Branched-Chain Fatty Acids Alter the Expression of Genes Responsible for Lipid Synthesis and Inflammation in Human Adipose Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. Real-Time PCR Analysis of mRNA Levels
2.3. Statistical Analysis
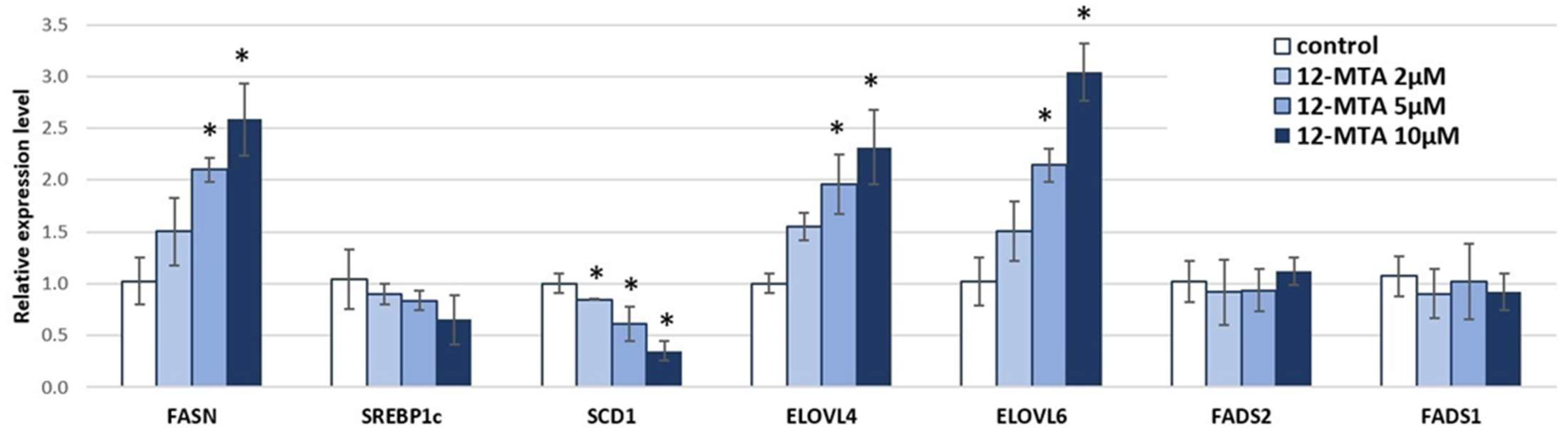
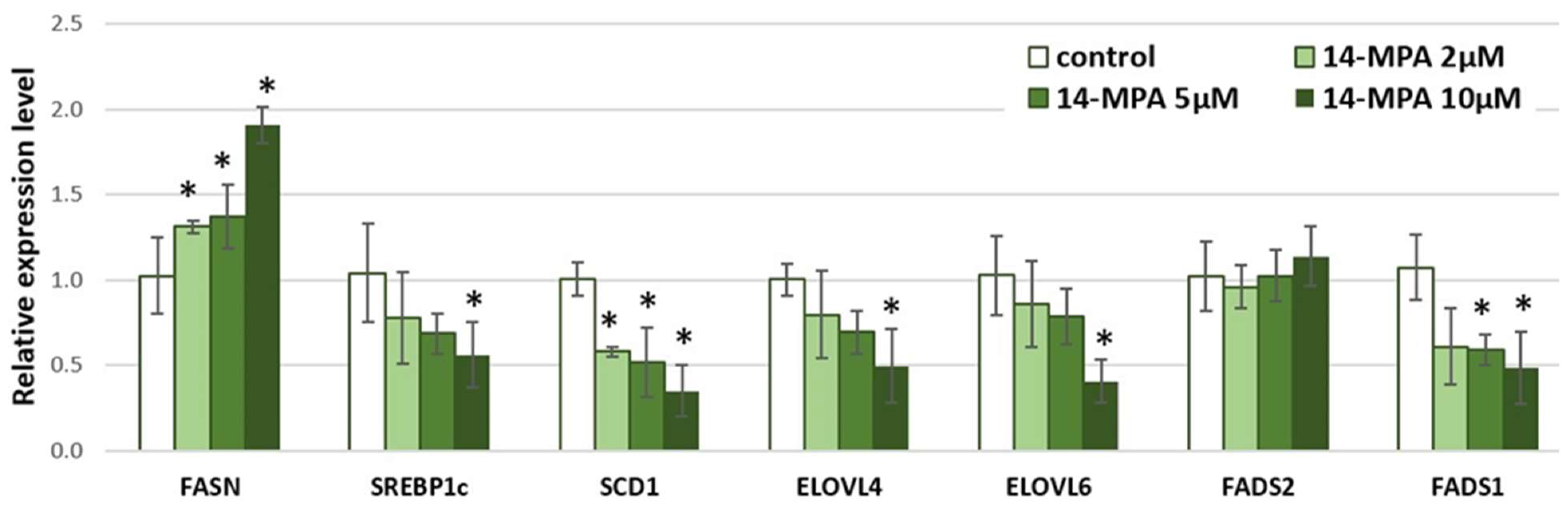
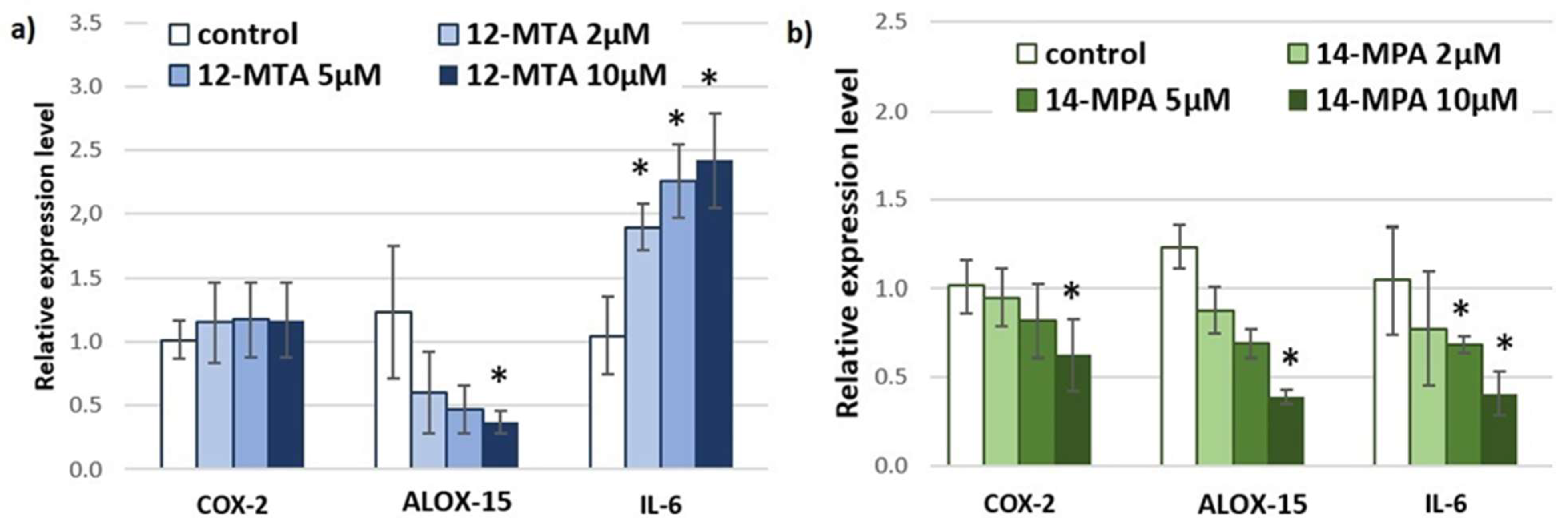
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, J.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity-Induced Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction as Determinant of Obesity-Associated Metabolic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Gaal, L.F.; Mertens, I.L.; De Block, C.E. Mechanisms linking obesity with cardiovascular disease. Nature 2006, 444, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Luo, Q.; Xu, D.; Yu, B. Interaction between adipocytes and high-density lipoprotein:new insights into the mechanism of obesity-induced dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran-Ressler, R.R.; Glahn, R.P.; Bae, S.; Brenna, J.T. Branched Chain Fatty Acids (BCFA) in the Neonatal Gut, and Estimated Dietary Intake in Infancy and Adulthood; Nestle Nutrition Institute Workshop Series; Nestec Ltd.: Basel, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 77, p. 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taormina, V.M.; Unger, A.L.; Schiksnis, M.R.; Torres-Gonzalez, M.; Kraft, J. Branched-Chain Fatty Acids—An Underexplored Class of Dairy-Derived Fatty Acids. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran-Ressler, R.R.; Devapatla, S.; Lawrence, P.; Brenna, J.T. Branched Chain Fatty Acids Are Constituents of the Normal Healthy Newborn Gastrointestinal Tract. 2008. Available online: www.lipidlibrary.co.uk (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Dingess, K.A.; Valentine, C.J.; Ollberding, N.J.; Davidson, B.S.; Woo, J.; Summer, S.; Peng, Y.M.; Guerrero, M.L.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Ran-Ressler, R.R.; et al. Branched-chain fatty acid composition of human milk and the impact of maternal diet: The Global Exploration of Human Milk (GEHM) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Magkos, F.; Zhou, D.; Eagon, J.C.; Fabbrini, E.; Okunade, A.L.; Klein, S. Adipose tissue monomethyl branched-chain fatty acids and insulin sensitivity: Effects of obesity and weight loss. Obesity 2015, 23, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mika, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Kaska, L.; Proczko, M.; Wisniewski, P.; Sledzinski, M.; Sledzinski, T. A comprehensive study of serum odd- and branched-chain fatty acids in patients with excess weight. Obesity 2016, 24, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakiet, A.; Wilczynski, M.; Rostkowska, O.; Korczynska, J.; Jabłonska, P.; Kaska, L.; Proczko-Stepaniak, M.; Sobczak, E.; Stepnowski, P.; Magkos, F.; et al. The Effect of One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass on Branched-Chain Fatty Acid and Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Subjects with Morbid Obesity. Obes. Surg. 2019, 30, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Lawrence, P.; Wang, X.; Kothapalli, K.S.D.; Greenwald, J.; Liu, R.; Park, H.G.; Brenna, J.T. BCFA-enriched vernix-monoacylglycerol reduces LPS-induced inflammatory markers in human enterocytes in vitro. