Burden of Nutritional Deficiencies in China: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Framework of the GBD 2019 Study
2.2. Data Sources of the China Study
2.3. Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
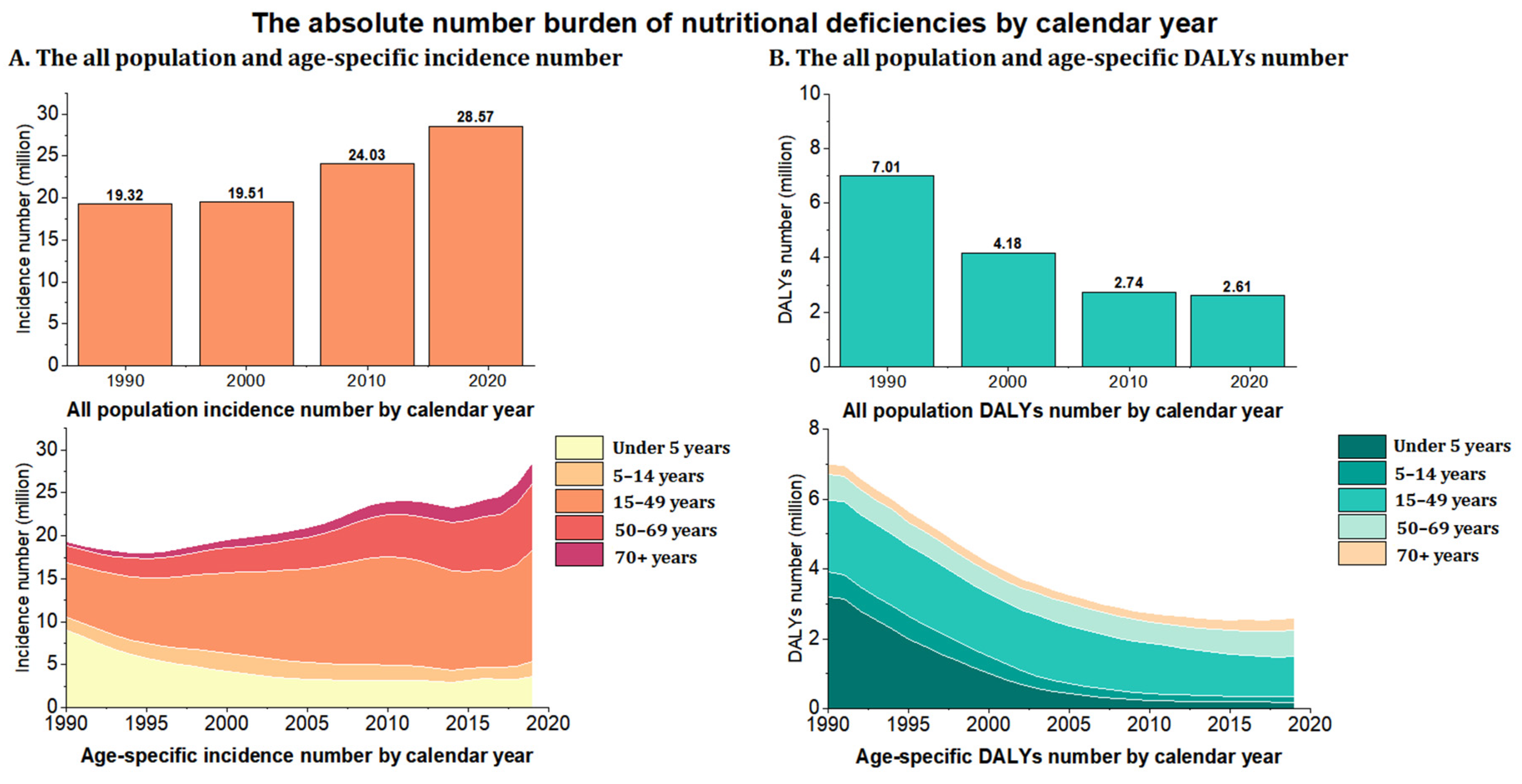
3.1. China’s Burden of Overall Nutritional Deficiency from 1990 to 2019
3.2. China’s Burden of Nutritional Deficiency from 1990 to 2019 by Subcategories of Nutritional Deficiency
3.3. Burden of Overall Nutritional Deficiency from 1990 to 2019 at the Provincial Level
3.4. Burden of Subcategories of Nutritional Deficiency from 1990 to 2019 at the Provincial Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jile, C.; Yu, W. Chinese Nutrition and Health Status Survey Report: 2010–2013 Comprehensive Report; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Secular trends in dietary micronutrient intakes and demographic characteristics of adults in nine provinces (autonomous regions) of China from 1991 to 2015. Chin. J. Environ. Occup. Med. 2019, 36, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- General Office of the State Council. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/201707/13/content_5210199.htm (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, O.B.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Lopez, A.D.; Murray, C.J.; Inoue, M. Age Standardization of Rates: A New WHO Standard; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/paper31.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Fang, Q.; Cai, N.; Suo, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X. The trends in incidence of primary liver cancer caused by specific etiologies: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 and implications for liver cancer prevention. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obatolu, V.A. Growth pattern of infants fed with a mixture of extruded malted maize and cowpea. Nutrition 2003, 19, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Cheng, H.S.; Liang, J.; Wu, C.C.; Shyu, Y.I. Functional recovery of older people with hip fracture: Does malnutrition make a difference? J. Adv. Nurs. 2013, 69, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaunyte, I.; Stojceska, V.; Plunkett, A. Iron and the female athlete: A review of dietary treatment methods for improving iron status and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helman, S.L.; Anderson, G.J.; Frazer, D.M. Dietary iron absorption during early postnatal life. Biometals 2019, 32, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Weaver, C.M. Decreased Iron Intake Parallels Rising Iron Deficiency Anemia and Related Mortality Rates in the US Population. