Enterohepatic Takeda G-Protein Coupled Receptor 5 Agonism in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Related Glucose Dysmetabolism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatments
2.2. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) and Serum Tests
2.3. Liver Density
2.4. TGR5 Reporter Assay
2.5. Profiling of Bile Acids
2.6. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.7. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription and Real-Time qPCR
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
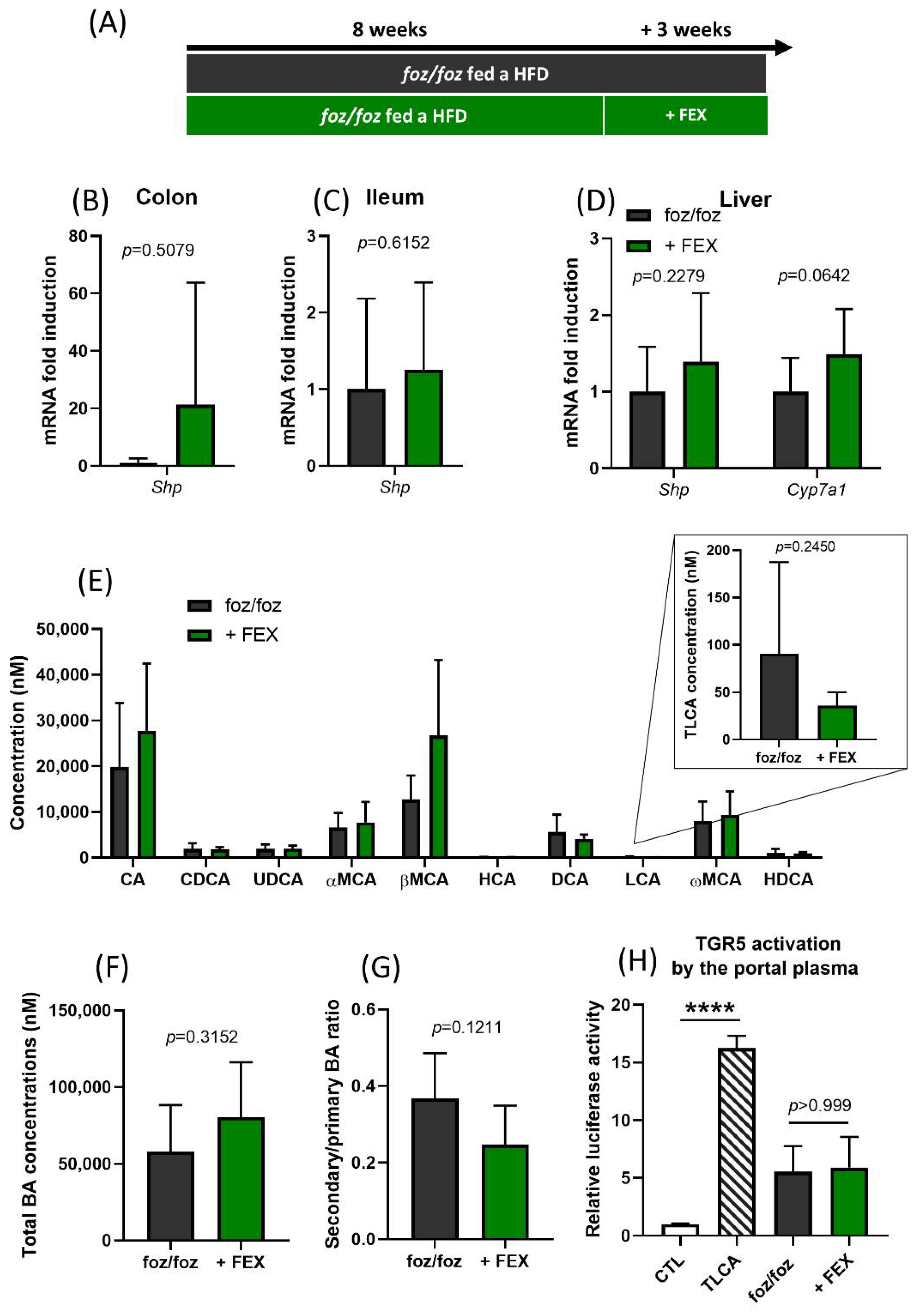
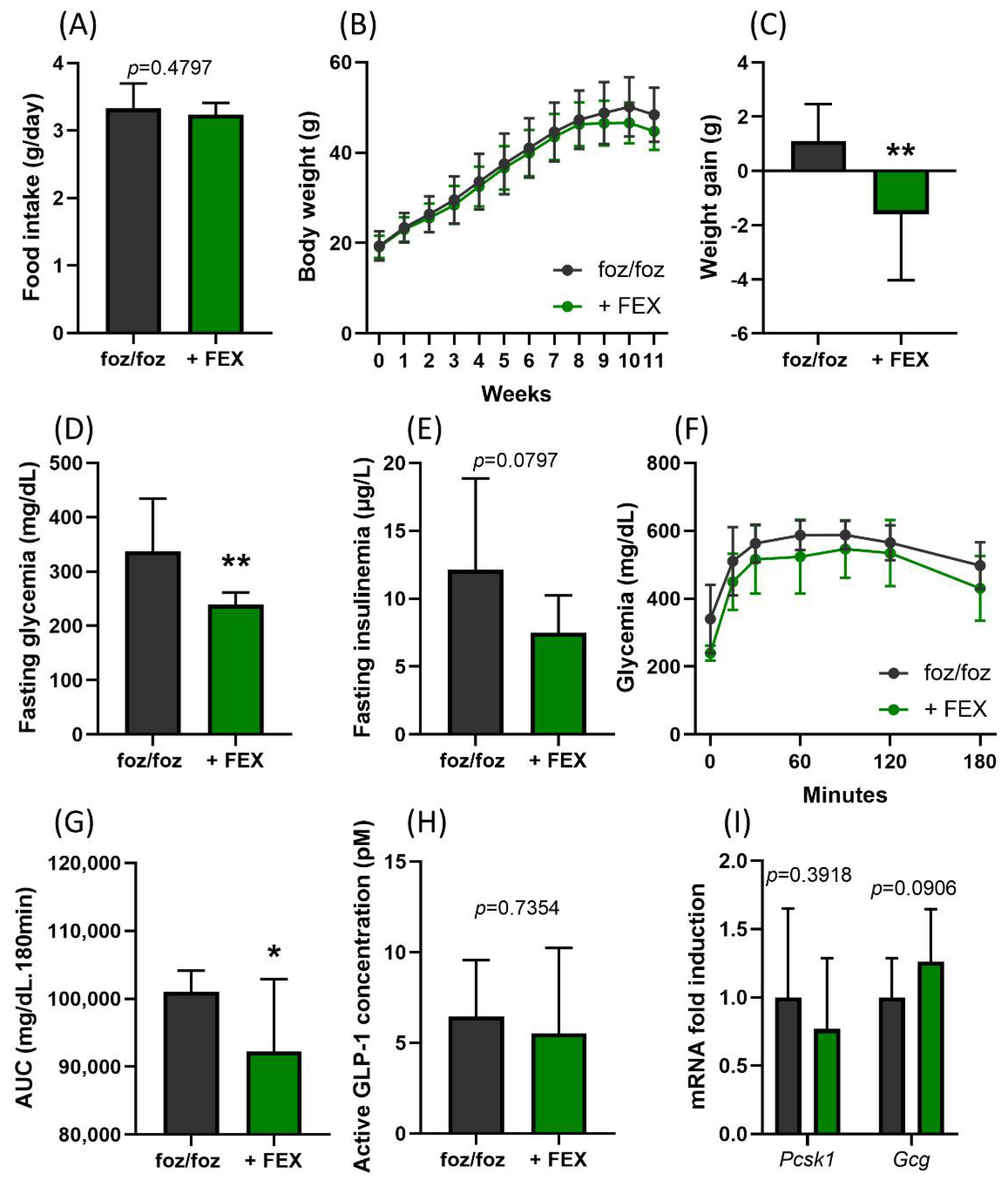
3.1. Indirect Activation of TGR5 through Fexaramine
3.2. Direct Activation of TGR5 by INT-777 and RO5527239
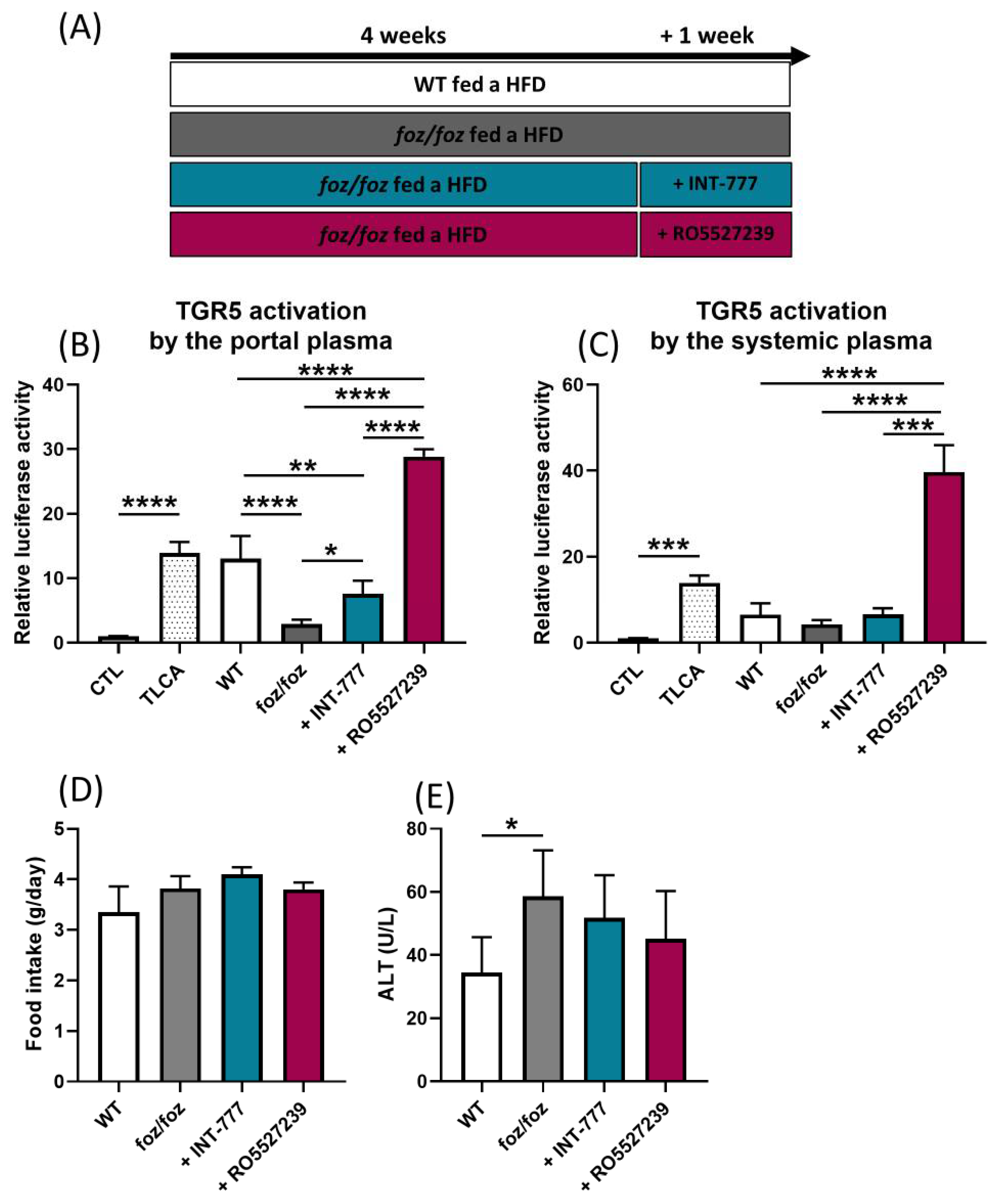
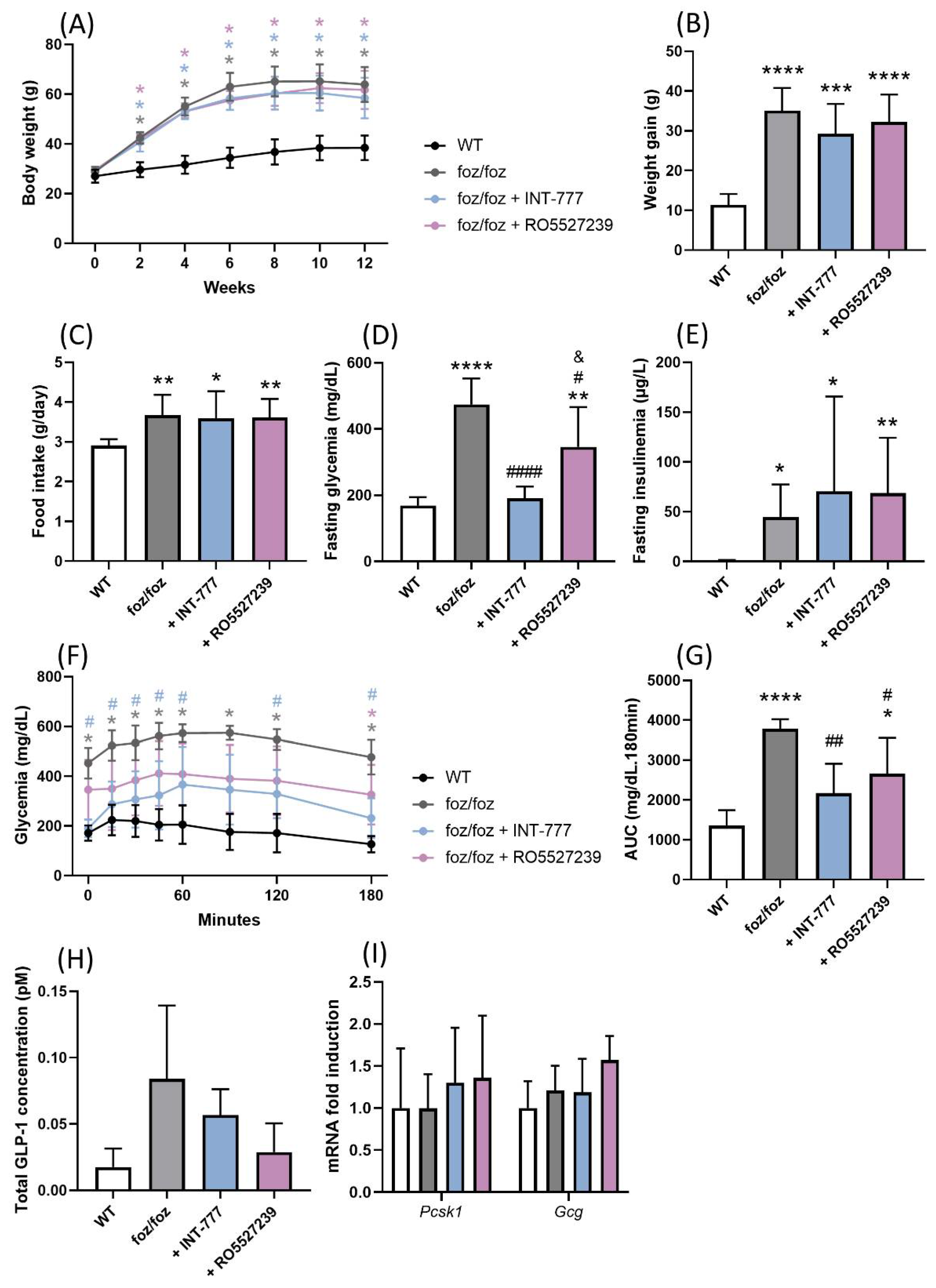
3.2.1. INT-777 and RO5527239 Are Well Tolerated and Reactivate TGR5
3.2.2. Effects of Chronic TGR5 Activation on NASH and Associated Metabolic Features
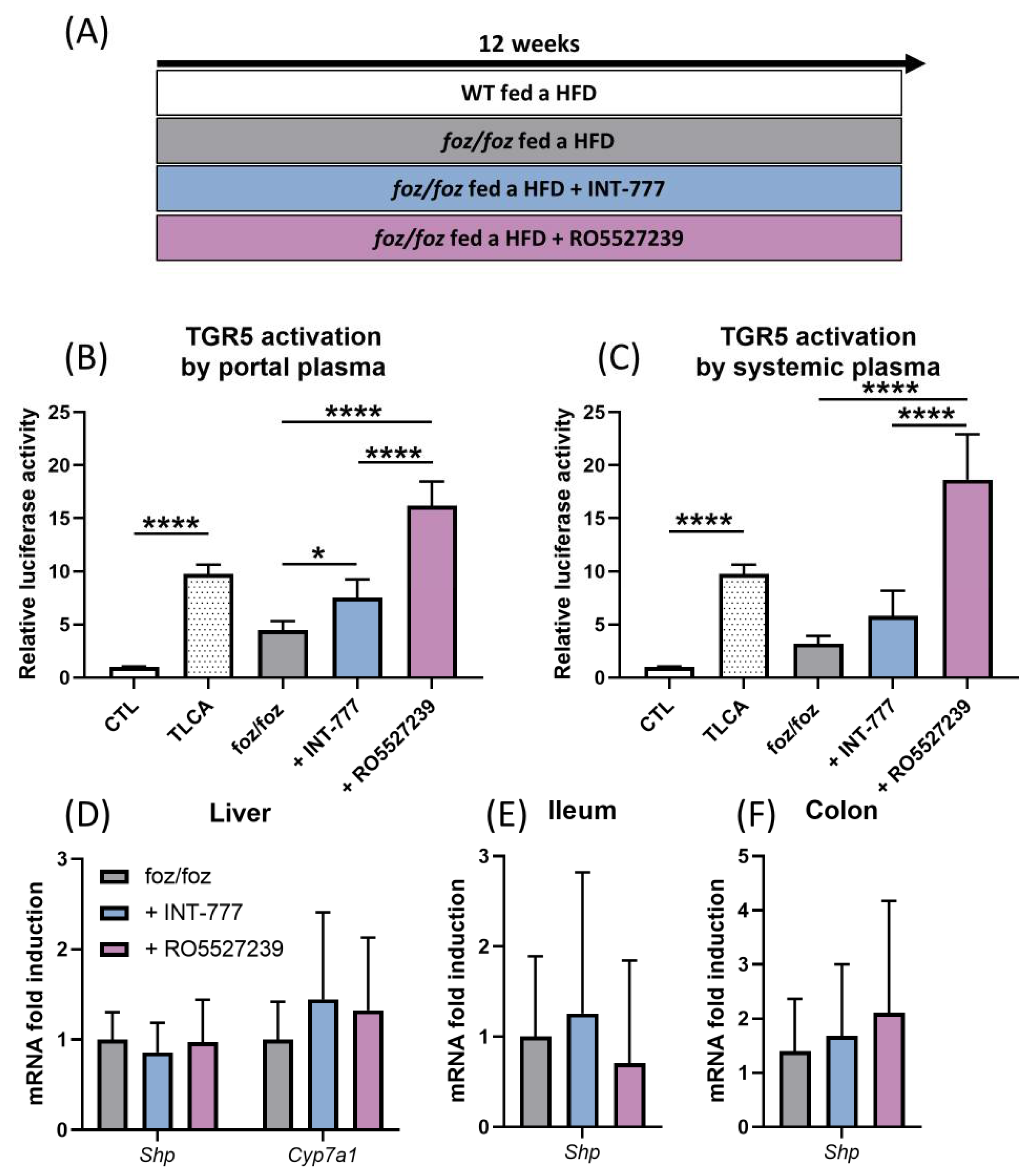
3.2.3. Both INT-777 and RO5527239 Stimulate TGR5 Signaling, with No Effect on FXR Signaling
3.2.4. Both INT-777 and RO5527239 Improved Glucose Tolerance
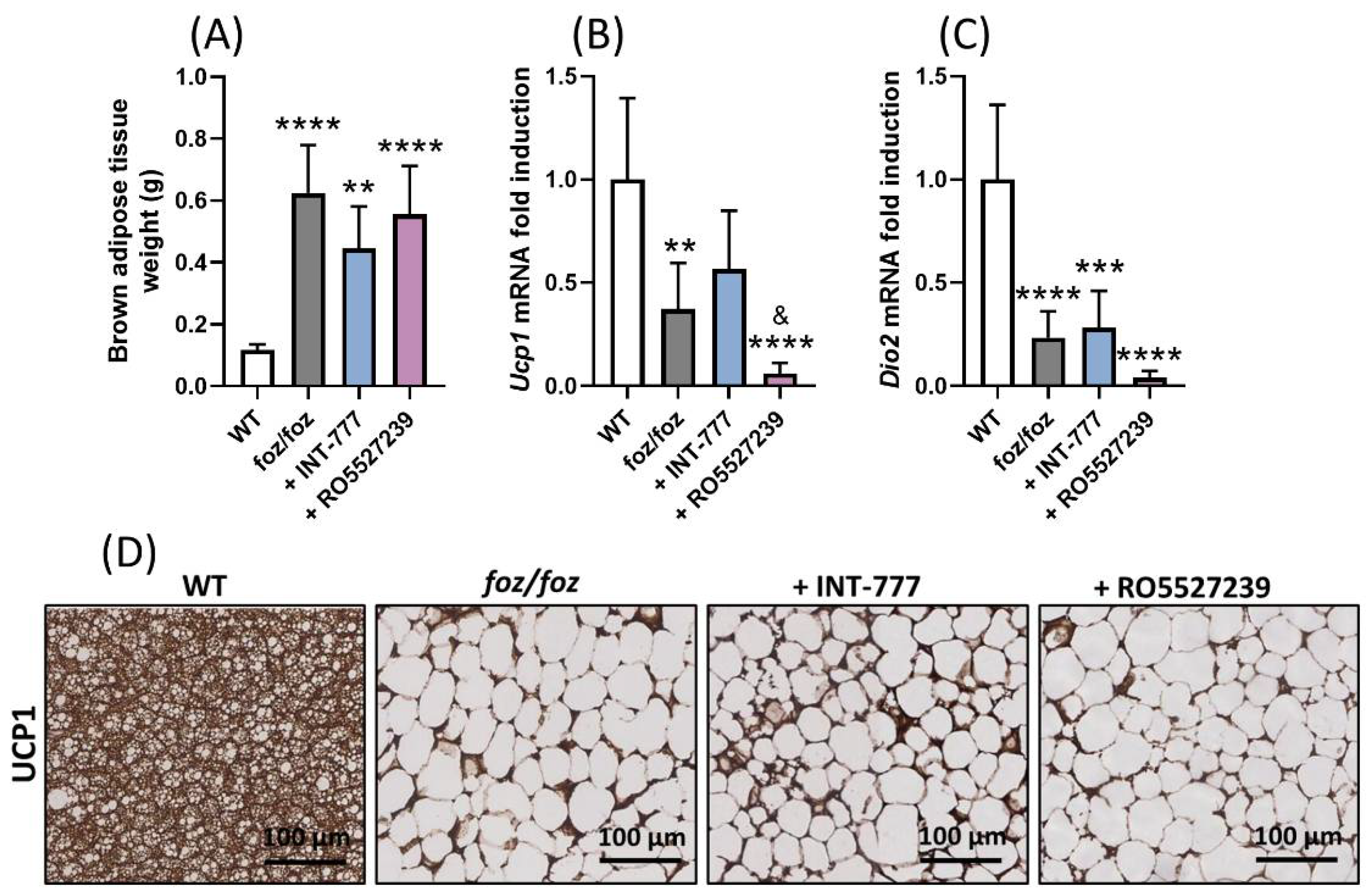
3.2.5. RO5527239 Activation of TGR5 in Peripheral Tissues Does Not Rescue Brown Adipose Thermogenesis
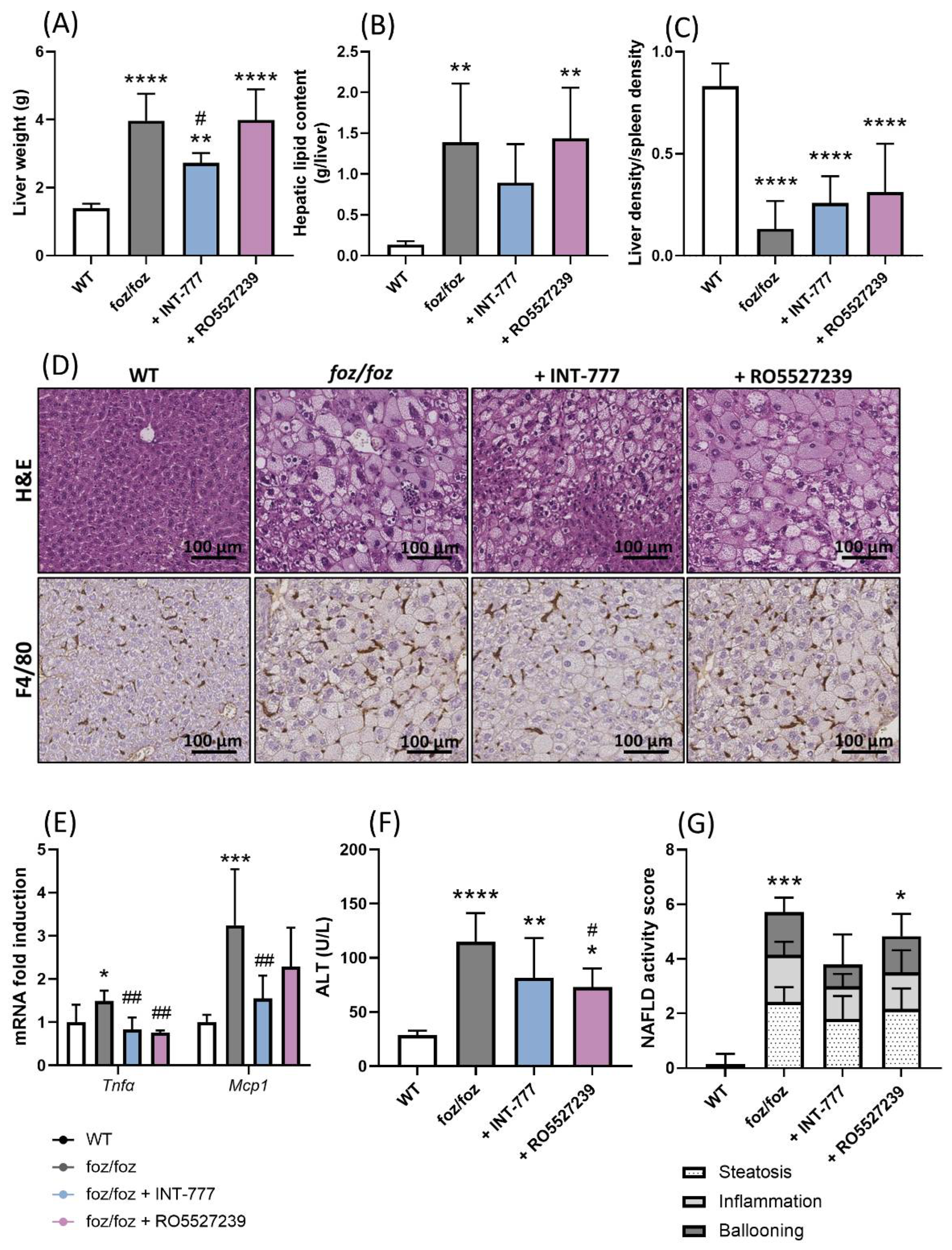
3.2.6. INT-777, but Not RO5527239, Partially Improves NASH
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and Validation of a Histological Scoring System for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease—Meta-Analytic Assessment of Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A New Definition for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An International Expert Consensus Statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Cusi, K. From NASH to Diabetes and from Diabetes to NASH: Mechanisms and Treatment Options. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelmalek, M.F. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Another Leap Forward. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Gioiello, A.; Noriega, L.; Strehle, A.; Oury, J.; Rizzo, G.; Macchiarulo, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Mataki, C.; Pruzanski, M.; et al. TGR5-Mediated Bile Acid Sensing Controls Glucose Homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potthoff, M.J.; Boney-Montoya, J.; Choi, M.; He, T.; Sunny, N.E.; Satapati, S.; Suino-Powell, K.; Xu, H.E.; Gerard, R.D.; Finck, B.N.; et al. FGF15/19 Regulates Hepatic Glucose Metabolism by Inhibiting the CREB-PGC-1α Pathway. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Dammron, H.A.; Hillgartner, F.B. Fibroblast Growth Factor-19, a Novel Factor That Inhibits Hepatic Fatty Acid Synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 10023–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kir, S.; Beddow, S.A.; Samuel, V.T.; Miller, P.; Previs, S.F.; Suino-Powell, K.; Xu, H.E.; Shulman, G.I.; Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. FGF19 as a Postprandial, Insulin-Independent Activator of Hepatic Protein and Glycogen Synthesis. Science 2011, 331, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ploton, M.; Mazuy, C.; Gheeraert, C.; Dubois, V.; Berthier, A.; Dubois-Chevalier, J.; Maréchal, X.; Bantubungi, K.; Diemer, H.; Cianférani, S.; et al. The Nuclear Bile Acid Receptor FXR Is a PKA- and FOXA2-Sensitive Activator of Fasting Hepatic Gluconeogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.D.; Chen, W.D.; Yu, D.; Forman, B.M.; Huang, W. The G-Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor, Gpbar1 (TGR5), Negatively Regulates Hepatic Inflammatory Response through Antagonizing Nuclear Factor Kappa Light-Chain Enhancer of Activated B Cells (NF-ΚB) in Mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, S.; Suh, J.M.; Reilly, S.M.; Yu, E.; Osborn, O.; Lackey, D.; Yoshihara, E.; Perino, A.; Jacinto, S.; Lukasheva, Y.; et al. Intestinal FXR Agonism Promotes Adipose Tissue Browning and Reduces Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gadaleta, R.M.; Van Erpecum, K.J.; Oldenburg, B.; Willemsen, E.C.L.; Renooij, W.; Murzilli, S.; Klomp, L.W.J.; Siersema, P.D.; Schipper, M.E.I.; Danese, S.