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ran-Ressler, R.R.; Khailova, L.; Arganbright, K.M.; Adkins-Rieck, C.K.; Jouni, Z.E.; Koren, O.; Ley, R.; Brenna, J.T.; Dvorak, B. Branched chain fatty acids reduce the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis and alter gastrointestinal microbial ecology in a neonatal rat model. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Greenwald, J.; Kothapalli, K.; Park, H.; Liu, R.; Mendralla, E.; Lawrence, P.; Wang, X.; Brenna, J. BCFA suppresses LPS induced IL-8 mRNA expression in human intestinal epithelial cells. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids. 2017, 116, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpsøe, M.C.; Basit, S.; Andersson, M.; Nielsen, N.M.; Frisch, M.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Nohr, E.A.; Linneberg, A.; Jess, T. Body mass index and risk of autoimmune diseases: A study within the Danish National Birth Cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.-N.; Ma, H.; He, Z.-H.; Tang, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Ding, M.; Qian, S.-W.; Tang, Q.-Q. SCD1 promotes lipid mobilization in subcutaneous white adipose tissue. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1589–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragos, S.; Bergeron, K.F.; Desmarais, F.; Suitor, K.; Wright, D.C.; Mounier, C.; Mutch, D. Reduced SCD1 activity alters markers of fatty acid reesterification, glyceroneogenesis, and lipolysis in murine white adipose tissue and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2017, 313, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, J.C.; Badoud, F.; Cattrysse, B.; McNicholas, P.D.; Mutch, D.M. Inhibition of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes upregulates elongase 6 and downregulates genes affecting triacylglycerol synthesis. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareie, R.; Yuzbashian, E.; Rahimi, H.; Asghari, G.; Zarkesh, M.; Hedayati, M.; Djazayery, A.; Movahedi, A.; Mirmiran, P.; Khalaj, A. Dietary fat content and adipose triglyceride lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase gene expressions in adults’ subcutaneous and visceral fat tissues. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2021, 165, 102244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, A.; Meneses, M.E.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Rangel-Zúñiga, O.A.; Marín, C.; Almadén, Y.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; González-Guardia, L.; Fuentes, F.; et al. Dietary fat modifies lipid metabolism in the adipose tissue of metabolic syndrome patients. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, F.H.; Liou, T.H.; Chiu, W.C.; Shieh, M.J.; Chien, Y.W. Differential effects of high MUFA with high or low P/S ratio (polyunsaturated to saturated fatty acids) on improving hepatic lipolytic enzymes and mediating PPARγ related with lipoprotein lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase of white adipose tissue in diet-induced obese hamster. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 1608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eissing, L.; Scherer, T.; Tödter, K.; Knippschild, U.; Greve, J.W.; Buurman, W.A.; Pinnschmidt, H.O.; Rensen, S.S.; Wolf, A.M.; Bartelt, A.; et al. De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-β and metabolic health. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carobbio, S.; Hagen, R.M.; Lelliott, C.J.; Slawik, M.; Medina-Gomez, G.; Tan, C.Y.; Sicard, A.; Atherton, H.J.; Barbarroja, N.; Bjursell, M.; et al. Adaptive changes of the Insig1/SREBP1/SCD1 set point help adipose tissue to cope with increased storage demands of obesity. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Lay, S.; Lefrère, I.; Trautwein, C.; Dugail, I.; Krief, S. Insulin and Sterol-regulatory Element-binding Protein-1c (SREBP-1C) Regulation of Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes: Identification of ccaat/enhancer-binding protein β as an SREBP-1C target. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35625–35634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, M.; Yahagi, N.; Matsuzaka, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Okazaki, H.; Iizuka, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Gotoda, T.; et al. SREBP-1-independent regulation of lipogenic gene expression in adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuzaka, T.; Shimano, H.; Yahagi, N.; Kato, T.; Atsumi, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Inoue, N.; Ishikawa, M.; Okada, S.; Ishigaki, N.; et al. Crucial role of a long-chain fatty acid elongase, Elovl6, in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaka, T.; Shimano, H. Elovl6: A new player in fatty acid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuzaka, T. Role of fatty acid elongase Elovl6 in the regulation of energy metabolism and pathophysiological significance in diabetes. Diabetol. Int. 2021, 12, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takumansang, R.; Warouw, S.M.; Lestari, H. Interleukin-6 and insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Paediatr. Indones. 2013, 53, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mikkawy, D.M.E.; El-Sadek, M.A.; El-Badawy, M.A.; Samaha, D. Circulating level of interleukin-6 in relation to body mass indices and lipid profile in Egyptian adults with overweight and obesity. Egypt. Rheumatol. Rehabil. 2020, 47, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidowicz, A.; Regula, J. Effect of Nutritional Status and Dietary Patterns on Human Serum C-Reactive Protein and Interleukin-6 Concentrations. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qing, H.; Desrouleaux, R.; Israni-Winger, K.; Mineur, Y.S.; Fogelman, N.; Zhang, C.; Rashed, S.; Palm, N.W.; Sinha, R.; Picciotto, M.R.; et al. Origin and Function of Stress-Induced IL-6 in Murine Models. Cell 2020, 182, 372–387.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicennati, V.; Vottero, A.; Friedman, C.; Papanicolaou, D. Hormonal regulation of interleukin-6 production in human adipocytes. Int. J. Obes. 2002, 26, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasconcelos, E.D.S.; Salla, R.F. Role of interleukin-6 and interleukin-15 in exercise. MOJ Immunol. 2018, 6, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinhold, B.; Rüther, U. Interleukin-6-dependent and -independent regulation of the human C-reactive protein gene. Biochem. J. 1997, 327, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganapathi, M.K.; May, L.T.; Schultz, D.; Brabenec, A.; Weinstein, J.; Sehgal, P.B.; Kushner, I. Role of interleukin-6 in regulating synthesis of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A in human hepatoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 157, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, D.C.; Brotman, J.J.; Hatcher, M.A.; Aye, M.S.; Cole, B.K.; Haynes, B.A.; Wohlgemuth, S.D.; Fontana, M.A.; Beydoun, H.; Nadler, J.L.; et al. Adipose tissue 12/15 lipoxygenase pathway in human obesity and diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1713–E1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, B.K.; Morris, M.A.; Grzesik, W.J.; Leone, K.A.; Nadler, J.L. Adipose tissue-specific deletion of 12/15-lipoxygenase protects mice from the consequences of a high-fat diet. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 851798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobrian, A.D.; Lieb, D.C.; Ma, Q.; Lindsay, J.W.; Cole, B.K.; Ma, K.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Kuhn, N.S.; Wohlgemuth, S.D.; Fontana, M.; et al. Differential expression and localization of 12/15 lipoxygenases in adipose tissue in human obese subjects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 403, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunemaker, C.S.; Chen, M.; Pei, H.; Kimble, S.D.; Keller, S.R.; Carter, J.D.; Yang, Z.; Smith, K.M.; Wu, R.; Bevard, M.H.; et al. 12-Lipoxygenase-knockout mice are resistant to inflammatory effects of obesity induced by Western diet. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E1065–E1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, D.D.; Miles, P.D.; Chapman, J.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Almazan, F.; Thapar, D.; Miller, Y.I. 12/15-lipoxygenase is required for the early onset of high fat diet-induced adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Rao, G.N. Emerging role of 12/15-Lipoxygenase (ALOX15) in human pathologies. Pergamon 2019, 73, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Cole, B.; Wen, Y.; Keller, S.; Nadler, J. 12/15-lipoxygenase products induce inflammation and impair insulin signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Obesity 2009, 17, 1657–1663. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19521344/ (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Tian, R.; Zuo, X.; Jaoude, J.; Mao, F.; Colby, J.; Shureiqi, I. ALOX15 as a suppressor of inflammation and cancer: Lost in the link. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 132, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.; Kuhn, H.; Heydeck, D. Structural and functional biology of arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase-1 (ALOX15). Gene 2015, 573, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, G.; Salmon, J.; Spayne, J. The inflammatory effects of hydroperoxy and hydroxy acid products of arachidonate lipoxygenase in rabbit skin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1981, 74, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, B.K.; Lieb, D.C.; Dobrian, A.D.; Nadler, J.L. 2-and 15-Lipoxygenases in Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2012, 104–105, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Rao, J.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, D. 15-Lipoxygenase promotes chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery inflammation via positive interaction with nuclear factor-κB. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.C.; Hsiao, F.C.; Chang, H.M.; Wabitsch, M.; Hsieh, P.S. Importance of adipocyte cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2-prostaglandin E receptor 3 signaling in the development of obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2282–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fain, J.N.; Leffler, C.W.; Cowan, G.S.; Buffington, C.; Pouncey, L.; Bahouth, S.W. Stimulation of leptin release by arachidonic acid and prostaglandin E2 in adipose tissue from obese humans. Metabolism 2001, 50, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.-C.; Liao, M.-T.; Hsieh, P.