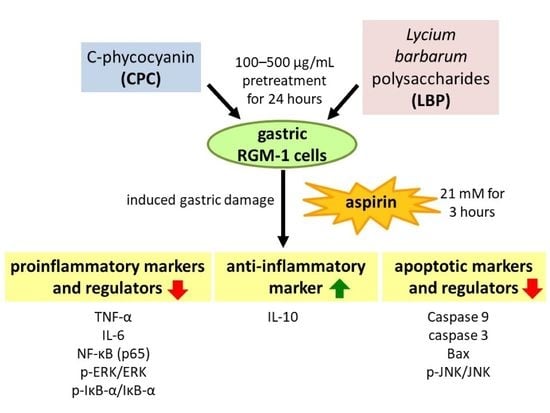
C-Phycocyanin and Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Protect against Aspirin-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Gastric RGM-1 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Treatments
2.2. Proinflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Markers and Regulators
2.3. Apoptotic Markers and Regulators
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability
3.2. Effects of CPC and LBP on Proinflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Markers
3.3. Effects of CPC and LBP on Inflammatory Regulators
3.4. Actions of CPC and LBP on Apoptotic Markers
3.5. Effects of CPC and LBP on Apoptotic Regulators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Damman, P.; van’t Hof, A.W.; Ten Berg, J.M.; Jukema, J.W.; Appelman, Y.; Liem, A.H.; de Winter, R.J. 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: Comments from the Dutch ACS working group. Neth. Heart J. 2017, 25, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, P.I.; Tsai, T.J. Epidemiology of upper gastrointestinal damage associated with low-dose aspirin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 5049–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, R.L.; Romero, J.J.; Dial, E.J.; Akunda, J.K.; Langenbach, R.; Lichtenberger, L.M. The effects of aspirin on gastric mucosal integrity, surface hydrophobicity, and prostaglandin metabolism in cyclooxygenase knockout mice. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firdaus, S.B.; Ghosh, D.; Chattyopadhyay, A.; Jana, K.; Bandyopadhyay, D. A combination of aqueous curry (Murraya koenigii) leaf extract and melatonin protects against piroxicam induced gastric ulcer in male albino rats: Involvement of antioxidant mechanism(s). J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 8, 428–436. [Google Scholar]
- Musumba, C.; Pritchard, D.M.; Pirmohamed, M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of NSAID-induced peptic ulcers. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 3, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Slomiany, A. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation in the amplification of Helicobacter pylori-elicited induction in gastric mucosal expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase. OA Inflamm. 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Inoguchi, T.; Sasaki, S.; Maeda, Y.; McCarty, M.F.; Fujii, M.; Ikeda, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Sonoda, N.; Takayanagi, R. Phycocyanin and phycocyanobilin from Spirulina platensis protect against diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R110–R120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuddus, M.; Singh, P.; Thomas, G.; Al-Hazimi, A. Recent developments in production and biotechnological applications of C-phycocyanin. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 742859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madhyastha, H.K.; Radha, K.S.; Nakajima, Y.; Omura, S.; Maruyama, M. uPA dependent and independent mechanisms of wound healing by C-phycocyanin. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2691–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gur, C.S.; Erdogan, D.K.; Onbasılar, I.; Atilla, P.; Cakar, N.; Gurhan, I.D. In vitro and in vivo investigations of the wound healing effect of crude Spirulina extract and C-phycocyanin. J. Med. Plants Res. 2013, 7, 425–433. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.F.; Wan, L.L.; Peng, J.L.; Guo, C. Alleviation of the acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by Lycium barbarum polysaccharides through the suppression of oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zhou, Z.W.; Sheng, H.P.; He, L.J.; Fan, X.W.; He, Z.X.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.J.; Gu, L.; et al. An evidence-based update on the pharmacological activities and possible molecular targets of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 33–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z. Extraction, structural characterization, and biological functions of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides: A review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.; Kong, H. The effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on alcohol-induced oxidative stress in rats. Molecules 2011, 16, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, I.; Kawano, S.; Tsuji, S.; Matsui, H.; Nakama, A.; Sawaoka, H.; Ohno, T. RGM1, a cell line derived from normal gastric mucosa of rat. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 1996, 32, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Hanif, R.; Sphicas, E.; Shiff, S.J.; Rigas, B. Effect of aspirin on induction of apoptosis in HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 55, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, R.; Tamura, M.; Matsui, H.; Nagano, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, T.; Mizokami, Y.; Hyodo, I. Qing Dai attenuates nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in gastrointestinal epithelial cells. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 56, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mustonen, H.; Puolakkainen, P.; Kemppainen, E.; Kiviluoto, T.; Kivilaakso, E. Taurocholate potentiates ethanol-induced NF-κB activation and inhibits caspase-3 activity in cultured rat gastric mucosal cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, G.S.; Drapeau, C.; Lenninger, M.; Benson, K.F. Clinical safety of a high dose of phycocyanin-enriched aqueous extract from arthrospira (spirulina) platensis: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled study with a focus on anticoagulant activity and platelet activation. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amagase, H.; Sun, B.; Borek, C. Lycium barbarum (goji) juice improves in vivo antioxidant biomarkers in serum of healthy adults. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Adhikary, B.; Chand, S.; Maity, B.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. Molecular mechanism of indomethacin-induced gastropathy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.E.; Chen, Y.; Ho, E.A.; Martinez, S.A.; Davies, N.M. Pharmacological effects of a C-phycocyanin-based multicomponent nutraceutical in an in-vitro canine chondrocyte model of osteoarthritis. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 79, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, C.M.; Cheng, S.N.; Wong, C.S.; Kuo, Y.L.; Chou, T.C. Antiinflammatory and antihyperalgesic activity of C-phycocyanin. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 108, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, A.K.; Ahmed, H.B.; Hagar, Y.R. Spirulina supplements: An approach moderating aspirin persuaded histological and ultra-structural alterations in albino rats gastric mucosa. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2022, 46, 204–216. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, P.; Li, Y.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y. Neuroprotective effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youchao, Q.; Guozhen, D.; Guanghui, F.; Ning, P. Effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on cell signal transduction pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112620. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Liong, E.C.; Ching, Y.P.; Chang, R.C.C.; So, K.F.; Fung, M.L.; Tipoe, G.L. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect mice liver from carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress and necroinflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Scheiman, J.; Abraham, N.S.; Antman, E.M.; Chan, F.K.; Furberg, C.D.; Johnson, D.A.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Quigley, E.M.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Power, J.J.; Dennis, M.S.; Redlak, M.J.; Miller, T.A. Aspirin-induced mucosal cell death in human gastric cells: Evidence supporting an apoptotic mechanism. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlak, M.J.; Power, J.J.; Miller, T.A. Role of mitochondria in aspirin-induced apoptosis in human gastric epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G731–G738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Varadharaj, S.; Shobha, J.C.; Naidu, M.U.; Parinandi, N.L.; Kutala, V.K.; Kuppusamy, P. C-phycocyanin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in adult rat cardiomyocytes. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Xu, G.; Chen, T.; Wong, Y.S.; Zhao, H.L.; Fan, R.R.; Chan, J.C. Phycocyanin protects INS-1E pancreatic beta cells against human islet amyloid polypeptide-induced apoptosis through attenuating oxidative stress and modulating JNK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, B.; Ji, Q.; Wen, Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Hou, G.; Zhong, J. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect human lens epithelial cells against oxidative stress–induced apoptosis and senescence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Ma, L.; Hao, Y.; Yu, J. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide prevents focal cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wan, Q. Mechanism of licoflavone in protecting human gastric mucosal epithelial cells from aspirin-induced injury. Chin. Gen. Pract. 2018, 21, 3971–3975. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Li, X.; Yu, H.; Zhu, S.; He, Y.; Komatsu, K.; Guo, D.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Luo, H.; et al. Gastroprotective effect of araloside A on ethanol- and aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in mice: Involvement of H+/K+-ATPase and mitochondrial-mediated signaling pathway. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 73, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneh, V.; Vijay, L.K. Artesunate affords protection against aspirin–induced gastric injury by targeting oxidative stress and proinflammatory signaling. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 390–397. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, Y.I.; Abd El-Ghffar, E.A. Spirulina ameliorates aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in albino mice by alleviating oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghffar, E.A.; Al-Sayed, E.; Safia, S.M.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Efferth, T. The protective role of Ocimum basilicum L. (Basil) against aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in mice: Impact on oxidative stress, inflammation, motor deficits and anxiety-like behavior. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4457–4468. [Google Scholar]
- Morufu, E.B.; Elizabeth, E.B.; Jacinta, N.O.; Ogochukwu, S.M.; Fankou, S.A.D. Protective roles of Vigna subterranea (Bambara nut) in rats with aspirin-induced gastric mucosal injury. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 16, 342–349. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Mabrok, H.B. Protective Effect of pomegranate peel powder against gastric ulcer in rats. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 12, 4888–4899. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.T.; Wang, M.R.; Hua, G.D.; Li, Q.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Lang, R.; Weng, W.L.; Xue, C.M.; Zhu, B.C. Inhibition of aspirin-induced gastrointestinal injury: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 730681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, F.A.; El Dib, R.A.; Wahman, L.F.; El-Shenawy, S.M.; El-Awdan, S. Gastro protective effect of pentagalloyl glucose on aspirin induced gastric mucosal ulcer in comparison with omeprazole, Famotidine and Melatonin. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 785–795. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.; Govindhan, S.; Baiju, E.C.; Padmavathi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Padikkala, J. Cyperus rotundus L. prevents non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastric mucosal damage by inhibiting oxidative stress. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 26, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Matsui, H.; Chao, J.C.-J. C-Phycocyanin and Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Protect against Aspirin-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Gastric RGM-1 Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235113
Liu Y-C, Chang C-C, Matsui H, Chao JC-J. C-Phycocyanin and Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Protect against Aspirin-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Gastric RGM-1 Cells. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):5113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yu-Chen, Chun-Chao Chang, Hirofumi Matsui, and Jane C.-J. Chao. 2022. "C-Phycocyanin and Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Protect against Aspirin-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Gastric RGM-1 Cells" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 5113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235113
APA StyleLiu, Y.-C., Chang, C.-C., Matsui, H., & Chao, J. C.-J. (2022). C-Phycocyanin and Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Protect against Aspirin-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Gastric RGM-1 Cells. Nutrients, 14(23), 5113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235113