Aerobic Exercise Prevents Chronic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle of High-Fat Diet Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Exercise Protocol
2.3. Glucose Tolerance Test and Insulin Tolerance Test
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Serum Analysis
2.6. Morphometric Analysis
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analyses
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Aerobic Exercise Attenuated HFD-Induced Adiposity
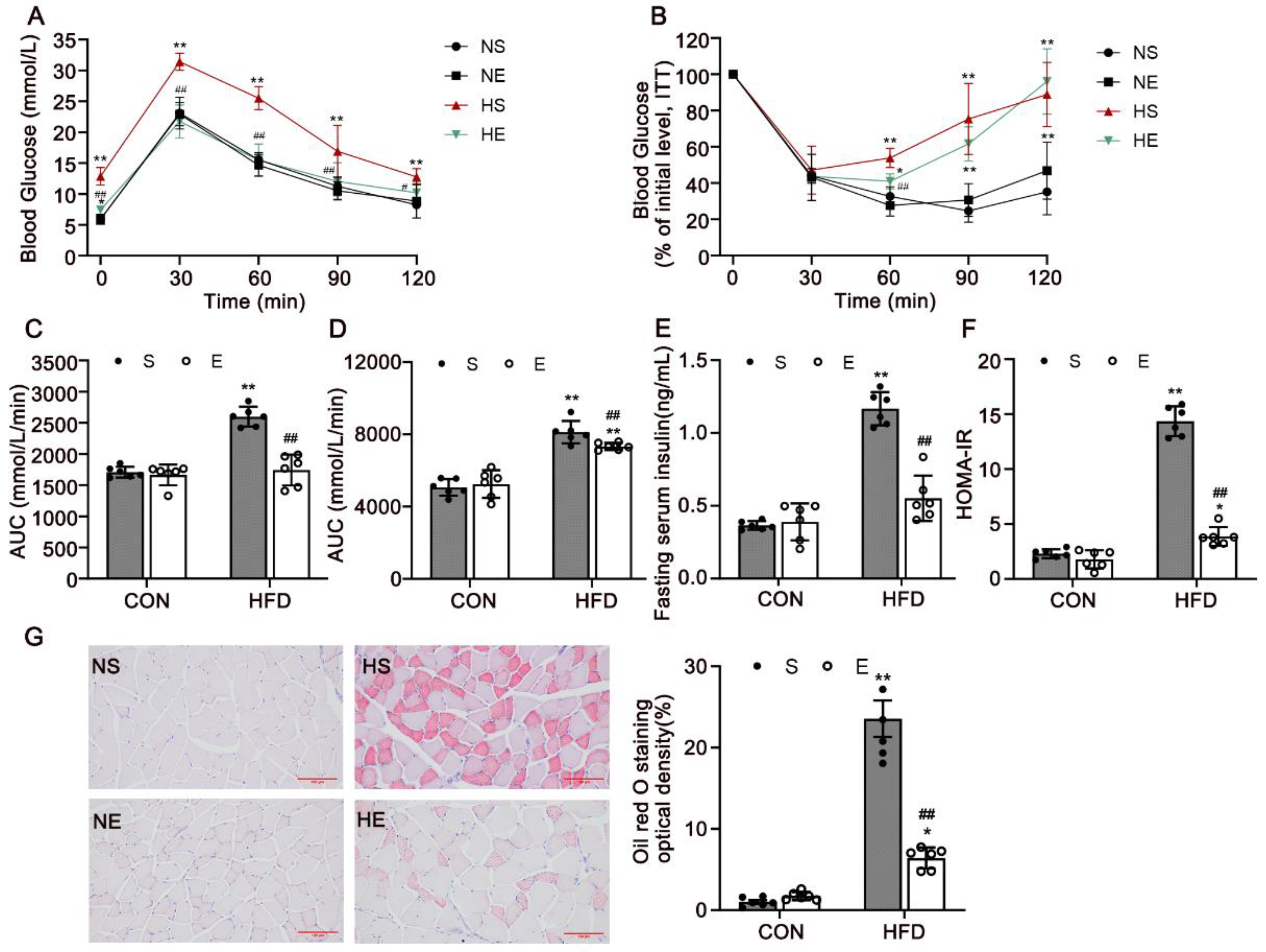
3.2. Aerobic Exercise Reduced HFD-Induced IR and Dyslipidemia
3.3. Aerobic Exercise Upregulated IRS-1/PI3K/AKT Signaling in Skeletal Muscle
3.4. Aerobic Exercise Attenuated Skeletal Muscle Inflammation in HFD Mice
3.5. Aerobic Exercise Attenuated HFD-Activated NF-κB Signaling and Regulated Inflammatory Cytokines in Skeletal Muscle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collaborators, G.B.D.O.; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Olefsky, J. Chronic tissue inflammation and metabolic disease. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circul. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Ingerslev, L.R.; Bork-Jensen, J.; Wohlwend, M.; Hansen, A.N.; Small, L.; Ribel-Madsen, R.; Astrup, A.; Pedersen, O.; Auwerx, J.; et al. Skeletal muscle enhancer interactions identify genes controlling whole-body metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Skeletal muscle inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, I.; Deldicque, L.; Francaux, M.; Zbinden-Foncea, H. Toll like receptor expression induced by exercise in obesity and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 24, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kalliolias, G.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.M.; Perrard, X.Y.; Brunner, G.; Lui, H.; Sparks, L.M.; Smith, S.R.; Wang, X.; Shi, Z.Z.; Lewis, D.E.; Wu, H.; et al. Intermuscular and perimuscular fat expansion in obesity correlates with skeletal muscle T cell and macrophage infiltration and insulin resistance. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2015, 39, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.S.; Jung, D.Y.; Morel, C.; Lakhani, S.A.; Kim, J.K.; Flavell, R.A.; Davis, R.J. JNK expression by macrophages promotes obesity-induced insulin resistance and inflammation. Science 2013, 339, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkan, M.C.; Hevener, A.L.; Greten, F.R.; Maeda, S.; Li, Z.W.; Long, J.M.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Poli, G.; Olefsky, J.; Karin, M. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, S.; Zarini, S.; Kahn, D.E.; Harrison, K.A.; Perreault, L.; Phang, T.; Newsom, S.A.; Strauss, A.; Kerege, A.; Schoen, J.A.; et al. Intermuscular adipose tissue directly modulates skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 316, E866–E879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, S.R.; Hawley, J.A. Update on the effects of physical activity on insulin sensitivity in humans. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.; Gower, B.A.; Ovalle, F.; Behrens, C.E.; Hunter, G.R. Acute Effects of Exercise Intensity on Insulin Sensitivity under Energy Balance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Matos, M.A.; Vieira, D.V.; Pinhal, K.C.; Lopes, J.F.; Dias-Peixoto, M.F.; Pauli, J.R.; de Castro Magalhães, F.; Little, J.P.; Rocha-Vieira, E.; Amorim, F.T. High-Intensity Interval Training Improves Markers of Oxidative Metabolism in Skeletal Muscle of Individuals With Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Qiu, R.; Wu, B.; Gui, W.; Lin, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, F. Transthyretin contributes to insulin resistance and diminishes exercise-induced insulin sensitivity in obese mice by inhibiting AMPK activity in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E808–E821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhling, M.; Herder, C.; Stemper, T.; Müssig, K. Influence of Acute and Chronic Exercise on Glucose Uptake. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2868652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xia, Z.; Liong, E.C.; Tipoe, G.L. Chronic aerobic exercise improves insulin sensitivity and modulates Nrf2 and NFkappaB/IkappaBalpha pathways in the skeletal muscle of rats fed with a high fat diet. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4963–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwijitkamol, A.; Christ-Roberts, C.; Berria, R.; Eagan, P.; Pratipanawatr, T.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Mandarino, L.J.; Musi, N. Reduced skeletal muscle inhibitor of kappaB beta content is associated with insulin resistance in subjects with type 2 diabetes: Reversal by exercise training. Diabetes 2006, 55, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoydal, M.A.; Wisloff, U.; Kemi, O.J.; Ellingsen, O. Running speed and maximal oxygen uptake in rats and mice: Practical implications for exercise training. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2007, 14, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, K.; Boguslavsky, S.; Klip, A. Endocytosis, recycling, and regulated exocytosis of glucose transporter 4. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 3048–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douen, A.G.; Ramlal, T.; Rastogi, S.; Bilan, P.J.; Cartee, G.D.; Vranic, M.; Holloszy, J.O.; Klip, A. Exercise induces recruitment of the “insulin-responsive glucose transporter”. Evidence for distinct intracellular insulin- and exercise-recruitable transporter pools in skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 13427–13430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Khodabukus, A.; Rao, L.; Vandusen, K.; Abutaleb, N.; Bursac, N. Engineered skeletal muscles for disease modeling and drug discovery. Biomaterials 2019, 221, 119416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, L.N.; Costford, S.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Jensen, T.E.; Bilan, P.J.; Oberbach, A.; Bluher, M.; Olefsky, J.M.; Sams, A.; Klip, A. Pro-inflammatory macrophages increase in skeletal muscle of high fat-fed mice and correlate with metabolic risk markers in humans. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014, 22, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.E.; Lauritzen, H.; O’Neill, B.T.; Wang, C.H.; Cai, W.; Brandao, B.B.; Sakaguchi, M.; Tao, R.; Hirshman, M.F.; Softic, S.; et al. Role of p110a subunit of PI3-kinase in skeletal muscle mitochondrial homeostasis and metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, V.; Yaligar, J.; Michael, N.; Kaur, K.; Anantharaj, R.; Verma, S.K.; Sadananthan, S.A.; Le, G.T.T.; Goh, J.; Velan, S.S. A 12-week aerobic exercise intervention results in improved metabolic function and lower adipose tissue and ectopic fat in high-fat diet fed rats. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20201707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Dun, Y.; Cheng, J.; Ripley-Gonzalez, J.W.; Jiang, W.; You, B.; Liu, S. Exercise activates autophagy and regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress in muscle of high-fat diet mice to alleviate insulin resistance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 601, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillon, N.J.; Gabriel, B.M.; Dollet, L.; Smith, J.A.B.; Sardon Puig, L.; Botella, J.; Bishop, D.J.; Krook, A.; Zierath, J.R. Transcriptomic profiling of skeletal muscle adaptations to exercise and inactivity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suchacki, K.J.; Tavares, A.A.S.; Mattiucci, D.; Scheller, E.L.; Papanastasiou, G.; Gray, C.; Sinton, M.C.; Ramage, L.E.; McDougald, W.A.; Lovdel, A.; et