Preconception Hemoglobin Concentration and Risk of Low Birth Weight and Small-for-Gestational-Age: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Background and Original Cohort
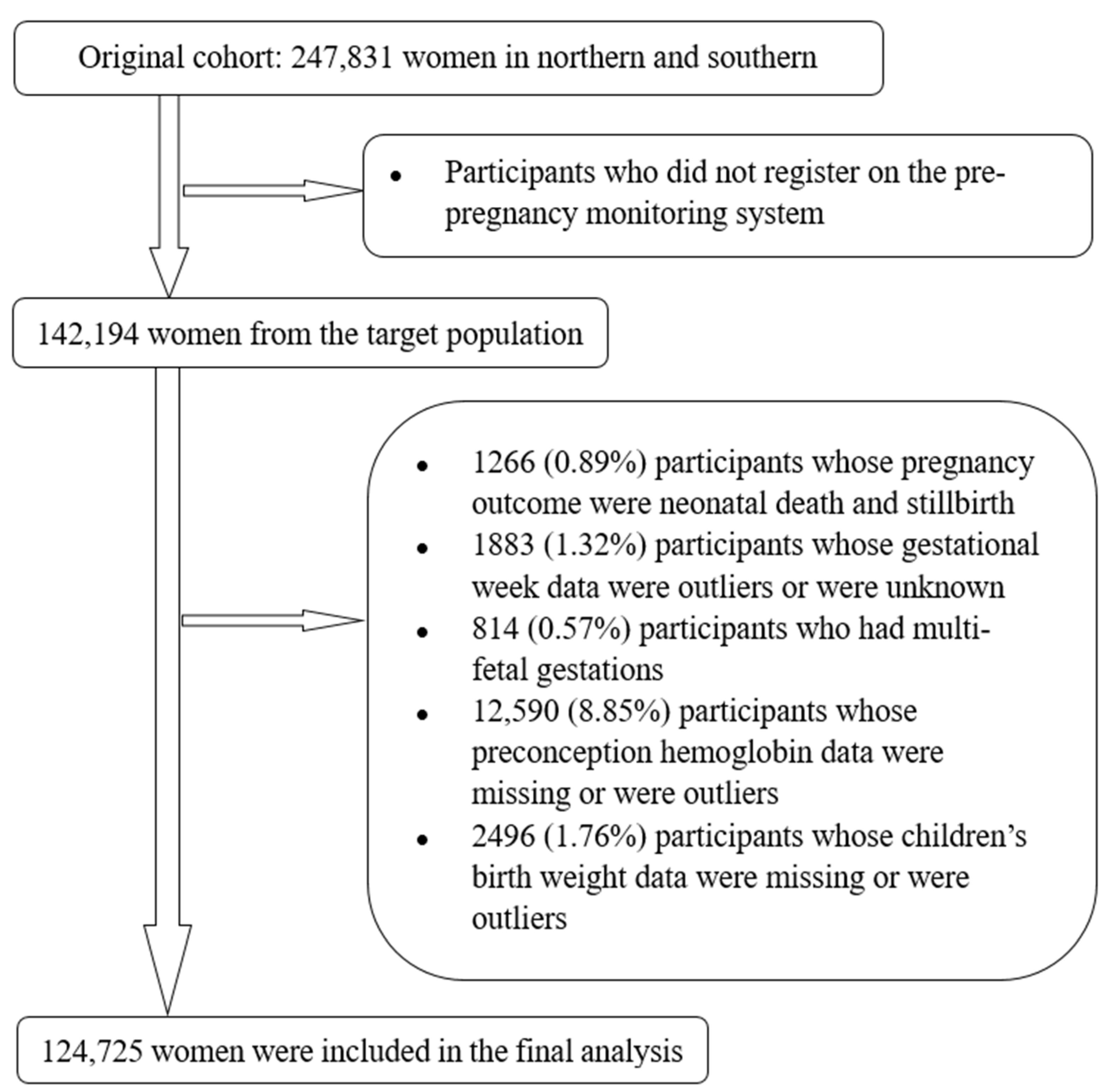
2.2. Selection of Study Subjects
2.3. Definition of Anemia and Hb Classification
2.4. Definition of LBW, SGA, and BWSDS
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Associations between Preconception Hb Concentrations with LBW and SGA
4.2. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Katz, J.; Martorell, R.; et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.A.; Finucane, M.M.; De-Regil, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Flaxman, S.R.; Branca, F.; Peña-Rosas, J.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Ezzati, M. Global, regional, and national trends in haemoglobin concentration and prevalence of total and severe anaemia in children and pregnant and non-pregnant women for 1995-2011: A systematic analysis of population-representative data. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e16–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abeysena, C.; Jayawardana, P.; Seneviratne, R.D.A. Maternal haemoglobin level at booking visit and its effect on adverse pregnancy outcome. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2010, 50, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ananth, C.V.; Li, Z.; Smulian, J.C. Maternal anaemia and preterm birth: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 38, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, M.F.; Oaks, B.M.; Tandon, S.; Martorell, R.; Dewey, K.G.; Wendt, A.S. Maternal hemoglobin concentrations across pregnancy and maternal and child health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1450, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jornayvaz, F.R.; Vollenweider, P.; Bochud, M.; Mooser, V.; Waeber, G.; Marques-Vidal, P. Low birth weight leads to obesity, diabetes and increased leptin levels in adults: The CoLaus study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christian, P.; Lee, S.E.; Donahue Angel, M.; Adair, L.S.; Arifeen, S.E.; Ashorn, P.; Barros, F.C.; Fall, C.H.D.; Fawzi, W.W.; Hao, W.; et al. Risk of childhood undernutrition related to small-for-gestational age and preterm birth in low- and middle-income countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1340–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.F.; Ramakrishnan, U. Maternal Undernutrition before and during Pregnancy and Offspring Health and Development. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 7641–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, R.K.; Deo, K.K.; Neupane, U.; Chaudhary Bhaskar, S.; Yadav, B.K.; Pokharel, H.P.; Pokharel, P.K. A Case Control Study on Risk Factors Associated with Low Birth Weight Babies in Eastern Nepal. Int. J. Pediatr. 