-S. The Dualistic Effect of COX-2-Mediated Signaling in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ran-Ressler, R.R.; Bae, S.; Lawrence, P.; Wang, D.; Brenna, J.T. Branched-chain fatty acid content of foods and estimated intake in the USA. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran-Ressler, R.R.; Sim, D.; O’Donnell-Megaro, A.M.; Bauman, D.E.; Barbano, D.M. Branched Chain Fatty Acid Content of United States Retail Cow’s Milk and Implications for Dietary Intake. Lipids 2011, 46, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashaolu, T.J.; Saibandith, B.; Yupanqui, C.T.; Wichienchot, S. Human colonic microbiota modulation and branched chain fatty acids production affected by soy protein hydrolysate. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caraballo, S.C.G.; Comhair, T.M.; Houten, S.M.; Dejong, C.H.; Lamers, W.H.; Koehler, S.E. High-protein diets prevent steatosis and induce hepatic accumulation of monomethyl branched-chain fatty acids. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.V.; Murthy, V.L.; Abbasi, S.A.; Blankstein, R.; Kwong, R.Y.; Goldfine, A.; Jerosch-Herold, M.; Lima, J.A.; Ding, J.; Allison, M. Visceral Adiposity and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome Across Body Mass Index: The MESA Study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wajchenberg, B.L. Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue: Their Relation to the Metabolic Syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 697–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, J.; Kovacs, P.; Ruschke, K.; Klöting, N.; Fasshauer, M.; Schön, M.R.; Körner, A.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M. Fatty acid synthase gene expression in human adipose tissue: Association with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Ding, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, D.; Silva, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; et al. Adipose mTORC1 Suppresses Prostaglandin Signaling and Beige Adipogenesis via the CRTC2-COX-2 Pathway. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 3180–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Type of Fatty Acid | 15 Carbon-Atom Fatty Acid |
|---|---|
| Straight-chain fatty acid | 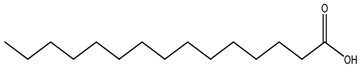 Pentadecanoic acid |
| Iso-BCFA | 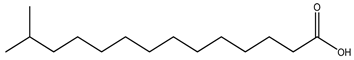 13-Methyltetradecanoic acid |
| Anteiso-BCFA | 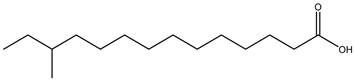 12-Methyltetradecanoic acid |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czumaj, A.; Śledziński, T.; Mika, A. Branched-Chain Fatty Acids Alter the Expression of Genes Responsible for Lipid Synthesis and Inflammation in Human Adipose Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112310
Czumaj A, Śledziński T, Mika A. Branched-Chain Fatty Acids Alter the Expression of Genes Responsible for Lipid Synthesis and Inflammation in Human Adipose Cells. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112310
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzumaj, Aleksandra, Tomasz Śledziński, and Adriana Mika. 2022. "Branched-Chain Fatty Acids Alter the Expression of Genes Responsible for Lipid Synthesis and Inflammation in Human Adipose Cells" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112310
APA StyleCzumaj, A., Śledziński, T., & Mika, A. (2022). Branched-Chain Fatty Acids Alter the Expression of Genes Responsible for Lipid Synthesis and Inflammation in Human Adipose Cells. Nutrients, 14(11), 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112310







