Daily Habits of Brazilians at Different Moments of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
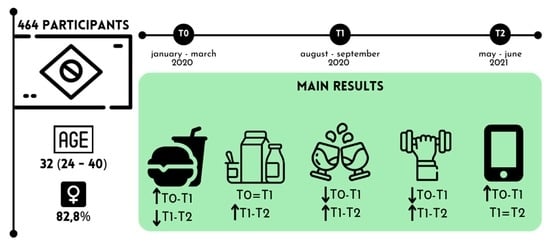
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection Questionnaire and Procedure
2.3. Variables
2.4. Daily Habits
2.5. Eating Habits
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zanke, A.; Thenge, R.; Adhao, V. COVID-19: A Pandemic Declare by World Health Organization. IP Int. J. Compr. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 5, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://Covid19.Who.Int/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Burki, T. The Origin of SARS-CoV-2. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1018–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chiesa, V.; Antony, G.; Wismar, M.; Rechel, B. COVID-19 Pandemic: Health Impact of Staying at Home, Social Distancing and “lockdown” Measures—A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews. J. Public Health 2021, 43, E462–E481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracale, R.; Vaccaro, C.M. Changes in Food Choice following Restrictive Measures Due to COVID-19. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Cinelli, G.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; et al. Eating Habits and Lifestyle Changes during COVID-19 Lockdown: An Italian Survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.; Oliveira, L.A.; Daniel, M.M.; Ferreira, L.G.; della Lucia, C.M.; Liboredo, J.C.; Anastácio, L.R. Lifestyle and Eating Habits before and during COVID-19 Quarantine in Brazil. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 25, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liboredo, J.C.; Anastácio, L.R.; Ferreira, L.G.; Oliveira, L.A.; della Lucia, C.M. Quarantine during COVID-19 Outbreak: Eating Behavior, Perceived Stress, and Their Independently Associated Factors in a Brazilian Sample. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 704619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Roso, M.B.; de Padilha, P.C.; Mantilla-Escalante, D.C.; Ulloa, N.; Brun, P.; Acevedo-Correa, D.; Peres, W.A.F.; Martorell, M.; Aires, M.T.; de Cardoso, L.O.; et al. Confinamiento Del COVID-19 y Cambios En Las Tendencias Alimentarias de Los Adolescentes En Italia, España, Chile, Colombia y Brasil. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, A.F.; Sun, X.; Zheng, J.; Mi, B.; Zuo, H.; Ruan, G.; Hussain, A.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z. Perceived Risk, Behavior Changes and Health-Related Outcomes during COVID-19 Pandemic: Findings among Adults with and without Diabetes in China. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 167, 108350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdas, D.I.; Zacharakis, E.D. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Physical Activity in a Sample of Greek Adults. Sports 2020, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnicka, M.; Drywień, M.E.; Zielinska, M.A.; Hamułka, J. Dietary and Lifestyle Changes during COVID-19 and the Subsequent Lockdowns among Polish Adults: PLifeCOVID-19 Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, C.; Kheir, M.B.; Zakhour, M.; Haddad, R.; Hachach, M.; Sacre, H.; Salameh, P. Association between Eating Behavior and Quarantine/Confinement Stressors during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.R.; Werneck, A.O.; Malta, D.C.; Souza-Júnior, P.R.B.; Azevedo, L.O.; Barros, M.B.A.; Szwarcwald, C.L. Incidence of Physical Inactivity and Excessive Screen Time during the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Brazil: What Are the Most Affected Population Groups? Ann. Epidemiol. 2021, 62, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, C.S.; Caria, A.C.I.; Júnior, R.A.; Pitanga, F.J.G. The Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Levels of Physical Fitness. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2020, 66, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Pugliese, G.; Framondi, L.; di Matteo, R.; Laudisio, D.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Does SARS-CoV-2 Threaten Our Dreams? Effect of Quarantine on Sleep Quality and Body Mass Index. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornili, M.; Petri, D.; Berrocal, C.; Fiorentino, G.; Ricceri, F.; Macciotta, A.; Bruno, A.; Farinella, D.; Baccini, M.; Severi, G.; et al. Psychological Distress in the Academic Population and Its Association with Socio-Demographic and Lifestyle Characteristics during COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown: Results from a Large Multicenter Italian Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.; Maciejewski, G.; Hand, C.J. Changes in Diet, Sleep, and Physical Activity Are Associated with Differences in Negative Mood during COVID-19 Lockdown. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 588604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, S.J.; Coyne, P.; St-Pierre, E. Stress, Physical Activity, and Screen-Related Sedentary Behaviour within the First Month of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Appl. Psychol. Health Well Being 2021, 13, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.M.; Liboredo, J.C.; Anastácio, L.R.; Souza, T.C.D.M.; Oliveira, L.A.; della Lucia, C.M.; Ferreira, L.G. Incidence and Associated Factors of Weight Gain during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 818632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werneck, A.O.; Silva, D.R.; Malta, D.C.; Gomes, C.S.; Souza-Júnior, P.R.B.; Azevedo, L.O.; Barros, M.B.A.; Szwarcwald, C.L. Associations of Sedentary Behaviours and Incidence of Unhealthy Diet during the COVID-19 Quarantine in Brazil. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, E.M.; Rauber, F.; Costa, C.D.S.; Leite, M.A.; Gabe, K.T.; Louzada, M.L.D.C.; Levy, R.B.; Monteiro, C.A. Dietary Changes in the NutriNet Brasil Cohort during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Rev. Saude Publica 2020, 54, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szwarcwald, C.L.; Damacena, G.N.; de Azevedo Barros, M.B.; Malta, D.C.; de Souza Júnior, P.R.B.; Azevedo, L.O.; Machado, Í.E.; Lima, M.G.; Romero, D.; Gomes, C.S.; et al. Factors Affecting Brazilians’ Self-Rated Health during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Cad. Saude Publica 2021, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, R.L.; Ivine, A.; Santana, C.; Carlos, P.; de Figueiredo, M.; Lucciola, M.; Almeida, D.; Marques, V.; Suen, M.; Conceição, M. Relação Entre a Pandemia Da COVID-19, Compulsão Alimentar e Sofrimento Mental Em Profissionais de Saúde No Brasil: Um Estudo Transversal Suffering in Health Professionals in Brazil: A Cross-Sectional Study. Rev. Bras. Med. Trab. 2021, 19, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Shinkawa, H.; Mori, H.; Nishimura, T.; Nakamura, K. Longitudinal Association between Smartphone Ownership and Depression among Schoolchildren under COVID-19 Pandemic. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2022, 57, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caso, D.; Guidetti, M.; Capasso, M.; Cavazza, N. Finally, the Chance to Eat Healthily: Longitudinal Study about Food Consumption during and after the First COVID-19 Lockdown in Italy. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 95, 104275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aro, F.; Pereira, B.V.; Bernardo, D.N.D.A. Comportamento Alimentar Em Tempos de Pandemia Por COVID-19/Eating Behavior in Times by COVID-19. Braz. J. Dev. 2021, 7, 59736–59748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, J.; Seto, S.; Fukuda, Y.; Ito, K.; Imamura, F.; Funakoshi, S.; Izumi, S.-I. Life Alterations and Stress During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Japan: Two-Time Comparison. J. Disaster Res. 2022, 17, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.M.; Lauren, B.N.; Woo Baidal, J.A.; Ozanne, E.M.; Hur, C. Persistent Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Diet, Exercise, Risk for Food Insecurity, and Quality of Life: A Longitudinal Study among U.S. Adults. Appetite 2021, 167, 105639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Carvalho, L.; da Silva, M.V.; dos Santos Costa, T.; de Oliveira, T.E.; de Oliveira, G.A. Impacto Do Isolamento Social Na Vida Das Pessoas No Período Da Pandemia Da COVID-19. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Neira, C.; Godinho, R.; Rincón, F.; Mardones, R.; Pedroso, J. Consequences of the COVID-19 Syndemic for Nutritional Health: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-leyva, D.; Pierce, G.N. The Impact of Nutrition on the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Nutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Smith, J. “Covibesity”, a New Pandemic. Obes. Med. 2020, 19, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipioni, M.E.; Riquieri, M.R.L.; Barbosa, J.P.M.; Biscotto, D.B.; Sarti, T.D.; Andrade, M.A.C. Masks Cover the Face, Hunger Unmasks the Rest: COVID-19 and the Fighting against Hunger in Brazil. Scielo Prepr. Health Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowiak-Szymanik, A.; Wdowiak, A.; Szymanik, P.; Grocholewicz, K. Pandemic COVID-19 Influence on Adult’s Oral Hygiene, Dietary Habits and Caries Disease—Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegelund, M.H.; Fjordside, L.; Faurholt-Jepsen, D.; Christensen, D.L.; Bygbjerg, I.C. Opportunistic Non-Communicable Diseases in Times of COVID-19. APMIS 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki, Ethical Principles for Scientific Requirements and Research Protocols. Bull. World Health Organ. 2013, 79, 373.
