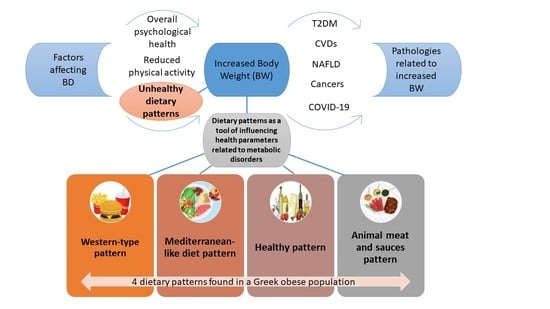
Dietary Patterns, Cardiometabolic and Lifestyle Variables in Greeks with Obesity and Metabolic Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Biochemical Parameters
2.4. Physical Activity and Quality of Life Assessment
2.5. Dietary Assesment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cefalu, W.T.; Rodgers, G.P. COVID-19 and metabolic diseases: A heightened awareness of health inequities and a renewed focus for research priorities. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. Resources. Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/resources/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Yang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C. The Related Metabolic Diseases and Treatments of Obesity. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, S.; Sockalingam, S.; Dash, S. Obesity as a multisystem disease: Trends in obesity rates and obesity-related complications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Leech, R.M.; McNaughton, S.A.; Abdollahi, M.; Houshiarrad, A.; Livingstone, K.M. Associations between diet quality and obesity in a nationally representative sample of Iranian households: A cross-sectional study. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2021, 8, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre-Millán, M.; Rupérez, A.I.; González-Gil, E.M.; Santaliestra-Pasías, A.; Vázquez-Cobela, R.; Gil-Campos, M.; Aguilera, C.M.; Gil, Á.; Moreno, L.A.; Leis, R.; et al. Dietary Patterns and Their Association with Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Markers in Children and Adolescents: Genobox Cohort. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romieu, I.; Dossus, L.; Barquera, S.; Blottière, H.M.; Franks, P.W.; Gunter, M.; Hwalla, N.; Hursting, S.D.; Leitzmann, M.; Margetts, B.; et al. Energy balance and obesity: What are the main drivers? Cancer Causes Control 2017, 28, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina-Remón, A.; Kirwan, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Estruch, R. Dietary patterns and the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, asthma, and neurodegenerative diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 262–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleftaki, S.A.; Amerikanou, C.; Gioxari, A.; Lantzouraki, D.Z.; Sotiroudis, G.; Tsiantas, K.; Tsiaka, T.; Tagkouli, D.; Tzavara, C.; Lachouvaris, L.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial on Pleurotuseryngii Mushrooms with Antioxidant Compounds and Vitamin D2 in Managing Metabolic Disorders. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Björgvinsson, T.; Kertz, S.J.; Bigda-Peyton, J.S.; McCoy, K.L.; Aderka, I.M. Psychometric properties of the CES-D-10 in a psychiatric sample. Assessment 2013, 20, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, M. Society and the Adolescent Self-Image; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Soldatos, C.R.; Dikeos, D.G.; Paparrigopoulos, T.J. Athens Insomnia Scale: Validation of an instrument based on ICD-10 criteria. J. Psychosom. Res. 2000, 48, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bountziouka, V.; Bathrellou, E.; Giotopoulou, A.; Katsagoni, C.; Bonou, M.; Vallianou, N.; Barbetseas, J.; Avgerinos, P.C.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Development, repeatability and validity regarding energy and macronutrient intake of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire: Methodological considerations. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denova-Gutiérrez, E.; Castañón, S.; Talavera, J.O.; Gallegos-Carrillo, K.; Flores, M.; Dosamantes-Carrasco, D.; Willett, W.C.; Salmerón, J. Dietary patterns are associated with metabolic syndrome in an urban Mexican population. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, Z.; Whiting, S.J.; Vatanparast, H. Current evidence on the association of the metabolic syndrome and dietary patterns in a global perspective. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Monforte, M.; Sánchez, E.; Barrio, F.; Costa, B.; Flores-Mateo, G. Metabolic syndrome and dietary patterns: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaillzadeh, A.; Kimiagar, M.; Mehrabi, Y.; Azadbakht, L.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C. Dietary patterns, insulin resistance, and prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Steffen, L.M.; Stevens, J. Dietary intake and the development of the metabolic syndrome: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Circulation. 2008, 117, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Chrysohoou, C.; Skoumas, J.; Tousoulis, D.; Toutouza, M.; Toutouzas, P.; Stefanadis, C. Impact of lifestyle habits on the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among Greek adults from the ATTICA study. Am. Heart J. 2004, 147, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Skoumas, Y.; Stefanadis, C. The association between food patterns and the metabolic syndrome using principal components analysis: The ATTICA Study. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, Y.; Lai, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Fu, P.; Yang, X.; Qi, L. Dietary patterns as compared with physical activity in relation to metabolic syndrome among Chinese adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Dallongeville, J.; Haas, B.; Ruidavets, J.B.; Amouyel, P.; Ferrières, J.; Simon, C.; Arveiler, D. Sedentary behaviour, physical activity and dietary patterns are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2012, 38, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Garcia, E.; Schulze, M.B.; Fung, T.T.; Meigs, J.B.; Rifai, N.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Major dietary patterns are related to plasma concentrations of markers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seifu, C.N.; Fahey, P.P.; Hailemariam, T.G.; Frost, S.A.; Atlantis, E. Dietary patterns associated with obesity outcomes in adults: An umbrella review of systematic reviews. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 6390–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaugh, M.A.; Herrick, J.S.; Sweeney, C.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Guiliano, A.R.; Byers, T.; Slattery, M.L. Diet composition and risk of overweight and obesity in women living in the southwestern United States. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.B.; Fung, T.T.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Dietary patterns and changes in body weight in women. Obesity 2006, 14, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talenezhad, N.; Mirzavandi, F.; Rahimpour, S.; Amel Shahbaz, A.P.; Mohammadi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M. Empirically derived dietary pattern and odds of non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases in overweight and obese adults: A case-control study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffey, K.J.; Steffen, L.M.; Van Horn, L.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Popkin, B.M. Dietary patterns matter: Diet beverages and cardiometabolic risks in the longitudinal Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrijvers, J.K.; McNaughton, S.A.; Beck, K.L.; Kruger, R. Exploring the Dietary Patterns of Young New Zealand Women and Associations with BMI and Body Fat. Nutrients 2016, 8, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, T.T.; Rimm, E.B.; Spiegelman, D.; Rifai, N.; Tofler, G.H.