The Effect of Resveratrol on Blood Lipid Profile: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
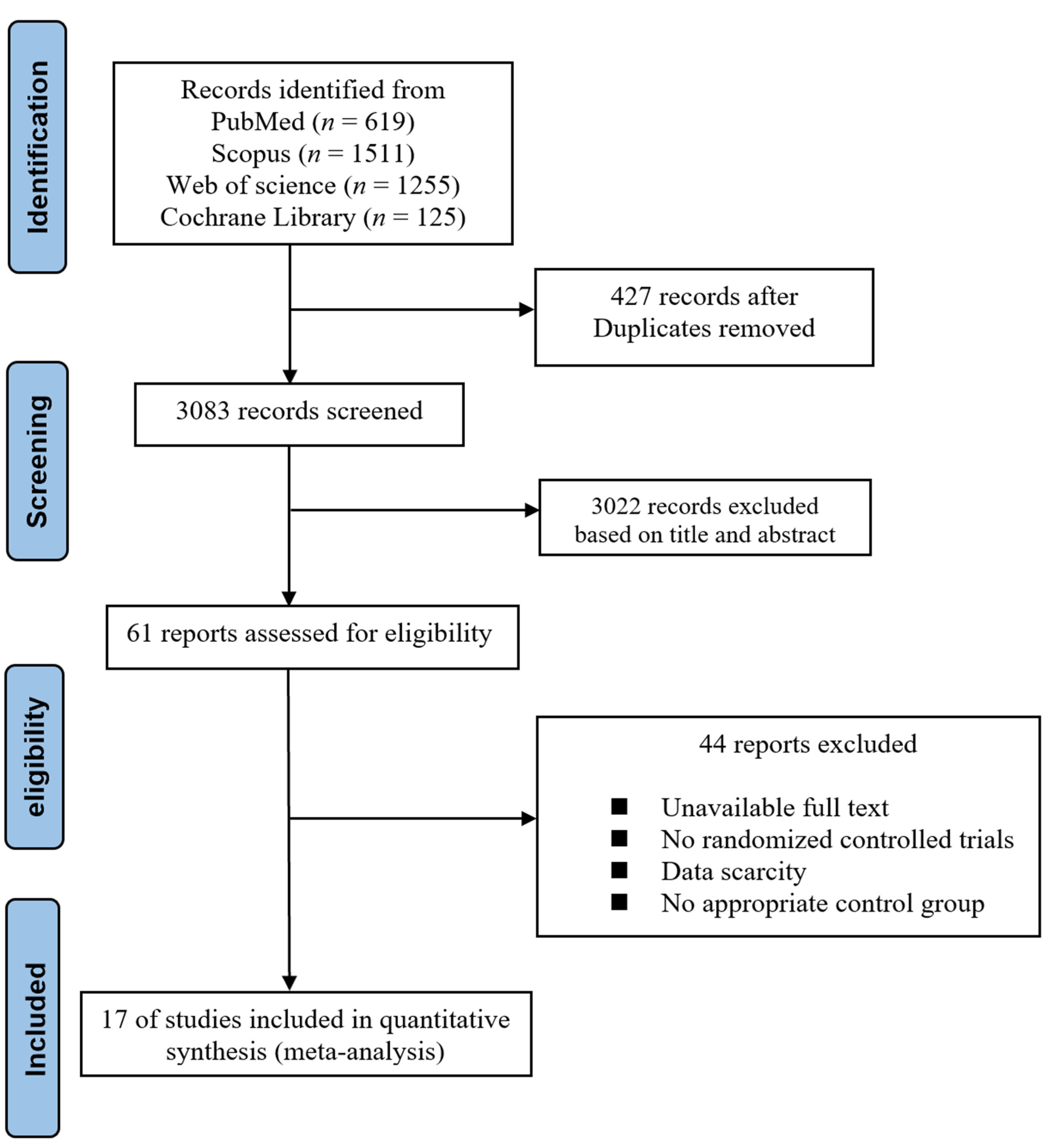
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Included Studies
3.2. Study Characteristics
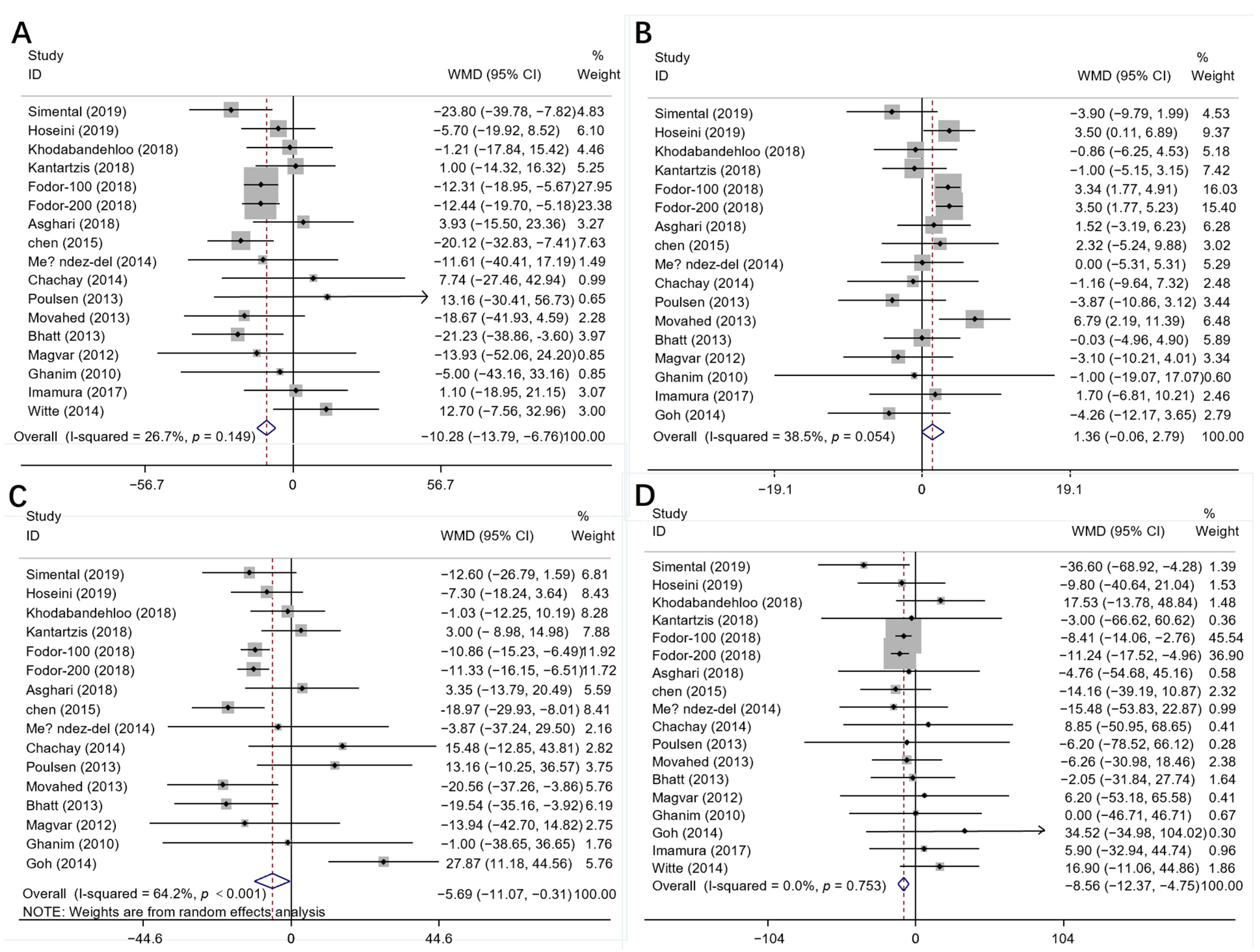
3.3. Results of Meta-Analysis
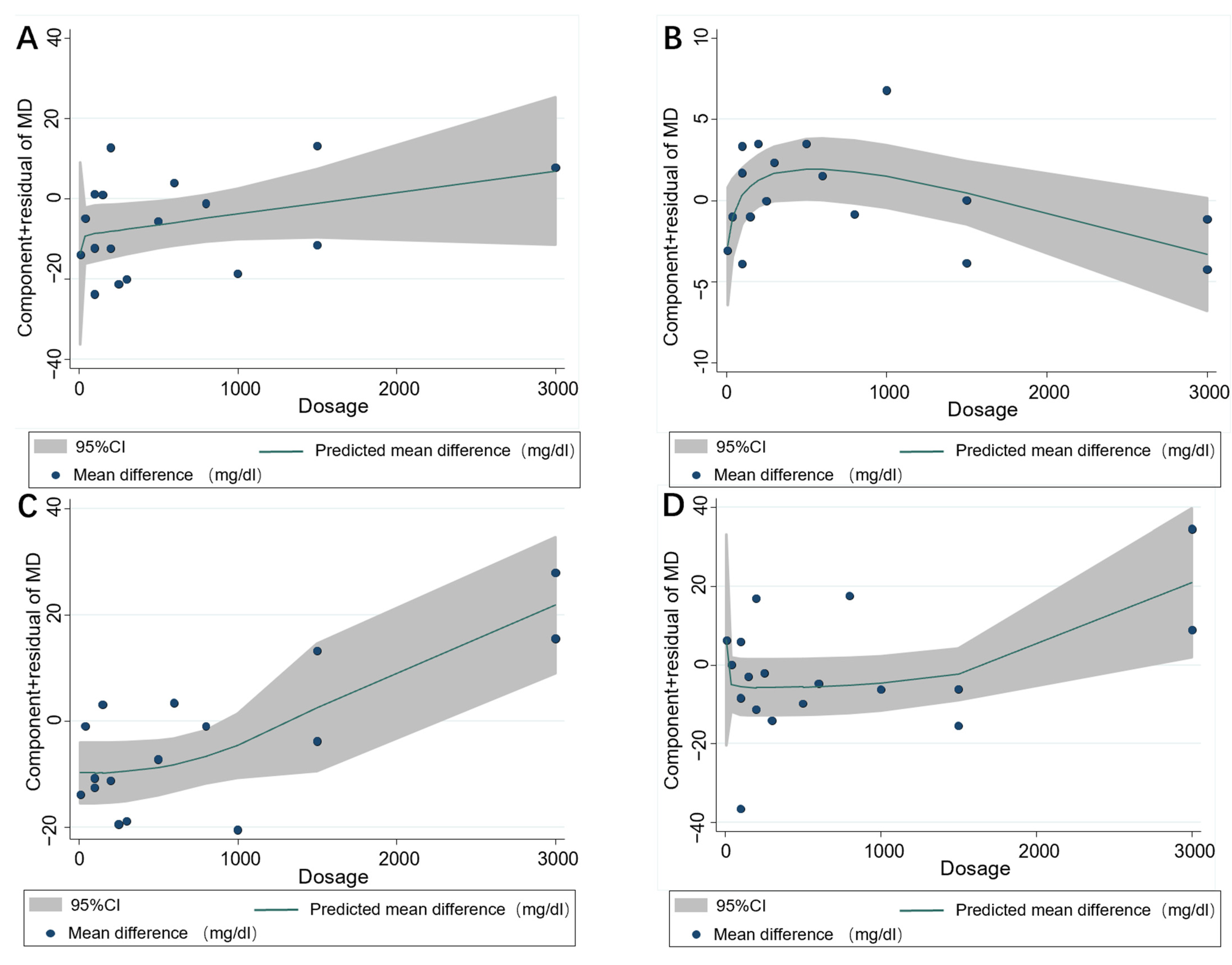
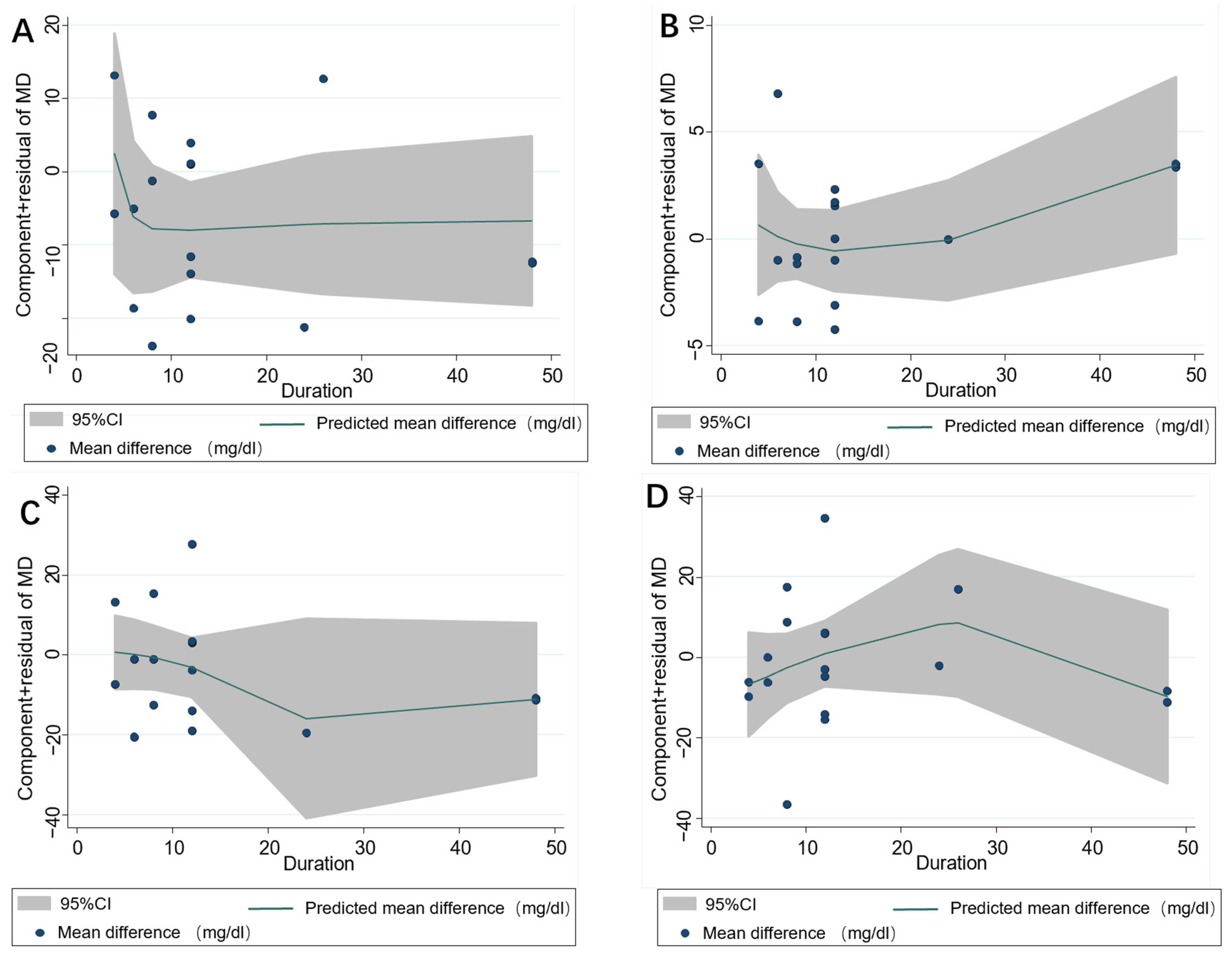
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
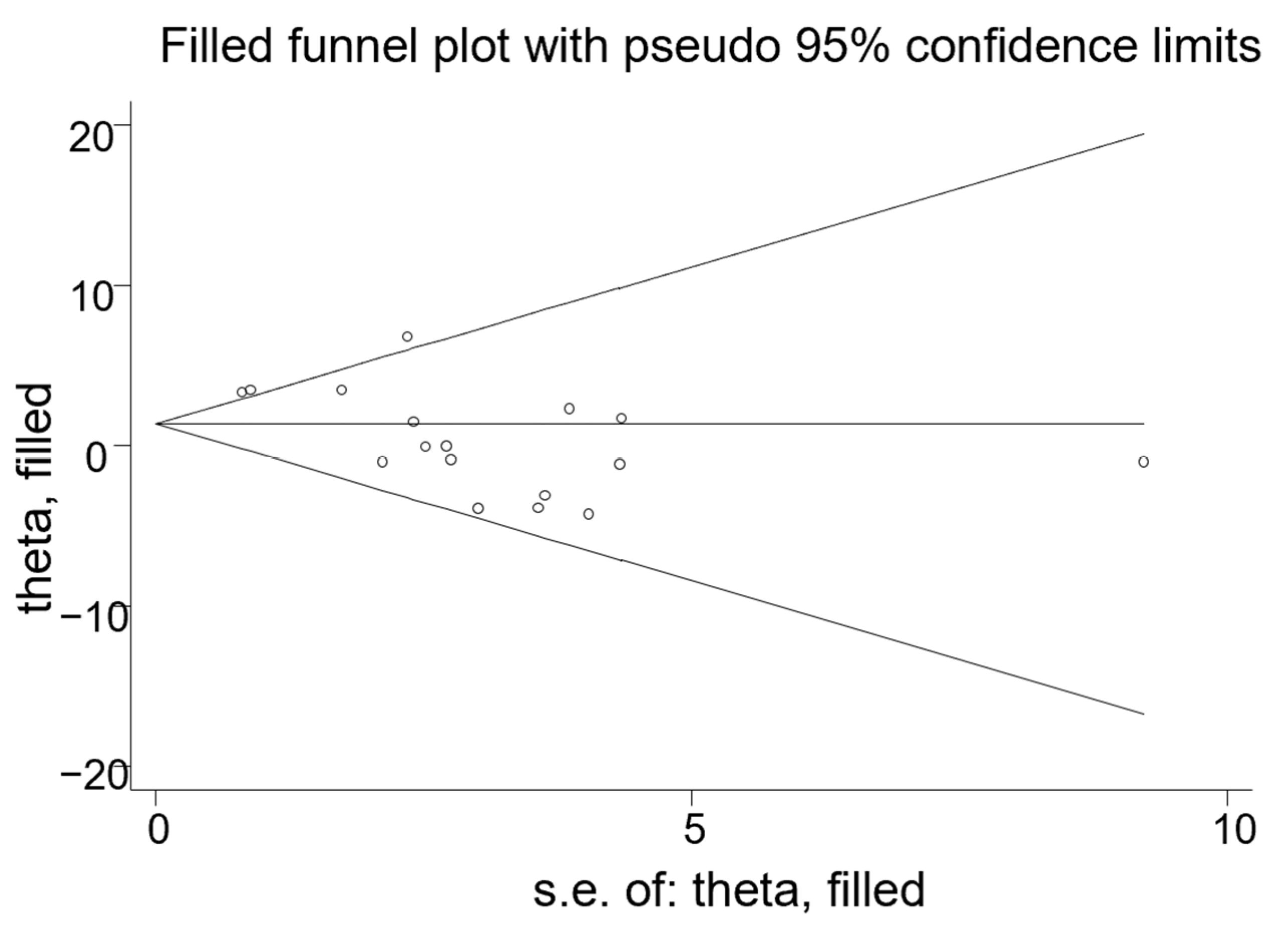
3.5. Publication Bias and Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, X.; Xia, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.; Liao, W.; Sun, G. The Effect of MUFA-Rich Food on Lipid Profile: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Controlled-Feeding Trials. Foods 2022, 11, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighatdoost, F.; Hariri, M. Effect of resveratrol on lipid profile: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized clinical trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, M.C.; Fazio, S.; Chilton, F.H.; Wise, D.E.; Jones, K.B.; Barringer, T.A.; Bramlet, D.A. Nonpharmacologic treatment of dyslipidemia. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 52, 61–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giner-Galvañ, V.; Esteban-Giner, M.J.; Pallarés-Carratalá, V. Overview of guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia: EU perspectives. Vasc. Heal. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Javed, S.; Javed, S.; Tariq, A.; Šamec, D.; Tejada, S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M. Resveratrol and Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanistic Insights. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2622–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Larrosa, M.; González-Sarrías, A.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Espín, J.C. Resveratrol and clinical trials: The crossroad from in vitro studies to human evidence. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6064–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Mazza, G. Simultaneous analysis of serotonin, melatonin, piceid and resveratrol in fruits using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3890–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, R.; Hamada, H.; Uesugi, D.; Iwahara, N.; Nojima, I.; Horio, Y.; Kuno, A. Different Antioxidative and Antiapoptotic Effects of Piceatannol and Resveratrol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 376, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.D.; Chang, J.; Qin, B.Y.; Zhong, C.; Chu, Z.B.; Huang, J.; Zhou, W.J.; Sun, X. Synthesis, estrogenic activity, and anti-osteoporosis effects in ovariectomized rats of resveratrol oligomer derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsu, P.; Murthy, B.V.; Akula, A. Cerebroprotective potential of resveratrol through anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms in rats. J. Neural Transm. 2013, 120, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, L.S.; Zancan, P.; Marcondes, M.C.; Ramos-Santos, L.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; Sola-Penna, M.; Da Silva, D. Resveratrol decreases breast cancer cell viability and glucose metabolism by inhibiting 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Moreno, J.J. Effect of resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound, on reactive oxygen species and prostaglandin production. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.N.; Kim, M.Y.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Shin, S.J.; Park, C.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Yoon, H.E.; Choi, B.S. The protective effect of resveratrol on vascular aging by modulation of the renin-angiotensin system. Atherosclerosis 2018, 270, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankauskas, S.S.; Mone, P.; Santulli, G. From resveratrol to ISIDE11: How to activate SIRT1 and improve endothelial function? New therapeutic insights for methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.M.; Rodrigues, D.; Alemi, M.; Silva, S.C.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Cardoso, I. Resveratrol administration increases Transthyretin protein levels ameliorating AD features: The importance of transthyretin tetrameric stability. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Deng, M. Deciphering the Anti-obesity Benefits of Resveratrol: The “Gut Microbiota-Adipose Tissue” Axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, X.; Bi, S.; Pan, Z.