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Activation Inhibits Inflammation and Preserves the Intestinal Barrier in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut 2011, 60, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pols, T.W.H.; Nomura, M.; Harach, T.; Lo Sasso, G.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Thomas, C.; Rizzo, G.; Gioiello, A.; Adorini, L.; Pellicciari, R.; et al. TGR5 Activation Inhibits Atherosclerosis by Reducing Macrophage Inflammation and Lipid Loading. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiorucci, S.; Antonelli, E.; Rizzo, G.; Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; Riccardi, L.; Orlandi, S.; Pellicciari, R.; Morelli, A. The Nuclear Receptor SHP Mediates Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cells by FXR and Protects against Liver Fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carino, A.; Cipriani, S.; Marchianò, S.; Biagioli, M.; Scarpelli, P.; Zampella, A.; Monti, M.C.; Fiorucci, S. Gpbar1 Agonism Promotes a Pgc-1α-Dependent Browning of White Adipose Tissue and Energy Expenditure and Reverses Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carino, A.; Marchianò, S.; Biagioli, M.; Bucci, M.; Vellecco, V.; Brancaleone, V.; Fiorucci, C.; Zampella, A.; Monti, M.C.; Distrutti, E.; et al. Agonism for the Bile Acid Receptor GPBAR1 Reverses Liver and Vascular Damage in a Mouse Model of Steatohepatitis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2809–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullmer, C.; Alvarez Sanchez, R.; Sprecher, U.; Raab, S.; Mattei, P.; Dehmlow, H.; Sewing, S.; Iglesias, A.; Beauchamp, J.; Conde-Knape, K. Systemic Bile Acid Sensing by G Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor 1 (GPBAR1) Promotes PYY and GLP-1 Release. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.E.; Billeschou, A.; Windeløv, J.A.; Hartmann, B.; Ullmer, C.; Holst, J.J.; Kissow, H. Pharmacological Activation of TGR5 Promotes Intestinal Growth via a GLP-2-Dependent Pathway in Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G980–G987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Xie, C.; Nichols, R.G.; Ferrell, J.M.; Boehme, S.; Krausz, K.W.; Patterson, A.D.