Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Clinical Relevance in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Shanghai Aging Study and Shanghai Memory Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Demographics and Assessment of Covariables
2.3. Neuropsychological Assessment
2.4. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.5. PCR Amplification and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.6. Processing of Sequencing Data
2.7. Alpha and Beta Diversity Analyses
2.8. LEfSe Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
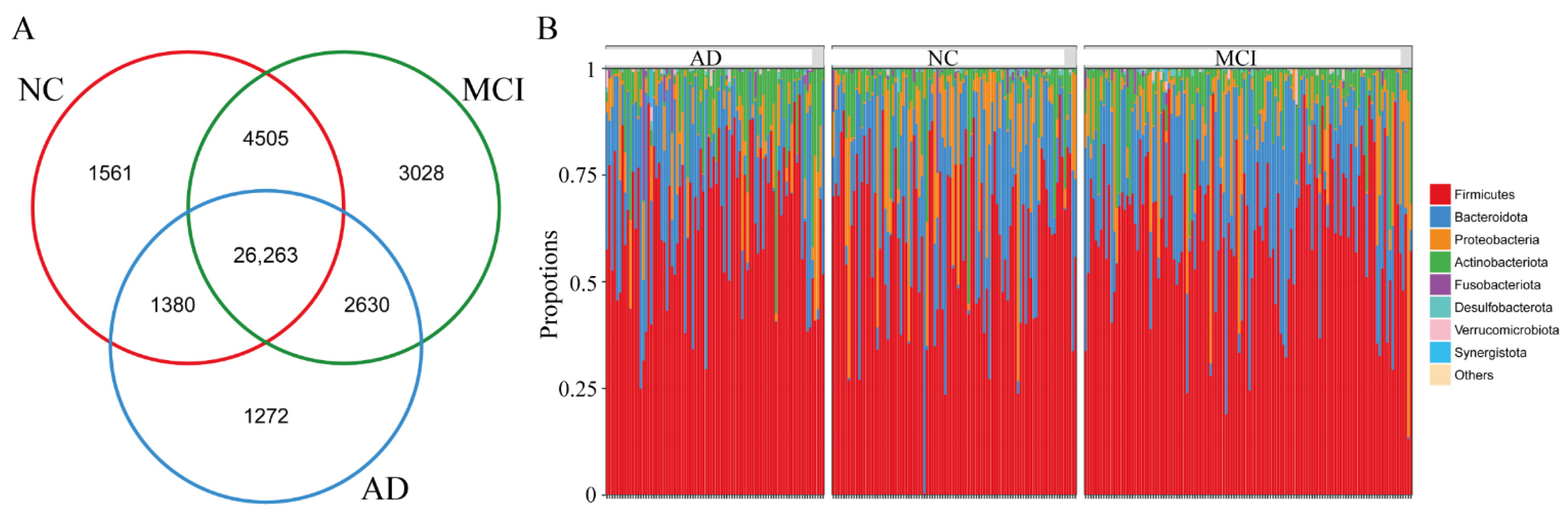
3.2. The Overall Structure of Gut Microbiota among NC, MCI, and AD
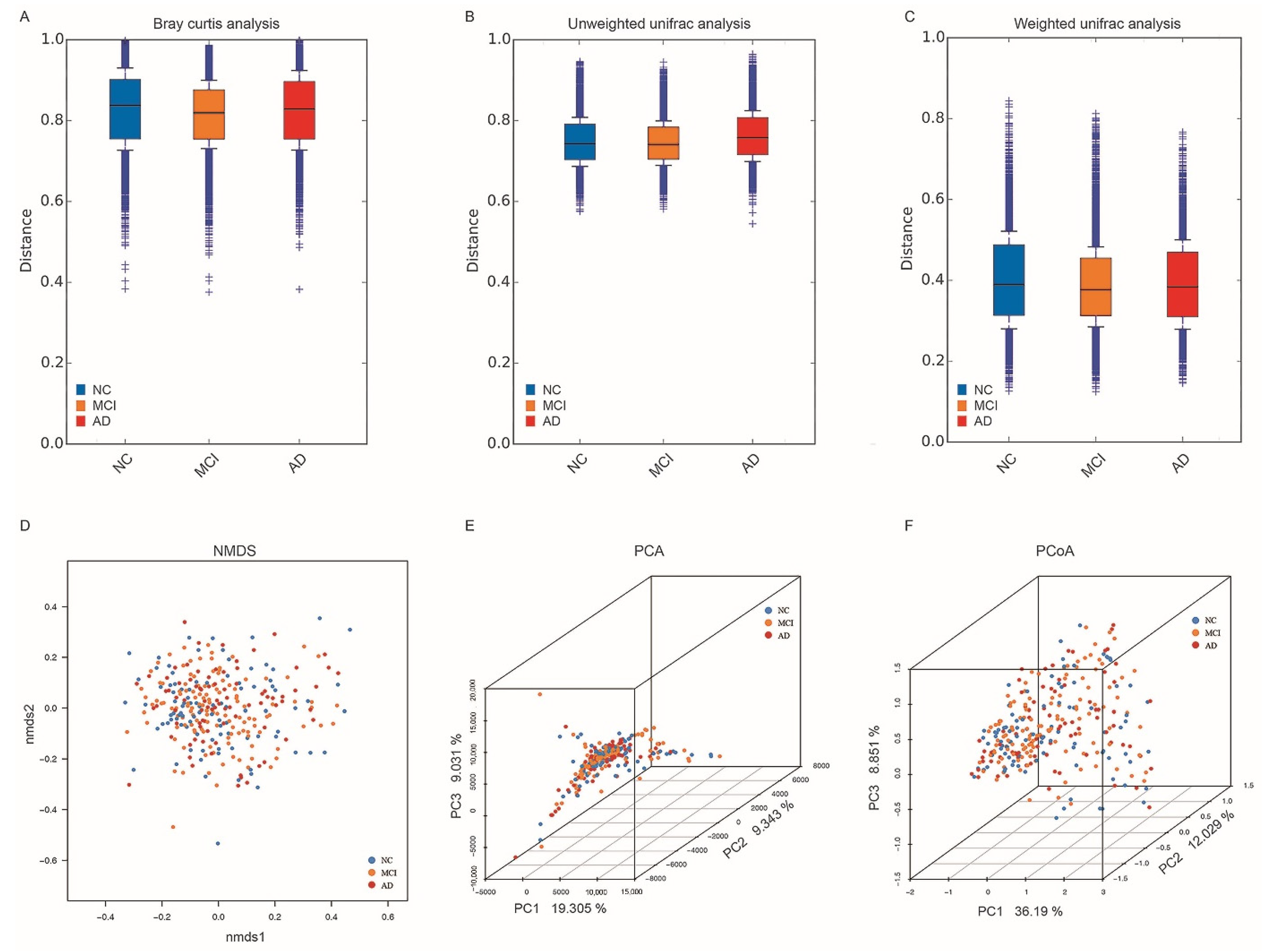
3.3. Alpha and Beta Diversity in NC, MCI, and AD
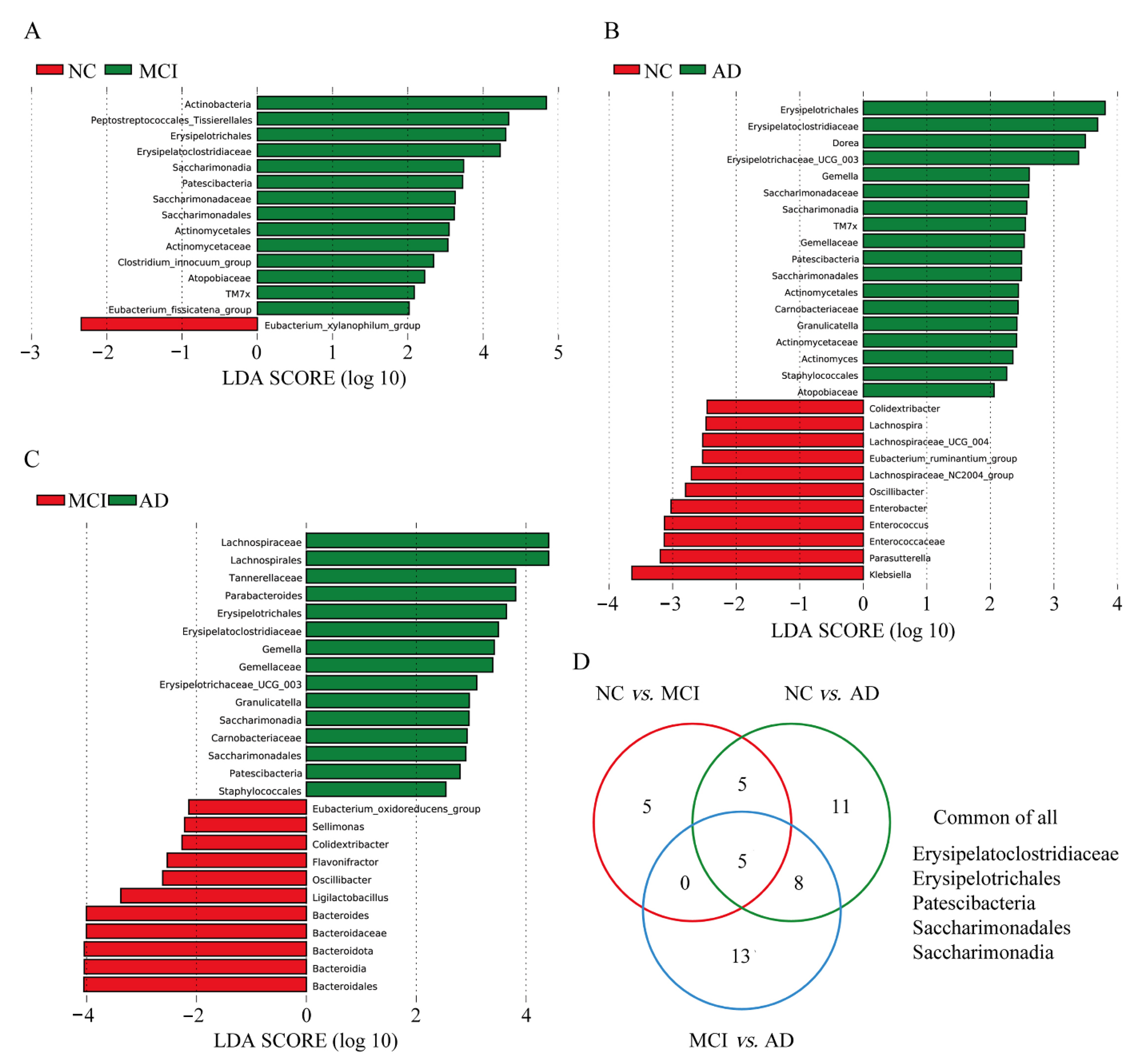
3.4. Differences in Specific Microbiota of NC, MCI, and AD
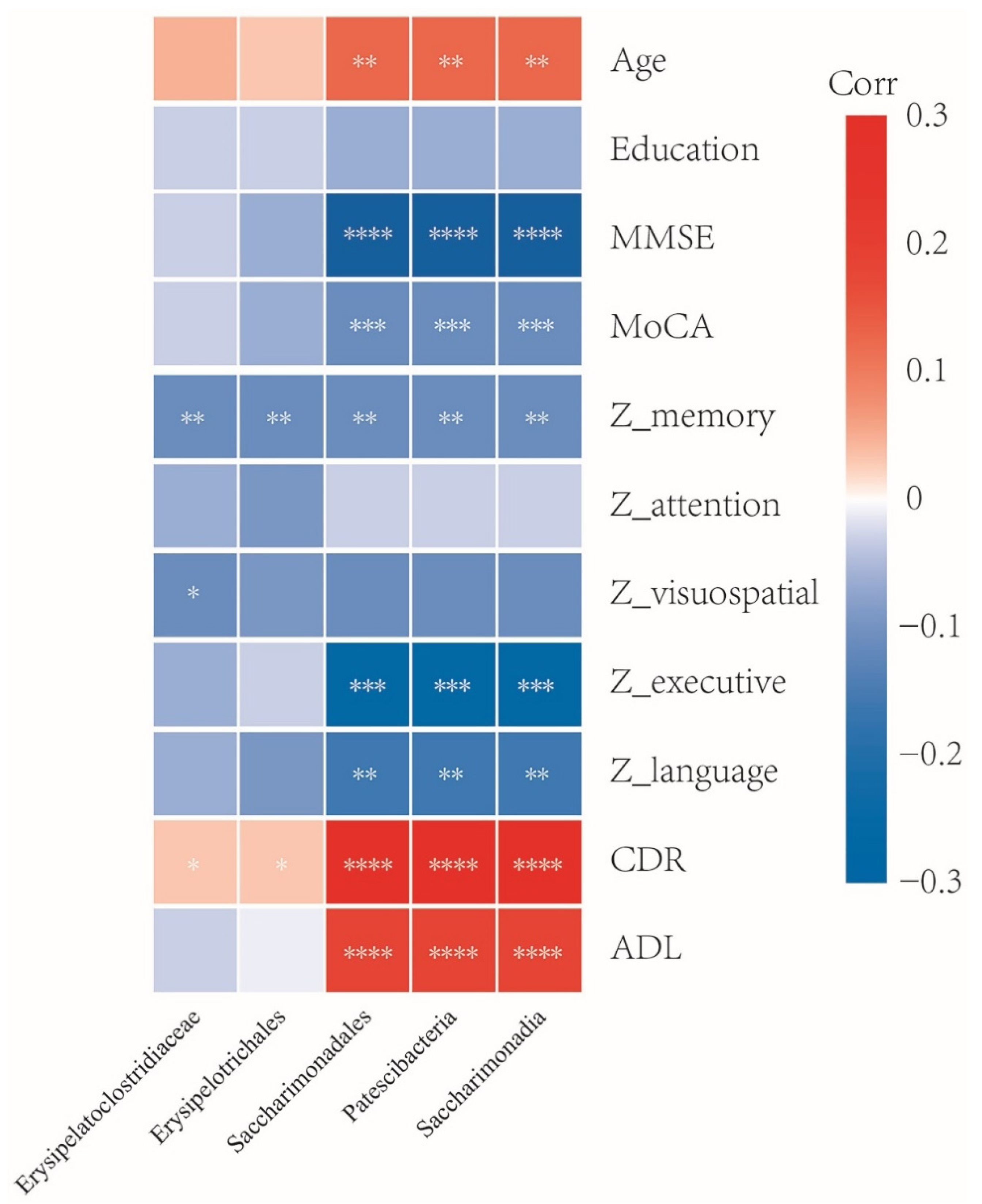
3.5. Association between Gut Microbiota and Clinical Characteristics
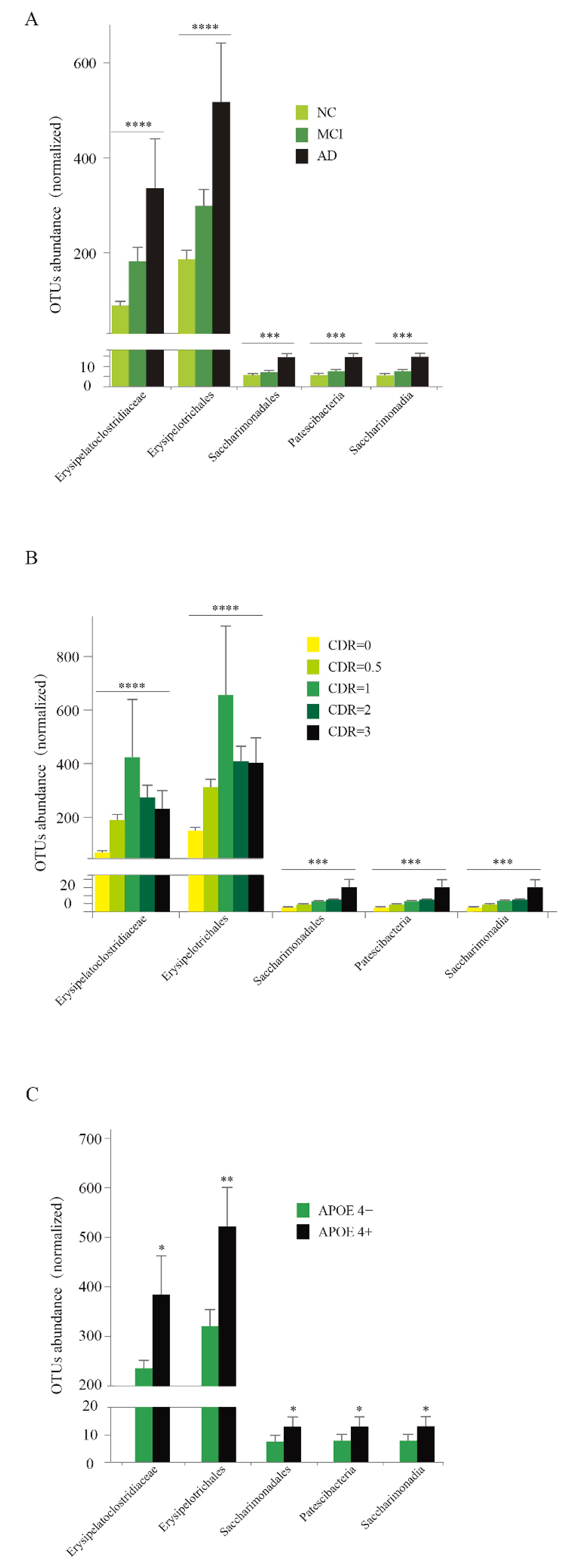
3.6. Abundance Analysis of Five Specific Taxa
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chételat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldırım, S.; Nalbantoğlu, U.; Bayraktar, A.; Ercan, F.B.; Gündoğdu, A.; Velioğlu, H.A.; Göl, M.F.; Soylu, A.E.; Koç, F.; Gülpınar, E.A.; et al. Stratification of the Gut Microbiota Composition Landscape across the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum in a Turkish Cohort. mSystems 2022, 7, e0000422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Chipi, E.; Salvadori, N.; D’Andrea, K.; Eusebi, P. Prevalence and risk of progression of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease stages: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.-Q.; Shen, L.-L.; Li, W.-W.; Fu, X.; Zeng, F.; Gui, L.; Lü, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhu, C.; Tan, Y.