Sleep Deprivation and Central Appetite Regulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sleep Deprivation
2.1. Pathophysiology of Sleep Deprivation
2.2. Animal Model of Sleep Deprivation
3. Sleep Curtailment and Appetite Regulation in Human
4. Mechanisms of Sleep Deprivation on Regulating Appetite
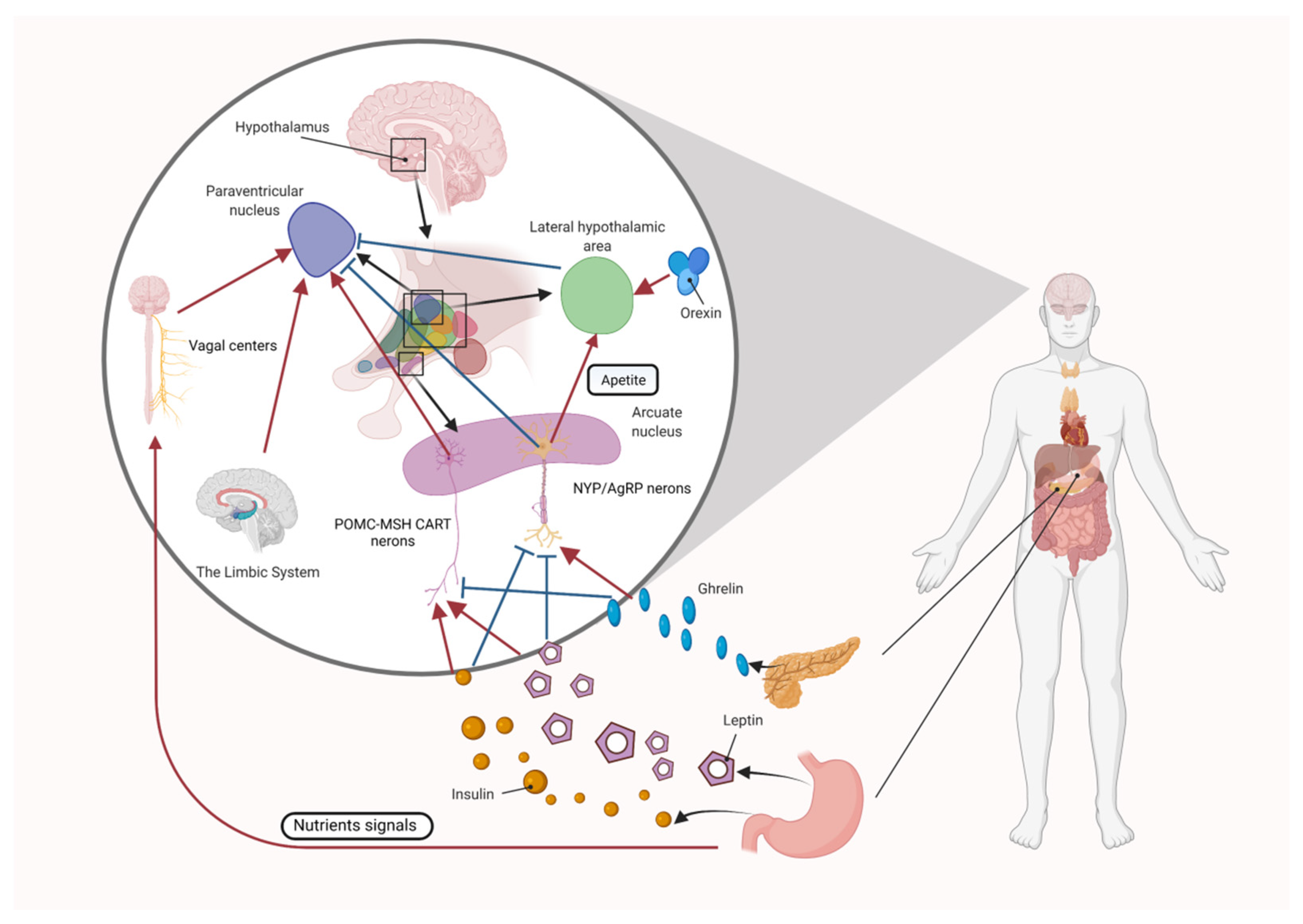
4.1. Central Appetite Regulation
4.1.1. The Role of the Melanocortin System in Central Appetite Regulation
4.1.2. The Role of Orexin and Ghrelin in Central Appetite Regulation
4.1.3. The Role of Leptin in Central Appetite Regulation
4.1.4. The Role of Insulin in Central Appetite Regulation
4.2. Central Regulatory Mechanism of Appetite by Sleep Deprivation in Animal Models
4.2.1. Orexin and Ghrelin
4.2.2. Leptin
4.2.3. Insulin
4.3. Central Regulatory Mechanism of Appetite by Sleep Deprivation in Human
5. Discussion and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, C.; Longcore, T.; Benbow, J.; Chung, N.T.; Chau, K.; Wang, S.S.; Lacey, J.V., Jr.; Franklin, M. Environmental influences on sleep in the California Teachers Study Cohort. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 191, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheaton, A.G.; Olsen, E.O.; Miller, G.F.; Croft, J.B. Sleep Duration and Injury-Related Risk Behaviors Among High School Students—United States, 2007–2013. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juda, M.; Vetter, C.; Roenneberg, T. Chronotype modulates sleep duration, sleep quality, and social jet lag in shift-workers. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2013, 28, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palimaru, A.I.; Dong, L.; Brown, R.A.; D’Amico, E.J.; Dickerson, D.L.; Johnson, C.L.; Troxel, W.M. Mental health, family functioning, and sleep in cultural context among American Indian/Alaska Native urban youth: A mixed methods analysis. Soc. Sci. Med. 2022, 292, 114582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palimaru, A.I.; Brown, R.A.; Troxel, W.M.; Dickerson, D.L.; Johnson, C.L.; D’Amico, E.J. Understanding sleep facilitators, barriers, and cultural dimensions in Native American urban youth. Sleep Health 2020, 6, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, E.; Vecchierini, M.F.; Heude, B.; Charles, M.A.; Plancoulaine, S. Sleep and its relation to cognition and behaviour in preschool-aged children of the general population: A systematic review. J. Sleep Res. 2018, 27, e12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touchette, E.; Petit, D.; Tremblay, R.E.; Boivin, M.; Falissard, B.; Genolini, C.; Montplaisir, J.Y. Associations between sleep duration patterns and overweight/obesity at age 6. Sleep 2008, 31, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landhuis, C.E.; Poulton, R.; Welch, D.; Hancox, R.J. Childhood sleep time and long-term risk for obesity: A 32-year prospective birth cohort study. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. (2005) 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlisky, J.D.; Hartman, T.J.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Rogers, C.J.; Sharkey, N.A.; Nickols-Richardson, S.M. Partial sleep deprivation and energy balance in adults: An emerging issue for consideration by dietetics practitioners. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Onge, M.P. The role of sleep duration in the regulation of energy balance: Effects on energy intakes and expenditure. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Blair, H.T.; Liang, H.; Wu, P.; Yu, Q. Targeting GNAQ in hypothalamic nerve cells to regulate seasonal estrus in sheep. Theriogenology 2022, 181, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, G.E.; Cheong, E. Chronic Restraint Stress Decreases the Excitability of Hypothalamic POMC Neuron and Increases Food Intake. Exp. Neurobiol. 