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Intestine Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist and the Gut Microbiota Activate G-Protein Bile Acid Receptor-1 Signaling to Improve Metabolism. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Liu, H.; Boehme, S.; Xie, C.; Krausz, K.W.; Gonzalez, F.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Farnesoid X Receptor Induces Takeda G-Protein Receptor 5 Cross-Talk to Regulate Bile Acid Synthesis and Hepatic Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 11055–11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillard, J.; Clerbaux, L.A.; Nachit, M.; Sempoux, C.; Staels, B.; Bindels, L.B.; Tailleux, A.; Leclercq, I.A. Bile Acids Contribute to the Development of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.R.; Haeusler, R.A. Bile Acids in Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Signalling—Mechanisms and Research Needs. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, G.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Leclercq, I.; Yeh, M.M.; Goldin, R.; Teoh, N.; Schuppan, D. Mouse Models of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Toward Optimization of Their Relevance to Human Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2241–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arsov, T.; Silva, D.G.; O’Bryan, M.K.; Sainsbury, A.; Lee, N.J.; Kennedy, C.; Manji, S.S.M.; Nelms, K.; Liu, C.; Vinuesa, C.G.; et al. Fat Aussie—A New Alström Syndrome Mouse Showing a Critical Role for ALMS1 in Obesity, Diabetes, and Spermatogenesis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Rudder, M.; Bouzin, C.; Nachit, M.; Louvegny, H.; Vande Velde, G.; Julé, Y.; Leclercq, I.A. Automated Computerized Image Analysis for the User-Independent Evaluation of Disease Severity in Preclinical Models of NAFLD/NASH. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, V.; Lalloyer, F.; Baud, G.; Osto, E.; Kouach, M.; Daoudi, M.; Vallez, E.; Raverdy, V.; Goossens, J.-F.; Descat, A.; et al. Influence of Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass on Plasma Bile Acid Profiles: A Comparative Study between Rats, Pigs and Humans. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Holmstrom, S.R.; Kir, S.; Umetani, M.; Schmidt, D.R.; Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. The G Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor, TGR5, Stimulates Gallbladder Filling. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poekes, L.; Legry, V.; Schakman, O.; Detrembleur, C.; Bol, A.; Horsmans, Y.; Farrell, G.C.; Leclercq, I.A. Defective Adaptive Thermogenesis Contributes to Metabolic Syndrome and Liver Steatosis in Obese Mice. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poekes, L.; Gillard, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Horsmans, Y.; Leclercq, I.A. Activation of Brown Adipose Tissue Enhances the Efficacy of Caloric Restriction for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Song, A.; Yang, X.; Zhen, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Ma, H. Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist Decreases Lipid Accumulation by Promoting Hepatic Fatty Acid Oxidation in Db/Db Mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartmann, P.; Hochrath, K.; Horvath, A.; Chen, P.; Seebauer, C.T.; Llorente, C.; Wang, L.; Alnouti, Y.; Fouts, D.E.; Stärkel, P.; et al. Modulation of the Intestinal Bile Acid/Farnesoid X Receptor/Fibroblast Growth Factor 15 Axis Improves Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2150–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorribas, M.; Jakob, M.O.; Yilmaz, B.; Li, H.; Stutz, D.; Noser, Y.; de Gottardi, A.; Moghadamrad, S.; Hassan, M.; Albillos, A.; et al. FXR Modulates the Gut-Vascular Barrier by Regulating the Entry Sites for Bacterial Translocation in Experimental Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1126–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Muench, G.A.; Shang, L.; Rosenthal, S.B.; Rahman, G.