-L.; et al. Gut Microbiota is Altered in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Sandhu, K.; Peterson, V.; Dinan, T.G. The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ikram, M.; Park, J.S.; Park, T.J.; Kim, M.O. Gut Microbiota, Its Role in Induction of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology, and Possible Therapeutic Interventions: Special Focus on Anthocyanins. Cells 2020, 9, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Han, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Peng, G.; Liu, P.; Yue, S.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Lv, H.; Shao, L.; et al. Altered Gut Microbial Metabolites in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Signals in Host–Microbe Interplay. Nutrients 2021, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Neth, B.J.; Wang, S.; Mishra, S.P.; Craft, S.; Yadav, H. Gut mycobiome and its interaction with diet, gut bacteria and alzheimer’s disease markers in subjects with mild cognitive impairment: A pilot study. eBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naomi, R.; Embong, H.; Othman, F.; Ghazi, H.F.; Maruthey, N.; Bahari, H. Probiotics for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varesi, A.; Pierella, E.; Romeo, M.; Piccini, G.B.; Alfano, C.; Bjørklund, G.; Oppong, A.; Ricevuti, G.; Esposito, C.; Chirumbolo, S.; et al. The Potential Role of Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Peng, J.; Huang, X.; Xiao, L.; Huang, F.; Zuo, Z. Gut Microbiome Features of Chinese Patients Newly Diagnosed with Alzheimer’s Disease or Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 80, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; Lin, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Liu, S.-L. Altered Gut Microbiota in Adults with Subjective Cognitive Decline: The SILCODE Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 82, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Quan, M.; Zhao, H.; Jia, J. Gut Microbiota Changes and Their Correlation with Cognitive and Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 81, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, Y.; Ma, J.; Huang, P.; Du, J.