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Association between dietary patterns and plasma biomarkers of obesity and cardiovascular disease risk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zad, N.D.; Yusof, R.M.; Esmaili, H.; Jamaluddin, R.; Mohseni, F. Association of dietary pattern with biochemical blood profiles and bodyweight among adults with Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Tehran, Iran. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2015, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerver, J.M.; Yang, E.J.; Bianchi, L.; Song, W.O. Dietary patterns associated with risk factors for cardiovascular disease in healthy US adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moradi, S.; Kermani, M.A.H.; Bagheri, R.; Mohammadi, H.; Jayedi, A.; Lane, M.M.; Asbaghi, O.; Mehrabani, S.; Suzuki, K. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Adult Diabetes Risk: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chiou, H.Y.; Lee, H.A.; Hsu, L.M.; Chang, P.Y.; Kurniawan, A.L.; Chao, J.C. Association between Dietary Patterns and Serum Hepatic Enzyme Levels in Adults with Dyslipidemia and Impaired Fasting Plasma Glucose. Nutrients 2021, 13, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorzadeh, E.; Akhondi-Meybodi, M.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Mirzaei, M.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. Association between empirically derived dietary patterns and liver function tests in adults: Shahedieh cohort study. Nutrition 2021, 81, 110897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifan, P.; Yaghooti-Khorasani, M.; Asadi, Z.; Darroudi, S.; Rezaie, M.; Safarian, M.; Vatanparast, H.; Eslami, S.; Tayefi, M.; Pourrahim, E.; et al. Association of dietary patterns with serum vitamin D concentration among Iranian adults with abdominal obesity. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2021, 40, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denova-Gutiérrez, E.; Clark, P.; Muñoz-Aguirre, P.; Flores, M.; Talavera, J.O.; Chico-Barba, L.G.; Rivas, R.; Ramírez, P.; Salmerón, J. Dietary patterns are associated with calcium and vitamin D intake in an adult Mexican population. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grigoriou, E.; Trovas, G.; Papaioannou, N.; Dontas, I.; Makris, K.; Apostolou-Karampelis, K.; Dedoussis, G. Dietary Patterns of Greek Adults and Their Associations with Serum Vitamin D Levels and Heel Quantitative Ultrasound Parameters for Bone Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Ros, E.; Estruch, R.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Martínez-González, M.A.; PREDIMED Investigators. The PREDIMED trial. Mediterranean diet and health outcomes: How strong is the evidence? Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakaloudi, D.R.; Chrysoula, L.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Theodoridis, X.; Chourdakis, M. Impact of the Level of Adherence to Mediterranean Diet on the Parameters of Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.S.; Yan, E.C.; Chow, C.K. Interpreting SF-12 mental component score: An investigation of its convergent validity with CESD-10. Qual. Life Res. 2015, 24, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackett, B. The vicious cycle of depression and obesity. Nature 2022, 608, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Simmons, W.K.; van Rossum, E.F.C.; Penninx, B.W. Depression and obesity: Evidence of shared biological mechanisms. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Aguadero, N.; Alonso-Dominguez, R.; Garcia-Ortiz, L.; Agudo-Conde, C.; Rodriguez-Martin, C.; de Cabo-Laso, A.; Sanchez-Salgado, B.; Ramos, R.; Maderuelo-Fernandez, J.A.; Gomez-Marcos, M.A.; et al. Diet and physical activity in people with intermediate cardiovascular risk and their relationship with the health-related quality of life: Results from the MARK study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2016, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Noale, M.; Solmi, M.; Luchini, C.; Maggi, S. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with better quality of life: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Tasigchana, R.F.; León-Muñoz, L.M.; López-García, E.; Banegas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Guallar-Castillón, P. Correction: Mediterranean Diet and Health-Related Quality of Life in Two Cohorts of Community-Dwelling Older Adults. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0155171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, M.A.; Fíto, M.; Marrugat, J.; Covas, M.I.; Schröder, H.; REGICOR and HERMES investigators. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with better mental and physical health. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, T. A review of statistical methods for dietary pattern analysis. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics of the Study Participants | |
|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Men | 55 (37.7) |
| Women | 91 (62.3) |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 53.5 (11.4) |
| Educational years, mean (SD) | 15.3 (3.4) |
| Family status, n (%) | |
| Married | 109 (74.6) |
| Divorced | 7 (4.8) |
| Single | 20 (13.7) |
| Widowed | 5 (3.4) |
| Other | 5 (3.4) |
| Smoking, n (%) | |
| No | 109 (74.7) |
| Yes | 33 (22.6) |
| N/A | 4 (2.7) |
| Antihypertensive treatment, n (%) | |
| No | 91 (62.3) |
| Yes | 55 (37.7) |
| Statins, n (%) | |
| No | 104 (71.2) |
| Yes | 42 (28.8) |
| Antidiabetic agents, n (%) | |
| No | 111 (76.0) |
| Yes | 35 (24.0) |
| Anthropometric parameters | |
| ΒΜΙ (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 34 (6.3) |
| WC (cm), mean (SD) | 110.4 (13.4) |
| HC (cm), mean (SD) | 117.9 (14.9) |
| Lifestyle parameters | |
| IPAQ-SF (total MET- min/week), mean (SD) | 1723 (2142) |
| AII, mean (SD) | 5.4 (3.7) |
| CESD-R, mean (SD) | 16 (10) |
| Rosenberg Self-Esteem scale, mean (SD) | 31 (5) |
| PCS-12, mean (SD) | 45.7 (9.1) |
| MCS-12, mean (SD) | 48.6 (9.5) |
| Dietary Patterns | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Groups | Western-Type Pattern | Mediterranean-Like Diet Pattern | Healthy Pattern | Animal Meat and Sauces Pattern |
| Dairy (High-fat) | 0.57 | |||
| Dairy (Low-fat) | 0.59 | |||
| Refined grains | 0.66 | |||
| Whole grains | 0.60 | |||
| Fast Food | 0.74 | |||
| Red Meat | 0.50 | |||
| Processed Meat | 0.57 | |||
| Fish | 0.59 | |||
| Vegetables|cooked mixed vegetables | 0.75 | |||
| Fruits|fruit juices | 0.53 | |||
| Pies | 0.66 | |||
| Sweets | 0.56 | |||
| Salty Snacks | 0.63 | |||
| Olive oil | olives | 0.63 | |||
| Soft drinks | 0.52 | |||
| Sauces | 0.43 | |||
| Animal & HydrogenatedFats | 0.54 | |||
| Poultry | 0.70 | |||
| Pulses | 0.50 | |||
| Dried fruits | 0.62 | |||
| Nuts | 0.66 | |||
| Coffee and Tea | 0.55 | |||
| Seed oil | 0.53 | |||
| Alcohol | −0.29 | |||
| Eggs | 0.29 | |||
| Cronbach’s a | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 0.73 |
| Parameters | Western-Type Pattern | Mediterranean-Like Diet Pattern | Healthy Pattern | Animal Meat and Sauces Pattern | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometrics | |||||
| BW (kg) | rho | 0.19 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.29 |