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1947–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shen, X.; Fang, A.; Song, J.; Li, H.; Guo, M.; Li, K. Association between predominantly plant-based diets and iron status in Chinese adults: A cross-sectional analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Hurrell, R.F. Nutritional iron deficiency. Lancet 2007, 370, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.L.; Heath, A.L. Dietary approaches to assessing iron-related nutrition. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.L.; Conlon, C.A.; Kruger, R.; Coad, J. Dietary determinants of and possible solutions to iron deficiency for young women living in industrialized countries: A review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3747–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, T.; Cheng, Q.; Li, T. Vitamin A Levels among Pre-School Children of Central and Western China. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 694106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Chang, X.; Wang, M.; An, L. The Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency in Chinese Children: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yang, L. Serum Vitamin A Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescents Aged 6–17 Years—China, 2016–2017. China CDC Wkly. 2021, 3, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Q.; Yu, L.; Yang, T.; Chen, J.; Miao, J.; Li, T. Changes in Vitamin A Levels and the Effect of Early Vitamin A Supplementation on Vitamin A Levels in Infants throughout the First 6 Months of Life: A Prospective Cohort Study in Chongqing, China. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 650823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.X.; Lin, L.M.; Lian, G.L.; Greiner, T. Vitamin A deficiency and child feeding in Beijing and Guizhou, China. World J. Pediatr. 2008, 4, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, R.E.; Kachurak, A.; Davison, K.K.; Klabunde, R.; Fisher, J.O. Food parenting and child snacking: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Lou, X.; Ding, G.; Mo, Z.; Zhu, W.; Mao, G. A cross-sectional comparison study on the iodine nutritional status between rural and urban residents in Zhejiang Province, China. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yue, A.; Zhang, L.; Sylvia, S.; Medina, A.; Rozelle, S. Micronutrient deficiencies and developmental delays among infants: Evidence from a cross-sectional survey in rural China. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M. Mood, food, and obesity. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havermans, R.C.; Vancleef, L.; Kalamatianos, A.; Nederkoorn, C. Eating and inflicting pain out of boredom. Appetite 2015, 85, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, A.C.; Myhre, S.K.; Rokke, P.D. Boredom proneness and emotion regulation predict emotional eating. J. Health Psychol. 