Gut Microbiota, the Potential Biological Medicine for Prevention, Intervention and Drug Sensitization to Fight Diseases
Abstract
:1. Gut Microbiota
2. Classification and Function of Gut Microbiota
2.1. Pathogen Protection
2.2. Synthesis and Absorption of Nutrients
2.3. Metabolism
2.4. Immune System
2.5. Drug Biotransformation
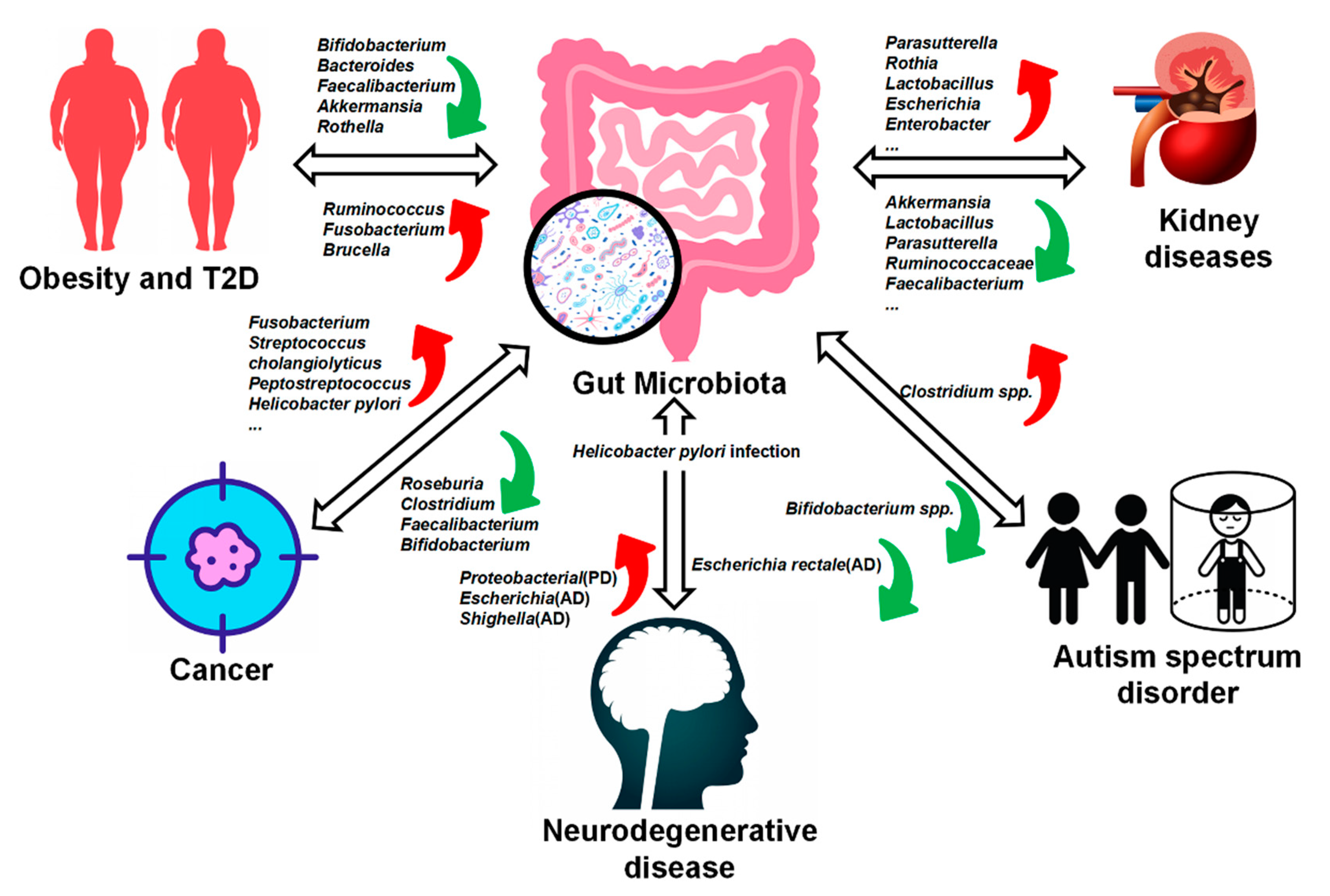
3. The Relationship between Gut Microbiota and Disease
3.1. Obesity and Type II Diabetes (T2D)
3.2. Cancer
3.3. Neurodegenerative Disease
3.4. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
3.5. Kidney Diseases
| Disease | Gut Microbiota | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obesity | Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Fusobacterium, Lactobacillus, Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratios ↑ | N/A | [31] |
| Bacteroidetes, Faecalibacterium palau, Akkermansia, Methanobacter smithii, Bifidobacterium ↓ | |||
| Type II Diabetes | Ruminococcus, Fusobacterium, Brucella ↑ | LPS ↑SCFA ↓ | [36,37] |
| Bifidobacterium, Akkermansia, Bacteroides, Faecalibacterium, Rothella ↓ | |||
| Colorectal Cancer | Fusobacterium nucleatum, Escherichia coli, Bacteroides fragilis, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus cholangiolyticus, Peptostreptococcu ↑ | Genotoxicity (DNA damage), Gut Barrier Disruption, Inflammation ↑ | [41] |
| Roseburia, Clostridium, Faecalibacterium, Bifidobacterium ↓ | |||
| Pancreatic Cancer | Helicobacter pylori, Fusobacterium, Porphyromonas gingivalis ↑ | NF-κB, MAPK signaling pathways ↑ | [43] |
| Enterococcus, Enterobacter (in bile) | |||
| Gastric Cancer | Helicobacter pylori, Lactobacillus coleohominis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii ↑ | MAP kinase, ERK1/2, VEGF, Wnt/β-catenin ↑ | [42] |
| Porphyromonas, Neisseria, the TM7 group, Prevotella pallens, and Streptococcus sinensis ↓ | |||
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Helicobacter pylori, Escherichia, Shighella ↑ | Proinflammatory cytokines ↑ | [48] |
| Escherichia rectale ↓ | |||
| Autism Spectrum Disorder | Clostridium spp. ↑ | Amino acid metabolism (Taurine) | [50,51] |
| Bifidobacterium spp. ↓ | |||
| Chronic Kidney Disease | Parasutterella, Rothia, Lactobacillus, Olsenella, Paraprevotella, Lactococcus, Helicobacter ↑ | IL-10, IL-4, IL-6 | [58] |
| Akkermansia, Lactobacillus, Parasutterella, Clostridium IV ↓ | |||
| Acute Kidney Disease | Escherichia, Enterobacter ↑ | IL-17, TNF-α, IFN-γ | [59] |
| Lactobacillus, Ruminococcaceae, Faecalibacterium, Lachnospiraceae ↓ |
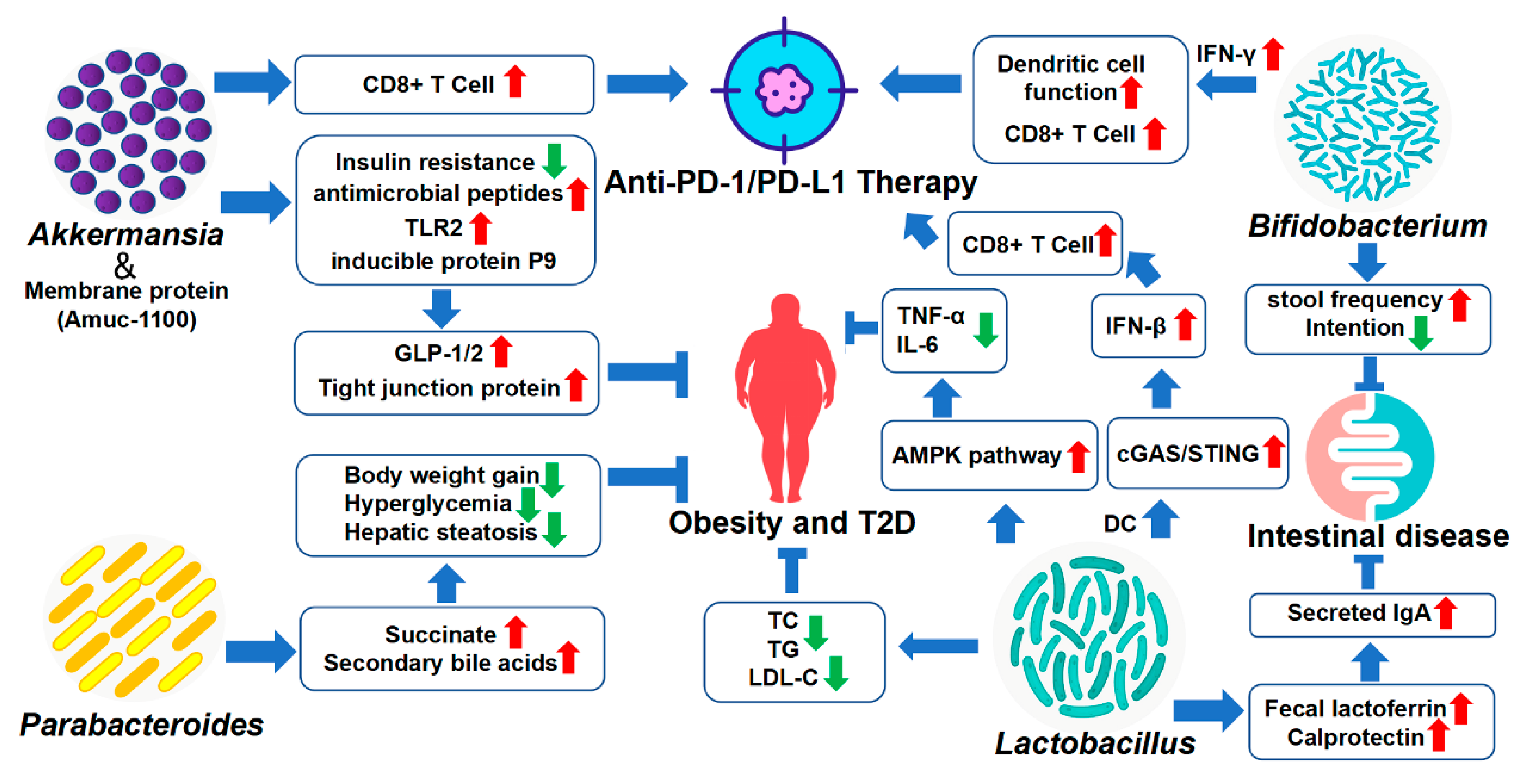
4. Therapeutic and Sensitizing Effects of Gut Microbiota on Disease Treatment
4.1. Akkermansia
4.2. Bifidobacterium
4.3. Lactobacillus
4.4. Parabacteroides
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virili, C.; Fallahi, P.; Antonelli, A.; Benvenga, S.; Centanni, M. Gut microbiota and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018, 19, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Nunez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Inoue, R.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Naito, Y.; Andoh, A. Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, T.; Luo, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; et al. Research progress in the relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and intestinal flora. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Q.; Cai, L. The gut microbiota and its interactions with cardiovascular disease. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangiola, F.; Ianiro, G.; Franceschi, F.; Fagiuoli, S.; Gasbarrini, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Gut microbiota in autism and mood disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.C.; Kumar, N.; Anonye, B.O.; Almeida, A.; Viciani, E.; Stares, M.D.; Dunn, M.; Mkandawire, T.T.; Zhu, A.; Shao, Y.; et al. A human gut bacterial genome and culture collection for improved metagenomic analyses. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Gasbarrini, A. Antibiotics as deep modulators of gut microbiota: Between good and evil. Gut 2016, 65, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, C.L.; Dong, J.; Galipeau, H.J.; Jury, J.; McCarville, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.Y.; Naidoo, A.; Anbazhagan, A.N.; Libertucci, J.; et al. Commensal microbiota induces colonic barrier structure and functions that contribute to homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Surface components and metabolites of probiotics for regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ducarmon, Q.R.; Zwittink, R.D.; Hornung, B.V.H.; van Schaik, W.; Young, V.B.; Kuijper, E.J. Gut Microbiota and Colonization Resistance against Bacterial Enteric Infection. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2019, 83, e00007-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, M.C.; Sit, C.S.; Clayton, E.; O’Connor, P.M.; Whittal, R.M.; Zheng, J.; Vederas, J.C.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Thuricin CD, a posttranslationally modified bacteriocin with a narrow spectrum of activity against Clostridium difficile. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9352–9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Milani, C.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bacteria as vitamin suppliers to their host: A gut microbiota perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranto, M.P.; Vera, J.L.; Hugenholtz, J.; De Valdez, G.F.; Sesma, F. Lactobacillus reuteri CRL1098 produces cobalamin. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 5643–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, M.; Amaretti, A.; Raimondi, S. Folate production by probiotic bacteria. Nutrients 2011, 3, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Backhed, F. Diet-microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature 2016, 535, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.; Rani, K.; Datt, C. Molecular link between dietary fibre, gut microbiota and health. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6229–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, R.L.; Morgun, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Bridging immunity and lipid metabolism by gut microbiota. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 253–262; quiz 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. Inducible Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell development by a commensal bacterium of the intestinal microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12204–12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottiere, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Lu, C.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Gut microbiota as an “invisible organ” that modulates the function of drugs. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Kong, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, S. Gut microbiota enhances the chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma to 5-fluorouracil in vivo by increasing curcumin bioavailability. Phytother. Res. PTR 2021, 35, 5823–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H. Gut microbiota-mediated pharmacokinetics of ginseng saponins. J. Ginseng. Res. 2018, 42, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Choi, M.S.; Jeung, W.; Ra, J.; Yoo, H.H.; Kim, D.H. Effects of gut microbiota on the pharmacokinetics of protopanaxadiol ginsenosides Rd, Rg3, F2, and compound K in healthy volunteers treated orally with red ginseng. J. Ginseng. Res. 2020, 44, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullingham, R.E.; Nicholls, A.J.; Kamm, B.R. Clinical pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 34, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouwel, F.; Buiter, H.J.C.; de Boer, N.K. Gut microbiota-driven drug metabolism in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 15, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, P. Gut microbiota and obesity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovesy, L.; Masterson, D.; Rosado, E.L. Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechelotte, P.; Breton, J.; Trotin-Picolo, C.; Grube, B.; Erlenbeck, C.; Bothe, G.; Fetissov, S.O.; Lambert, G. The Probiotic Strain H. alvei HA4597((R)) Improves Weight Loss in Overweight Subjects under Moderate Hypocaloric Diet: A Proof-of-Concept, Multicenter Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, N.; Legrand, R.; Deroissart, C.; Dominique, M.; Azhar, S.; Le Solliec, M.A.; Leon, F.; do Rego, J.C.; Dechelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O.; et al. Hafnia alvei HA4597 Strain Reduces Food Intake and Body Weight Gain and Improves Body Composition, Glucose, and Lipid Metabolism in a Mouse Model of Hyperphagic Obesity. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uusitupa, H.M.; Rasinkangas, P.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Makela, S.M.; Airaksinen, K.; Anglenius, H.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Maukonen, J. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis 420 for Metabolic Health: Review of the Research. Nutrients 2020, 12, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, E.; Ryan, P.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Gut microbiota, obesity and diabetes. Postgrad. Med. J. 2016, 92, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; You, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Jump, D.B.; Morgun, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Neculae, E.; Costea, C.F.; Ciocoiu, M.; Hurjui, L.L.; Tarniceriu, C.C.; Maranduca, M.A.; Lacatusu, C.M.; Floria, M.; et al. Role of Gut Microbiota on Onset and Progression of Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM). Nutrients 2020, 12, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Yu, J. The role of gut microbiota in cancer treatment: Friend or foe? Gut 2020, 69, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Chu, Q.; Zhang, P. Gut microbiome and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 447, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. The Intestinal Microbiota and Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 615056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janney, A.; Powrie, F.; Mann, E.H. Host-microbiota maladaptation in colorectal cancer. Nature 2020, 585, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Bai, C.; Brown, T.D.; Hood, L.E.; Tian, Q. Human Gut Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jin, M.; Liu, Y.; Jin, L. Gut Microbiota: Its Potential Roles in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 572492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Schwabe, R.F. The gut microbiome and liver cancer: Mechanisms and clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liao, M.; Yao, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Ji, Y.; Wei, W.; Tan, A.; et al. Breast cancer in postmenopausal women is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Microbiome 2018, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaye, K.; Li, C.G.; Bhuyan, D.J. The complex interplay of gut microbiota with the five most common cancer types: From carcinogenesis to therapeutics to prognoses. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 165, 103429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.F.; Shen, Y.Q. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and microbial metabolites in Parkinson’s Disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 45, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.; Cechova, K.; Amlerova, J.; Hort, J. Antibiotics, gut microbiota, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflam. 2019, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, H.K.; Rose, D.; Ashwood, P. The Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikantha, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. The Possible Role of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain-Axis in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Cruz, N.J.; Kang, D.W.; Gandal, M.J.; Wang, B.; Kim, Y.M.; Zink, E.M.; Casey, C.P.; Taylor, B.C.; Lane, C.J.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota from Autism Spectrum Disorder Promote Behavioral Symptoms in Mice. Cell 2019, 177, 1600–1618.e1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Xin, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shi, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, X. Skimmin, a Coumarin from Hydrangea paniculata, Slows down the Progression of Membranous Glomerulonephritis by Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Inhibiting Immune Complex Deposition. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 819296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, W.; Chen, X. Skimmin, a coumarin, suppresses the streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in wistar rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 692, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluznick, J.L. The gut microbiota in kidney disease. Science 2020, 369, 1426–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, D.Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.R.; Vaziri, N.D.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.Y. Microbiome-metabolome reveals the contribution of gut-kidney axis on kidney disease. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Xin, W.; Xiong, J.; Yao, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, J. The Intestinal Microbiota and Metabolites in the Gut-Kidney-Heart Axis of Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Richards, E.M.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y. Alterations to the Gut Microbiota and Their Correlation With Inflammatory Factors in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Kim, C.J.; Go, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, M.G.; Oh, S.W.; Cho, W.Y.; Im, S.H.; Jo, S.K. Intestinal microbiota control acute kidney injury severity by immune modulation. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Cheng, L.; Buch, H.; Zhang, F. Akkermansia muciniphila is a promising probiotic. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1109–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Y. Function of Akkermansia muciniphila in Obesity: Interactions With Lipid Metabolism, Immune Response and Gut Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Tang, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Han, M.