2021, 30, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, R.M.; Can, A.S. Physiology, Appetite And Weight Regulation; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, A.J.; Simon, E.B.; Mander, B.A.; Greer, S.M.; Saletin, J.M.; Goldstein-Piekarski, A.N.; Walker, M.P. The sleep-deprived human brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, R. The Prevalence of Insufficient Sleep and Bedtime Delay Among Kindergarten Children Aged 3 to 6 Years in a Rural Area of Shanghai: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 759318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leproult, R.; Van Cauter, E. Role of sleep and sleep loss in hormonal release and metabolism. Endocr. Dev. 2010, 17, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.; Cui, B.; Cao, M. The Role of Morning Plasma Cortisol in Obesity: A Bi-directional Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol Metab 2022, 107, e1954–e1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysta, K.; Krzystanek, M.; Bratek, A.; Krupka-Matuszczyk, I. Sleep and inflammatory markers in different psychiatric disorders. J. Neural. Transm. 2017, 124, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.B.; Dement, W.C. Sleep: Suppression of rapid eye movement phase in the cat after electroconvulsive shock. Science 1966, 154, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafuerte, G.; Miguel-Puga, A.; Rodriguez, E.M.; Machado, S.; Manjarrez, E.; Arias-Carrion, O. Sleep deprivation and oxidative stress in animal models: A systematic review. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 2015, 234952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novozhilova, M.; Mishchenko, T.; Kondakova, E.; Lavrova, T.; Gavrish, M.; Aferova, S.; Franceschi, C.; Vedunova, M. Features of age-related response to sleep deprivation: In vivo experimental studies. Aging 2021, 13, 19108–19126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deurveilher, S.; Antonchuk, M.; Saumure, B.S.C.; Baldin, A.; Semba, K. No loss of orexin/hypocretin, melanin-concentrating hormone or locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons in a rat model of chronic sleep restriction. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 6027–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.P.; Zhang, L.N.; Zhang, J.; Chang, X.M.; Ding, S.; Xiao, F.; Guo, L.X. Evaluating the Effects of Different Sleep Supplement Modes in Attenuating Metabolic Consequences of Night Shift Work Using Rat Model. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2020, 12, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Wu, D.; Lin, R.; Wen, D.; Jia, L. Chronic Timed Sleep Restriction Attenuates LepRb-Mediated Signaling Pathways and Circadian Clock Gene Expression in the Rat Hypothalamus. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, A.; Eu, K.L.; Faris, A.N.A.; Wan Ahmad, W.A.N.; Noordin, L. Lipid peroxidation in the descending thoracic aorta of rats deprived of REM sleep using the inverted flowerpot technique. Exp. Physiol. 2020, 105, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.F.; Shen, Y.L.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.S.; Lee, P.Y.; Er, N.X.; Huang, W.C.; Tung, Y.T. Sleep deprivation reduces the recovery of muscle injury induced by high-intensity exercise in a mouse model. Life Sci. 2019, 235, 116835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wu, H.W.; Song, G.Q.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.H.; Qu, L.N.; Chen, S.G.; Liu, X.M.; Chang, Q. Chronical sleep interruption-induced cognitive decline assessed by a metabolomics method. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 302, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, N.C.; da Cruz, N.S.; de Paula Nascimento, C.; da Conceição, R.R.; da Silva, A.C.; Olivares, E.L.; Marassi, M.P. Sleep deprivation alters thyroid hormone economy in rats. Exp. Physiol. 