| p | 0.030 | 0.947 | 0.801 | 0.001 | |
| BF (%) | rho | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| p | 0.136 | 0.470 | 0.504 | 0.844 | |
| BF (kg) | rho | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.19 |
| p | 0.004 | 0.457 | 0.499 | 0.036 | |
| FFM (kg) | rho | 0.05 | −0.11 | −0.05 | 0.26 |
| p | 0.565 | 0.246 | 0.616 | 0.004 | |
| TBW (kg) | rho | 0.11 | −0.05 | −0.08 | 0.23 |
| p | 0.226 | 0.579 | 0.355 | 0.012 | |
| ΒΜΙ (kg/m2) | rho | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.18 |
| p | 0.130 | 0.687 | 0.390 | 0.044 | |
| WC (cm) | rho | 0.20 | −0.08 | 0.03 | 0.18 |
| p | 0.028 | 0.381 | 0.747 | 0.041 | |
| HC(cm) | rho | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.10 |
| p | 0.102 | 0.312 | 0.470 | 0.236 | |
| Biochemical | |||||
| Urea (mg/dL) | Rho | −0.04 | −0.11 | −0.09 | 0.10 |
| p | 0.648 | 0.214 | 0.284 | 0.265 | |
| Uricacid (mg/dL) | Rho | −0.09 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| p | 0.295 | 0.289 | 0.726 | 0.693 | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | Rho | −0.02 | −0.12 | −0.02 | 0.13 |
| p | 0.863 | 0.190 | 0.805 | 0.159 | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | Rho | −0.03 | −0.13 | 0.09 | −0.08 |
| p | 0.752 | 0.151 | 0.337 | 0.349 | |
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | Rho | 0.23 | −0.20 | 0.00 | 0.11 |
| p | 0.014 | 0.037 | 0.964 | 0.236 | |
| TC (mg/dL) | Rho | 0.11 | −0.14 | −0.08 | −0.03 |
| p | 0.220 | 0.119 | 0.373 | 0.768 | |
| TG (mg/dL) | Rho | 0.12 | −0.12 | −0.02 | −0.05 |
| p | 0.190 | 0.168 | 0.817 | 0.603 | |
| HDL (mg/dL) | Rho | −0.10 | 0.22 | 0.02 | −0.09 |
| p | 0.281 | 0.011 | 0.789 | 0.331 | |
| LDL (mg/dL) | Rho | 0.10 | 0.11 | −0.10 | −0.04 |
| p | 0.274 | 0.205 | 0.270 | 0.665 | |
| AST (iu/L) | Rho | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.05 | −0.02 |
| p | 0.997 | 0.625 | 0.588 | 0.819 | |
| ALT (iu/L) | Rho | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.06 |
| p | 0.041 | 0.843 | 0.131 | 0.492 | |
| γ-GT (iu/L) | Rho | 0.16 | −0.09 | 0.03 | 0.11 |
| p | 0.090 | 0.338 | 0.764 | 0.227 | |
| ALP (U/L) | Rho | 0.20 | 0.05 | −0.01 | −0.02 |
| p | 0.029 | 0.576 | 0.925 | 0.825 | |
| Fe (μg/dL) | Rho | −0.19 | 0.02 | −0.05 | −0.21 |
| p | 0.043 | 0.831 | 0.579 | 0.024 | |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | Rho | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| p | 0.538 | 0.316 | 0.991 | 0.556 | |
| Albumin (g/dL) | Rho | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.05 | −0.08 |
| p | 0.390 | 0.131 | 0.568 | 0.404 | |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) | Rho | −0.22 | 0.01 | −0.07 | −0.10 |
| p | 0.013 | 0.917 | 0.433 | 0.254 | |
| CRP (mg/L) | Rho | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.24 |
| p | 0.409 | 0.326 | 0.655 | 0.010 | |
| LDH (U/L) | Rho | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| p | 0.712 | 0.433 | 0.555 | 0.719 | |
| Lifestyle | |||||
| AII | Rho | 0.19 | −0.14 | −0.12 | 0.17 |
| p | 0.042 | 0.120 | 0.205 | 0.059 | |
| CESD-R | Rho | 0.17 | −0.21 | 0.00 | 0.09 |
| p | 0.088 | 0.033 | 0.991 | 0.340 | |
| Rosenberg Self-Esteem scale | Rho | −0.07 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.12 |
| p | 0.482 | 0.014 | 0.443 | 0.212 | |
| PCS-12 | Rho | −0.03 | 0.26 | −0.07 | 0.03 |
| p | 0.785 | 0.006 | 0.444 | 0.759 | |
| MCS-12 | Rho | −0.15 | 0.20 | 0.04 | −0.12 |
| p | 0.121 | 0.038 | 0.679 | 0.200 | |
| IPAQ-SF (total MET- min/week) | Rho | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.05 | −0.22 |
| p | 0.748 | 0.023 | 0.567 | 0.012 | |
| Western-Type Pattern | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variables | β1 (SE) | p | β2 (SE) | p | β3 (SE) | p | β4 (SE) | p |