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, G.; Zhu, J.; Cao, S.; Wu, Q.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurised bacterium blunts colitis associated tumourigenesis by modulation of CD8(+) T cells in mice. Gut 2020, 69, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cani, P.D.; de Vos, W.M. Next-Generation Beneficial Microbes: The Case of Akkermansia muciniphila. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubourg, G.; Lagier, J.C.; Armougom, F.; Robert, C.; Audoly, G.; Papazian, L.; Raoult, D. High-level colonisation of the human gut by Verrucomicrobia following broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 41, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Cho, C.H.; Yun, M.S.; Jang, S.J.; You, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Han, D.; Cha, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, K.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgia, N.J.; Bergerot, P.G.; Maia, M.C.; Dizman, N.; Hsu, J.; Gillece, J.D.; Folkerts, M.; Reining, L.; Trent, J.; Highlander, S.K.; et al. Stool Microbiome Profiling of Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Receiving Anti-PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routy, B.; Le Chatelier, E.; Derosa, L.; Duong, C.P.M.; Alou, M.T.; Daillère, R.; Fluckiger, A.; Messaoudene, M.; Rauber, C.; Roberti, M.P.; et al. Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science 2018, 359, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, L.; Routy, B.; Thomas, A.M.; Iebba, V.; Zalcman, G.; Friard, S.; Mazieres, J.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Goldwasser, F.; et al. Intestinal Akkermansia muciniphila predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, A.; Latreille-Barbier, M.; Donazzolo, Y.; Pelletier, X.; Ouwehand, A.C. Effects of 28-day Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis HN019 supplementation on colonic transit time and gastrointestinal symptoms in adults with functional constipation: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, and dose-ranging trial. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. Bifidobacterium Longum: Protection against Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 8030297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, A.; Corrales, L.; Hubert, N.; Williams, J.B.; Aquino-Michaels, K.; Earley, Z.M.; Benyamin, F.W.; Lei, Y.M.; Jabri, B.; Alegre, M.L.; et al. Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science 2015, 350, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Yoon, Y.; Park, C.; Sohn, J.; Jeong, J.J.; Jeon, B.N.; Jang, M.; An, C.; Lee, S.; et al. Bifidobacterium bifidum strains synergize with immune checkpoint inhibitors to reduce tumour burden in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zheng, J.; Zong, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Man, C.; Jiang, Y. Preventive Effect and Molecular Mechanism of Lactobacillus rhamnosus JL1 on Food-Borne Obesity in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mian, M.F.; McVey Neufeld, K.A.; Forsythe, P. CD4(+)CD25(+) T Cells are Essential for Behavioral Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus JB-1 in Male BALB/c mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2020, 88, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voo, P.Y.; Wu, C.T.; Sun, H.L.; Ko, J.L.; Lue, K.H. Effect of combination treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus and corticosteroid in reducing airway inflammation in a mouse asthma model. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Liang, H.; Bugno, J.; Xu, Q.; Ding, X.; Yang, K.; Fu, Y.