2015, 100, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barf, R.P.; Van Dijk, G.; Scheurink, A.J.; Hoffmann, K.; Novati, A.; Hulshof, H.J.; Fuchs, E.; Meerlo, P. Metabolic consequences of chronic sleep restriction in rats: Changes in body weight regulation and energy expenditure. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 107, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrivelan, R.; Fuller, P.M.; Yokota, S.; Lu, J.; Saper, C.B. Metabolic effects of chronic sleep restriction in rats. Sleep 2012, 35, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husse, J.; Hintze, S.C.; Eichele, G.; Lehnert, H.; Oster, H. Circadian clock genes Per1 and Per2 regulate the response of metabolism-associated transcripts to sleep disruption. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koban, M.; Sita, L.V.; Le, W.W.; Hoffman, G.E. Sleep deprivation of rats: The hyperphagic response is real. Sleep 2008, 31, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Taggart, F.M.; Kandala, N.B.; Currie, A.; Peile, E.; Stranges, S.; Miller, M.A. Meta-analysis of short sleep duration and obesity in children and adults. Sleep 2008, 31, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, K. Sleep duration and obesity in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J. Paediatr Child. Health 2017, 53, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Kruisbrink, M.; Wallace, J.; Ji, C.; Cappuccio, F.P. Sleep duration and incidence of obesity in infants, children, and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sleep 2018, 41, zsy018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Bates, S.; Ji, C.; Cappuccio, F.P. Systematic review and meta-analyses of the relationship between short sleep and incidence of obesity and effectiveness of sleep interventions on weight gain in preschool children. Obes Rev. 2021, 22, e13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwald, R.R.; Melanson, E.L.; Smith, M.R.; Higgins, J.; Perreault, L.; Eckel, R.H.; Wright, K.P., Jr. Impact of insufficient sleep on total daily energy expenditure, food intake, and weight gain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5695–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nedeltcheva, A.V.; Kilkus, J.M.; Imperial, J.; Kasza, K.; Schoeller, D.A.; Penev, P.D. Sleep curtailment is accompanied by increased intake of calories from snacks. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koban, M.; Stewart, C.V. Effects of age on recovery of body weight following REM sleep deprivation of rats. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 87, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.M.; Tschann, J.M.; Butte, N.F.; Gregorich, S.E.; Penilla, C.; Flores, E.; Greenspan, L.C.; Pasch, L.A.; Deardorff, J. Short Sleep Duration Is Associated With Eating More Carbohydrates and Less Dietary Fat in Mexican American Children. Sleep 2017, 40, zsw057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hjorth, M.F.; Quist, J.S.; Andersen, R.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Tetens, I.; Astrup, A.; Chaput, J.P.; Sjodin, A. Change in sleep duration and proposed dietary risk factors for obesity in Danish school children. Pediatr. Obes 2014, 9, e156–e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorth, M.F.; Sjödin, A.; Dalskov, S.M.; Damsgaard, C.T.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Biltoft-Jensen, A.; Andersen, R.; Ritz, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Astrup, A. Sleep duration modifies effects of free ad libitum school meals on adiposity and blood pressure. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Et Metab. 2016, 41, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.W. Network of hypothalamic neurons that control appetite. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnol, D.; Lu, X.Y.; Kaelin, C.B.; Day, H.E.; Ollmann, M.; Gantz, I.; Akil, H.; Barsh, G.S.; Watson, S.J. Anatomy of an endogenous antagonist: Relationship between Agouti-related protein and proopiomelanocortin in brain. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1999, 19, Rc26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; He, X.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, Q.; Lin, R.; Sun, Y.; Ding, T.; Xu, F.; Luo, M.; Zhan, C. Whole-brain mapping of the direct inputs and axonal projections of POMC and AgRP neurons. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyron, C.; Tighe, D.K.; van den Pol, A.N.; de Lecea, L.; Heller, H.C.; Sutcliffe, J.G.; Kilduff, T.S. Neurons containing hypocretin (orexin) project to multiple neuronal systems. J. Neurosci 1998, 18, 9996–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Date, Y.; Ueta, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Matsukura, S.; Kangawa, K.; Sakurai, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Nakazato, M. Orexins, orexigenic hypothalamic peptides, interact with autonomic, neuroendocrine and neuroregulatory systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, C.M.; Abusnana, S.; Sunter, D.; Murphy, K.G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. The effect of the orexins on food intake: Comparison with neuropeptide Y, melanin-concentrating hormone and galanin. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 160, R7–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, T.; Amemiya, A.; Ishii, M.; Matsuzaki, I.; Chemelli, R.M.; Tanaka, H.; Williams, S.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Kozlowski, G.P.; Wilson, S.; et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 1998, 92, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, T.L.; Gao, X.B. Input organization and plasticity of hypocretin neurons: Possible clues to obesity’s association with insomnia. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haynes, A.C.; Jackson, B.; Chapman, H.; Tadayyon, M.; Johns, A.; Porter, R.A.; Arch, J.R. A selective orexin-1 receptor antagonist reduces food consumption in male and female rats. Regul. Pept. 2000, 96, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, L.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Cifani, C.; Costantini, V.J.; Massagrande, M.; Montanari, D.; Martinelli, P.; Antolini, M.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Massi, M.; et al. Role of orexin-1 receptor mechanisms on compulsive food consumption in a model of binge eating in female rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1999–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.K.; Yip, L.; Fredholm, B.B.; Kieffer, T.J.; Kwok, Y.N. Involvement of adenosine signaling in controlling the release of ghrelin from the mouse stomach. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Correa, A.A.; Estrada, J.A.; Contreras, I. Leptin Signaling in the Control of Metabolism and Appetite: Lessons from Animal Models. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 66, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Cook, J.R.; Kon, N.; Accili, D. Gpr17 in AgRP Neurons Regulates Feeding and Sensitivity to Insulin and Leptin. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3670–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molnar, G.; Farago, N.; Kocsis, A.K.; Rozsa, M.; Lovas, S.; Boldog, E.; Baldi, R.; Csajbok, E.; Gardi, J.; Puskas, L.G.; et al. GABAergic neurogliaform cells represent local sources of insulin in the cerebral cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Caceres, C.; Quarta, C.; Varela, L.; Gao, Y.; Gruber, T.; Legutko, B.; Jastroch, M.; Johansson, P.; Ninkovic, J.; Yi, C.X.; et al. Astrocytic Insulin Signaling Couples Brain Glucose Uptake with Nutrient Availability. Cell 2016, 166, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brianza-Padilla, M.; Bonilla-Jaime, H.; Almanza-Pérez, J.C.; López-López, A.L.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Vázquez-Palacios, G. Effects of different periods of paradoxical sleep deprivation and sleep recovery on lipid and glucose metabolism and appetite hormones in rats. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Et Metab. 2016, 41, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, C.; Hirasawa, M.; Semba, K. Sleep Deprivation Distinctly Alters Glutamate Transporter 1 Apposition and Excitatory Transmission to Orexin and MCH Neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 2505–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gong, L. Effects of Sleep Deprivation (SD) on Rats via ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2019, 25, 2886–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, J.; Alberto, C.O.; Parsons, M.P.; Hirasawa, M. Local network regulation of orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R572–R580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Song, Y.; Li, F.; He, X.; Ma, J.; Feng, T.; Guan, B.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Wen-dan decoction improves negative emotions in sleep-deprived rats by regulating orexin-a and leptin expression. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2014, 2014, 872547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, S.C.; Chen, P.N.; Chen, J.R.; Yu, C.H.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Kuo, D.Y. Role of hypothalamic leptin-LepRb signaling in NPY-CART-mediated appetite suppression in amphetamine-treated rats. Horm. Behav. 2018, 98, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvers, D.J.; Scheer, F.; Schrauwen, P.; la Fleur, S.E.; Kalsbeek, A. Circadian clocks and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robles, M.S.; Humphrey, S.J.; Mann, M. Phosphorylation Is a Central Mechanism for Circadian Control of Metabolism and Physiology. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panda, S. Circadian physiology of metabolism. Science 2016, 354, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikegami, K.; Refetoff, S.; Van Cauter, E.; Yoshimura, T. Interconnection between circadian clocks and thyroid function. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Lazar, M.A. Interconnections between circadian clocks and metabolism. J Clin. Invest. 2021, 131, e148378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedernaes, J.; Osler, M.E.; Voisin, S.; Broman, J.E.; Vogel, H.; Dickson, S.L.; Zierath, J.R.; Schioth, H.B.; Benedict, C. Acute Sleep Loss Induces Tissue-Specific Epigenetic and Transcriptional Alterations to Circadian Clock Genes in Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab 2015, 100, E1255–E1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, M.J.; Moffitt, T.E.; Gregory, A.M.; Goldman-M.Mellor, S.; Nolan, P.M.; Poulton, R.; Caspi, A. Social jetlag, obesity and metabolic disorder: Investigation in a cohort study. Int J. Obes. 2015, 39, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kettner, N.M.; Mayo, S.A.; Hua, J.; Lee, C.; Moore, D.D.; Fu, L. Circadian Dysfunction Induces Leptin Resistance in Mice. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Shu, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhou, Z.; Jia, X.; Jian, C.; Jin, S. Insulin resistance induced by long-term sleep deprivation in rhesus macaques can be attenuated by Bifidobacterium. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 322, E165–E172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, D.A.; Venancio, D.P.; Suchecki, D. Sleep deprivation alters energy homeostasis through non-compensatory alterations in hypothalamic insulin receptors in Wistar rats. Horm. Behav. 2014, 66, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaniuk, U.V.; Gospodaryov, D.V.; Feden’ko, K.M.; Yurkevych, I.S.; Vaiserman, A.M.; Storey, K.B.; Simpson, S.J.; Lushchak, O. Insulin-Like Peptides Regulate Feeding Preference and Metabolism in Drosophila. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chruvattil, R.; Banerjee, S.; Nath, S.; Machhi, J.; Kharkwal, G.; Yadav, M.R.; Gupta, S. Dexamethasone Alters the Appetite Regulation via Induction of Hypothalamic Insulin Resistance in Rat Brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7483–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felso, R.; Lohner, S.; Hollody, K.; Erhardt, E.; Molnar, D. Relationship between sleep duration and childhood obesity: Systematic review including the potential underlying mechanisms. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussard, J.L.; Kilkus, J.M.; Delebecque, F.; Abraham, V.; Day, A.; Whitmore, H.R.; Tasali, E. Elevated ghrelin predicts food intake during experimental sleep restriction. Obes. (Silver Spring) 2016, 24, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.M.; Hallschmid, M.; Jauch-Chara, K.; Wilms, B.; Benedict, C.; Lehnert, H.; Born, J.; Schultes, B. Short-term sleep loss decreases physical activity under free-living conditions but does not increase food intake under time-deprived laboratory conditions in healthy men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sweeney, E.L.; Peart, D.J.; Ellis, J.G.; Walshe, I.H. Impairments in glycaemic control do not increase linearly with repeated nights of sleep restriction in healthy adults: A randomised controlled trial. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Et Metab. 2021, 46, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondrup, N.; Termannsen, A.D.; Eriksen, J.N.; Hjorth, M.F.; Færch, K.; Klingenberg, L.; Quist, J.S. Effects of sleep manipulation on markers of insulin sensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Med. Rev. 2022, 62, 101594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, C.; Barclay, J.L.; Ott, V.; Oster, H.; Hallschmid, M. Acute sleep deprivation delays the glucagon-like peptide 1 peak response to breakfast in healthy men. Nutr. Diabetes 2013, 3, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Research Animal | Sleep Deprivation Method | Sleep Deprivation Time | Experiment Time | Food Intake | Weight | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 mouse/1.5 months | Flowerpot | 10 h (10:00–20:00) | 5 days | Increased | ↓ | [23] |
| C57 mouse/7–9 months | 10 h (10:00–20:00) | ↑ | ||||
| Wistar rat | Motorized activity wheels | 18 h (3 h SD * with 1 h recovery) | 5 days | / | ↓ | [24] |
| 18 h (3 h SD * with 1 h recovery) | 23 days | |||||
| Wistar rat | Platform | 16 h (7:00–23:00) | 8 weeks | Increased | ↑ | [25] |
| 16 h (7:00–19:00, 3:00–7:00) | ||||||
| 16 h (7:00–19:00, 23:00–3:00) | ||||||
| SD rat | Gentle handling | 4 h (8:00–12:00) | 4 weeks | Increased | ↑ | [26] |
| SD rat | Platform | 24 h | 3 days | Increased | ↓ | [27] |
| C57BL/6J mouse | Platform | 24 h | 3 days | Increased | ↓ | [28] |
| ICR mouse | Rotating drum | 24 h | 14 days | / | ↓ | [29] |
| Wistar rat | Platform | 6 h (10:00–16:00) | 21 days | / | ↓ | [30] |
| 24 h | 1 day | |||||
| 24 h | 4 days | |||||
| Wistar rat | Slowly rotating cages | 20 h (14:00–10:00) | 8 days | Increased # | ↓ | [31] |
| SD rat | VLPO- lesioned | / | 60 days | Increased | ↓ | [32] |
| C57 mouse | Gentle handling | 6 h (first six hours of the light phase) | 5 days | Increased | ↓ | [33] |
| SD rat | platform | 1 h (9:00–10:00) | 10 days | Increased | ↓ | [34] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Gao, L.; Sun, Q. Sleep Deprivation and Central Appetite Regulation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245196
Liu S, Wang X, Zheng Q, Gao L, Sun Q. Sleep Deprivation and Central Appetite Regulation. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245196
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuailing, Xiya Wang, Qian Zheng, Lanyue Gao, and Qi Sun. 2022. "Sleep Deprivation and Central Appetite Regulation" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245196
APA StyleLiu, S., Wang, X., Zheng, Q., Gao, L., & Sun, Q. (2022). Sleep Deprivation and Central Appetite Regulation. Nutrients, 14(24), 5196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245196