2015, 20, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.J.; Barrientos, R.M. The impact of nutrition on COVID-19 susceptibility and long-term consequences. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiten, D.J.; Namasté, S.; Brabin, B.; Combs, G., Jr.; L’Abbe, M.R.; Wasantwisut, E.; Darnton-Hill, I. Executive summary—Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development: Building a Consensus. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 633s–650s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corish, C.A.; Bardon, L.A. Malnutrition in older adults: Screening and determinants. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Incidence | DALYs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case (Thousands) | Percentage Change in Absolute Numbers, 1990–2019 | Age-Standardized Incidence Rates (per 100,000) | EAPC 1990–2019 | Case (Thousands) | Percentage Change in Absolute Numbers, 1990–2019 | Age-Standardized DALYs Rates (per 100,000) | EAPC 1990–2019 | |
| Overall | ||||||||
| Overall nutritional deficiencies | 28,569.88 (22,553.25, 35,422.13) | 47.90% | 2058.90 (1633.50, 2570.63) | 0.11 (−0.19, 0.41) | 2606.93 (1815.57, 3659.29) | −62.80% | 174.78 (122.20, 241.15) | −5.54 (−5.96, −5.12) |
| Protein-energy malnutrition | 27,834.27 (21,809.61, 34,701.83) | 50.29% | 1996.51(1570.05,2498.19) | 0.08(−0.23,0.40) | 790.44(551.66,1082.06) | −73.85% | 54.57(39.44,74.30) | −6.93 (−7.65,−6.20) |
| Iodine deficiency | 735.61 (574.29, 917.58) | −7.76% | 62.40 (48.58, 78.16) | 0.63(0.10,1.16) | 264.71 (122.77, 521.29) | 9.84% | 15.57 (7.16, 30.67) | −0.64 (−1.00, −0.28) |
| Vitamin A deficiency | 25,263.60 (21,390.09, 30,021.08) | −79.35% | 2113.34 (1764.06, 2553.64) | −5.83 (−6.17, −5.48) | 40.32 (25.94, 61.11) | −67.30% | 3.69 (2.34, 5.55) | −4.29 (−4.66, −3.93) |
| Dietary iron deficiency | - | - | - | - | 1206.62 (764.18, 1842.70) | −64.05% | 80.69 (51.12, 122.73) | −5.88 (−6.16, −5.60) |
| Other nutritional deficiency | - | - | - | - | 304.83 (210.26, 419.73) | 14.67% | 20.26 (14.30, 27.86) | 0.68 (0.00, 1.37) |
| Under 5 years | ||||||||
| Overall nutritional deficiencies | 3597.19 (2597.14, 5101.01) | −60.26% | 4414.22 (3187.04, 6259.62) | −2.63 (−3.10, −2.16) | 182.42 (131.15, 253.72) | −94.31% | 223.85 (160.94, 311.35) | −10.53 (−11.00, −10.06) |
| Protein-energy malnutrition | 3587.61 (2589.36, 5091.06) | −60.23% | 4402.47 (3177.49, 6247.40) | −2.63 (−3.09, −2.16) | 56.01 (44.72, 68.00) | −97.77% | 68.74 (54.88, 83.45) | −13.86 (−14.15, −13.56) |
| Iodine deficiency | 9.58 (4.85, 16.76) | −68.81% | 11.75 (5.96, 20.56) | −2.83 (−3.71, −1.95) | 0.17 (0.06, 0.37) | −82.85% | 0.21 (0.08, 0.46) | −5.95 (−7.53, −4.33) |
