Alanyl-Glutamine Protects Mice against Methionine- and Choline-Deficient-Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Materials
2.3. Histology
2.4. IHC Assay
2.5. Biochemical Assay
2.6. ELISA
2.7. Western Blots
2.8. Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
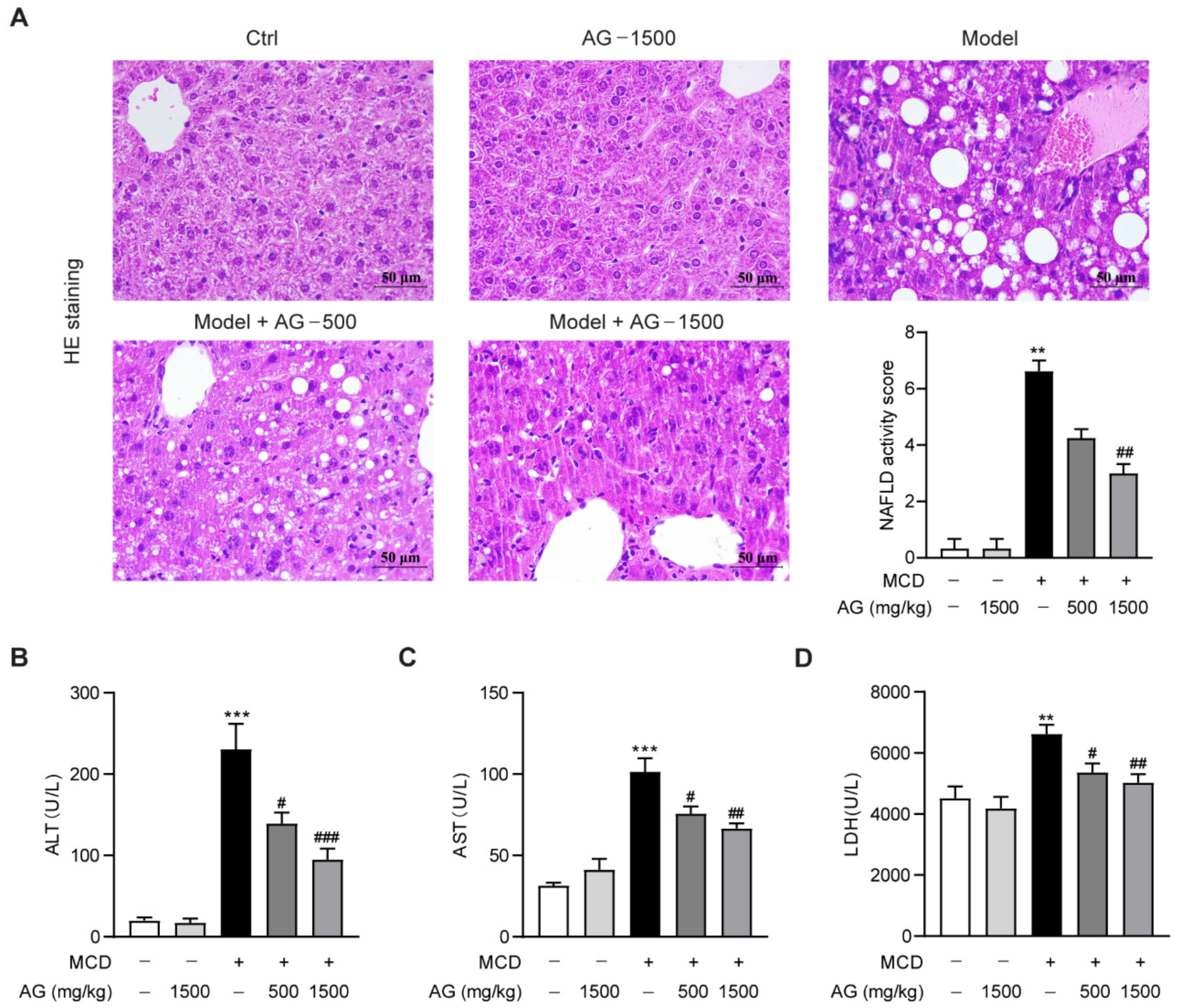
3.1. Hepatoprotective Effects of Ala-Gln on MCD-Induced NASH Mice
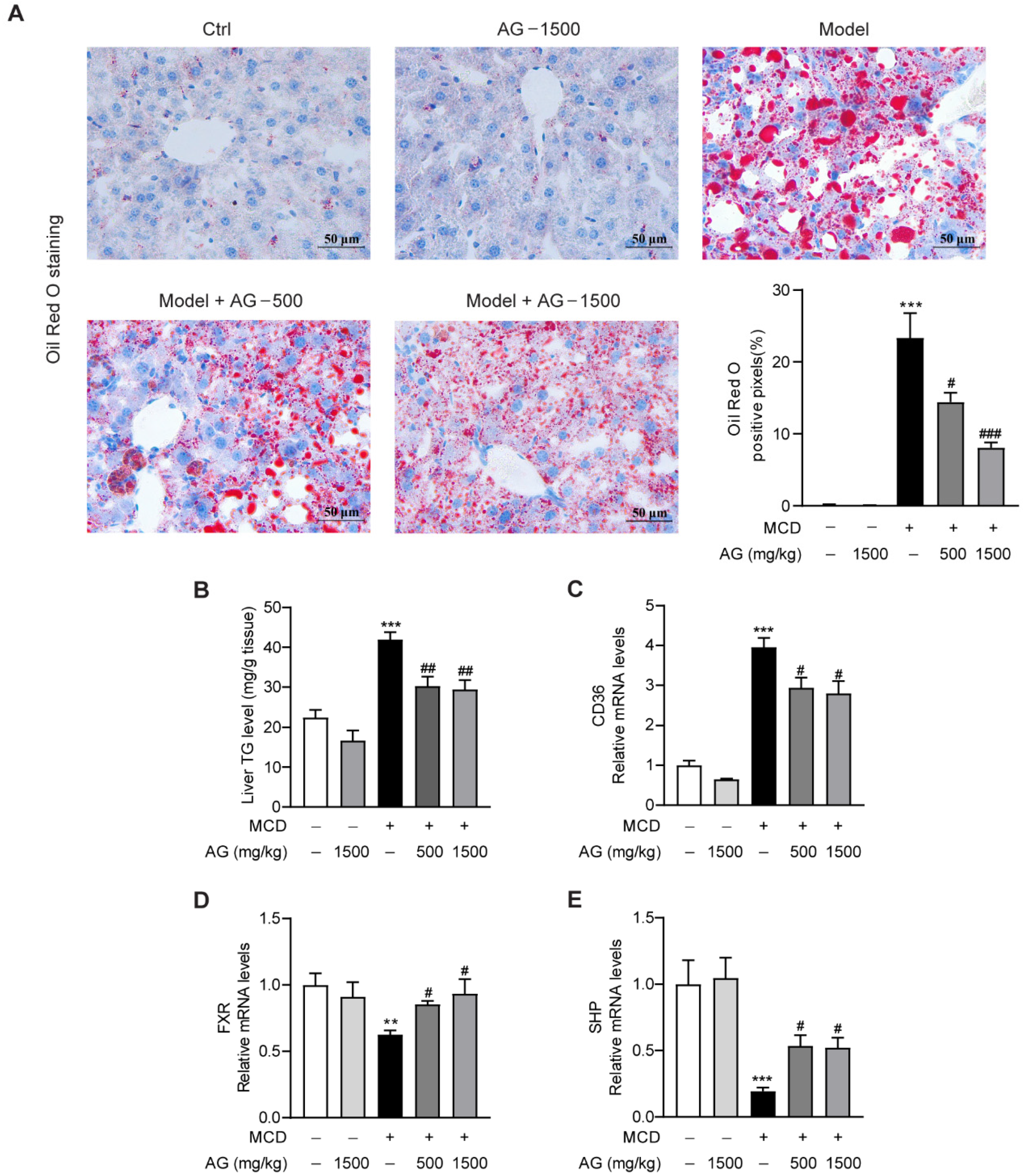
3.2. Ala-Gln Ameliorates MCD-Induced Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Regulating CD36 and FXR Expression
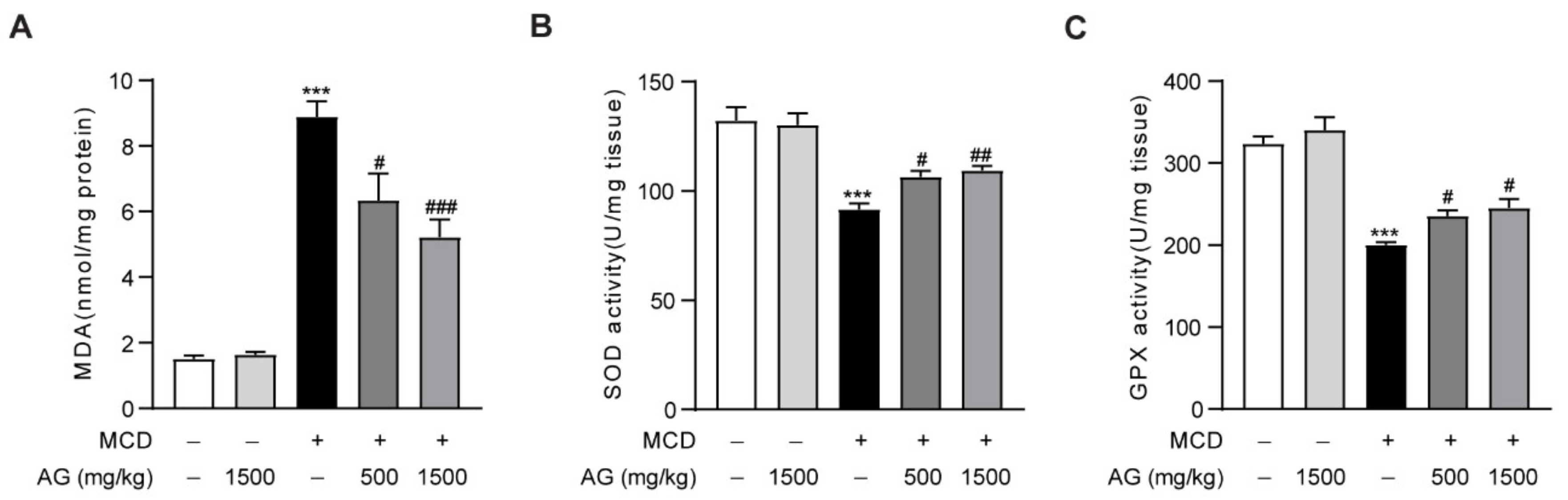
3.3. Ala-Gln Protects against Oxidative Stress in MCD-Fed Mice
3.4. Ala-Gln Inhibits MCD-Induced Liver Inflammation in Mice
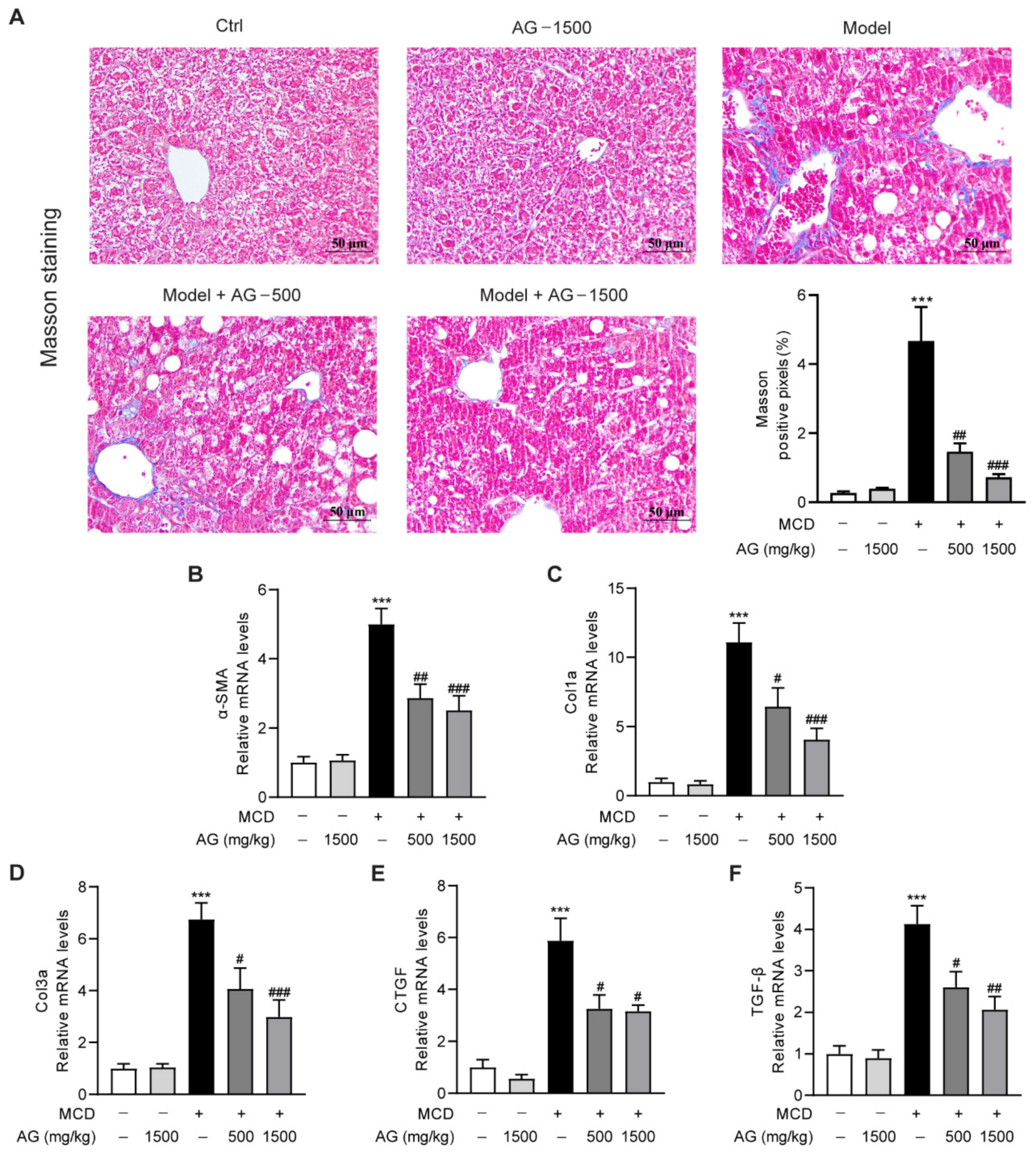
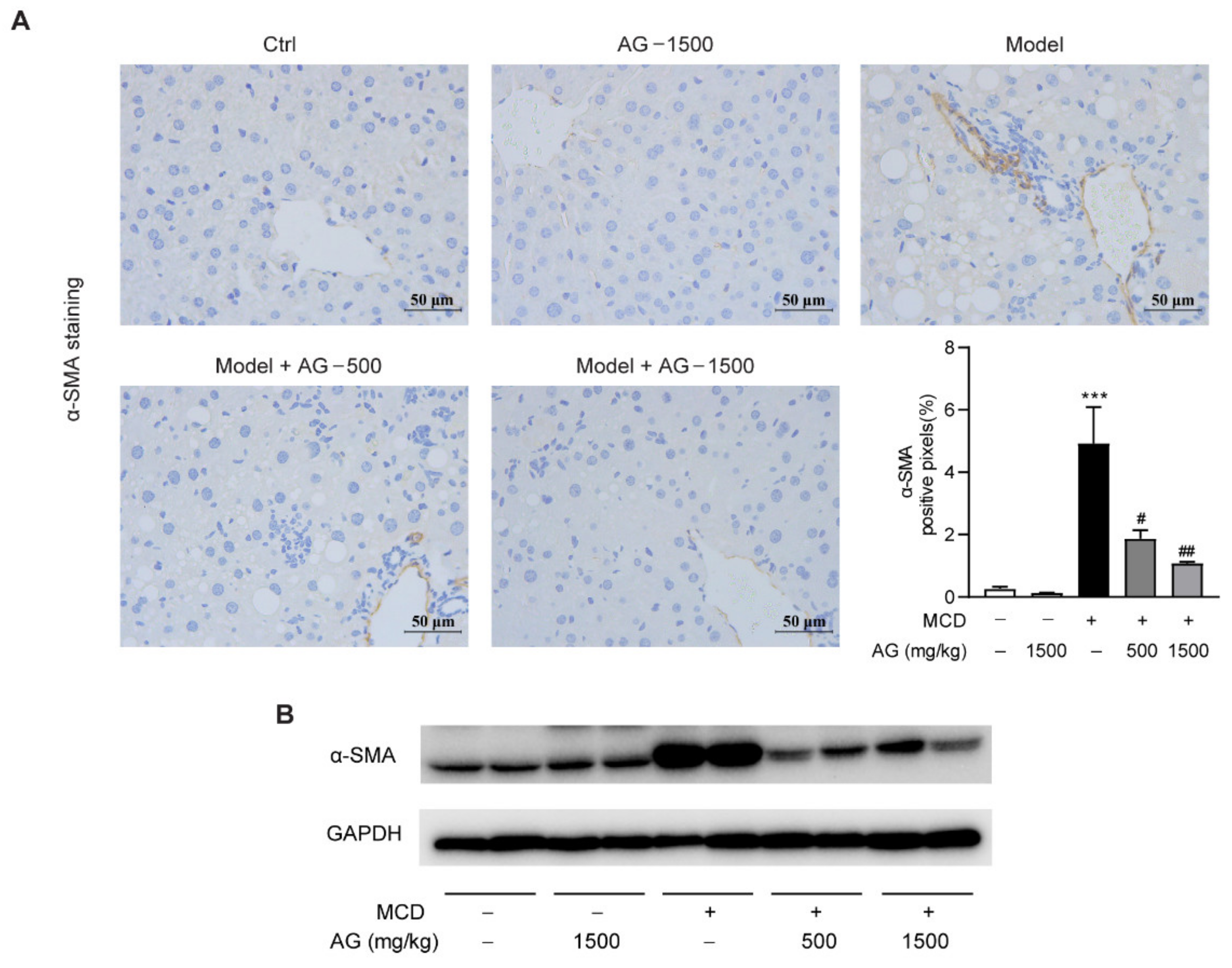
3.5. Ala-Gln Suppresses MCD-Induced Liver Fibrosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, B.; Sun, K.; Wang, H.; Qin, L.; Bai, F.; Leng, Y.; Tang, W. A new mechanism of obeticholic acid on NASH treatment by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophage. Metabolism 2021, 120, 154797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Kim, K.; Bartolome, A.; Dongiovanni, P.; Yates, K.P.; Valenti, L.; Carrer, M.; Sadowski, T.; et al. Hepatocyte TLR4 triggers inter-hepatocyte Jagged1/Notch signaling to determine NASH-induced fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabe1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wu, D.; Huang, X.; Chen, B.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tang, X.; Bai, T.; et al. Targeting epigenetically maladapted vascular niche alleviates liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternostro, R.; Trauner, M. Current treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Heianza, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, T.; Sun, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, F.B.; Rexrode, K.M.; Manson, J.E.; Qi, L. Dietary glutamine, glutamate and mortality: Two large prospective studies in US men and women. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizel, R.; Leite, J.S.; Hypolito, T.M.; Coqueiro, A.Y.; Newsholme, P.; Cruzat, V.F.; Tirapegui, J. Determination of the anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects of l-glutamine and l-alanine, or dipeptide, supplementation in rats submitted to resistance exercise. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lin, M.; Yu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, P.; Yang, W.; Gao, F.; Zhou, G. Alanyl-glutamine supplementation regulates mTOR and ubiquitin proteasome proteolysis signaling pathways in piglets. Nutrition 2016, 32, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coqueiro, A.Y.; Raizel, R.; Bonvini, A.; Rogero, M.M.; Tirapegui, J. Effects of glutamine and alanine supplementation on muscle fatigue parameters of rats submitted to resistance training. Nutrition 2019, 65, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrantelli, E.; Liappas, G.; Vila Cuenca, M.; Keuning, E.D.; Foster, T.L.; Vervloet, M.G.; Lopez-Cabrera, M.; Beelen, R.H. The dipeptide alanyl-glutamine ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis and attenuates IL-17 dependent pathways during peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, R.; Bartosova, M.; Tarantino, S.; Wagner, A.; Unterwurzacher, M.; Sacnun, J.M.; Lichtenauer, A.M.; Kuster, L.; Schaefer, B.; Alper, S.L.; et al. Peritoneal Dialysis Fluid Supplementation with Alanyl-Glutamine Attenuates Conventional Dialysis Fluid-Mediated Endothelial Cell Injury by Restoring Perturbed Cytoprotective Responses. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Son, D.O. Food-derived peptides and intestinal functions. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruzat, V.F.; Keane, K.N.; Scheinpflug, A.L.; Cordeiro, R.; Soares, M.J.; Newsholme, P. Alanyl-glutamine improves pancreatic beta-cell function following ex vivo inflammatory challenge. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 224, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Santos, R.; da Silva Cardoso, G.; da Costa Lima, L.; de Sousa Cavalcante, M.L.; Silva, M.S.; Cavalcante, A.K.M.; Severo, J.S.; de Melo Sousa, F.B.; Pacheco, G.; Alves, E.H.P.; et al. L-Glutamine and Physical Exercise Prevent Intestinal Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Without Improving Gastric Dysmotility in Rats with Ulcerative Colitis. Inflammation 2021, 44, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petry, E.R.; Dresch, D.F.; Carvalho, C.; Medeiros, P.C.; Rosa, T.G.; de Oliveira, C.M.; Martins, L.A.M.; Schemitt, E.; Bona, S.; Guma, F.C.R.; et al. Oral glutamine supplementation attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress-mediated skeletal muscle protein content degradation in immobilized rats: Role of 70kDa heat shock protein. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 145, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo Junior, R.J.; Silva Junior, R.G.; Vasconcelos, M.P.; Guimaraes, S.B.; Vasconcelos, P.R.; Garcia, J.H. Preconditioning with L-alanyl-glutamine reduces hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2011, 26 (Suppl. S1), 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ying, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y. Alanyl-Glutamine Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via Alleviating Oxidative Stress, Inhibiting Inflammation, and Regulating Autophagy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Zhao, Y. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of the effects of alanyl-glutamine supplementation on C2C12 myoblasts injured by energy deprivation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16114–16125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ying, H.; Yao, J.; Yang, L.; Jin, W.; Ma, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y. Micronized Palmitoylethanolamide Ameliorates Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis via Inhibiting Inflammation and Restoring Autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 744483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, S.; Khan, A.; Chan, S.M.H.; Mahzari, A.; Zhou, X.; Qin, C.X.; Vlahos, R.; Ye, J.M. Exposure to cigarette smoke precipitates simple hepatosteatosis to NASH in high-fat diet fed mice by inducing oxidative stress. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 2103–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska-Bouta, B.; Struzynska, L.; Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz, M.; Sulkowski, G. Memantine Modulates Oxidative Stress in the Rat Brain following Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, W.; Gan, L.; Liu, S.; Ni, Q.; Bi, Y.; Han, T.; Liu, Q.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; et al. Silencing HIF-1alpha aggravates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in vitro through inhibiting PPAR-alpha/ANGPTL4 singling pathway. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 44, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.X.; Wu, X.Q.; Li, X.F.; Ma, T.T.; Zhang, L.; Meng, X.M.; Li, J. Hyperin attenuates inflammation by activating PPAR-gamma in mice with acute liver injury (ALI) and LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.N.; Lee, Y.; Wu, D.; Pae, M. Luteolin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation via blocking ASC oligomerization. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 92, 108614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.; Hu, Y.; Hu, F.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Weng, Q.; Tian, S.; et al. Hepatocyte glutathione S-transferase mu 2 prevents non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by suppressing ASK1 signaling. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.H.; Feigh, M.; Veidal, S.S.; Rigbolt, K.T.; Vrang, N.; Fosgerau, K. Mouse models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in preclinical drug development. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Revelo, X.; Malhi, H. Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Overview. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, P.; Liu, B.; Ren, X.; Bian, H.; Xie, L.; et al. The Nuclear Orphan Receptor NR2F6 Promotes Hepatic Steatosis through Upregulation of Fatty Acid Transporter CD36. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2002273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, K.; Zhao, J.; Le, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, P.; Xiao, X.; et al. B-cell lymphoma 6 alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through suppression of fatty acid transporter CD36. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, E.; Melendez-Rodriguez, F.; Maranon, P.; Gil-Valle, M.; Carrasco, A.G.; Torres-Capelli, M.; Chavez, S.; Del Pozo-Maroto, E.; Rodriguez de Cia, J.; Aragones, J.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha drives hepatosteatosis through the fatty acid translocase CD36. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cai, J.; Gonzalez, F.J. The role of farnesoid X receptor in metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.Y.; Chen, S.M.; Pan, C.X.; Li, Y. FXR: Structures, biology, and drug development for NASH and fibrosis diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Biagioli, M.; Baldoni, M.; Ricci, P.; Sepe, V.; Zampella, A.; Distrutti, E. The identification of farnesoid X receptor modulators as treatment options for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, P.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.; Garcia-Monzon, C.; Valverde, A.M. Understanding lipotoxicity in NAFLD pathogenesis: Is CD36 a key driver? Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Xie, Z.F.; Song, Q.; Li, J.Y. Mitochondria homeostasis: Biology and involvement in hepatic steatosis to NASH. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ye, S.T.; Leng, Y.R.; Yang, T.; Zhang, H.; Kong, L.Y. Physalin B ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by stimulating autophagy and NRF2 activation mediated improvement in oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 164, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podszun, M.C.; Frank, J. Impact of vitamin E on redox biomarkers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.A.; Vasconcelos, P.R.; Souza, C.M.; Andrade, G.M.; Moraes, M.O.; Costa, P.E.; Coelho, G.R.; Garcia, J.H. L-Alanyl-Glutamine Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Liver Transplantation Patients. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 2478–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibaut, R.; Gage, M.C.; Pineda-Torra, I.; Chabrier, G.; Venteclef, N.; Alzaid, F. Liver macrophages and inflammation in physiology and physiopathology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 3024–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.; Cabrera, D.; Arrese, M.; Feldstein, A.E. Triggering and resolution of inflammation in NASH. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Usman, T.O.; Yamauchi, J.; Chhetri, G.; Wang, X.; Coudriet, G.M.; Zhu, C.; Gao, J.; McConnell, R.; Krantz, K.; et al. Myeloid FoxO1 depletion attenuates hepatic inflammation and prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreby, E.; Chen, P.; Aouadi, M. Macrophage functional diversity in NAFLD—More than inflammation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.R.A.; Albuquerque, A.O.; Silva, C.; Silva, J.M.; Casadevall, M.; Azevedo, O.G.R.; Albuquerque, V.; Vasconcelos, P.R.L. Preconditioning with L-Ala-Gln reduces the expression of inflammatory markers (TNF-alpha, NF-kappaB, IL-6 and HO-1) in an injury animal model of cerebrovascular ischemia in Meriones unguiculatus (gerbils). Acta Cir. Bras. 2020, 35, e202000601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; You, W.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Jin, Q.; Wei, C.; Wan, F.; Zhao, H. Alanyl-glutamine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and barrier function injury in bovine jejunum epithelial cells. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Ouyang, H.; Guo, Q.; Wei, M.; Lu, B.; Kai, G.; Ji, L. Chlorogenic acid alleviated liver fibrosis in methionine and choline deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice and its mechanism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 106, 109020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Lee, K.C.; Lei, H.J.; Lan, K.H.; Huo, T.I.; Lin, Y.T.; Chan, C.C.; Schnabl, B.; Huang, Y.H.; Hou, M.C.; et al. (Pro)renin Receptor Knockdown Attenuates Liver Fibrosis Through Inactivation of ERK/TGF-beta1/SMAD3 Pathway. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Tang, Q.; Yang, X.; et al. Inhibition of 5-Lipoxygenase in Hepatic Stellate Cells Alleviates Liver Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 628583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Tabas, I.; Pajvani, U.B. Mechanisms of Fibrosis Development in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Park, E.Y.; Ku, S.K.; Cho, I.J.; Yang, J.H.; Ki, S.H. REDD1 attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis via inhibiting of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 176, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ying, H.; Ma, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y. Alanyl-Glutamine Protects Mice against Methionine- and Choline-Deficient-Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183796
Hu J, Zheng Y, Ying H, Ma H, Li L, Zhao Y. Alanyl-Glutamine Protects Mice against Methionine- and Choline-Deficient-Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183796
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jiaji, Yigang Zheng, Hanglu Ying, Huabin Ma, Long Li, and Yufen Zhao. 2022. "Alanyl-Glutamine Protects Mice against Methionine- and Choline-Deficient-Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183796
APA StyleHu, J., Zheng, Y., Ying, H., Ma, H., Li, L., & Zhao, Y. (2022). Alanyl-Glutamine Protects Mice against Methionine- and Choline-Deficient-Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Nutrients, 14(18), 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183796