2015, 2015, 807373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahmati, S.; Delpishe, A.; Azami, M.; Hafezi Ahmadi, M.R.; Sayehmiri, K. Maternal Anemia during pregnancy and infant low birth weight: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2017, 15, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McArdle, H.J.; Gambling, L.; Kennedy, C. Iron deficiency during pregnancy: The consequences for placental function and fetal outcome. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, X.-M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C.-Y.; Lv, S.-Y.; Li, S.-F.; Zhong, C.-Y.; Geng, S.-S. Adverse effects of iron deficiency anemia on pregnancy outcome and offspring development and intervention of three iron supplements. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, A.C.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Wojczyk, B.S.; Spitalnik, S.L.; Hod, E.A.; Prestia, K.A. Effect of dietary iron on fetal growth in pregnant mice. Comp. Med. 2013, 63, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, A.; Gomes-Filho, I.S.; Silva, R.B.; Pereira, P.P.S.; Mata, F.; Lyrio, A.O.; Souza, E.S.; Cruz, S.S.; Pereira, M.G. Maternal Anemia and Low Birth Weight: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berry, R.J.; Li, Z.; Erickson, J.D.; Li, S.; Moore, C.A.; Wang, H.; Mulinare, J.; Zhao, P.; Wong, L.Y.; Gindler, J.; et al. Prevention of neural-tube defects with folic acid in China. China-U.S. Collaborative Project for Neural Tube Defect Prevention. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Li, Z.; Ye, R.; Liu, J.; Ren, A. Impact of Periconceptional Folic Acid Supplementation on Low Birth Weight and Small-for-Gestational-Age Infants in China: A Large Prospective Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2017, 187, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Haemoglobin Concentrations for the Diagnosis of Anaemia and Assessment of Severity; Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System (VMNIS): Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. Available online: http://www.who.int/vmnis/indicators/haemoglobin.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Liu, J.M.; Ye, R.; Ren, A. Maternal haemoglobin concentrations before and during pregnancy as determinants of the concentrations of children at 3-5 years of age: A large follow-up study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, L. A national sampling survey on birth weight in 1998 in China: Mean value and standard deviation. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002, 36, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fleming, T.P.; Watkins, A.J.; Velazquez, M.A.; Mathers, J.C.; Prentice, A.M.; Stephenson, J.; Barker, M.; Saffery, R.; Yajnik, C.S.; Eckert, J.J.; et al. Origins of lifetime health around the time of conception: Causes and consequences. Lancet 2018, 391, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C. A Summary of Pathways or Mechanisms Linking Preconception Maternal Nutrition with Birth Outcomes. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahrens, K.A.; Nelson, H.; Stidd, R.L.; Moskosky, S.; Hutcheon, J.A. Short interpregnancy intervals and adverse perinatal outcomes in high-resource settings: An updated systematic review. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2019, 33, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Su, R.; Feng, H.; Yang, H.; Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prevalence Survey (GPS) Study Group. Prevalence, risk factors and associated adverse pregnancy outcomes of anaemia in Chinese pregnant women: A multicentre retrospective study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.; Ji, M.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Preconception Hb concentration and risk of preterm birth in over 2·7 million Chinese women aged 20-49 years: A population-based cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, C.C.; Moore, J.E.; Felix, H.C.; Stewart, M.K.; Bird, T.M.; Lowery, C.L.; Tilford, J.M. Association of State Medicaid Expansion Status With Low Birth Weight and Preterm Birth. JAMA 2019, 321, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronnenberg, A.G.; Wood, R.J.; Wang, X.; Xing, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, D.; Guang, W.; Huang, A.; Wang, L.; Xu, X. Preconception hemoglobin and ferritin concentrations are associated with pregnancy outcome in a prospective cohort of Chinese women. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2586–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, S.W.; Han, Y.J.; Ohrr, H. Anemia before pregnancy and risk of preterm birth, low birth weight and small-for-gestational-age birth in Korean women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, L.; Stefanidou, C.; Chadborn, T.; Thompson, K.; Michie, S.; Lorencatto, F. Influences on NHS Health Check behaviours: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Tedroff, K.; Villamor, E.; Lu, D.; Cnattingius, S. Risk of intellectual disability in children born appropriate-for-gestational-age at term or post-term: Impact of birth weight for gestational age and gestational age. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, K. Is There a Causal Relationship between Iron Deficiency or Iron-Deficiency Anemia and Weight at Birth, Length of Gestation and Perinatal Mortality? J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronnenberg, A.G.; Goldman, M.B.; Chen, D.; Aitken, I.W.; Willett, W.C.; Selhub, J.; Xu, X. Preconception homocysteine and B vitamin status and birth outcomes in Chinese women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daru, J.; Allotey, J.; Peña-Rosas, J.P.; Khan, K.S. Serum ferritin thresholds for the diagnosis of iron deficiency in pregnancy: A systematic review. Transfus. Med. 2017, 27, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Anemic Group (n = 27,783) | Non-Anemic Group (n = 96,942) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Age (years, mean (SD)) | 24.46 (2.11) | 24.35 (2.03) | <0.001 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2, mean (SD)) | 20.42 (2.18) | 20.47 (2.15) | 0.001 | ||
| Education | <0.001 | ||||
| High school or higher | 2688 | 18.42 | 11,906 | 81.58 | |
| Junior high school | 17,689 | 21.71 | 63,771 | 78.29 | |
| Primary school or Lower, or unknown | 7406 | 25.83 | 21,265 | 74.17 | |
| Occupation | <0.001 | ||||
| Farmer | 16,108 | 22.80 | 54,549 | 77.20 | |
| Factory worker | 10,432 | 22.07 | 36,843 | 77.93 | |
| Other or unknown | 1243 | 18.30 | 5550 | 81.70 | |
| Parity | <0.001 | ||||
| Primiparous | 26,650 | 22.09 | 93,975 | 77.91 | |
| Multiparous | 1133 | 27.63 | 2967 | 72.37 | |
| Ethnicity | 0.037 | ||||
| Han | 27,544 | 22.25 | 96,228 | 77.75 | |
| Other race | 239 | 25.08 | 714 | 74.92 | |
| Folic acid use | <0.001 | ||||
| No | 6582 | 27.69 | 17,186 | 72.31 | |
| Yes | 21,201 | 21.00 | 79,756 | 79.00 | |
| Characteristics | No. of Participants (n = 124,725) | LBW (n = 2610) | SGA (n = 7064) | BWSDS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence, % | RR | 95%CI | Incidence, % | RR | 95%CI | Mean ± SD | ß | 95%CI | ||
| Age, years | ||||||||||
| <20 | 114 | 2.63 | 1.36 | 0.42, 4.42 | 2.63 | 0.63 | 0.20, 2.01 | −0.25 ± 1.04 | −0.40 | −0.59, −0.21 |
| 20–25 | 86,242 | 2.07 | 1.07 | 0.81, 1.41 | 5.75 | 1.42 | 1.17, 1.72 | −0.01 ± 1.00 | −0.15 | −0.19, −0.12 |
| 25–30 | 35,700 | 2.15 | 1.10 | 0.83, 1.47 | 5.58 | 1.38 | 1.13, 1.67 | 0.01 ± 1.00 | −0.14 | −0.18, −0.10 |
| ≥30 | 2669 | 1.95 | 1 | N/A | 4.12 | 1 | N/A | 0.15 ± 1.03 | 0 | N/A |
| BMI, kg/m2 | ||||||||||
| <18.5 | 19,835 | 2.94 | 1.53 | 1.39, 1.68 | 7.98 | 1.56 | 1.47, 1.66 | −0.18 ± 1.00 | −0.20 | −0.21, −0.18 |
| 18.5–23.9 | 98,190 | 1.95 | 1 | N/A | 5.25 | 1 | N/A | 0.02 ± 0.99 | 0 | N/A |
| 24–27.9 | 6174 | 1.67 | 0.85 | 0.70, 1.04 | 4.91 | 0.93 | 0.83, 1.05 | 0.22 ± 1.06 | 0.20 | 0.17, 0.22 |
| ≥28 | 526 | 1.52 | 0.78 | 0.39, 1.56 | 3.80 | 0.71 | 0.46, 1.12 | 0.35 ± 1.13 | 0.33 | 0.24, 0.41 |
| Education | ||||||||||
| High school or higher | 14,594 | 1.81 | 1 | N/A | 4.69 | 1 | N/A | 0.05 ± 0.99 | 0 | N/A |
| Junior high school | 81,460 | 2.03 | 1.12 | 0.99, 1.28 | 5.43 | 1.17 | 1.07, 1.27 | 0.01 ± 0.99 | −0.04 | −0.05, −0.02 |
