The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Dietary Patterns of Pregnant Women: A Comparison between Two Mother-Child Cohorts in Sicily, Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
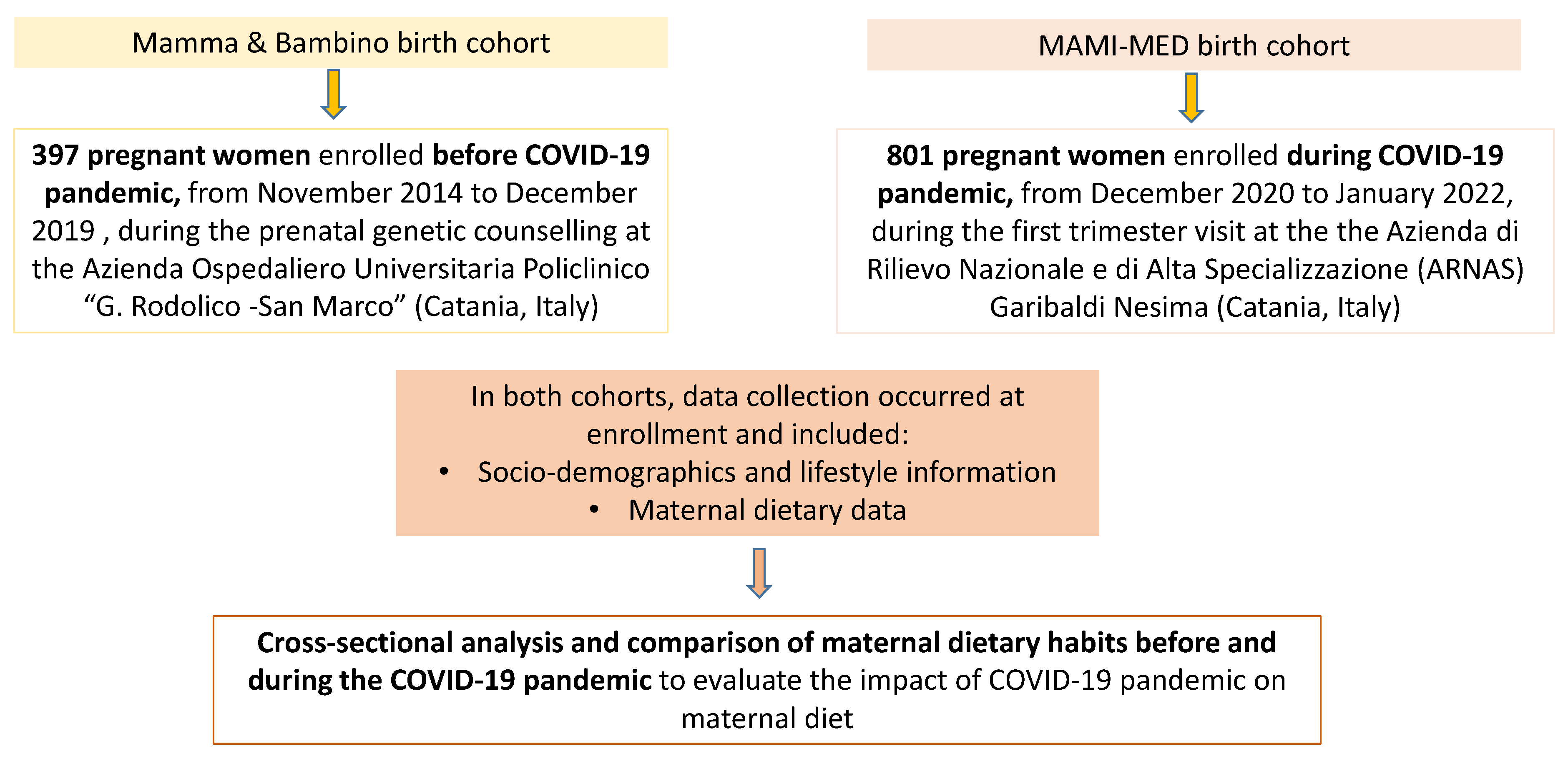
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Dietary Assessment
2.4. Principal Component Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Population
3.2. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Maternal Consumption of Foods
3.3. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Maternal Adherence to Mediterranean Diet
3.4. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Maternal Dietary Patterns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattioli, A.V.; Sciomer, S.; Cocchi, C.; Maffei, S.; Gallina, S. Quarantine during COVID-19 outbreak: Changes in diet and physical activity increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.; Young, E.; Butler, I.; Coe, S. The Impact of Lockdown during the COVID-19 Outbreak on Dietary Habits in Various Population Groups: A Scoping Review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 626432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; Scerbo, F.; et al. Eating habits and lifestyle changes during COVID-19 lockdown: An Italian survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhang, D.; Yu, W.; Luo, M.; Yang, S.; Jia, P. Impacts of lockdown on dietary patterns among youths in China: The COVID-19 Impact on Lifestyle Change Survey. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 3221–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh Ismail, L.; Hashim, M.; Mohamad, M.N.; Hassan, H.; Ajab, A.; Stojanovska, L.; Jarrar, A.H.; Hasan, H.; Abu Jamous, D.O.; Saleh, S.T.; et al. Dietary Habits and Lifestyle During Coronavirus Pandemic Lockdown: Experience from Lebanon. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 730425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Retraction and Republication: Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2441–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Badimon, L.; Estruch, R. Latest evidence of the effects of the Mediterranean diet in prevention of cardiovascular disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitan, E.B.; Ahmed, A.; Arnett, D.K.; Polak, J.F.; Hundley, W.G.; Bluemke, D.A.; Heckbert, S.R.; Jacobs, D.R.; Nettleton, J.A. Mediterranean diet score and left ventricular structure and function: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E. The role of the Mediterranean diet on weight loss and obesity-related diseases. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardener, H.; Rundek, T.; Wright, C.B.; Gu, Y.; Scarmeas, N.; Homma, S.; Russo, C.; Elkind, M.S.; Sacco, R.L.; Di Tullio, M.R. A Mediterranean-style diet and left ventricular mass (from the Northern Manhattan Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Valle, P.G.; Mosconi, G.; Nucci, D.; Vigezzi, G.P.; Gentile, L.; Gianfredi, V.; Bonaccio, M.; Gianfagna, F.; Signorelli, C.; Iacoviello, L.; et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet during the COVID-19 national lockdowns: A systematic review of observational studies. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidi Fakari, F.; Simbar, M. Coronavirus Pandemic and Worries during Pregnancy; a Letter to Editor. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 8, e21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; La Rosa, M.C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Favara, G.; Panella, M.; Cianci, A.; Agodi, A. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Vitamin D Receptor Gene Affect Birth Weight and the Risk of Preterm Birth: Results From the “Mamma & Bambino” Cohort and A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Favara, G.; La Rosa, M.C.; La Mastra, C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Agodi, A. Maternal Dietary Patterns Are Associated with Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Gestational Weight Gain: Results from the “Mamma & Bambino” Cohort. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; He, J.R.; Lin, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S.; Lu, J.; Yuan, M.; Chen, N.; Zhang, L.; et al. The influence of maternal dietary patterns on gestational weight gain: A large prospective cohort study in China. Nutrition 2019, 59, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northstone, K.; Emmett, P.; Rogers, I. Dietary patterns in pregnancy and associations with socio-demographic and lifestyle factors. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkkola, T.; Uusitalo, U.; Kronberg-Kippilä, C.; Männistö, S.; Virtanen, M.; Kenward, M.G.; Veijola, R.; Knip, M.; Ovaskainen, M.L.; Virtanen, S.M. Seven distinct dietary patterns identified among pregnant Finnish women--associations with nutrient intake and sociodemographic factors. Public Health Nutr. 2008, 11, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amataiti, T.A.; Hood, F.; Krebs, J.D.; Weatherall, M.; Hall, R.M. The Impact of COVID-19 on diet and lifestyle behaviours for pregnant women with diabetes. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 45, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Qi, H.; Ma, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, C.; Wei, J.; et al. Food Intake and Diet Quality of Pregnant Women in China During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A National Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 853565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, K.M.; Hung, P.; Alberg, A.J.; Hair, N.L.; Liu, J. Variations in health behaviors among pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic. Midwifery 2021, 95, 102929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biviá-Roig, G.; La Rosa, V.L.; Gómez-Tébar, M.; Serrano-Raya, L.; Amer-Cuenca, J.J.; Caruso, S.; Commodari, E.; Barrasa-Shaw, A.; Lisón, J.F. Analysis of the Impact of the Confinement Resulting from COVID-19 on the Lifestyle and Psychological Wellbeing of Spanish Pregnant Women: An Internet-Based Cross-Sectional Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durankuş, F.; Aksu, E. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on anxiety and depressive symptoms in pregnant women: A preliminary study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, G.; Baker, P.N.; et al. Prenatal anxiety and obstetric decisions among pregnant women in Wuhan and Chongqing during the COVID-19 outbreak: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 127, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, S.B.; Mainali, A.; Schwank, S.E.; Acharya, G. Maternal mental health in the time of the COVID-19 pandemic. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Godfrey, K.M.; Poston, L.; Szajewska, H.; van Goudoever, J.B.; de Waard, M.; Brands, B.; Grivell, R.M.; Deussen, A.R.; Dodd, J.M.; et al. Nutrition During Pregnancy, Lactation and Early Childhood and its Implications for Maternal and Long-Term Child Health: The Early Nutrition Project Recommendations. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudasama, Y.V.; Gillies, C.L.; Zaccardi, F.; Coles, B.; Davies, M.J.; Seidu, S.; Khunti, K. Impact of COVID-19 on routine care for chronic diseases: A global survey of views from healthcare professionals. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osendarp, S.; Akuoku, J.K.; Black, R.E.; Headey, D.; Ruel, M.; Scott, N.; Shekar, M.; Walker, N.; Flory, A.; Haddad, L.; et al. The COVID-19 crisis will exacerbate maternal and child undernutrition and child mortality in low- and middle-income countries. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Favara, G.; La Mastra, C.; La Rosa, M.C.; Agodi, A. Dietary Folate Intake and Folic Acid Supplements among Pregnant Women from Southern Italy: Evidence from the “Mamma & Bambino” Cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Agrifoglio, O.; Favara, G.; La Mastra, C.; La Rosa, M.C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Panella, M.; Cianci, A.; Agodi, A. The impact of social determinants and lifestyles on dietary patterns during pregnancy: Evidence from the “Mamma & Bambino” study. Ann. Ig. 2019, 31, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Magnano San Lio, R.; Maugeri, A.; La Rosa, M.C.; Cianci, A.; Panella, M.; Giunta, G.; Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M. The Impact of Socio-Demographic Factors on Breastfeeding: Findings from the “Mamma & Bambino” Cohort. Medicina 2021, 57, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Magnano San Lio, R.; La Rosa, M.C.; La Mastra, C.; Favara, G.; Giunta, G.; Cianci, A.; Agodi, A. Vaccination Status of Mothers and Children from the ‘Mamma & Bambino’ Cohort. Vaccines 2021, 9, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Magnano San Lio, R.; La Rosa, M.C.; La Mastra, C.; Favara, G.; Ferlito, M.; Giunta, G.; Panella, M.; Cianci, A.; et al. The Effect of Alcohol on Telomere Length: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Evidence and a Pilot Study during Pregnancy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eveleth, P.B.; Andres, R.; Chumlea, W.C.; Eiben, O.; Ge, K.; Harris, T.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Launer, L.J.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Solomons, N.W.; et al. Uses and interpretation of anthropometry in the elderly for the assessment of physical status. Report to the Nutrition Unit of the World Health Organization: The Expert Subcommittee on the Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry in the Elderly. J. Nutr. Health Aging 1998, 2, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Barone, G.; Mazzoleni, P.; Catalfo, A.; De Guidi, G.; Iemmolo, M.G.; Crimi, N.; Agodi, A. Mediterranean Diet and Particulate Matter Exposure Are Associated With LINE-1 Methylation: Results From a Cross-Sectional Study in Women. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Agrifoglio, O.; Scalisi, A.; Agodi, A. The Association of Dietary Patterns with High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Infection and Cervical Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study in Italy. Nutrients 2018, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M.; Valenti, G.; Marzagalli, R.; Frontini, V.; Marchese, A.E. Increase in the prevalence of the MTHFR 677 TT polymorphism in women born since 1959: Potential implications for folate requirements. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willet, W.; Stampfer, M.J. Total energy intake: Implications for epidemiologic analyses. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 124, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Fiore, V.; Rosta, G.; Favara, G.; La Mastra, C.; La Rosa, M.C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Agodi, A. Determinants of Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet: Findings from a Cross-Sectional Study in Women from Southern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlar, B.; Gerson, E.; Petrillo, S.; Langer, A.; Tiemeier, H. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and perinatal health: A scoping review. Reprod. Health 2021, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Ranjan, P.; Sharma, K.A.; Sahu, A.; Bharti, J.; Zangmo, R.; Bhatla, N. Impact of COVID-19 on psychosocial functioning of peripartum women: A qualitative study comprising focus group discussions and in-depth interviews. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2021, 152, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.; Depenbusch, L.; Pal, A.A.; Nair, R.M.; Ramasamy, S. Food system disruption: Initial livelihood and dietary effects of COVID-19 on vegetable producers in India. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, T.G. COVID-19 and disruptions to food systems. Agric. Hum. Values 2020, 37, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hassen, T.; El Bilali, H.; Allahyari, M.S.; Berjan, S.; Fotina, O. Food purchase and eating behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional survey of Russian adults. Appetite 2021, 165, 105309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Zarah, A.; Enriquez-Marulanda, J.; Andrade, J.M. Relationship between Dietary Habits, Food Attitudes and Food Security Status among Adults Living within the United States Three Months Post-Mandated Quarantine: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, M.R.; Brito-Silva, F.; Kirkland, T.; Moore, C.E.; Davis, K.E.; Patterson, M.A.; Miketinas, D.C.; Tucker, W.J. Prevalence and Social Determinants of Food Insecurity among College Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza-Martí, A.; Ruiz-Ródenas, N.; Herranz-Chofre, I.; Sánchez-SanSegundo, M.; Serrano Delgado, V.C.; Hurtado-Sánchez, J.A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Pregnancy and Its Benefits on Maternal-Fetal Health: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 813942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet Gastroenterology Hepatology. Obesity: Another ongoing pandemic. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladejo, A.O. Overview of the metabolic syndrome; an emerging pandemic of public health significance. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2011, 9, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Stefan, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Schulze, M.B. Global pandemics interconnected—obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotnicka, M.; Karwowska, K.; Kłobukowski, F.; Wasilewska, E.; Małgorzewicz, S. Dietary Habits before and during the COVID-19 Epidemic in Selected European Countries. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Rosenberg, I.; Uauy, R. History of modern nutrition science-implications for current research, dietary guidelines, and food policy. BMJ 2018, 361, k2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talai Rad, N.; Ritterath, C.; Siegmund, T.; Wascher, C.; Siebert, G.; Henrich, W.; Buhling, K.J. Longitudinal analysis of changes in energy intake and macronutrient composition during pregnancy and 6 weeks post-partum. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2011, 283, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crozier, S.R.; Robinson, S.M.; Godfrey, K.M.; Cooper, C.; Inskip, H.M. Women’s dietary patterns change little from before to during pregnancy. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agodi, A.; Maugeri, A.; Kunzova, S.; Sochor, O.; Bauerova, H.; Kiacova, N.; Barchitta, M.; Vinciguerra, M. Association of Dietary Patterns with Metabolic Syndrome: Results from the Kardiovize Brno 2030 Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Before COVID-19 Pandemic (n = 397) | During COVID-19 Pandemic (n = 801) | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years b | 37.0 (4.0) | 31.0 (7.0) | <0.001 |
