Predictive Validity of Image-Based Motivation-to-Eat Visual Analogue Scales in Normal Weight Children and Adolescents Aged 9–14 Years
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
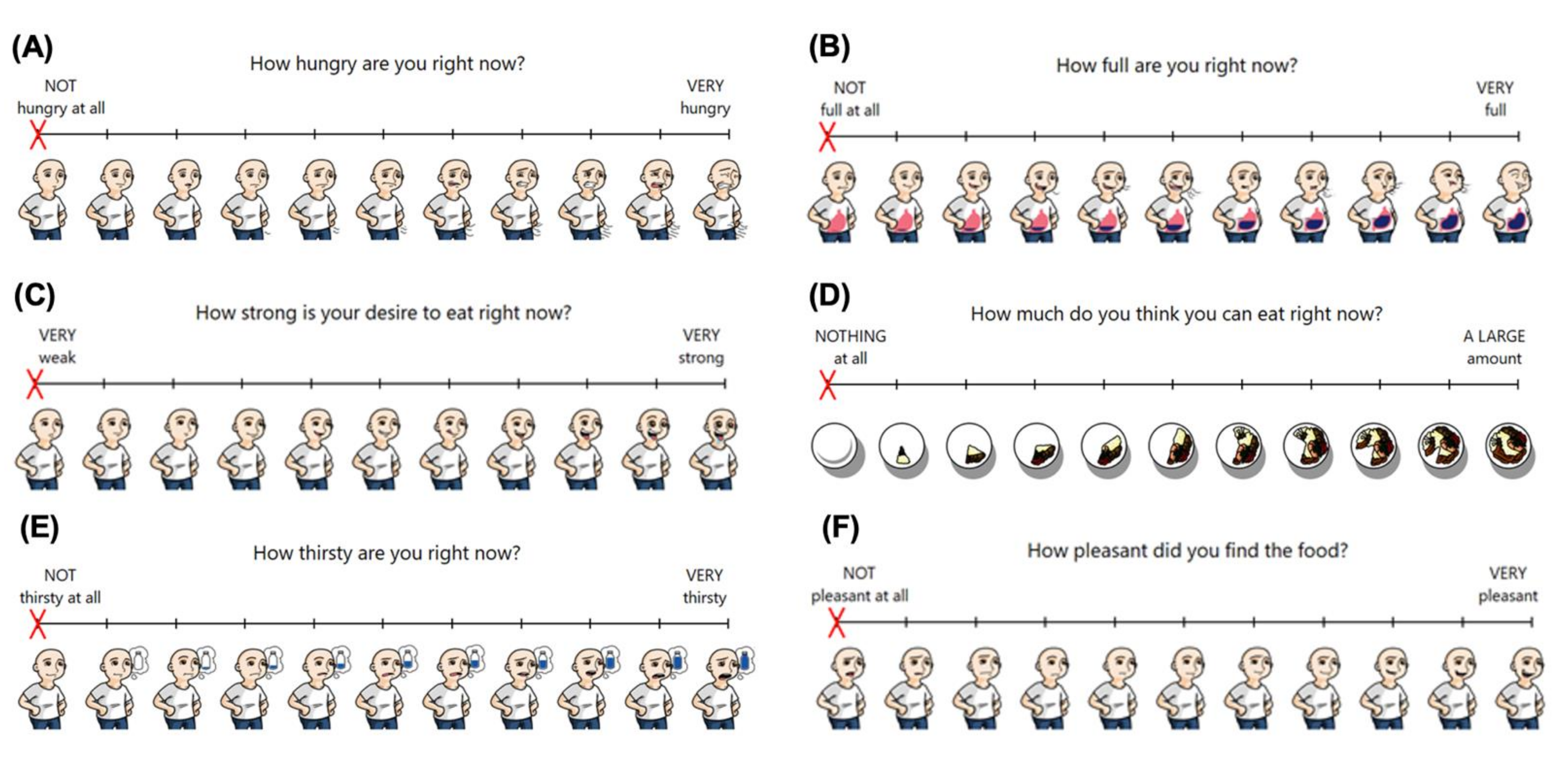
2.3. Visual Analogue Scales
2.4. Ad Libitum Food Intake
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Agreement between Visual Analogue Scale Instruments
3.2.1. Bland–Altman Plots
3.2.2. Intraclass Correlation Coefficients
3.2.3. Analysis of Variance
3.3. Predictive Validity of Visual Analogue Scale Instruments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerstein, D.E.; Woodward-Lopez, G.; Evans, A.E.; Kelsey, K.; Drewnowski, A. Clarifying concepts about macronutrients’ effects on satiation and satiety. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.J.; Blundell, J.E. Nutrients and behaviour: Research strategies for the investigation of taste characteristics, food preferences, hunger sensations and eating patterns in man. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1982, 17, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellissimo, N.; Amalraj, R.; Lee, J.J.; Brett, N.R.; Totosy de Zepetnek, J.O.; Proteau, S.; Rousseau, D. Effect of White Potatoes on Subjective Appetite, Food Intake, and Glycemic Response in Healthy Older Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellissimo, N.; Fansabedian, T.; Wong, V.C.H.; Totosy de Zepetnek, J.O.; Brett, N.R.; Schwartz, A.; Cassin, S.; Suitor, K.; Rousseau, D. Effect of Increasing the Dietary Protein Content of Breakfast on Subjective Appetite, Short-Term Food Intake and Diet-Induced Thermogenesis in Children. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.M.; Leidy, H.J. Novel Methodological Considerations Regarding the Use of Visual Analog Scale (VAS) Appetite Questionnaires in Tightly Controlled Feeding Trials. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2019, 3, nzz061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, B.J.; Laster, L.J.; Summerfelt, A. Hunger and food intake following consumption of low-calorie foods. Appetite 1989, 13, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Huot, P.S.P.; Lee, Y.T.; Vien, S.; Luhovyy, B.L.; Anderson, G.H. The effect of dairy and nondairy beverages consumed with high glycemic cereal on subjective appetite, food intake, and postprandial glycemia in young adults. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reister, E.J.; Leidy, H.J. An Afternoon Hummus Snack Affects Diet Quality, Appetite, and Glycemic Control in Healthy Adults. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Mattes, R.D. Effects of learning and food form on energy intake and appetitive responses. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 137, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drapeau, V.; Jacob, R.; Panahi, S.; Tremblay, A. Effect of Energy Restriction on Eating Behavior Traits and Psychobehavioral Factors in the Low Satiety Phenotype. Nutrients 2019, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blundell, J.; de Graaf, C.; Hulshof, T.; Jebb, S.; Livingstone, B.; Lluch, A.; Mela, D.; Salah, S.; Schuring, E.; van der Knaap, H.; et al. Appetite control: Methodological aspects of the evaluation of foods. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flint, A.; Raben, A.; Blundell, J.E.; Astrup, A. Reproducibility, power and validity of visual analogue scales in assessment of appetite sensations in single test meal studies. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunger, L.; Smith, A.; Re, R.; Wickham, M.; Philippides, A.; Watten, P.; Yeomans, M.R. Validation of an iPad visual analogue rating system for assessing appetite and satiety. Appetite 2015, 84, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, C.; Caudwell, P.; Finlayson, G.; King, N.; Blundell, J. Validation of a new hand-held electronic data capture method for continuous monitoring of subjective appetite sensations. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rumbold, P.L.S.; Dodd-Reynolds, C.J.; Stevenson, E. Agreement between paper and pen visual analogue scales and a wristwatch-based electronic appetite rating system (PRO-Diary©), for continuous monitoring of free-living subjective appetite sensations in 7–10 year old children. Appetite 2013, 69, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, R.J.; Hughes, D.A.; Johnstone, A.M.; Rowley, E.; Reid, C.; Elia, M.; Stratton, R.; Delargy, H.; King, N.; Blundell, J.E. The use of visual analogue scales to assess motivation to eat in human subjects: A review of their reliability and validity with an evaluation of new hand-held computerized systems for temporal tracking of appetite ratings. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holliday, A.; Johnson, K.O.; Kaiseler, M.; Crabtree, D.R. APPetite: Validation of a smartphone app-based tool for the remote measure of free-living subjective appetite. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almiron-Roig, E.; Green, H.; Virgili, R.; Aeschlimann, J.M.; Moser, M.; Erkner, A. Validation of a new hand-held electronic appetite rating system against the pen and paper method. Appetite 2009, 53, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whybrow, S.; Stephen, J.R.; Stubbs, R.J. The evaluation of an electronic visual analogue scale system for appetite and mood. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shields, B.J.; Palermo, T.M.; Powers, J.D.; Grewe, S.D.; Smith, G.A. Predictors of a child’s ability to use a visual analogue scale. Child Care Health Dev. 2003, 29, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellissimo, N.; Thomas, S.G.; Pencharz, P.B.; Goode, R.C.; Anderson, G.H. Reproducibility of short-term food intake and subjective appetite scores after a glucose preload, ventilation threshold, and body composition in boys. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 33, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, C.; Blissett, J. Measuring hunger and satiety in primary school children. Validation of a new picture rating scale. Appetite 2014, 78, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, M.S.; Kermanshah, M.; Kissileff, H.R. Development and preliminary validation of a silhouette satiety scale for children. Physiol. Behav. 2002, 76, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.L.; Assur, S.A.; Torres, M.; Lofink, H.E.; Thornton, J.C.; Faith, M.S.; Kissileff, H.R. Potential of an analog scaling device for measuring fullness in children: Development and preliminary testing. Appetite 2006, 47, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triador, L.; Colin-Ramirez, E.; Mackenzie, M.L.; Tomaszewski, E.; Shah, K.; Gulayets, H.; Field, C.J.; Mager, D.R.; Haqq, A.M. A two-component pictured-based appetite assessment tool is capable of detecting appetite sensations in younger children: A pilot study. Nutr. Res. 2021, 89, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, C.L.; Kuczmarski, R.J.; Flegal, K.M.; Mei, Z.; Guo, S.; Wei, R.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M.; Curtin, L.R.; Roche, A.F.; Johnson, C.L. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2000 growth charts for the United States: Improvements to the 1977 National Center for Health Statistics version. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lohman, T.G. The Use of Skinfold to Estimate Body Fatness on Children and Youth. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Danc. 1987, 58, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin Bland, J.; Altman, D. STATISTICAL METHODS FOR ASSESSING AGREEMENT BETWEEN TWO METHODS OF CLINICAL MEASUREMENT. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J Chiropr Med 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolever, T.M.; Jenkins, D.J.; Jenkins, A.L.; Josse, R.G. The glycemic index: Methodology and clinical implications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 54, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkeling, B.; Rössner, S.; Sjöberg, A. Methodological studies on single meal food intake characteristics in normal weight and obese men and women. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1995, 19, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadoul, B.C.; Schuring, E.A.; Symersky, T.; Mela, D.J.; Masclee, A.A.; Peters, H.P. Measuring satiety with pictures compared to visual analogue scales. An exploratory study. Appetite 2012, 58, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, G.M.; Owen, L.J.; Till, S.; Cheng, Y.; Grant, V.A.; Harden, C.J.; Corfe, B.M. Systematic literature review shows that appetite rating does not predict energy intake. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3577–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, B.J.; Wood, R.J.; Rolls, E.T.; Lind, H.; Lind, W.; Ledingham, J.G. Thirst following water deprivation in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1980, 239, R476–R482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard-Stafford, M.; Wendland, D.M.; O’Dea, N.K.; Norman, T.L. Thirst and hydration status in everyday life. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70 (Suppl. 2), S147–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattes, R.D. Physiologic responses to sensory stimulation by food: Nutritional implications. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1997, 97, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Means ± SEM | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 11.5 ± 0.3 | 9–14 |
| Height (cm) | 154.5 ± 2.1 | 140.5–169.0 |
| Body mass (kg) | 44.5 ± 2.1 | 29.9–62.5 |
| BMI percentile * | 50.1 ± 6.6 | 6–85 |
| Fat mass 1 (%) | 25.9 ± 1.6 | 12.5–38.7 |
| Fat-free mass 1 (%) | 74.1 ± 6.7 | 61.3–87.5 |
| Ratings Instruments | 0 min | 5 min | 20 min | 35 min | 65 min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hunger | VASpaper vs. VASno-images | 0.95 (0.85–0.98) | 0.85 (0.60–0.95) | 0.90 (0.72–0.96) | 0.94 (0.83–0.98) | 0.92 (0.78–0.97) |
| VASpaper vs. VASimages | 0.92 (0.77–0.97) | 0.94 (0.82–0.98) | 0.90 (0.74–0.97) | 0.94 (0.83–0.98) | 0.95 (0.86–0.98) | |
| VASimages vs. VASno-images | 0.97 (0.90–0.99) | 0.94 (0.82–0.98) | 0.96 (0.88–0.99) | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | |
| Fullness | VASpaper vs. VASno-images | 0.94 (0.83–0.98) | 0.86 (0.60–0.95) | 0.89 (0.70–0.96) | 0.98 (0.95–0.99) | 0.94 (0.83–0.98) |
| VASpaper vs. VASimages | 0.89 (0.69–0.96) | 0.80 (0.47–0.93) | 0.77 (0.32–0.92) | 0.90 (0.72–0.96) | 0.94 (0.83–0.98) | |
| VASimages vs. VASno-images | 0.89 (0.71–0.96) | 0.80 (0.45–0.93) | 0.86 (0.63–0.95) | 0.91 (0.75–0.97) | 0.97 (0.89–0.99) | |
| DTE | VASpaper vs. VASno-images | 0.91 (0.75–0.97) | 0.90 (0.70–0.96) | 0.91 (0.75–0.97) | 0.92 (0.77–0.97) | 0.72 (0.25–0.90) |
| VASpaper vs. VASimages | 0.83 (0.52–0.94) | 0.94 (0.83–0.98) | 0.88 (0.67–0.96) | 0.89 (0.69–0.96) | 0.72 (0.25–0.90) | |
| VASimages vs. VASno-images | 0.89 (0.69–0.96) | 0.93 (0.82–0.98) | 0.94 (0.82–0.98) | 0.95 (0.82–0.99) | 0.96 (0.90–0.99) | |
| PFC | VASpaper vs. VASno-images | 0.98 (0.94–0.99) | 0.98 (0.95–0.995) | 0.98 (0.96–0.99) | 0.95 (0.86–0.98) | 0.92 (0.79–0.97) |
| VASpaper vs. VASimages | 0.95 (0.86–0.98) | 0.94 (0.84–0.98) | 0.95 (0.84–0.984) | 0.97 (0.85–0.99) | 0.88 (0.67–0.96) | |
| VASimages vs. VASno-images | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | 0.95 (0.85–0.98) | 0.96 (0.89–0.99) | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | 0.90 (0.72–0.96) | |
| AA | VASpaper vs. VASno-images | 0.97 (0.92–0.99) | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | 0.98 (0.95–0.99) | 0.99 (0.97–0.996) | 0.94 (0.83–0.98) |
| VASpaper vs. VASimages | 0.94 (0.85–0.98) | 0.95 (0.83–0.98) | 0.93 (0.79–0.97) | 0.97 (0.93–0.99) | 0.92 (0.78–0.97) | |
| VASimages vs. VASno-images | 0.98 (0.94–0.99) | 0.94 (0.85–0.98) | 0.94 (0.85–0.98) | 0.97 (0.93–0.99) | 0.98 (0.94–0.99) | |
| Thirst | VASpaper vs. VASno-images | 0.96 (0.90–0.99) | 0.95 (0.87–0.98) | 0.96 (0.90–0.99) | 0.96 (0.88–0.98) | 0.93 (0.78–0.97) |