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Lu, H.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, T.; et al. Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on foam cell formation are mediated through monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and lipid metabolism-related proteins. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Cho, I.; Kim, S.; Kwon, D.; Ha, T. Dietary resveratrol alters lipid metabolism-related gene expression of mice on an atherogenic diet. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Effect of resveratrol supplementation on lipid profile in subjects with dyslipidemia: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition 2019, 58, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, A.; Namazi, G.; Farrokhian, A.; Reiner, Z.; Aghadavod, E.; Bahmani, F.; Asemi, Z. The effects of resveratrol on metabolic status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6042–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Ran, L.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Shu, F.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Resveratrol improves insulin resistance, glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.P.; Lee, H.Y.; Lau, D.P.; Supaat, W.; Chan, Y.H.; Koh, A.F. Effects of resveratrol in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on skeletal muscle SIRT1 expression and energy expenditure. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014, 24, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magvar, K.; Halmosi, R.; Palfi, A.; Feher, G.; Czopf, L.; Fulop, A.; Battyany, I.; Sumegi, B.; Toth, K.; Szabados, E. Cardioprotection by resveratrol: A human clinical trial in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 50, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabandehloo, H.; Seyyedebrahimi, S.; Esfahani, E.; Razi, F.; Meshkani, R. Resveratrol supplementation decreases blood glucose without changing the circulating CD14 + CD16 + monocytes and inflammatory cytokines in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr. Res. 2018, 54, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, S.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Somi, M.H.; Ghavami, S.M.; Rafraf, M. Comparison of Calorie-Restricted Diet and Resveratrol Supplementation on Anthropometric Indices, Metabolic Parameters, and Serum Sirtuin-1 Levels in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-del Villar, M.; González-Ortiz, M.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Pérez-Rubio, K.G.; Lizárraga-Valdez, R. Effect of resveratrol administration on metabolic syndrome, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2014, 12, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachay, V.S.; Macdonald, G.A.; Martin, J.H.; Whitehead, J.P.; O’Moore-Sullivan, T.M.; Lee, P.; Franklin, M.; Klein, K.; Taylor, P.J.; Ferguson, M.; et al. Resveratrol does not benefit patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 2092–2103.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Q.; He, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.R.; Hu, H.J. Efficacy and Safety of Resveratrol Supplements on Blood Lipid and Blood Glucose Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5644171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Lankarani, K.B.; Tabrizi, R.; Dadgostar, E.; Haghighat, N.; Kolahdooz, F.; Ghaderi, A.; Mansournia, M.A.; Asemi, Z. The effects of resveratrol on lipid profiles and liver enzymes in patients with metabolic syndrome and related disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2020, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Song, A.; Zhang, Y.J.; Shu, L.Y.; Song, G.Y.; Ma, H.J. Effect of Resveratrol on Blood Lipid Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obesity 2019, 27, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahebkar, A. Effects of resveratrol supplementation on plasma lipids: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, K.; Tit, D.M.; Pasca, B.; Bustea, C.; Uivarosan, D.; Endres, L.; Iovan, C.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Bungau, S. Long-Term resveratrol supplementation as a secondary prophylaxis for stroke. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4147320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022); Cochrane: London, UK, 2022; Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 27 November 2017).