al. Bone marrow adipose tissue is a unique adipose subtype with distinct roles in glucose homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ibi, D.; Taniguchi, K.; Lee, J.; Herrema, H.; Akosman, B.; Mucka, P.; Salazar Hernandez, M.A.; Uyar, M.F.; Park, S.W.; et al. Inflammation Improves Glucose Homeostasis through IKKbeta-XBP1s Interaction. Cell 2016, 167, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burini, R.C.; Anderson, E.; Durstine, J.L.; Carson, J.A. Inflammation, physical activity, and chronic disease: An evolutionary perspective. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2020, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisaka, S. The role of adipose tissue M1/M2 macrophages in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Int. 2021, 12, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orliaguet, L.; Ejlalmanesh, T.; Alzaid, F. Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation and Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazaud, B. Inflammation and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: Leave It to the Macrophages! Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Pacher, P.; Hasko, G. Role of Macrophages in the Endocrine System. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchgessner, T.G.; Uysal, K.T.; Wiesbrock, S.M.; Marino, M.W.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha contributes to obesity-related hyperleptinemia by regulating leptin release from adipocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2777–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wree, A.; McGeough, M.D.; Inzaugarat, M.E.; Eguchi, A.; Schuster, S.; Johnson, C.D.; Pena, C.A.; Geisler, L.J.; Papouchado, B.G.; Hoffman, H.M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome driven liver injury and fibrosis: Roles of IL-17 and TNF in mice. Hepatology 2018, 67, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S.; Li, P.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Lu, M.; Kim, J.I.; Ham, M.; Talukdar, S.; Chen, A.; Lu, W.J.; et al. Inflammation is necessary for long-term but not short-term high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.G.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-kappaB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, J.M.; Pieri, B.; Luciano, T.F.; Marques, S.O.; Guglielmo, L.G.A.; Souza, C.T. Muscular resistance, hypertrophy and strength training equally reduce adiposity, inflammation and insulin resistance in mice with diet-induced obesity. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 2020, 18, eAO4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ai, L.; Zhang, Y. Modulation of TRIB3 and Macrophage Phenotype to Attenuate Insulin Resistance After Downhill Running in Mice. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 637432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Tang, J.; Ji, K. Exercise prevents HFD-induced insulin resistance risk: Involvement of TNF-alpha level regulated by vagus nerve-related anti-inflammatory pathway in the spleen. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yu, P.; Liu, X. Swim Training Attenuates Inflammation and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 5940732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.M.; de Paula Souza, A.; Nunes, P.R.P.; Michelin, M.A.; Murta, E.F.C.; Resende, E.