| Primary school or lower, or unknown | 28,671 | 2.42 | 1.34 | 1.17, 1.55 | 6.82 | 1.49 | 1.36, 1.63 | −0.05 ± 1.02 | −0.10 | −0.12, −0.08 |
| Occupation | ||||||||||
| Farmer | 70,657 | 2.00 | 1 | N/A | 5.54 | 1 | N/A | −0.01 ± 0.99 | 0 | N/A |
| Factory worker | 47,275 | 2.31 | 1.16 | 1.07, 1.26 | 6.02 | 1.09 | 1.04, 1.15 | −0.002 ± 1.02 | 0.004 | −0.01, 0.02 |
| Other or unknown | 6793 | 1.60 | 0.80 | 0.66, 0.98 | 4.49 | 0.80 | 0.71, 0.90 | 0.08 ± 1.01 | 0.09 | 0.07, 0.12 |
| Parity | ||||||||||
| Primiparous | 120,625 | 2.09 | 1.02 | 0.82, 1.27 | 5.70 | 1.27 | 1.09, 1.47 | −0.01 ± 1.00 | −0.15 | −0.18, −0.12 |
| Multiparous | 4100 | 2.05 | 1 | N/A | 4.56 | 1 | N/A | 0.14 ± 1.07 | 0 | N/A |
| Ethnicity | ||||||||||
| Han | 123,772 | 2.08 | 1 | N/A | 5.65 | 1 | N/A | 0.001 ± 1.00 | 0 | N/A |
| Other race | 953 | 3.67 | 1.79 | 1.28, 2.52 | 7.35 | 1.32 | 1.04, 1.69 | −0.16 ± 1.01 | −0.16 | −0.22, −0.10 |
| Folic acid use | ||||||||||
| No | 23768 | 2.28 | 1 | N/A | 5.80 | 1 | N/A | −0.02 ± 1.01 | 0 | N/A |
| Yes | 100,957 | 2.05 | 0.90 | 0.81, 0.99 | 5.63 | 0.97 | 0.91, 1.03 | 0.004 ± 1.00 | 0.02 | 0.01, 0.04 |
| Preconception anemia | ||||||||||
| No | 96,942 | 2.01 | 1 | N/A | 5.48 | 1 | N/A | 0.01 ± 0.99 | 0 | N/A |
| Yes | 27,783 | 2.37 | 1.18 | 1.08, 1.29 | 6.30 | 1.16 | 1.10, 1.23 | −0.03 ± 1.02 | −0.04 | −0.05, −0.03 |
| Risk Factors | LBW | SGA | BWSDS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted RR | 95% CI | Adjusted RR | 95% CI | ß | 95% CI | |
| Age | ||||||
| <20 | 1.27 | 0.38, 4.12 | 0.61 | 0.19, 1.96 | −0.40 | −0.58, −0.21 |
| 20–25 | 1.00 | 0.76, 1.33 | 1.35 | 1.11, 1.64 | −0.13 | −0.16, −0.09 |
| 25–30 | 1.04 | 0.78, 1.38 | 1.30 | 1.07, 1.59 | −0.11 | −0.15, −0.07 |
| ≥30 | 1 | N/A | 1 | N/A | 0 | N/A |
| BMI | 1.10 | 1.08, 1.13 | 1.11 | 1.09, 1.12 | −0.05 | −0.06, −0.05 |
| Education | ||||||
| High school or higher | 1 | N/A | 1 | N/A | 0 | N/A |
| Junior high school | 1.21 | 1.06, 1.38 | 1.23 | 1.13, 1.34 | −0.06 | −0.08, −0.04 |
| Primary school or lower, or unknown | 1.50 | 1.29, 1.73 | 1.63 | 1.49, 1.79 | −0.14 | −0.16, −0.12 |
| Occupation | ||||||
| Farmer | 1 | N/A | 1 | N/A | 0 | N/A |
| Factory worker | 1.20 | 1.11, 1.30 | 1.13 | 1.07, 1.19 | 0.001 | −0.01, 0.01 |
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| Han | 1 | N/A | 1 | N/A | 0 | N/A |
| Other race | 1.83 | 1.30, 2.58 | 1.34 | 1.05, 1.72 | −0.16 | −0.22, −0.10 |
| Folic acid use | ||||||
| No | 1 | N/A | 1 | N/A | 0 | N/A |
| Yes | 0.88 | 0.80, 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.89, 1.01 | 0.03 | 0.02, 0.05 |
| Preconception anemia | ||||||
| No | 1 | N/A | 1 | N/A | 0 | N/A |
| Yes | 1.16 | 1.02, 1.31 | 1.13 | 1.07, 1.20 | −0.03 | −0.04, −0.02 |