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Kwon, H.C.; Diomino, A.M.; Kisseleva, T.; et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and HCC in a Hyperphagic Mouse Accelerated by Western Diet. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 891–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, M.; Daoudi, M.; Prawitt, J.; Ducastel, S.; Touche, V.; Sayin, S.I.; Perino, A.; Brighton, C.A.; Sebti, Y.; Kluza, J.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Inhibits Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Production by Enteroendocrine L Cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ducastel, S.; Touche, V.; Trabelsi, M.-S.; Boulinguiez, A.; Butruille, L.; Nawrot, M.; Peschard, S.; Chávez-Talavera, O.; Dorchies, E.; Vallez, E.; et al. The Nuclear Receptor FXR Inhibits Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Secretion in Response to Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Xie, C.; Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Krausz, K.W.; Shi, J.; Brocker, C.N.; Desai, D.; Amin, S.G.; Bisson, W.H.; et al. Intestine-Selective Farnesoid X Receptor Inhibition Improves Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harach, T.; Pols, T.W.H.; Nomura, M.; Maida, A.; Watanabe, M.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K. TGR5 Potentiates GLP-1 Secretion in Response to Anionic Exchange Resins. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seon, M.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Son, Y.; Song, J.; Kim, O.Y. Circulating Glp-1 Levels as a Potential Indicator of Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Adult Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Pellicciari, R.; Gioiello, A.; Neri, F.; Camborata, C.; Passeri, D.; De Franco, F.; Spinozzi, S.; Colliva, C.; Adorini, L.; et al. Semisynthetic Bile Acid FXR and TGR5 Agonists: Physicochemical Properties, Pharmacokinetics, and Metabolism in the Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, M.; Houten, S.M.; Mataki, C.; Christoffolete, M.A.; Kim, B.W.; Sato, H.; Messaddeq, N.; Harney, J.W.; Ezaki, O.; Kodama, T.; et