Body Mass Index and Risk for COVID-19-Related Hospitalization in Adults Aged 50 and Older in Europe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Sample
2.3. Observation Period
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
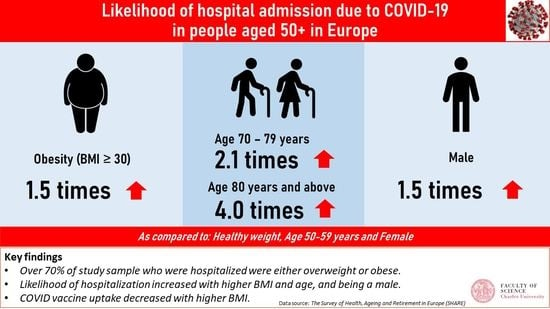
3. Results
3.1. Description of the Study Sample
3.2. Hospitalization Associated with COVID-19 Infection, BMI, and Other Covariates
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, H.; Alsalhe, T.A.; Chalghaf, N.; Riccò, M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Wu, J. The Global Burden of Disease Attributable to High Body Mass Index in 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: An Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO European Regional Obesity Report 2022; World Health Organization: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- OECD; WHO. Health at a Glance: Asia/Pacific 2020; OECD: Paris, France, 2020; ISBN 9789264445673. [Google Scholar]
- Eurostat Body Mass Index (BMI) by Sex, Age and Educational Attainment Level. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/HLTH_EHIS_BM1E__custom_3099913/default/table?lang=en (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Cercato, C.; Fonseca, F.A. Cardiovascular Risk and Obesity. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Paul Poirier, C.; Chair Lora Burke, V.E.; Jean-Pierre Després, F.; Penny Gordon-Larsen, F.; Carl Lavie, F.J.; Lear, S.A.; Chiadi Ndumele, F.E.; Ian Neeland, F.J.; Prashanthan Sanders, F.; et al. Aha Scientific Statement: Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease, A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-Mass Index and Incidence of Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guh, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Bansback, N.; Amarsi, Z.; Birmingham, C.L.; Anis, A.H. The Incidence of Co-Morbidities Related to Obesity and Overweight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Coleman, S.; Nixon, J.; Sharples, L.; Hamilton-Shield, J.; Rutter, H.; Bryant, M. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Estimating the Population Prevalence of Comorbidities in Children and Adolescents Aged 5 to 18 Years. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Ciavaglia, C.E.; Neder, J.A. When Obesity and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Collide: Physiological and Clinical Consequences. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.; Kim, L.; Whitaker, M.; O’Halloran, A.; Cummings, C.; Holstein, R.; Prill, M.; Chai, S.J.; Kirley, P.D.; Alden, N.B.; et al. Hospitalization Rates and Characteristics of Patients Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019—COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1–30, 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottoli, M.; Bernante, P.; Belvedere, A.; Balsamo, F.; Garelli, S.; Giannella, M.; Cascavilla, A.; Tedeschi, S.; Ianniruberto, S.; del Turco, E.R.; et al. How Important Is Obesity as a Risk Factor for Respiratory Failure, Intensive Care Admission and Death in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients? Results from a Single Italian Centre. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompaniyets, L.; Goodman, A.B.; Belay, B.; Freedman, D.S.; Sucosky, M.S.; Lange, S.J.; Gundlapalli, A.V.; Boehmer, T.K.; Blanck, H.M. Body Mass Index and Risk for COVID-19-Related Hospitalization, Intensive Care Unit Admission, Invasive Mechanical Ventilation, and Death—United States, March-December 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; Barnaby, D.P.; Becker, L.B.; Chelico, J.D.; Cohen, S.L.; et al. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA 2020, 323, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honce, R.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Impact of Obesity on Influenza A Virus Pathogenesis, Immune Response, and Evolution. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidich, S.D.; Green, W.D.; Rebeles, J.; Karlsson, E.A.; Schultz-Cherry, S.; Noah, T.L.; Chakladar, S.; Hudgens, M.G.; Weir, S.S.; Beck, M.A. Increased Risk of Influenza among Vaccinated Adults Who Are Obese. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/situations/covid-19 (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Wang, H.; Paulson, K.R.; Pease, S.A.; Watson, S.; Comfort, H.; Zheng, P.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Bisignano, C.; Barber, R.M.; Alam, T.; et al. Estimating Excess Mortality Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Analysis of COVID-19-Related Mortality, 2020–2021. Lancet 2022, 399, 1513–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.; Dubey, P.; Benitez, J.; Torres, J.P.; Reddy, S.; Shokar, N.; Aung, K.; Mukherjee, D.; Dwivedi, A.K. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Geographic Differences in Comorbidities and Associated Severity and Mortality among Individuals with COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IHME COVID-19 Cumulative Deaths. Available online: https://covid19.healthdata.org/japan?view=cumulative-deaths&tab=compare (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Gao, M.; Piernas, C.; Astbury, N.M.; Hippisley-Cox, J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Aveyard, P.; Jebb, S.A. Associations between Body-Mass Index and COVID-19 Severity in 6·9 Million People in England: A Prospective, Community-Based, Cohort Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawadogo, W.; Tsegaye, M.; Gizaw, A.; Adera, T. Overweight and Obesity as Risk Factors for COVID-19-Associated Hospitalisations and Death: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2022, 5, e000375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamer, M.; Gale, C.R.; Kivimäki, M.; Batty, G.D. Overweight, Obesity, and Risk of Hospitalization for COVID-19: A Community-Based Cohort Study of Adults in the United Kingdom. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21011–21013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloka, J.A.; Blum, L.V.; Old, O.; Zacharowski, K.; Friedrichson, B. Characteristics and Mortality of 561,379 Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in Germany until December 2021 Based on Real-Life Data. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, E.; Kassim, G.; Soffer, S.; Freeman, R.; Levin, M.A.; Reich, D.L. Severe Obesity as an Independent Risk Factor for COVID-19 Mortality in Hospitalized Patients Younger than 50. Obesity 2020, 28, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartof, S.Y.; Qian, L.; Hong, V.; Wei, R.; Nadjafi, R.F.; Fischer, H.; Li, Z.; Shaw, S.F.; Caparosa, S.L.; Nau, C.L.; et al. Obesity and Mortality Among Patients Diagnosed With COVID-19: Results From an Integrated Health Care Organization. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanad, C.; García-Blas, S.; Tarazona-Santabalbina, F.; Sanchis, J.; Bertomeu-González, V.; Fácila, L.; Ariza, A.; Núñez, J.; Cordero, A. The Effect of Age on Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis with 611,583 Subjects. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulíková Tesárková, K.; Dzúrová, D. The Age Structure of Cases as the Key of COVID-19 Severity: Longitudinal Population-Based Analysis of European Countries during 150 Days. Scand. J. Public Health 2021, 50, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, Z.; Odish, F.; Gill, I.; O’Connor, D.; Armstrong, J.; Vanood, A.; Ibironke, O.; Hanna, A.; Ranski, A.; Halalau, A. Older Age and Comorbidity Are Independent Mortality Predictors in a Large Cohort of 1305 COVID-19 Patients in Michigan, United States. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez, N.D.; Weiss, N.S.; Romand, J.A.; Treggiari, M.M. COVID-19 Mortality Risk for Older Men and Women. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börsch-Supan, A.; Brandt, M.; Hunkler, C.; Kneip, T.; Korbmacher, J.; Malter, F.; Schaan, B.; Stuck, S.; Zuber, S. Data Resource Profile: The Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (Share). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börsch-Supan, A. Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) Wave 9. COVID-19 Survey 2. Release Version: 8.0.0. SHARE-ERIC. Data Set. 2022. Available online: http://www.share-project.org/special-data-sets/share-corona-survey-2.html (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An Interactive Web-Based Dashboard to Track COVID-19 in Real Time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Overview of COVID-19 Vaccination Strategies and Vaccine Deployment Plans in the EU/EEA and the UK Key Findings; ECDC: Solna, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dicker, D.; Bettini, S.; Farpour-Lambert, N.; Frühbeck, G.; Golan, R.; Goossens, G.; Halford, J.; O’malley, G.; Mullerova, D.; Ramos Salas, X.; et al. Position Statement Obesity and COVID-19: The Two Sides of the Coin. Obes. Facts 2020, 13, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plourde, G.; Fournier-Ross, E.; Tessier-Grenier, H.; Mullie, L.A.; Chassé, M.; Carrier, F.M. Association between Obesity and Hospital Mortality in Critical COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 2617–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscarini, S.; Colaneri, M.; Ludovisi, S.; Seminari, E.; Pieri, T.C.; Valsecchi, P.; Gallazzi, I.; Giusti, E.; Cammà, C.; Zuccaro, V.; et al. The Obesity Paradox: Analysis from the SMAtteo COvid-19 REgistry (SMACORE) Cohort. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1920–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’hearn, M.; Liu, J.; Cudhea, F.; Micha, R.; Mozaffarian, D. Coronavirus Disease 2019 Hospitalizations Attributable to Cardiometabolic Conditions in the United States: A Comparative Risk Assessment Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piernas, C.; Patone, M.; Astbury, N.M.; Gao, M.; Dixon MRCGP, S.; Coupland, C.; Aveyard FRCGP, P.; Hippisley-Cox FRCP, J.; Jebb, S.A.; Piernas, C.; et al. Associations of BMI with COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake, Vaccine Effectiveness, and Risk of Severe COVID-19 Outcomes after Vaccination in England: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, T.; Zaccardi, F.; Islam, N.; Razieh, C.; Gillies, C.L.; Lawson, C.A.; Chudasama, Y.; Rowlands, A.; Davies, M.J.; Docherty, A.B.; et al. Obesity, Chronic Disease, Age, and in-Hospital Mortality in Patients with Covid-19: Analysis of ISARIC Clinical Characterisation Protocol UK Cohort. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smati, S.; Tramunt, B.; Wargny, M.; Caussy, C.; Gaborit, B.; Vatier, C.; Vergès, B.; Ancelle, D.; Amadou, C.; Bachir, L.A.; et al. Relationship between Obesity and Severe COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Results from the CORONADO Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, M.; Toska, T.; Alex, C.; Lundberg, C.E.; Cronie, O.; Rosengren, A.; Adiels, M.; Sjöland, H. BMI, Sex and Outcomes in Hospitalised Patients in Western Sweden during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; Du, S.; Green, W.D.; Beck, M.A.; Algaith, T.; Herbst, C.H.; Alsukait, R.F.; Alluhidan, M.; Alazemi, N.; Shekar, M. Individuals with Obesity and COVID-19: A Global Perspective on the Epidemiology and Biological Relationships. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijls, B.G.; Jolani, S.; Atherley, A.; Derckx, R.T.; Dijkstra, J.I.R.; Franssen, G.H.L.; Hendriks, S.; Richters, A.; Venemans-Jellema, A.; Zalpuri, S.; et al. Demographic Risk Factors for COVID-19 Infection, Severity, ICU Admission and Death: A Meta-Analysis of 59 Studies. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e044640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Heredia, F.P.; Gómez-Martínez, S.; Marcos, A. Obesity, Inflammation and the Immune System. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2012, 71, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.B.; Vogel, P.; Duan, S.; Govorkova, E.A.; Webby, R.J.; McCullers, J.A.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Impaired Wound Healing Predisposes Obese Mice to Severe Influenza Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honce, R.; Karlsson, E.A.; Wohlgemuth, N.; Estrada, L.D.; Meliopoulos, V.A.; Yao, J.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Obesity-Related Microenvironment Promotes Emergence of Virulent Influenza Virus Strains. mBio 2020, 11, e03341-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefan, N. Metabolic Disorders, COVID-19 and Vaccine-Breakthrough Infections. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 18, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Mizoue, T.; Tanaka, A.; Oshiro, Y.; Inamura, N.; Konishi, M.; Ozeki, M.; Miyo, K.; Sugiura, W.; Sugiyama, H.; et al. Sex-Associated Differences between BMI and SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Titers Following the BNT162b2 Vaccine. Obesity 2022, 30, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizilkaya, M.C.; Kilic, S.S.; Oncel, D.; Mamidanna, S.; Daliparty, V.; Yilmaz, S.; Bozkurt, M.A.; Sibic, O.; Sayan, M. Barriers to Coronavirus Disease 19 Vaccination in Patients with Obesity. Am. J. Surg. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallis, M.; Glazer, S. Protecting Individuals Living with Overweight and Obesity: Attitudes and Concerns toward COVID-19 Vaccination in Canada. Obesity 2021, 29, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafilyan, V.; Dolby, T.; Razieh, C.; Gaughan, C.H.; Morgan, J.; Ayoubkhani, D.; Walker, S.; Khunti, K.; Glickman, M.; Yates, T. Sociodemographic Inequality in COVID-19 Vaccination Coverage among Elderly Adults in England: A National Linked Data Study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e053402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valckx, S.; Crèvecoeur, J.; Verelst, F.; Vranckx, M.; Hendrickx, G.; Hens, N.; van Damme, P.; Pepermans, K.; Beutels, P.; Neyens, T. Individual Factors Influencing COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance in between and during Pandemic Waves (July–December 2020). Vaccine 2022, 40, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmot, M.; Allen, J.; Goldblatt, P.; Herd, E.; Morrison, J. Build. Back Fairer: The COVID-19 Marmot Review, The Pandemic, Socioeconomic and Health Inequalities in England; The Health Foundation: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- UK Health Security Agency COVID-19 Vaccination Programme—GOV.UK. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/covid-19-vaccination-programme (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Race Disparity Unit; Cabinet Office. Final Report on Progress to Address COVID-19 Health Inequalities—GOV.UK; Race Disparity Unit: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alban, C.; Posner , X.; Fox, B.; Rubin-Miller, L. Pandemic Pound Theories Don’t Hold Weight. 2 July 2021. Available online: https://epicresearch.org/articles/pandemic-pound-theories-dont-hold-weight (accessed on 21 July 2022).



| Study Sample in the Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tested Positive for COVID-19 (N = 1936) | Hospitalized for COVID-19 (N = 307) | |||
| N | (%) | N | (%) | |
| Not Hospitalized | 1629 | (84.1) | - | - |
| Hospitalized | 307 | (15.9) | - | - |
| BMI categories (kg/m2) | ||||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 17 | (0.9) | 2 | (0.7) |
| Healthy weight (18.5–24.9) | 542 | (28.0) | 74 | (24.1) |
| Overweight (25–29.9) | 794 | (41.0) | 125 | (40.7) |
| Obese (≥30) | 583 | (30.1) | 106 | (34.5) |
| BMI continuous variable (kg/m2) | Mean | ±SD | Mean | ±SD |
| 28.00 | ±4.90 | 28.82 | ±5.68 | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 792 | (40.9) | 155 | (50.5) |