| Category of Hb Concentrations (g/L) | No. of Participants | LBW | SGA | BWSDS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence % | Crude RR (95% CI) | Adjusted * RR (95% CI) | Incidence % | Crude RR (95% CI) | Adjusted * RR (95% CI) | Mean ± SD | ß (95% CI) | ||
| Classification 1 | |||||||||
| No anemia | 96,942 | 2.01 | 1 | 1 | 5.48 | 1 | 1 | 0.01 ± 0.99 | 0 |
| Mild anemia | 22,495 | 2.39 | 1.19 (1.08, 1.31) | 1.17 (1.06, 1.28) | 6.33 | 1.16 (1.10, 1.24) | 1.14 (1.07, 1.21) | −0.03 ± 1.02 | −0.03 (−0.05, −0.02) |
| Moderate-to-severe anemia | 5288 | 2.29 | 1.14 (0.95, 1.37) | 1.10 (0.92, 1.33) | 6.18 | 1.14 (1.01, 1.28) | 1.34 (0.99, 1.24) | −0.02±1.03 | −0.02 (−0.05, 0.01) |
| Classification 2 | |||||||||
| <80 | 164 | 3.05 | 1.67 (0.69, 4.09) | 1.61 (0.66, 3.95) | 7.32 | 1.50 (0.83, 2.71) | 1.46 (0.81, 2.63) | −0.05 ± 1.08 | −0.07 (−0.22, −0.88) |
| 80–109 | 27,619 | 2.37 | 1.29 (1.16, 1.44) | 1.24 (1.11, 1.38) | 6.29 | 1.28 (1.19, 1.37) | 1.23 (1.15, 1.32) | −0.03 ± 1.02 | −0.05 (−0.06, −0.03) |
| 110–119 | 45,570 | 2.12 | 1.15 (1.04, 1.28) | 1.12 (1.02, 1.24) | 5.96 | 1.21 (1.13, 1.28) | 1.17 (1.10, 1.25) | −0.01 ± 1.00 | −0.03 (−0.04, −0.01) |
| 120–129 | 36,114 | 1.84 | 1 | 1 | 5.00 | 1 | 1 | 0.03 ± 0.98 | 0 |
| 130–139 | 11,196 | 1.94 | 1.05 (0.90, 1.23) | 1.05 (0.90, 1.22) | 5.04 | 1.01 (0.92, 1.11) | 1.00 (0.91, 1.11) | 0.02 ± 0.97 | −0.01 (−0.03, 0.01) |
| ≥140 | 4062 | 2.49 | 1.36 (1.10, 1.68) | 1.33 (1.08, 1.65) | 5.69 | 1.15 (1.00, 1.32) | 1.13 (0.98, 1.30) | 0.01 ± 1.05 | −0.01 (−0.05, 0.02) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; An, H.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Ye, R. Preconception Hemoglobin Concentration and Risk of Low Birth Weight and Small-for-Gestational-Age: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020271
Liu X, An H, Li N, Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Li H, Liu J, Ye R. Preconception Hemoglobin Concentration and Risk of Low Birth Weight and Small-for-Gestational-Age: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in China. Nutrients. 2022; 14(2):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020271
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaojing, Hang An, Nan Li, Zhiwen Li, Yali Zhang, Le Zhang, Hongtian Li, Jianmeng Liu, and Rongwei Ye. 2022. "Preconception Hemoglobin Concentration and Risk of Low Birth Weight and Small-for-Gestational-Age: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in China" Nutrients 14, no. 2: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020271
APA StyleLiu, X., An, H., Li, N., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Li, H., Liu, J., & Ye, R. (2022). Preconception Hemoglobin Concentration and Risk of Low Birth Weight and Small-for-Gestational-Age: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in China. Nutrients, 14(2), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020271