| BF (kg) | 9.01 (2.55) | 0.001 | 5.87 (1.11) | <0.001 | 5.66 (1.14) | <0.001 | 4.38 (1.26) | 0.001 |
| WC(cm) | 6.19 (2.99) | 0.041 | 5.13 (1.56) | 0.001 | 5.42 (1.60) | 0.001 | 4.95 (1.77) | 0.006 |
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | 0.21 (0.09) | 0.016 | 0.23 (0.09) | 0.009 | 0.23 (0.09) | 0.009 | 0.24 (0.09) | 0.008 |
| ALT (iu/L) | 0.20 (0.10) | 0.035 | 0.24 (0.10) | 0.014 | 0.24 (0.10) | 0.017 | 0.25 (0.10) | 0.019 |
| ALP (U/L) | 9.91 (4.35) | 0.025 | 8.83 (4.68) | 0.062 | 9.55 (4.75) | 0.047 | 9.78 (4.97) | 0.041 |
| Fe (μg/dL) | −0.36 (0.18) | 0.040 | −0.27 (0.2) | 0.176 | −0.28 (0.2) | 0.174 | −0.19 (0.22) | 0.393 |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) | −0.41 (0.2) | 0.046 | −0.44 (0.21) | 0.043 | −0.44 (0.21) | 0.041 | −0.55 (0.23) | 0.021 |
| AII | 1.99 (0.85) | 0.021 | 1.51 (0.87) | 0.085 | 1.42 (0.91) | 0.121 | 1.10 (0.98) | 0.263 |
| Mediterranean-like diet pattern | ||||||||
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | −0.17 (0.09) | 0.050 | −0.17 (0.09) | 0.050 | −0.16 (0.09) | 0.070 | −0.16 (0.10) | 0.102 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 4.34 (1.7) | 0.012 | 3.86 (1.5) | 0.011 | 3.44 (1.53) | 0.026 | 4.03 (1.73) | 0.022 |
| CESD-R | −4.13 (1.9) | 0.032 | −3.86 (1.88) | 0.043 | −4.09 (1.92) | 0.036 | −5.63 (2.07) | 0.008 |
| Rosenberg Self-Esteem scale | 0.19 (0.08) | 0.023 | 0.18 (0.08) | 0.034 | 0.19 (0.08) | 0.020 | 0.28 (0.35) | 0.417 |
| PCS-12 | 0.22 (0.08) | 0.009 | 0.18 (0.08) | 0.025 | 0.18 (0.08) | 0.031 | 0.53 (0.34) | 0.124 |
| MCS-12 | 0.19 (0.08) | 0.026 | 0.19 (0.08) | 0.023 | 0.19 (0.08) | 0.025 | 0.87 (0.35) | 0.016 |
| Animal meat and sauces pattern | ||||||||
| BF (kg) | 8.09 (2.48) | 0.001 | 3.54 (1.21) | 0.004 | 4.01 (1.22) | 0.001 | 6.17 (2.88) | 0.033 |
| FFM (kg) | 0.04 (0.02) | 0.048 | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.033 | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.040 | 0.03 (0.02) | 0.034 |
| TBW (kg) | 0.20 (0.09) | 0.033 | 0.15 (0.06) | 0.016 | 0.16 (0.06) | 0.010 | 0.17 (0.07) | 0.011 |
| ΒΜΙ (kg/m2) | 2.63 (1.27) | 0.041 | 2.24 (1.40) | 0.113 | 2.47 (1.44) | 0.089 | 2.23 (1.52) | 0.1445 |
| WC (cm) | 5.74 (2.89) | 0.049 | 3.78 (1.60) | 0.020 | 4.33 (1.63) | 0.009 | 2.89 (1.74) | 0.100 |
| Fe (μg/dL) | −0.42 (0.2) | 0.041 | −0.41 (0.22) | 0.067 | −0.42 (0.23) | 0.067 | −0.40 (0.25) | 0.114 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 2.26 (1.13) | 0.048 | 2.21 (1.26) | 0.082 | 2.23 (1.3) | 0.089 | 2.09 (1.43) | 0.146 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amerikanou, C.; Kleftaki, S.-A.; Valsamidou, E.; Tzavara, C.; Gioxari, A.; Kaliora, A.C. Dietary Patterns, Cardiometabolic and Lifestyle Variables in Greeks with Obesity and Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235064
Amerikanou C, Kleftaki S-A, Valsamidou E, Tzavara C, Gioxari A, Kaliora AC. Dietary Patterns, Cardiometabolic and Lifestyle Variables in Greeks with Obesity and Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235064
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmerikanou, Charalampia, Stamatia-Angeliki Kleftaki, Evdokia Valsamidou, Chara Tzavara, Aristea Gioxari, and Andriana C. Kaliora. 2022. "Dietary Patterns, Cardiometabolic and Lifestyle Variables in Greeks with Obesity and Metabolic Disorders" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235064
APA StyleAmerikanou, C., Kleftaki, S.-A., Valsamidou, E., Tzavara, C., Gioxari, A., & Kaliora, A. C. (2022). Dietary Patterns, Cardiometabolic and Lifestyle Variables in Greeks with Obesity and Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients, 14(23), 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235064