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Tang, H.; Chen, S. Mild cognitive impairment has similar alterations as Alzheimer’s disease in gut microbiota. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 15, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wu, L.; Peng, G.; Han, Y.; Tang, R.; Ge, J.; Zhang, L.; Jia, L.; Yue, S.; Zhou, K.; et al. Altered microbiomes distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from amnestic mild cognitive impairment and health in a Chinese cohort. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, Q.; Meng, H.; Wang, B.; Yu, P.; Luo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, L.; Zheng, L.; et al. The Shanghai Aging Study: Study Design, Baseline Characteristics, and Prevalence of Dementia. Neuroepidemiology 2014, 43, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wu, X.; Wu, W.; Yi, J.; Liang, X.; Ding, S.; Zheng, L.; Luo, J.; Gu, H.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Plasma biomarker profiles and the correlation with cognitive function across the clinical spectrum of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, D. Cochrane Review Summary: Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of dementia in clinically unevaluated people aged 65 and over in community and primary care populations. Prim. Health Care Res. Dev. 2017, 18, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jia, J.; Yang, Z. Mini-Mental State Examination in Elderly Chinese: A Population-Based Normative Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 53, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julayanont, P.; Tangwongchai, S.; Hemrungrojn, S.; Tunvirachaisakul, C.; Phanthumchinda, K.; Hongsawat, J.; Suwichanarakul, P.; Thanasirorat, S.; Nasreddine, Z.S. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Basic: A Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment in Illiterate and Low-Educated Elderly Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 2550–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhao, Q.; Li, F.; Guo, Q. Short-term delayed recall of auditory verbal learning test provides equivalent value to long-term delayed recall in predicting MCI clinical outcomes: A longitudinal follow-up study. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2020, 27, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.; Berg, J.-L.; Banks, S.J.; Kaylegian, J.; Miller, J.B. Comparing the Boston Naming Test With the Neuropsychological Assessment Battery–Naming Subtest in a Neurodegenerative Disease Clinic Population. Assessment 2019, 28, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Shi, J.; Li, T.; Ni, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Kang, S.; Ma, F.; Xie, H.; Mingqing, W.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Chinese Version of the Trail-Making Test for Screening Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 66, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-N.; Wang, P.-N.; Chen, C.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Kuo, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-Y.; Liu, H.-C. The Three-Item Clock-Drawing Test: A Simplified Screening Test for Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. Neurol. 2003, 49, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C. The Clinical Dementia Rating (cdr): Current Version and Scoring Rules. Neurology 1991, 41, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Goebel, B.M. Taxonomic Note: A Place for DNA-DNA Reassociation and 16S rRNA Sequence Analysis in the Present Species Definition in Bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1994, 44, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Ahmed, M.I.; Zou, X.; Hussain, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, F.