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Orsatti, F.L. High-intensity body weight training is comparable to combined training in changes in muscle mass, physical performance, inflammatory markers and metabolic health in postmenopausal women at high risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 107, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. #N/A 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, B.; Guo, X. Different Effects of Leucine Supplementation and/or Exercise on Systemic Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 651303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, P.A.M.; Gregnani, M.F.; Henrique, J.S.; Ornellas, F.H.; Araujo, R.C. Aerobic but not Resistance Exercise Can Induce Inflammatory Pathways via Toll-Like 2 and 4: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. Open 2017, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athari, S.S. Targeting cell signaling in allergic asthma. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Alvaro, C.; Teruel, T.; Hernandez, R.; Lorenzo, M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha produces insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by activation of inhibitor kappaB kinase in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17070–17078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Product Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | Forward Primer | CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT | 199 bp |
| Reverse Primer | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG | ||
| MCP-1 | Forward Primer | AAGAAGGAATGGGTCCAGACA | 140 bp |
| Reverse Primer | GCTTCAGATTTACGGGTCAACT | ||
| iNOS | Forward Primer | TCCATGCTAATGCGAAAGG | 197 bp |
| Reverse Primer | CTTGTCACCACCAGCAGTAGTT | ||
| Arg-1 | Forward Primer | ACAGCAGAGGAGGTGAAGAGTAC | 100 bp |
| Reverse Primer | AGTCAGTCCCTGGCTTATGGT | ||
| IL-10 | Forward Primer | TTGCCAAGCCTTATCGGA | 103 bp |
| Reverse Primer | ACCCAGGGAATTCAAATGC | ||
| NF-κB | Forward Primer | AGGACCTATGAGACCTTCAAGAGTA | 145 bp |
| Reverse Primer | GGAAGGTGTAGGGCTGCG | ||
| GLUT4 | Forward Primer | TTGGCTCCCTTCAGTTTGG | 233 bp |
| Reverse Primer | CCTTTTCCTTCCCAACCATT | ||
| β-actin | Forward Primer | GTGCTATGTTGCTCTAGACTTCG | 174 bp |
| Reverse Primer | ATGCCACAGGATTCCATACC | ||
| Blood Lipids (mmol/L) | NS | NE | HS | HE | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 2.62 ± 0.43 | 3.02 ± 0.53 | 4.67 ± 0.40 ** | 3.89 ± 0.70 *,## | HS vs. NS p < 0.0001 HE vs. HS p = 0.007 HE vs. NS p = 0.041 |
| TG | 0.59 ± 0.07 | 0.60 ± 0.09 | 0.88 ± 0.19 ** | 0.72 ± 0.07 *,## | HS vs. NS p < 0.0001 HE vs. HS p = 0.008 HE vs. NS p = 0.017 |
| HDL | 3.14 ± 0.59 | 3.21 ± 0.55 | 3.75 ± 0.73 * | 3.55 ± 0.24 | HS vs. NS p =0.033 HE vs. HS p = 0.465 HE vs. NS p = 0.275 |
| LDL | 0.15 ± 0.08 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 0.32 ± 0.13 ** | 0.31 ± 0.13 | HS vs. NS p = 0.003 HE vs. HS p = 0.891 HE vs. NS p = 0.894 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Shi, H.; Guo, Q.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y. Aerobic Exercise Prevents Chronic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle of High-Fat Diet Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3730. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183730
Li N, Shi H, Guo Q, Gan Y, Zhang Y, Jia J, Zhang L, Zhou Y. Aerobic Exercise Prevents Chronic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle of High-Fat Diet Mice. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3730. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183730
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Nan, Haiyan Shi, Qiaofeng Guo, Yanming Gan, Yuhang Zhang, Jiajie Jia, Liang Zhang, and Yue Zhou. 2022. "Aerobic Exercise Prevents Chronic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle of High-Fat Diet Mice" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3730. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183730
APA StyleLi, N., Shi, H., Guo, Q., Gan, Y., Zhang, Y., Jia, J., Zhang, L., & Zhou, Y. (2022). Aerobic Exercise Prevents Chronic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle of High-Fat Diet Mice. Nutrients, 14(18), 3730. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183730