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG induces cGAS/STING-dependent type I interferon and improves response to immune checkpoint blockade. Gut 2022, 71, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.H.; Chiu, C.H.; Kong, M.S.; Chang, C.J.; Chen, C.C. Probiotic Lactobacillus casei: Effective for Managing Childhood Diarrhea by Altering Gut Microbiota and Attenuating Fecal Inflammatory Markers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, J.C.V.; Moura, I.C.G.; Gaspar, G.R.; Mendes, G.M.S.; Faria, B.A.V.; Jentzsch, N.S.; do Carmo Friche Passos, M.; Kurdi, A.; Godman, B.; Almeida, A.M. The use of probiotics as a supplementary therapy in the treatment of patients with asthma: A pilot study and implications. Clinics 2019, 74, e950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, S.; Hu, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, S.; Tang, X.; Tang, T.; et al. Parabacteroides produces acetate to alleviate heparanase-exacerbated acute pancreatitis through reducing neutrophil infiltration. Microbiome 2021, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.C.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, T.W.; Kuo, Y.L.; Chang, C.J.; Wu, T.R.; Shu, C.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Swift, S.; Lu, C.C. Gut microbiota modulates COPD pathogenesis: Role of anti-inflammatory Parabacteroides goldsteinii lipopolysaccharide. Gut 2022, 71, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liao, M.; Zhou, N.; Bao, L.; Ma, K.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Parabacteroides distasonis Alleviates Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunctions via Production of Succinate and Secondary Bile Acids. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 222–235.e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.H.; Lin, T.L.; Huang, M.Z.; Li, S.W.; Wu, H.Y.; Chiu, Y.F.; Yang, C.Y.; Chiu, C.H.; Lai, H.C. Gut Commensal Parabacteroides goldsteinii MTS01 Alters Gut Microbiota Composition and Reduces Cholesterol to Mitigate Helicobacter pylori-Induced Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 916848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, C.A.; Vuong, H.E.; Yano, J.M.; Liang, Q.Y.; Nusbaum, D.J.; Hsiao, E.Y. The Gut Microbiota Mediates the Anti-Seizure Effects of the Ketogenic Diet. Cell 2018, 173, 1728–1741.e1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Kump, P.; Satokari, R.; Sokol, H.; Arkkila, P.; Pintus, C.; Hart, A.; et al. European consensus conference on faecal microbiota transplantation in clinical practice. Gut 2017, 66, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Gut Microbiota, the Potential Biological Medicine for Prevention, Intervention and Drug Sensitization to Fight Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204220
Wu H, Chen X, Zhang S, Li J. Gut Microbiota, the Potential Biological Medicine for Prevention, Intervention and Drug Sensitization to Fight Diseases. Nutrients. 2022; 14(20):4220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204220
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Haijie, Xiaoguang Chen, Sen Zhang, and Jiaxin Li. 2022. "Gut Microbiota, the Potential Biological Medicine for Prevention, Intervention and Drug Sensitization to Fight Diseases" Nutrients 14, no. 20: 4220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204220
APA StyleWu, H., Chen, X., Zhang, S., & Li, J. (2022). Gut Microbiota, the Potential Biological Medicine for Prevention, Intervention and Drug Sensitization to Fight Diseases. Nutrients, 14(20), 4220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204220