al. Bile Acids Induce Energy Expenditure by Promoting Intracellular Thyroid Hormone Activation. Nature 2006, 439, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, R.H.; Wang, X.X.; Cheng, L.L.; Krisko, T.; Smith, M.; El Kasmi, K.; Pruzanski, M.; Adorini, L.; Golden-Mason, L.; Levi, M.; et al. Bile Acid Receptor Activation Modulates Hepatic Monocyte Activity and Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11761–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, J.D.; Feigh, M.; Veidal, S.S.; Fensholdt, L.K.D.; Rigbolt, K.T.; Hansen, H.H.; Chen, L.C.; Petitjean, M.; Friley, W.; Vrang, N.; et al. INT-767 Improves Histopathological Features in a Dietinduced Ob/Ob Mouse Model of Biopsy-Confirmed Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Calenda, C.D.; Petrasek, J.; Ambade, A.; Kodys, K.; Adorini, L.; Szabo, G. FXR and TGR5 Agonists Ameliorate Liver Injury, Steatosis, and Inflammation After Binge or Prolonged Alcohol Feeding in Mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carino, A.; Cipriani, S.; Marchianò, S.; Biagioli, M.; Santorelli, C.; Donini, A.; Zampella, A.; Monti, M.C.; Fiorucci, S. BAR502, a Dual FXR and GPBAR1 Agonist, Promotes Browning of White Adipose Tissue and Reverses Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.D.; Billon, C.; Losby, M.; Bedia-Diaz, G.; Fang, Y.; Avdagic, A.; Elgendy, B.; Burris, T.P.; Griffett, K. Emerging Role of Nuclear Receptors for the Treatment of NAFLD and NASH. Metabolites 2022, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Asbt | TGGATAGATGGCGACATGGA | GGCAAGCAGTGTGGAGCAA |
| Bsep | CTGCCAAGGATGCTAATGCA | CGATGGCTACCCTTTGCTTCT |
| Cyp7a1 | AGCAACTAAACAACCTGCCAGTACTA | GTCCGGATATTCAAGGATGCA |
| Dio2 | TCGGTCATTCTGCTCAAGCA | AGCATGCGCCTCCACTCT |
| Fabp6 | GTGGAAAGTAGACCGGAACGA | GGAAGCAGCAGAAGCTTGGT |
| Fgf15 | GACCAAAACGAACGAAATTTGTT | ACGTCCTTGATGGCAATCG |
| Fxr | AGGAGCCCCTGCTTGATGT | GCGGGTTCTCAGGCTGGTA |
| Gcg | CATTCACCAGCGACTACAGCAA | TCATCAACCACTGCACAAAATCT |
| Il1β | AGTTGACGGACCCCAAAAGA | GGACAGCCCAGGTCAAAGG |