- Zhang, Z. Multivariable fractional polynomial method for regression model. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantartzis, K.; Fritsche, L.; Bombrich, M.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Staiger, H.; Kunz, I.; Schoop, R.; Lehn-Stefan, A.; Heni, M.; et al. Effects of resveratrol supplementation on liver fat content in overweight and insulin-resistant subjects: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, M.M.; Vestergaard, P.F.; Clasen, B.F.; Radko, Y.; Christensen, L.P.; Stodkilde-Jorgensen, H.; Moller, N.; Jessen, N.; Pedersen, S.B.; Jorgensen, J.O. High-dose resveratrol supplementation in obese men: An investigator-initiated, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of substrate metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and body composition. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movahed, A.; Nabipour, I.; Lieben Louis, X.; Thandapilly, S.J.; Yu, L.; Kalantarhormozi, M.; Rekabpour, S.J.; Netticadan, T. Antihyperglycemic effects of short term resveratrol supplementation in type 2 diabetic patients. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 851267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, J.K.; Nanjan, M.J. Resveratrol supplementation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A prospective, open label, randomized controlled trial. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2013, 4, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, H.; Sia, C.L.; Abuaysheh, S.; Korzeniewski, K.; Patnaik, P.; Marumganti, A.; Chaudhuri, A.; Dandona, P. An antiinflammatory and reactive oxygen species suppressive effects of an extract of Polygonum cuspidatum containing resveratrol. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, E1–E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nagayama, D.; Saiki, A.; Shirai, K.; Tatsuno, I. Resveratrol Ameliorates Arterial Stiffness Assessed by Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. Hear. J. 2017, 58, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, A.V.; Kerti, L.; Margulies, D.S.; Flöel, A. Effects of resveratrol on memory performance, hippocampal functional connectivity, and glucose metabolism in healthy older adults. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 7862–7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, J.Q.; Yu, B.; Chen, J.L.; Chen, D.W. Effects of resveratrol on lipid metabolism in muscle and adipose tissues: A reevaluation in a pig model. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshyna, I.; Hussaini, S.M.; Reiss, A.B. Resveratrol in Cholesterol Metabolism and Atherosclerosis. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, A.Y.; Motechin, R.A.; Wiesenfeld, M.Y.; Holz, M.K. The therapeutic potential of resveratrol: A review of clinical trials. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrougui, H.; Grenier, G.; Loued, S.; Drouin, G.; Khalil, A. A new insight into resveratrol as an atheroprotective compound: Inhibition of lipid peroxidation and enhancement of cholesterol efflux. Atherosclerosis 2009, 207, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, P.; Almeida, L.M.; Dinis, T.C. The interaction of resveratrol with ferrylmyoglobin and peroxynitrite; protection against LDL oxidation. Free Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Milajerdi, A.; Sheikhi, A.; Kord-Varkaneh, H.