
| Ejection Fraction (%) | 43.9 ± 12.9 | 46.1 | 42.9 | ns |
| NYHA (%) | ns | |||
| I | 4 | 2.1 | 4.9 | |
| II | 83.4 | 77.1 | 86.4 | |
| III a | 12.6 | 20.8 | 8.7 | |
| Duration of disease (years) | 7.0 ± 2.5 | 9.8 ± 0.4 | 5.8 ± 2.1 | ns |
| Medication (%) | ||||
| ACEI or ARB | 84.8 | 68.8 | 92.2 | <0.001 |
| Beta blocker | 88.7 | 87.5 | 89.3 | ns |
| Statin | 68.2 | 79.2 | 63.1 | 0.048 |
| MNA (%) | 0.017 | |||
| Normal | 74.8 | 62.5 | 80.5 | |
| At risk of MN | 23.8 | 35.4 | 18.4 | |
| MN | 1.3 | 2 | 0.9 | |
| GLIM criteria (%) | ns | |||
| Normal | 80.1 | 70.8 | 84.5 | |
| Moderate MN | 14.6 | 20.8 | 11.7 | |
| Severe MN | 5.3 | 8.3 | 3.9 | |
| Hand grip strength | 28.6 ± 10.5 | 23.7 ± 9.1 | 31.0 ± 10.3 | |
| Kg | −0.4 | −0.6 | −0.38 | <0.001 |
| SD | (−1.07–0.07) | (−1.5–0.05) | (−0.93–0.11) | ns |
| Barthel index | 94 ± 14.2 | 90.3 ± 17.3 | 96.2 ± 12.2 | 0.036 |
| Physical disability b (%) | 23.8 | 41.7 | 15.6 | 0.003 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 169.4 ± 40.9 | 154.1 ± 37.7 | 176.4 ± 40.6 | 0.002 |
| Lymphocyte (count/mL) | 1600 | 1400 | 1800 | ns |
| (1300–2100) | (1020–1700) | (1375–2225) | ||
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 42.5 ± 3.0 | 42.2 ± 2.5 | 42.6 ± 3.2 | ns |
| Factor | 5-Year All-Cause Mortality | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate GLIM | Multivariate MNA | ||||
| HR (95%CI) | p-Value | HR 95%CI | p-Value | HR 95%CI | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.09 (1.05–1.12) | <0.001 | 1.09 (1.05–1.12) | <0.001 | 1.09 (1.06–1.13) | <0.001 |
| Sex | 1.12 (0.59–2.07) | 0.73 | - | - | - | - |
| NYHA class | 2.27 (1.18–4.36) | 0.013 | - | - | - | - |
| MNA a | 2.3 (1.28–4.15) | 0.005 | NE | NE | 2.3 1.23–4.43 | 0.009 |
| GLIM criteria | 1.93 (1.03–3.6) | 0.038 | - | - | NE | NE |
| Barthel index | 0.98 (0.96–0.99) | 0.014 | - | - | - | - |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 1.73 (0.98–3.05) | 0.056 | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joaquín, C.; Alonso, N.; Lupón, J.; Gastelurrutia, P.; Pérez-Monstesdeoca, A.; Domingo, M.; Zamora, E.; Socias, G.; Ramos, A.; Bayes-Genis, A.; et al. Nutritional Status According to the GLIM Criteria in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: Association with Prognosis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112244
Joaquín C, Alonso N, Lupón J, Gastelurrutia P, Pérez-Monstesdeoca A, Domingo M, Zamora E, Socias G, Ramos A, Bayes-Genis A, et al. Nutritional Status According to the GLIM Criteria in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: Association with Prognosis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112244
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoaquín, Clara, Nuria Alonso, Josep Lupón, Paloma Gastelurrutia, Alejandra Pérez-Monstesdeoca, Mar Domingo, Elisabet Zamora, Guillem Socias, Analía Ramos, Antoni Bayes-Genis, and et al. 2022. "Nutritional Status According to the GLIM Criteria in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: Association with Prognosis" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112244
APA StyleJoaquín, C., Alonso, N., Lupón, J., Gastelurrutia, P., Pérez-Monstesdeoca, A., Domingo, M., Zamora, E., Socias, G., Ramos, A., Bayes-Genis, A., & Puig-Domingo, M. (2022). Nutritional Status According to the GLIM Criteria in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: Association with Prognosis. Nutrients, 14(11), 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112244