| Vitamin A deficiency | 3140.90 (1924.50, 4995.49) | −85.35% | 3854.30 (2361.61, 6130.12) | −5.10 (−5.28, −4.92) | 9.91 (6.08, 15.04) | −81.81% | 12.16 (7.46, 18.45) | −5.35 (−5.76, −4.94) |
| Dietary iron deficiency | - | - | - | - | 98.85 (54.38, 158.00) | −81.34% | 121.30 (66.74, 193.89) | −5.43 (−5.86, −5.00) |
| Other nutritional deficiency | - | - | - | - | 17.48 (14.36, 21.30) | −83.44% | 21.45 (17.62, 26.14) | −2.09 (−3.20, −0.96) |
| 5–14 years | ||||||||
| Overall nutritional deficiencies | 1848.40 (1234.20, 2677.74) | 22.06% | 1290.64 (1220.22, 1361.05) | 1.12 (0.52, 1.72) | 160.13 (99.97, 241.65) | −77.44% | 111.66 (90.95, 132.37) | −5.23 (−5.55, −4.90) |
| Protein-energy malnutrition | 1762.30 (1153.92, 2593.48) | 34.38% | 1230.33 (1161.58, 1299.08) | 1.46 (0.78, 2.15) | 46.89 (25.91, 78.49) | −45.52% | 32.71 (21.50, 43.92) | −3.13 (−3.58, −2.67) |
| Iodine deficiency | 86.10 (61.30, 123.27) | −57.57% | 60.31 (45.09, 75.53) | −1.23 (−1.42, −1.03) | 3.84 (1.54, 8.02) | −81.55% | 2.69 (2.58, 2.82) | −5.28 (−6.63, −3.91) |
| Vitamin A deficiency | 4761.74 (3178.29, 6904.21) | −83.19% | 3320.22 (3207.28, 3433.16) | −4.87 (−5.30, −4.44) | 8.59 (4.87, 13.70) | −83.13% | 5.99 (5.81, 6.17) | −5.83 (−6.13, −5.52) |
| Dietary iron deficiency | - | - | - | - | 88.43 (48.73, 146.05) | −83.52% | 61.64 (46.25, 77.03) | −6.04 (−6.37, −5.71) |
| Other nutritional deficiency | - | - | - | - | 12.37 (7.12, 20.08) | −18.80% | 8.64(8.42,8.85) | 0.46 (−0.15, 1.07) |
| 15–49 years | ||||||||
| Overall nutritional deficiencies | 12,879.45 (10,024.63, 16,436.56) | 103.12% | 1759.71 (1677.49, 1841.93) | 1.51 (1.13, 1.90) | 1147.82 (750.82, 1663.03) | −44.33% | 153.02 (128.77, 177.26) | −3.62 (−3.83, −3.42) |
| Protein-energy malnutrition | 12,290.17 (9446.15, 15755.84) | 111.84% | 1664.20 (1584.24, 1744.16) | 1.54 (1.17, 1.90) | 306.02 (190.85, 458.77) | 37.50% | 41.26 (28.67, 53.85) | −0.95 (−1.30, −0.61) |
| Iodine deficiency | 589.28 (443.55, 767.32) | 9.29% | 95.51 (76.35, 114.66) | 1.32 (0.56, 2.09) | 168.23 (76.25, 336.26) | −5.02% | 22.07 (12.86, 31.28) | −0.40 (−0.78, −0.02) |
| Vitamin A deficiency | 14,682.02 (11,497.90, 18,280.38) | −78.16% | 2131.16 (2040.68, 2221.64) | −5.25 (−5.56, −4.93) | 14.03 (8.21, 22.83) | −7.32% | 2.01 (1.93, 2.10) | −0.57 (−0.96, −0.17) |
| Dietary iron deficiency | - | - | - | - | 522.77 (318.09, 821.77) | −66.27% | 68.74 (52.49, 84.99) | −5.98 (−6.23, −5.73) |
| Other nutritional deficiency | - | - | - | - | 136.77 (85.38, 204.73) | 40.92% | 18.93 (18.66, 19.20) | 1.07 (0.37, 1.78) |
| 50–69 years | ||||||||
| Overall nutritional deficiencies | 7726.77 (5914.47, 9892.05) | 310.71% | 2095.03 (2005.31, 2184.74) | 1.58 (1.35, 1.80) | 757.12 (1069.07, 504.77) | 2.84% | 205.05 (176.98, 233.12) | −3.61 (−3.89, −3.34) |