- Planalto. Federal Law no 14.035, August 2020. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2019-2022/2020/Lei/L14035.htm#art1 (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Planalto. LEI No 13.979, de 6 de Fevereiro de 2020. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2019-2022/2020/Lei/L13979.htm (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Brasil Decreto No 10.282, de 20 de Março de 2020. Diário Oficial Da União; Brasil 2020. Available online: https://www2.camara.leg.br/legin/fed/decret/2020/decreto-10282-20-marco-2020-789863-publicacaooriginal-160165-pe.html (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Scarmozzino, F.; Visioli, F. COVID-19 and the Subsequent Lockdown Modified Dietary Habits of Almost Half the Population in an Italian Sample. Foods 2020, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidor, A.; Rzymski, P. Dietary Choices and Habits during COVID-19 Lockdown: Experience from Poland. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltar, F.; Brunet, I. Social Research 2.0: Virtual Snowball Sampling Method Using Facebook. Internet Res. 2012, 22, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SISVAN. Orientações Para Avaliação de Marcadores de Consumo Alimentar Na Atenção Básica; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2015; ISBN 9788533422483. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil Decreto Legislativo No 6, de 2020. Diário Oficial da União; 2020. Available online: https://legislacao.presidencia.gov.br/atos/?tipo=DLG&numero=6&ano=2020&ato=b1fAzZU5EMZpWT794 (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Ministério da Saúde Pátria Vacinada. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/vacinacao/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Costa, R.; Ensp, D.C.S.; Jatobá, A.; Fiocruz, C.E.E. As Medidas de Enfrentamento à Pandemia Da COVID-19 No Brasil Na Percepção Da População Atuante Nas Mídias Sociais. Cent. Estud. Estratégicos Fiocruz Sp. Abr. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcanti, I.M.F. Educação e a Volta Às Aulas Presenciais Durante a Pandemia Da COVID-19. In Educação e a Volta às Aulas Presenciais Durante a Pandemia da COVID-19; UNICEF: Brasília, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.Z.; Silva, F.M.; Morigi, T.Z.; Zucoloto, M.L.; Silva, T.L.; Joaquim, A.G.; Dall’agnol, G.; Galdino, G.; Martinez, M.O.Z.; da Silva, W.R. Physical Activity in Periods of Social Distancing Due to COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Cienci. Saude Coletiva 2020, 25, 4157–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, R.; To, Q.G.; Khalesi, S.; Williams, S.L.; Alley, S.J.; Thwaite, T.L.; Fenning, A.S.; Vandelanotte, C. Depression, Anxiety and Stress during COVID-19: Associations with Changes in Physical Activity, Sleep, Tobacco and Alcohol Use in Australian Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.; Abdeen, S.; Kehyayan, V.; Bougmiza, I. Impact of Staying at Home Measures during COVID-19 Pandemic on the Lifestyle of Qatar’s Population: Perceived Changes in Diet, Physical Activity, and Body Weight. Prev. Med. Rep. 2020, 24, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primo, A. Emotions and Relationships during Social Isolation: Intensifying the Use of Social Media for Interaction during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Rev. Comun. Inovação 2020, 21, 176–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço, C.M.; Júnior, J.H.; Zanetti, H.R.; Mendes, E.L. Nomofobia: O Vício Em Gadgets Pode Ir Muito Além! Multi-Sci. J. 2018, 1, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, H.; Valentin, D.; Franco-Luesma, E.; Rakotosamimanana, V.R.; Gomez-Corona, C.; Saldana, E.; Saenz-Navajas, M. How Has COVID-19, Lockdown and Social Distancing Changed Alcohol Drinking Patterns? A Cross-Cultural Perspective between Britons and Spaniards. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 95, 104344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Weekly Epidemiological Update and Weekly Operational Update. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- Schmidt, B.; Crepaldi, M.A.; Bolze, S.D.A.; Neiva-silva, L.; Demenech, L.M. Mental Health and Psychological Interventions during the New Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). Estud. Psicol. 2020, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandifar, A.; Badrfam, R. Iranian Mental Health during the COVID-19 Epidemic. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2020, 51, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo-Arroyo, E.; Mora, M.; Vázquez-Araújo, L. Consumer Behavior in Confinement Times: Food Choice and Cooking Attitudes in Spain. Int. J. Gastron Food Sci. 2020, 21, 100226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.; della Lucia, C.; Rezende, F.; Ferreira, L.G.; Anastacio, L.; Souza, T.; Daniel, M.; Liboredo, J. Food Craving and Its Associated Factors during COVID-19 Outbreak in Brazil. Am. J. Health Educ. 2022, 53, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, B.; Brassard, D.; Lapointe, A.; Laramée, C.; Kearney, M.; Côté, M.; Bélanger-Gravel, A.; Desroches, S.; Lemieux, S.; Plante, C. Changes in Diet Quality and Food Security among Adults during the COVID-19-Related Early Lockdown: Results from NutriQuébec. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria, H.P. Some Considerations on the Nutritional (in)Security in Brazil during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pist. Periódico Interdiscip. 2021, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, A.C.V.; da Silva, C.E.M.; Soares, F.R.G.; da Silva, J.A.M. Factors Associated with People’s Behavior in Social Isolation during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Cienc. Saude Coletiva 2020, 25, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Variable | T1 Median (Q1–Q3) % (n) | T2 Median (Q1–Q3) % (n) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Female | 82.8% (384) | 82.8% (384) | - |
| Male | 17.2% (80) | 17.2% (80) | |
| Age (years) | 24.0 (32.0–40.0) | 24.0 (32.0–40.0) | - |
| Schooling | |||
| Complete middle school | 0.2% (1) | 0.2% (1) | |
| Incomplete high school | 3.7% (17) | 3.7% (17) | |
| Complete high school | 0.4% (2) | 0.4% (2) | - |
| Incomplete undergraduate degree | 19.8% (92) | 19.8% (92) | |
| Complete undergraduate degree | 23.3% (108) | 23.3% (108) | |
| Incomplete graduate degree | 41.6% (193) | 41.6% (193) | |
| Complete graduate degree | 11.0% (51) | 11.0% (51) | |
| Monthly per capita income (R$) | 4.702.5 (3.657.5–7.837.5) | 4.702.5 (2.612.5–7.837.5) | 0.779 1 |
| Social distancing | |||
| Total | 60.3% (280) | 45.5% (211) | <0.001 2 |
| Partial | 36.6% (170) | 48.1% (223) | (44.982) |
| None | 3.0% (14) | 6.5% (30) | |
| Occupational status | |||
| Unemployed | 7.8% (36) | 6.3% (29) | |
| Retired | 3.4% (16) | 3.9% (18) | <0.001 2 |
| Working/studying fully remotely | 44.8% (208) | 44.4% (206) | (40.503) |
| Working/studying partially remotely | 27.8% (129) | 22.8% (106) | |
| Working/studying in person | 10.6% (49) | 20.0% (93) | |
| Others | 5.6% (26) | 2.6% (12) |
| Variable Median (Q1–Q3) | T0 | T1 | T2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screen time (hours/day) | 6.50 a (3.00–6.50) | 10.50 b (6.50–14.50) | 10.50 b (6.50–10.50) | <0.001 ¹ |
| Frequency of alcoholic beverage intake (times/week) | 0.50 (0.00–1.00) | 0.50 (0.00–2.50) | 0.50 (0.00–1.00) | 0.216 ¹ |
| Number of standard drinks of alcoholic beverage (drinks/ocasion) | 2.50 a (0.00–2.50) | 1.00 b (0.00–2.50) | 1.75 c (0.00–2.50) | 0.007 ¹ |
| Cigarette (number/days) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.687 ¹ |
| Sleeping time (hours/day) | 8:00 (7:00–9:00) | 8:00 (7:00–9:00) | 8:00 (7:00–8:30) | 0.067 ¹ |
| Physical activity (minutes/week) | 120 a (80–180) | 80 b (0–120) | 120 a (0–180) | <0.001 ¹ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Melo Souza, T.C.; Liboredo, J.C.; Ferreira, L.G.; Daniel, M.M.; Di Renzo, L.; Pivari, F.; Anastácio, L.R. Daily Habits of Brazilians at Different Moments of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235136
de Melo Souza TC, Liboredo JC, Ferreira LG, Daniel MM, Di Renzo L, Pivari F, Anastácio LR. Daily Habits of Brazilians at Different Moments of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):5136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235136
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Melo Souza, Tamires Cássia, Juliana Costa Liboredo, Lívia Garcia Ferreira, Marina Martins Daniel, Laura Di Renzo, Francesca Pivari, and Lucilene Rezende Anastácio. 2022. "Daily Habits of Brazilians at Different Moments of the COVID-19 Pandemic" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 5136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235136
APA Stylede Melo Souza, T. C., Liboredo, J. C., Ferreira, L. G., Daniel, M. M., Di Renzo, L., Pivari, F., & Anastácio, L. R. (2022). Daily Habits of Brazilians at Different Moments of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients, 14(23), 5136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235136