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Beef, Casein, and Soy Proteins Differentially Affect Lipid Metabolism, Triglycerides Accumulation and Gut Microbiota of High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, B.J.H.; Hendriksen, H.M.A.; de Leeuw, F.A.; Doorduijn, A.S.; van Leeuwenstijn, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Kraaij, R.; van Duijn, C.M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Related to AD Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 794519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; Yang, K.; He, B.; Du, W.; Cai, Y.; Han, Y. Combination of gut microbiota and plasma amyloid-β as a potential index for identifying preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: A cross-sectional analysis from the SILCODE study. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Ko, B.-S.; Ryuk, J.A.; Park, S. Tetragonia tetragonioides Protected against Memory Dysfunction by Elevating Hippocampal Amyloid-β Deposition through Potentiating Insulin Signaling and Altering Gut Microbiome Composition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O. Insights into the Role of Erysipelotrichaceae in the Human Host. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, P.; Leung, F.C. Complete genome assembly and characterization of an outbreak strain of the causative agent of swine erysipelas—Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae SY1027. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Jiang, R.; Xie, W.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Gao, J.; Jia, Y.; Bai, Q. Intestinal Pathology and Gut Microbiota Alterations in a Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 1986–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, J.; Cheng, S.; Su, J.; Duan, X.; Gao, M.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Silicon dioxide nanoparticles induced neurobehavioral impairments by disrupting microbiota–gut–brain axis. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovnikova, I.; Gureev, A.; Ignatyeva, D.; Gryaznova, M.; Chernyshova, E.; Krutskikh, E.; Novikova, A.; Popov, V. Nrf2/ARE Activators Improve Memory in Aged Mice via Maintaining of Mitochondrial Quality Control of Brain and the Modulation of Gut Microbiome. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liao, J.; Xia, Y.; Liu, X.; Jones, R.; Haran, J.; McCormick, B.; Sampson, T.R.; Alam, A.; Ye, K. Gut microbiota regulate Alzheimer’s disease pathologies and cognitive disorders via PUFA-associated neuroinflammation. Gut 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, C.L.; Weir, T.L. The gut microbiota at the intersection of diet and human health. Science 2018, 362, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Rampelli, S.; Jeffery, I.B.; Santoro, A.; Neto, M.; Capri, M.; Giampieri, E.; Jennings, A.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; et al. Mediterranean diet intervention alters the gut microbiome in older people reducing frailty and improving health status: The NU-AGE 1-year dietary intervention across five European countries. Gut 2020, 69, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontifex, M.; Vauzour, D.; Minihane, A.-M. The effect of APOE genotype on Alzheimer’s disease risk is influenced by sex and docosahexaenoic acid status. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 69, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118, Correction in Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, S.C.; Pa, J.; Kukull, W.; Beekly, D.; Kuzma, A.; Gangadharan, P.; Wang, L.-S.; Romero, K.; Arneric, S.P.; Redolfi, A.; et al. Apolipoprotein E Genotype and Sex Risk Factors for Alzheimer Disease: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.T.; Corsini, S.; Kellingray, L.; Hegarty, C.; Le Gall, G.; Narbad, A.; Müller, M.; Tejera, N.; O’Toole, P.W.; Minihane, A.-M.; et al. APOE genotype influences the gut microbiome structure and function in humans and mice: Relevance for Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8221–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total (n = 302) | Clinical Diagnosis | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC (n = 94) | MCI (n = 125) | AD (n = 83) | |||