| Gestational age at recruitment b | 16.0 (4.0) | 12.0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Educational level | |||
| Low educational level c | 18.9% | 26.8% | 0.002 |
| Medium-high educational level | 81.1% | 73.2% | |
| Employment status | |||
| Employed | 59.2% | 50.7% | 0.005 |
| Unemployed | 40.8% | 49.3% | |
| Smoking (% yes) | 43.3% | 41.1% | 0.460 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI, kg/m2 b | 22.8 (5.2) | 23.2 (5.9) | 0.049 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI categories | |||
| Underweight | 6.6% | 5.4% | 0.140 |
| Normal weight | 64.6% | 59.2% | |
| Overweight | 18.2% | 22.8% | |
| Obese | 10.6% | 12.6% | |
| Dietary Consumption | Before COVID-19 Pandemic (n = 397) | During COVID-19 Pandemic (n = 801) | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cereals | 0.227 | ||
| Poor | 52.4% | 48.7% | |
| Ideal | 47.6% | 51.3% | |
| Vegetables | <0.001 | ||
| Poor | 37.5% | 56.1% | |
| Ideal | 62.5% | 43.9% | |
| Legumes | <0.001 | ||
| Poor | 42.3% | 52.9% | |
| Ideal | 57.7% | 47.1% | |
| Fruits | <0.001 | ||
| Poor | 32.7% | 58.6% | |
| Ideal | 67.3% | 41.4% | |
| Fish | <0.001 | ||
| Poor | 41.6% | 54.4% | |
| Ideal | 58.4% | 45.6% | |
| Dairy products | <0.001 | ||
| Poor | 45.7% | 58.9% | |
| Ideal | 54.3% | 41.1% | |
| Meat | 0.527 | ||
| Poor | 50.9% | 48.9% | |
| Ideal | 49.1% | 51.1% | |
| Unsaturated/saturated lipids ratio | 0.951 | ||
| Poor | 50.1% | 49.9% | |
| Ideal | 49.9% | 50.1% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magnano San Lio, R.; Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; La Rosa, M.C.; Giunta, G.; Panella, M.; Cianci, A.; Galvani, F.; Pappalardo, E.; Ettore, G.; et al. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Dietary Patterns of Pregnant Women: A Comparison between Two Mother-Child Cohorts in Sicily, Italy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163380
Magnano San Lio R, Barchitta M, Maugeri A, La Rosa MC, Giunta G, Panella M, Cianci A, Galvani F, Pappalardo E, Ettore G, et al. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Dietary Patterns of Pregnant Women: A Comparison between Two Mother-Child Cohorts in Sicily, Italy. Nutrients. 2022; 14(16):3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163380
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagnano San Lio, Roberta, Martina Barchitta, Andrea Maugeri, Maria Clara La Rosa, Giuliana Giunta, Marco Panella, Antonio Cianci, Fabiola Galvani, Elisa Pappalardo, Giuseppe Ettore, and et al. 2022. "The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Dietary Patterns of Pregnant Women: A Comparison between Two Mother-Child Cohorts in Sicily, Italy" Nutrients 14, no. 16: 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163380
APA StyleMagnano San Lio, R., Barchitta, M., Maugeri, A., La Rosa, M. C., Giunta, G., Panella, M., Cianci, A., Galvani, F., Pappalardo, E., Ettore, G., & Agodi, A. (2022). The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Dietary Patterns of Pregnant Women: A Comparison between Two Mother-Child Cohorts in Sicily, Italy. Nutrients, 14(16), 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163380