| Female | 1144 | (59.1) | 152 | (49.5) |
| Age group (years) | ||||
| 50–59 | 291 | (15.0) | 27 | (8.8) |
| 60–69 | 839 | (43.3) | 102 | (33.2) |
| 70–79 | 578 | (29.9) | 110 | (35.8) |
| 80+ | 228 | (11.8) | 68 | (22.1) |
| Age, years | Mean | ±SD | Mean | ±SD |
| 68.88 | ±8.69 | 72.38 | ±9.60 | |
| Education level | ||||
| None and primary | 251 | (13.0) | 66 | (21.5) |
| Secondary | 1168 | (60.3) | 176 | (57.3) |
| Post-secondary | 124 | (6.4) | 17 | (5.5) |
| Tertiary | 393 | (20.3) | 48 | (15.6) |
| European Regions | ||||
| CEEC | 1069 | (55.2) | 163 | (53.1) |
| All the other countries | 867 | (44.8) | 144 | (46.9) |
| Partner in household | ||||
| Yes | 1401 | (72.4) | 218 | (71.0) |
| No | 535 | (27.6) | 89 | (29.0) |
| COVID-19 Vaccination | ||||
| Yes | 1250 | (64.6) | 175 | (57.0) |
| No | 686 | (35.4) | 132 | (43.0) |
| Comorbidity | ||||
| Chronic lung disease | ||||
| Yes | 169 | (8.8) | 58 | (18.9) |
| No | 1762 | (91.2) | 249 | (81.1) |
| Diabetes or high blood sugar | ||||
| Yes | 320 | (16.6) | 73 | (23.9) |
| No | 1613 | (83.4) | 233 | (76.1) |
| (100) | (100) | |||
| Model 1 † | Model 2 ‡ | Model 3 § | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | (95% CI) | OR | (95% CI) | OR | (95% CI) | ||||
| BMI | |||||||||
| Healthy (Ref) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Underweight | 0.72 | (0.16, 3.31) | 0.74 | (0.16, 3.39) | 0.61 | (0.13, 2.94) | |||
| Overweight | 1.16 | (0.84, 1.60) | 1.16 | (0.84, 1.60) | 1.18 | (0.85, 1.64) | |||
| Obese | 1.47 | (1.05, 2.05) | 1.43 | (1.02, 2.01) | 1.34 | (0.94, 1.90) | |||
| Sex | |||||||||
| Female (Ref) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Male | 1.51 | (1.18, 1.94) | 1.58 | (1.23, 2.04) | 1.61 | (1.24, 2.08) | |||
| Age group | |||||||||
| 50–59 (Ref) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 60–69 | 1.26 | (0.80, 1.97) | 1.23 | (0.78, 1.93) | 1.20 | (0.76, 1.89) | |||
| 70–79 | 2.10 | (1.34, 3.29) | 1.95 | (1.24, 3.07) | 1.85 | (1.16, 2.95) | |||
| 80+ | 4.05 | (2.48, 6.62) | 3.40 | (2.05, 5.63) | 3.31 | (1.97, 5.54) | |||
| Education | |||||||||
| Tertiary (Ref) | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| None and primary | 1.87 | (1.20, 2.90) | 1.79 | (1.14, 2.80) | |||||
| Secondary | 1.14 | (0.80, 1.62) | 1.07 | (0.75, 1.54) | |||||
| Post-secondary | 1.07 | (0.59, 1.97) | 1.06 | (0.57, 1.98) | |||||
| European Regions | |||||||||
| All other countries (Ref) | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| CEEC | 1.02 | (0.78, 1.33) | 0.87 | (0.66, 1.15) | |||||
| COVID-19 Vaccination | |||||||||
| YES (Ref) | 1 | ||||||||
| No | 1.75 | (1.34, 2.30) | |||||||
| Diseases | |||||||||
| Chronic lung disease | |||||||||
| No (Ref) | 1 | ||||||||
| Yes | 3.06 | (2.14, 4.40) | |||||||
| Diabetes | |||||||||
| No (Ref) | 1 | ||||||||
| Yes | 1.40 | (1.02, 1.93) | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohno, M.; Dzúrová, D. Body Mass Index and Risk for COVID-19-Related Hospitalization in Adults Aged 50 and Older in Europe. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4001. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194001
Ohno M, Dzúrová D. Body Mass Index and Risk for COVID-19-Related Hospitalization in Adults Aged 50 and Older in Europe. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):4001. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194001
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhno, Maika, and Dagmar Dzúrová. 2022. "Body Mass Index and Risk for COVID-19-Related Hospitalization in Adults Aged 50 and Older in Europe" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 4001. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194001
APA StyleOhno, M., & Dzúrová, D. (2022). Body Mass Index and Risk for COVID-19-Related Hospitalization in Adults Aged 50 and Older in Europe. Nutrients, 14(19), 4001. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194001