| VASpaper vs. VASimages | 0.93 (0.82–0.98) | 0.94 (0.84–0.98) | 0.95 (0.85–0.98) | 0.94 (0.82–0.98) | 0.80 (0.46–0.93) | |
| VASimages vs. VASno-images | 0.94 (0.83–0.98) | 0.91 (0.75–0.97) | 0.97 (0.93–0.99) | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | 0.90 (0.71–0.96) | |
| Instrument | Domain | 0 min | 5 min | 20 min | 35 min | 65 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VASpaper | Hunger | 0.47 | 0.51 * | 0.64 ** | 0.49 * | −0.004 |
| Fullness | −0.20 | −0.47 | −0.64 ** | −0.21 | 0.26 | |
| DTE | 0.48 * | 0.57 * | 0.63 ** | 0.61 ** | −0.13 | |
| PFC | 0.64 ** | 0.75 *** | 0.75 *** | 0.74 *** | −0.16 | |
| AA | 0.50 * | 0.63 ** | 0.74 *** | 0.56 * | −0.18 | |
| Thirst | 0.19 | −0.06 | −0.01 | −0.32 | −0.16 | |
| Pleasantness 1 | - | 0.28 | - | - | 0.60 * | |
| VASno-images | Hunger | 0.49 * | 0.74 *** | 0.75 *** | 0.61 ** | 0.01 |
| Fullness | −0.33 | −0.30 | −0.37 | −0.26 | 0.38 | |
| DTE | 0.42 | 0.82 *** | 0.69 ** | 0.71 *** | 0.04 | |
| PFC | 0.70 ** | 0.80 *** | 0.74 *** | 0.71 *** | −0.16 | |
| AA | 0.54 * | 0.68 ** | 0.67 ** | 0.60 * | −0.18 | |
| Thirst | 0.21 | −0.12 | −0.12 | −0.34 | −0.32 | |
| Pleasantness 1 | - | 0.32 | - | - | 0.23 | |
| VASimages | Hunger | 0.50 * | 0.71 *** | 0.76 *** | 0.53 * | 0.04 |
| Fullness | −0.17 | −0.45 | −0.41 | −0.41 | 0.32 | |
| DTE | 0.53 * | 0.72 *** | 0.75 *** | 0.65 ** | 0.13 | |
| PFC | 0.63 ** | 0.74 *** | 0.77 *** | 0.76 *** | −0.08 | |
| AA | 0.53 * | 0.69 ** | 0.73 *** | 0.63 ** | −0.12 | |
| Thirst | 0.16 | −0.15 | −0.03 | −0.19 | −0.34 | |
| Pleasantness 1 | - | 0.20 | - | - | 0.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hammond, L.; Morello, O.; Kucab, M.; Totosy de Zepetnek, J.O.; Lee, J.J.; Doheny, T.; Bellissimo, N. Predictive Validity of Image-Based Motivation-to-Eat Visual Analogue Scales in Normal Weight Children and Adolescents Aged 9–14 Years. Nutrients 2022, 14, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030636
Hammond L, Morello O, Kucab M, Totosy de Zepetnek JO, Lee JJ, Doheny T, Bellissimo N. Predictive Validity of Image-Based Motivation-to-Eat Visual Analogue Scales in Normal Weight Children and Adolescents Aged 9–14 Years. Nutrients. 2022; 14(3):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030636
Chicago/Turabian StyleHammond, Leila, Olivia Morello, Michaela Kucab, Julia O. Totosy de Zepetnek, Jennifer J. Lee, Tarah Doheny, and Nick Bellissimo. 2022. "Predictive Validity of Image-Based Motivation-to-Eat Visual Analogue Scales in Normal Weight Children and Adolescents Aged 9–14 Years" Nutrients 14, no. 3: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030636
APA StyleHammond, L., Morello, O., Kucab, M., Totosy de Zepetnek, J. O., Lee, J. J., Doheny, T., & Bellissimo, N. (2022). Predictive Validity of Image-Based Motivation-to-Eat Visual Analogue Scales in Normal Weight Children and Adolescents Aged 9–14 Years. Nutrients, 14(3), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030636