| Protein-energy malnutrition | 7682.50 (5864.79, 9852.02) | 313.23% | 2083.01 (1993.55, 2172.46) | 1.59 (1.37, 1.82) | 209.16 (300.56, 135.50) | 117.75% | 56.68 (41.92, 71.43) | −1.41 (−1.89, −0.92) |
| Iodine deficiency | 44.27 (24.80, 72.68) | 99.82% | 12.02 (11.80, 12.24) | −0.82(−0.87,−0.77) | 77.00 (151.38, 35.01) | 115.52% | 20.86 (11.91, 29.82) | −0.27 (−0.67, 0.13) |
| Vitamin A deficiency | 2393.86 (1663.13, 3407.80) | −49.66% | 646.79 (596.94, 696.64) | −5.31 (−5.53, −5.09) | 6.03 (9.47, 3.60) | 177.83% | 1.63 (1.55, 1.71) | 1.05 (0.79, 1.30) |
| Dietary iron deficiency | - | - | - | - | 377.00 (580.16, 219.71) | −33.54% | 102.10 (82.29, 121.90) | −5.59 (−5.84, −5.35) |
| Other nutritional deficiency | - | - | - | - | 87.92 (126.47, 57.01) | 151.39% | 23.78 (14.22, 33.34) | 0.99 (−0.07, 2.07) |
| 70+ years | ||||||||
| Overall nutritional deficiencies | 2518.07 (1878.90, 3321.93) | 375.67% | 2328.89 (2234.30, 2423.48) | 1.66 (1.46, 1.87) | 359.44 (285.47, 450.28) | 21.40% | 345.89 (309.44, 382.35) | −3.43 (−3.96, −2.90) |
| Protein-energy malnutrition | 2511.69 (1872.02, 3312.45) | 376.73% | 2323.02 (2228.55, 2417.48) | 1.67(1.46,1.88) | 172.36(142.93,206.28) | 66.34% | 170.13(144.57,195.70) | −2.33(−3.11,−1.54) |
| Iodine deficiency | 6.39(3.52,10.49) | 153.60% | 5.87 (5.62, 6.14) | −0.38 (−0.40, −0.35) | 15.48 (7.26, 29.58) | 143.82% | 14.22 (13.82, 14.64) | −0.54 (−0.92, −0.16) |
| Vitamin A deficiency | 285.08(201.53,399.51) | −54.51% | 262.40(230.65,294.15) | −6.09(−6.25,−5.93) | 1.75(0.98,2.86) | 204.40% | 1.61 (1.48, 1.75) | 0.90 (0.63, 1.16) |
| Dietary iron deficiency | - | - | - | - | 119.57 (72.20, 185.77) | −30.71% | 111.35 (90.67, 132.03) | −6.38 (−6.73, −6.02) |
| Other nutritional deficiency | - | - | - | - | 304.83 (210.26, 304.83) | 287.44% | 21.43 (14.78, 29.51) | 1.86 (1.14, 2.58) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, R.; Hao, Y.; Jiao, M.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M. Burden of Nutritional Deficiencies in China: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193919
Han L, Zhao T, Zhang R, Hao Y, Jiao M, Wu Q, Liu J, Zhou M. Burden of Nutritional Deficiencies in China: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193919
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Liyuan, Tian Zhao, Ruijie Zhang, Yanhua Hao, Mingli Jiao, Qunhong Wu, Jingjing Liu, and Maigeng Zhou. 2022. "Burden of Nutritional Deficiencies in China: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193919
APA StyleHan, L., Zhao, T., Zhang, R., Hao, Y., Jiao, M., Wu, Q., Liu, J., & Zhou, M. (2022). Burden of Nutritional Deficiencies in China: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Nutrients, 14(19), 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193919