| Mdr2 | CCACAGATGCTGCGCAAGT | TGGCTGTGTTCTGTGCAATTAAA |
| Mcp1 | CCACTCACCTGCTGCTACTCAT | CTGCTGGTGATCCTCTTGT |
| Ntcp | CTTGCGCCATAGGGATCTTC | TGCCTGCCTTGAGGACGTA |
| Oatp1a1 | GCCAACGCAAGATCCAACAGAGTG | TCGGGCCAACAATCTTCCCCAT |
| Oatp1a4 | CAAGCTTTCTCCCTGCACTCTT | TCCTTCGCAGTGAGCTTCATT |
| Ostα | CCGTCAAGCCAAGATGCAT | CAAGCACCTGGAACAGAGCAA |
| Ostβ | CCGGGGGAACCTGAGTAGAA | GTTATGGGGCGTTATGGGGT |
| Pcsk1 | TGTACTGCTTTCGCCTTCTTTT | CGCCGCCCATTCATTAACA |
| Rpl19 | GAAGGTCAAAGGGAATGTGTTCA | CCTTGTCTGCCTTCAGCTTGT |
| Shp | AGGGTAGAGGCCATGAGGAG | ACGATCCTCTTCAACCCAGA |
| Tgr5 | GGCCTGGAACTCTGTTATCG | GTCCCTCTTGGCTCTTCCTC |
| Tnfα | GTGCCTATGTCTCAGCCTCTT | GCTCATACCAGGGTTTGAGCT |
| Ucp1 | CGTACCAAGCTGTGCGATGT | GAAGCCACAAACCCTTTGAAAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gillard, J.; Picalausa, C.; Ullmer, C.; Adorini, L.; Staels, B.; Tailleux, A.; Leclercq, I.A. Enterohepatic Takeda G-Protein Coupled Receptor 5 Agonism in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Related Glucose Dysmetabolism. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132707
Gillard J, Picalausa C, Ullmer C, Adorini L, Staels B, Tailleux A, Leclercq IA. Enterohepatic Takeda G-Protein Coupled Receptor 5 Agonism in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Related Glucose Dysmetabolism. Nutrients. 2022; 14(13):2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132707
Chicago/Turabian StyleGillard, Justine, Corinne Picalausa, Christoph Ullmer, Luciano Adorini, Bart Staels, Anne Tailleux, and Isabelle A. Leclercq. 2022. "Enterohepatic Takeda G-Protein Coupled Receptor 5 Agonism in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Related Glucose Dysmetabolism" Nutrients 14, no. 13: 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132707
APA StyleGillard, J., Picalausa, C., Ullmer, C., Adorini, L., Staels, B., Tailleux, A., & Leclercq, I. A. (2022). Enterohepatic Takeda G-Protein Coupled Receptor 5 Agonism in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Related Glucose Dysmetabolism. Nutrients, 14(13), 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132707