| Gender, female, n (%) | 187(61.9) | 58(61.7) | 76(60.8) | 53(63.9) | 0.905 |
| Age, yr, mean (SD) | 74.1(8.7) | 74.3(10.6) | 75.4(7.1) | 71.8 (8.3) &* | 0.004 |
| Education, yr, mean (SD) | 11.3(3.9) | 12.4(3.8) | 11.3(3.6) # | 9.9(4.1) & | <0.001 |
| APOE 4 positive, n (%) | 93(32.7) | 8(8.9) | 33(29.5) # | 52(63.4) &* | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 142(47.2) | 55(58.5) | 54(43.2) | 33(40.2) & | 0.027 |
| SBP, mmHg, median [Q1, Q3] | 140.0 [127.8, 152.0] | 142.0 [129.0, 153.0] | 139.5 [127.0, 152.0] | 138.0 [125.0, 152.5] | 0.307 |
| DBP, mmHg, median [Q1, Q3] | 76.0 [70.0, 83.0] | 78.0 [70.0, 84.0] | 75.5 [69.0, 83.0] | 75.0 [70.5, 81.5] | 0.782 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 43(14.3) | 13(13.8) | 20(16.0) | 10(12.2) | 0.738 |
| Stroke, n (%) | 48(15.9) | 11(11.7) | 25(20.0) | 12(14.6) | 0.234 |
| Alcohol intake, n (%) | 39(13.0) | 11(11.7) | 18(14.5) | 10(12.2) | 0.803 |
| MMSE score, median [Q1, Q3] | 27.0 [23.0, 29.0] | 29.0 [28.0, 30.0] | 27.0 [26.0, 29.0] # | 19.0 [14.0, 22.0] &* | <0.001 |
| MoCA score, median [Q1, Q3] | 20.0 [15.0, 24.0] | 25.0 [23.0, 27.0] | 22.0 [19.0, 24.0] # | 12.0 [7.5, 17.0] &* | <0.001 |
| ADL score, median [Q1, Q3] | 20.0 [20.0, 22.0] | 20.0 [20.0, 21.0] | 20.0 [20.0, 21.0] | 22.0 [20.0, 31.0] &* | <0.001 |
| CDR score, median [Q1, Q3] | 0.5 [0, 1] | 0 [0, 0] | 0.5 [0.5, 0.5] # | 2 [1, 2] &* | <0.001 |
| Z_memory, median [Q1, Q3] | −0.02 [−0.97, 0.79] | 0.92 [0.57, 1.5] | −0.22 [−0.81, 0.28] # | −1.31 [−1.31, −0.97] &* | <0.001 |
| Z_attention, median [Q1, Q3] | 0.02 [−0.63, 0.69] | 0.5 [−0.04, 1.03] | 0.03 [−0.45, 0.65] # | −1.02 [−1.62, −0.35] &* | <0.001 |
| Z_visuospatial, median [Q1, Q3] | 0.29 [−0.17, 0.61] | 0.57 [0.25, 0.72] | 0.22 [−0.17, 0.48] # | −0.42 [−1.75, 0.09] &* | <0.001 |