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Resveratrol supplementation significantly influences obesity measures: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dudley, J.I.; Das, D.K. Dose-dependency of resveratrol in providing health benefits. Dose-Response 2010, 8, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Scott, E.; Kholghi, A.; Andreadi, C.; Rufini, A.; Karmokar, A.; Britton, R.G.; Horner-Glister, E.; Greaves, P.; Jawad, D.; et al. Cancer chemoprevention: Evidence of a nonlinear dose response for the protective effects of resveratrol in humans and mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 298ra117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Ponzo, V.; Ciccone, G.; Evangelista, A.; Saba, F.; Goitre, I.; Procopio, M.; Pagano, G.F.; Cassader, M.; Gambino, R. Six months of resveratrol supplementation has no measurable effect in type 2 diabetic patients. A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Literature | Year | Study Region | Participant | Female% | Age Range | Sample (I/C) | Circle | Dose (mg/d) | Study Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simental [19] | 2019 | Mexico | Dyslipidemia | 74.2 | 20–65 | 31/31 | 8 week | 100 | parallel |
| Hoseini [20] | 2019 | Iran | T2DM and coronary heart disease (CHD) | NA | 40–85 | 28/28 | 4 week | 500 | parallel |
| Khodabandehloo [24] | 2018 | Iran | T2DM | 51.1 | 30–70 | 25/20 | 8 week | 800 | parallel |
| Kantartzis [35] | 2018 | Germany | BMI ≥ 27 | NA | 18–70 | 53/52 | 12 week | 150 | parallel |
| Fodor-100 [32] | 2018 | Romania | Stroke | 60.5 | ≥55 | 81/92 | 48 week | 100 | parallel |
| Fodor-200 [32] | 2018 | Romania | Stroke | 60.5 | ≥55 | 55/92 | 48 week | 200 | parallel |
| Asghari [25] | 2018 | Iran | NAFLD | 33.3 | 20–60 | 30/30 | 12 week | 600 | parallel |
| Chen [21] | 2015 | China | NAFLD | 30 | 20–60 | 30/30 | 12 week | 300 | parallel |
| Me’ ndez-del [26] | 2014 | Mexico | Metabolic syndrome | NA | 30–50 | 11/10 | 12 week | 1500 | parallel |
| Chachay [27] | 2014 | Australia | NAFLD | 0 | 36–61 | 10/10 | 8 week | 3000 | parallel |
| Poulsen [36] | 2013 | Denmark | Obese Men | 0 | 18–70 | 12/12 | 4 week | 1500 | parallel |
| Movahed [37] | 2013 | Iran | T2DM | 50 | 45–59 | 33/31 | 6 week (45 day) | 1000 | parallel |
| Bhatt [38] | 2013 | India | T2DM | 63.2 | 30–70 | 28/29 | 24 week (6 month) | 250 | parallel |
| Magvar [23] | 2012 | Hungary | Stable coronary artery disease | 35 | 42–80 | 20/20 | 12 week | 10 | parallel |
| Ghanim [39] | 2010 | America | Healthy | NA | 31–41 | 10/10 | 6 week | 40 | parallel |
| Imamura [40] | 2017 | Finland | T2DM | 48 | 47–68 | 25/25 | 12 week | 100 | parallel |
| Witte [41] | 2014 | Germany | Overweight | 39.1 | 50–75 | 23/23 | 26 week | 200 | parallel |
| Goh [22] | 2014 | Singapore | T2DM | 0 | 40–69 | 5/5 | 12 week | 3000 | parallel |
| Index | Subgroup | No. of Trials | Mean Difference | p | I2 (%) | p Value of Heterogeneity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 95%CI | ||||||
| LDL-C | Resveratrol dose (g/day) | ||||||
| ≥500 mg | 8 | 2.44 | −8.21, 13.08 | 0.004 | 66.4 | 0.654 | |
| <500 mg | 8 | −11.16 | −14.94, −7.38 | 0.267 | 20.5 | 0.001 | |
| Population condition | |||||||
| T2DM | 5 | −4.21 | −18.78, 10.36 | 0.001 | 82 | 0.571 | |
| NAFLD | 3 | −2.77 | −23.22, 17.69 | 0.018 | 75 | 0.791 | |
| Obese/Overweight | 2 | 5.11 | −0.86, −0.18 | 0.449 | 0 | 0.348 | |
| Stroke | 2 | −11.07 | −14.31, −7.84 | 0.887 | 0 | 0.001 | |
| Others | 4 | −10.75 | −22.09, 0.59 | 0.911 | 0 | 0.063 | |
| Duration of the trial | |||||||
| ≥12 weeks | 9 | −6.01 | −13.26, 1.25 | 0.001 | 73.4 | 0.105 | |
| <12 weeks | 7 | −5.12 | −13.13, 2.89 | 0.152 | 36.2 | 0.210 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Liao, W.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, G. The Effect of Resveratrol on Blood Lipid Profile: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183755
Cao X, Liao W, Xia H, Wang S, Sun G. The Effect of Resveratrol on Blood Lipid Profile: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183755
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xinyi, Wang Liao, Hui Xia, Shaokang Wang, and Guiju Sun. 2022. "The Effect of Resveratrol on Blood Lipid Profile: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183755
APA StyleCao, X., Liao, W., Xia, H., Wang, S., & Sun, G. (2022). The Effect of Resveratrol on Blood Lipid Profile: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 14(18), 3755. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183755