| Z_executive, median [Q1, Q3] | 0.25 [−0.08, 0.46] | 0.43 [0.26, 0.56] | 0.22 [−0.08, 0.43] # | −0.15 [−0.52, 0.05] &* | <0.001 |
| Z_language, median [Q1, Q3] | 0.15 [−0.33, 0.63] | 0.63 [0.29, 0.91] | 0.09 [−0.29, 0.47] # | −0.54 [−1.1, −0.17] &* | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Ma, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, W.; Ding, S.; Zheng, L.; Liang, X.; Luo, J.; Ding, D.; et al. Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Clinical Relevance in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Shanghai Aging Study and Shanghai Memory Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3959. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193959
Zhu Z, Ma X, Wu J, Xiao Z, Wu W, Ding S, Zheng L, Liang X, Luo J, Ding D, et al. Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Clinical Relevance in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Shanghai Aging Study and Shanghai Memory Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3959. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193959
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zheng, Xiaoxi Ma, Jie Wu, Zhenxu Xiao, Wanqing Wu, Saineng Ding, Li Zheng, Xiaoniu Liang, Jianfeng Luo, Ding Ding, and et al. 2022. "Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Clinical Relevance in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Shanghai Aging Study and Shanghai Memory Study" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3959. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193959
APA StyleZhu, Z., Ma, X., Wu, J., Xiao, Z., Wu, W., Ding, S., Zheng, L., Liang, X., Luo, J., Ding, D., & Zhao, Q. (2022). Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Clinical Relevance in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Shanghai Aging Study and Shanghai Memory Study. Nutrients, 14(19), 3959. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193959







