Eating out of Home: Influence on Nutrition, Health, and Policies: A Scoping Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
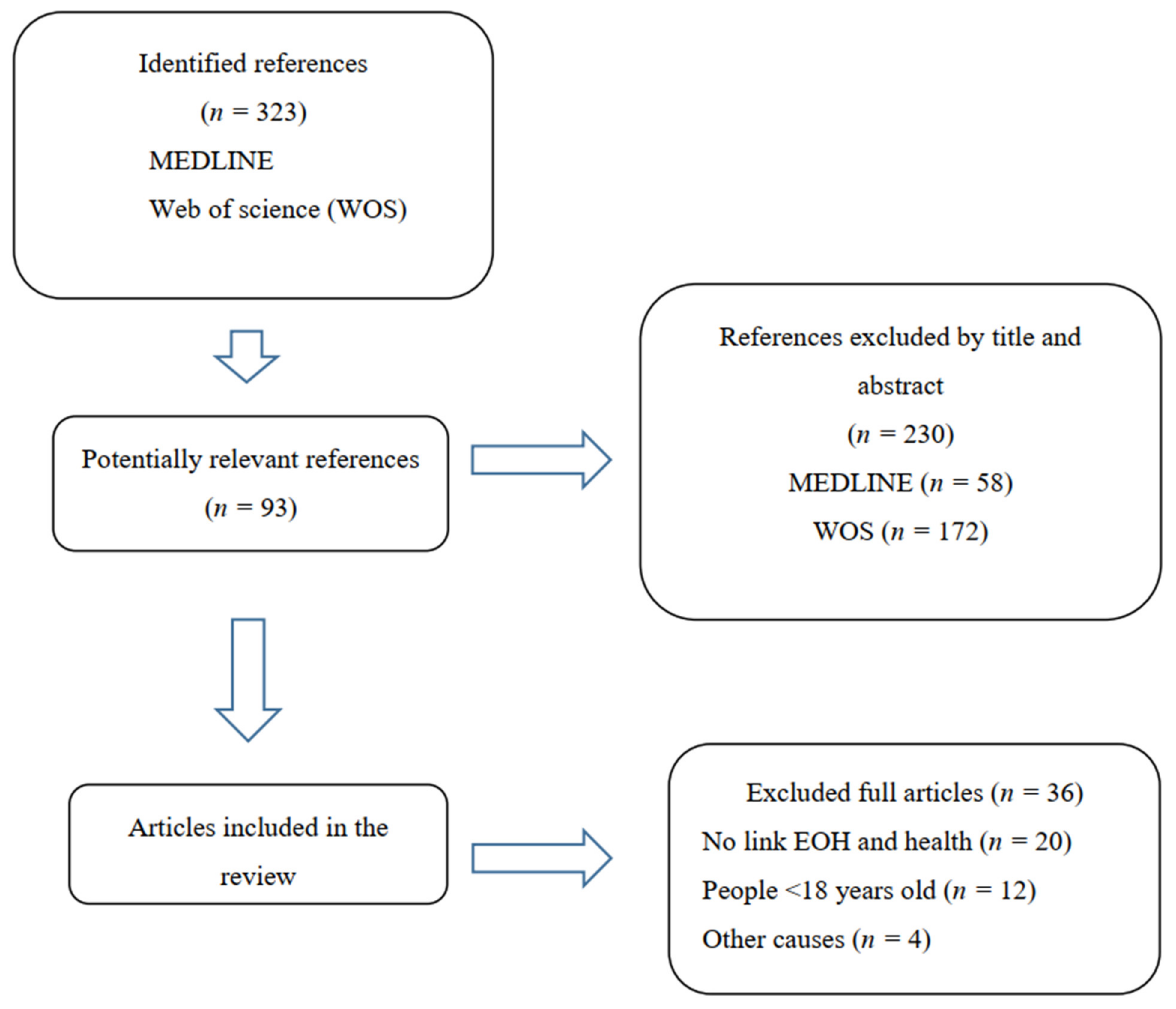
2. Materials and Methods
Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Definition for EOH
4.2. Nutritional Contribution of EOH and Their Relationship with Health Parameters in Adults
4.3. Healthy Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelsey, M.W. Dinning in Ancient Rome. In Oxford Symposium on Food and Cookery: Public Eating; Prospect Books: London, UK, 1991; p. 326. [Google Scholar]
- Oldest Restaurant. Available online: https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/76907-oldest-restaurant (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Lachat, C.; Nago, E.; Verstraeten, R.; Roberfroid, D.; Van Camp, J.; Kolsteren, P. Eating out of home and its association with dietary intake: A systematic review of the evidence. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.K.; Kim, T.Y.; Yoon, J.-S. Does Frequent Eating Out Cause Undesirable Food Choices? Association of Food Away from Home with Food Consumption Frequencies and Obesity among Korean Housewives. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2011, 50, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglestad, P.T.; Jeffery, R.W.; Sherwood, N.E. Lifestyle patterns associated with diet, physical activity, body mass index and amount of recent weight loss in a sample of successful weight losers. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssen, H.G.; Davies, I.G.; Richardson, L.D.; Stevenson, L. Determinants of takeaway and fast food consumption: A narrative review. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 31, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allman-Farinelli, M.; Rahman, H.; Nour, M.; Wellard-Cole, L.; Watson, W.L. The Role of Supportive Food Environments to Enable Healthier Choices When Eating Meals Prepared Outside the Home: Findings from Focus Groups of 18 to 30-Year-Olds. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, W.-W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.-J.; Wang, Z.-H.; Su, C.; Zhang, J.-G.; Jia, X.-F.; Jiang, H.-R. Gender difference in the association between food away-from-home consumption and body weight outcomes among Chinese adults. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasparian, M.; Mann, G.; Serrano, E.L.; Farris, A.R. Parenting practices toward food and children’s behavior: Eating away from home versus at home. Appetite 2017, 114, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfanos, P.; Naska, A.; Trichopoulos, D.; Slimani, N.; Ferrari, P.; van Bakel, M.; Deharveng, G.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A.; Halkjaer, J.; et al. Eating out of home and its correlates in 10 European countries. The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naska, A.; Katsoulis, M.; Orfanos, P.; Lachat, C.; Gedrich, K.; Rodrigues, S.S.; Freisling, H.; Kolsteren, P.; Engeset, D.; Lopes, C.; et al. Eating out is different from eating at home among individuals who occasionally eat out. A cross-sectional study among middle-aged adults from eleven European countries. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1951–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- IRI. New European Report on Out of Home Foodservice Sales. Available online: https://www.iriworldwide.com/es-es/insights/news/1-in-5-meals-eaten-out-of-home-as-european-consumers-favour-service-over-home-cooking-es (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Saksena, M.J.; Okrent, A.M.; Anekwe, T.D.; Cho, C.; Dicken, C.; Effland, A.; Elitzak, H.; Guthrie, J.; Hamrick, K.S.; Hyman, J.; et al. America’s Eating Habits: Food Away from Home; United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Drzewoski, J.; Hanefeld, M. The Current and Potential Therapeutic Use of Metformin—The Good Old Drug. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Powell, L.M.; Wang, Y. Reduced away-from-home food expenditure and better nutrition knowledge and belief can improve quality of dietary intake among US adults. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binkley, J.K.; Liu, Y. Food at Home and away from Home: Commodity Composition, Nutrition Differences, and Differences in Consumers. Agric. Resour. Econ. Rev. 2019, 48, 221–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleich, S.N.; Pollack, K.M. The publics’ understanding of daily caloric recommendations and their perceptions of calorie posting in chain restaurants. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dave, J.M.; An, L.C.; Jeffery, R.W.; Ahluwalia, J.S. Relationship of attitudes toward fast food and frequency of fast-food intake in adults. Obesity 2009, 17, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, J.M.; King, G.A.; Duarte-Gardea, M.; Gonzalez-Ayala, S.; Kooshian, C.H. Overweight and obese humans overeat away from home. Appetite 2012, 59, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffey, K.J.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Steffen, L.M.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Popkin, B.M. Regular consumption from fast food establishments relative to other restaurants is differentially associated with metabolic outcomes in young adults. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, M.; Kuczmarski, M.F.; Bodt, B.A.; Baker, S.D.; Fang, C.; Zonderman, A.B.; Evans, M.K. Breakfast Habits and Diet Quality in Economically Diverse African American and White Adults. Top. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 33, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunseit, A.C.; Cook, A.S.; Conti, J.; Gwizd, M.; Allman-Farinelli, M. “Doing a good thing for myself”: A qualitative study of young adults’ strategies for reducing takeaway food consumption. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillier-Brown, F.C.; Summerbell, C.D.; Moore, H.J.; Routen, A.; Lake, A.A.; Adams, J.; White, M.; Araujo-Soares, V.; Abraham, C.; Adamson, A.J.; et al. The impact of interventions to promote healthier ready-to-eat meals (to eat in, to take away or to be delivered) sold by specific food outlets open to the general public: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, E.K.; Han, E. Food away from home and body mass outcomes: Taking heterogeneity into account enhances quality of results. Nutrition 2014, 30, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, N.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Laska, M.N.; Story, M. Young adults and eating away from home: Associations with dietary intake patterns and weight status differ by choice of restaurant. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 1696–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McClain, A.C.; Ayala, G.X.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; Kaplan, R.C.; Gellman, M.D.; Gallo, L.C.; Van Horn, L.; Daviglus, M.L.; Perera, M.J.; et al. Frequency of Intake and Type of Away-from- Home Foods Consumed Are Associated with Diet Quality in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL). J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfanos, P.; Naska, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Grioni, S.; Boer, J.M.; van Bakel, M.M.; Ericson, U.; Rohrmann, S.; Boeing, H.; Rodríguez, L.; et al. Eating out of home: Energy, macro- and micronutrient intakes in 10 European countries. The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63 (Suppl. S4), S239–S262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.A.; Lopez, N.V.; Lawless, H.T.; Njike, V.; Beleche, M.; Katz, D.L. Reducing calories, fat, saturated fat, and sodium in restaurant menu items: Effects on consumer acceptance. Obesity 2016, 24, 2497–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, S.B.; Das, S.K.; Suen, V.M.M.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Kuriyan, R.; Steiner-Asiedu, M.; Taetzsch, A.; Anderson, A.K.; Silver, R.E.; Barger, K.; et al. Measured energy content of frequently purchased restaurant meals: Multi-country cross sectional study. BMJ 2018, 363, k4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, E.; Jones, A.; Whitelock, V.; Mead, B.R.; Haynes, A. (Over)eating out at major UK restaurant chains: Observational study of energy content of main meals. BMJ 2018, 363, k4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Horst, K.; Brunner, T.A.; Siegrist, M. Fast food and take-away food consumption are associated with different lifestyle characteristics. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2011, 24, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villacis, C.; Zazpe, I.; Santiago, S.; Fuente-Arrillaga, C.d.l.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Martínez-González, M.Á. Frecuencia de comidas fuera de casa y calidad de hidratos de carbono y de grasas en el Proyecto SUN. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 466–474. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.-S.; Ju, S.-Y. Trends in nutrient intakes and consumption while eating-out among Korean adults based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1998–2012) data. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- English, L.; Lasschuijt, M.; Keller, K.L. Mechanisms of the portion size effect. What is known and where do we go from here? Appetite 2015, 88, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffe, L.; Rushton, S.; White, M.; Adamson, A.; Adams, J. Relationship between mean daily energy intake and frequency of consumption of out-of-home meals in the UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, G.W.; Scalco, A.; Craig, T.; Whybrow, S.; Macdiarmid, J.I. Social, temporal and situational influences on meat consumption in the UK population. Appetite 2019, 138, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kant, A.K.; Whitley, M.I.; Graubard, B.I. Away from home meals: Associations with biomarkers of chronic disease and dietary intake in American adults, NHANES 2005–2010. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGuffin, L.E.; Wallace, J.M.; McCrorie, T.A.; Price, R.K.; Pourshahidi, L.K.; Livingstone, M.B. Family eating out-of-home: A review of nutrition and health policies. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2013, 72, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhong, L.; von Cramon-Taubadel, S.; Tu, H.; Wang, H. Restaurants in the Neighborhood, Eating Away from Home and BMI in China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Tian, X. Does Eating-Away-from-Home Increase the Risk of a Metabolic Syndrome Diagnosis? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zang, J.; Luo, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Wang, W.; Guo, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; et al. Eating Out-of-Home in Adult Residents in Shanghai and the Nutritional Differences among Dining Places. Nutrients 2018, 10, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Q.; Zeng, Y. Eating out and getting fat? A comparative study between urban and rural China. Appetite 2018, 120, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carús, J.P.; França, G.V.; Barros, A.J. Place and type of meals consumed by adults in medium sized cities. Rev. Saúde Pública 2014, 48, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.P.; Lorenzo, C.; Espinoza, S.E. Frailty Attenuates the Impact of Metformin on Reducing Mortality in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2014, 2, 1031. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.W.; Song, W.O.; Cho, M.S. Dietary quality differs by consumption of meals prepared at home vs. outside in Korean adults. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, L.K.; Edwards, K.L.; Cade, J.; Clarke, G.P. The geography of Fast Food outlets: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2290–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, A.G.; Proença, R.P.; Calvo, M.C.; Fiates, G.M. Overweight/obesity is associated with food choices related to rice and beans, colors of salads, and portion size among consumers at a restaurant serving buffet-by-weight in Brazil. Appetite 2012, 59, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, I.N.; Curioni, C.; Sichieri, R. Association between eating out of home and body weight. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, I.N.; Sichieri, R. Eating out of home and obesity: A Brazilian nationwide survey. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Myhre, J.B.; Løken, E.B.; Wandel, M.; Andersen, L.F. Eating location is associated with the nutritional quality of the diet in Norwegian adults. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Hou, W.; Wang, F.; Arcan, C. Factors Affecting Obesity and Waist Circumference Among US Adults. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2019, 16, E02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Basterra-Gortari, F.J.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Marti, A.; Martínez, J.A.; Martínez-González, M.A. A prospective study of eating away-from-home meals and weight gain in a Mediterranean population: The SUN (Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra) cohort. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zappala, G.; Platania, A.; Paladino, G.; Nicolosi, L.K.; Ragusa, R.; Marranzano, M. Meal habits and metabolic status in Southern Italian adults. Nutr. Healthy Aging 2019, 5, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.H.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, C.I.; Lin, S.H. Association of eating out with bone density in Taiwan. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 3151–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seguin, R.A.; Aggarwal, A.; Vermeylen, F.; Drewnowski, A. Consumption Frequency of Foods Away from Home Linked with Higher Body Mass Index and Lower Fruit and Vegetable Intake among Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Environ. Public Health 2016, 2016, 3074241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wellard-Cole, L.; Davies, A.; Allman-Farinelli, M. Contribution of foods prepared away from home to intakes of energy and nutrients of public health concern in adults: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, A.D.; Ernst, L.; Poulsen, S.; Andersen, K.K.; Hansen, G.L.; Biltoft-Jensen, A.; Tetens, I. Effectiveness of a Canteen Take Away concept in promoting healthy eating patterns among employees. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nago, E.S.; Lachat, C.K.; Dossa, R.A.; Kolsteren, P.W. Association of out-of-home eating with anthropometric changes: A systematic review of prospective studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auchincloss, A.H.; Li, J.; Moore, K.A.; Franco, M.; Mujahid, M.S.; Moore, L.V. Are neighbourhood restaurants related to frequency of restaurant meals and dietary quality? Prevalence and changes over time in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 4630–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziauddeen, N.; Almiron-Roig, E.; Penney, T.L.; Nicholson, S.; Kirk, S.F.L.; Page, P. Eating at Food Outlets and “On the Go” Is Associated with Less Healthy Food Choices in Adults: Cross-Sectional Data from the UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey Rolling Programme (2008–2014). Nutrients 2017, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schloegl, C.; Schmidt, J.; Boeckle, M.; Weiss, B.M.; Kotrschal, K. Grey parrots use inferential reasoning based on acoustic cues alone. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4135–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Saito, A.; Okada, C.; Okada, E.; Tajima, R.; Takimoto, H. Consumption of meals prepared away from home is associated with inadequacy of dietary fiber, vitamin C and mineral intake among Japanese adults: Analysis from the 2015 National Health and Nutrition Survey. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.A.; Cámara, M.; Giner, R.; González, E.; López, E.; Mañes, J.; Portillo, M.P.; Rafecas, M.; Gutiérrez, E.; García, M.; et al. Informe del Comité Científico de la Agencia Española de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición (AESAN) de revisión y actualización de las Recomendaciones Dietéticas para la población española. Rev. Com. Científico AESAN 2020, 32, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, S.; Adams, J.; Wrieden, W.; White, M.; Brown, H. Sociodemographic characteristics and frequency of consuming home-cooked meals and meals from out-of-home sources: Cross-sectional analysis of a population-based cohort study. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 2255–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thornton, L.E.; Crawford, D.A.; Ball, K. Neighbourhood-socioeconomic variation in women’s diet: The role of nutrition environments. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraone, S.V.; Banaschewski, T.; Coghill, D.; Zheng, Y.; Biederman, J.; Bellgrove, M.A.; Newcorn, J.H.; Gignac, M.; Al Saud, N.M.; Manor, I.; et al. The World Federation of ADHD International Consensus Statement: 208 Evidence-based conclusions about the disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 128, 789–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RD&I Christchurch. Pekapeka/Bats; Department of Conservation, Te Papa Atawhai: Wellington, New Zealand, 2005; Volume NS0054. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, S.A.; Weippert, M.V.; Dickinson, K.M.; Scourboutakos, M.J.; L’Abbé, M.R. Cross-Sectional Analysis of Calories and Nutrients of Concern in Canadian Chain Restaurant Menu Items in 2016. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 59, e149–e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Rong, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Wallace, R.B.; Bao, W. Association Between Frequency of Eating Away-From-Home Meals and Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 1741–1749.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlewood, J.A.; Lourenço, S.; Iversen, C.L.; Hansen, G.L. Menu labelling is effective in reducing energy ordered and consumed: A systematic review and meta-analysis of recent studies. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2106–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petimar, J.; Ramirez, M.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Linakis, S.; Mullen, J.; Roberto, C.A.; Block, J.P. Evaluation of the impact of calorie labeling on McDonald’s restaurant menus: A natural experiment. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesteiro, E.; Megía, A.; Guadalupe-Grau, A.; Fernandez-Veledo, S.; Vendrell, J.; González-Gross, M. Early identification of metabolic syndrome risk: A review of reviews and proposal for defining pre-metabolic syndrome status. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2557–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| ≥18 years old | ≤18 years old |
| Definition of EOH and evaluation of EOH with health parameters | Schools and/or educational interventions, COVID-19 studies |
| Studies that investigated EOH and its association with health | Studies that did not investigate the association between EOH with health |
| Type of Establishment | Country (Number of Articles) | Total Number of Articles | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast food | United States of America (12) Australia (1) United Kingdom (2) South Korea (1) Greece (1) Switzerland (1) Spain (1) | 19 | [5,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] |
| Restaurant | Australia (1) South Korea (1) China (4) United States of America (6) United Kingdom (3) Greece (1) | 16 | [4,7,8,9,15,19,20,27,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] |
| Cafeterias and bars | United States of America (2) Australia (1) Greece (1) Brazil (1) United Kingdom (2) South Korea (1) United States of America (1) China (3) | 12 | [15,16,22,26,27,33,35,36,39,42,43,44] |
| Ready to eat and take away | United Kingdom (3) United States of America (1) South Korea (1) Switzerland (1) | 6 | [23,26,31,35,38,45] |
| Full service | United Kingdom (2) South Korea (1) United States of America (2) | 5 | [24,25,28,29,46] |
| Buffet and buffet by weight | Brazil (2) United States of America (1) | 3 | [26,43,47] |
| Sit-down restaurant | United States of America (1) Brazil (1) | 2 | [19,47] |
| Chain restaurant | United States of America (1) United Kingdom (1) | 2 | [17,30] |
| À la carte | Brazil (1) | 1 | [43] |
| Eating at the table | Switzerland (1) | 1 | [31] |
| Topic Regarding EOH | Finding | References |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | ||
| Energy intake Energy dense foods | High High | [25,35,41,45,48,49] |
| Macronutrients intake | ||
| Protein | High | [45] |
| Fat | High | [5,15,25,41,45,50] |
| Saturated fat | High | [15] |
| Cholesterol | High | [51] |
| Trans fat | High | [52] |
| Monounsaturated fat | Low | [52] |
| Fiber | Low | [15,27,45,52,53] |
| Micronutrients intake | ||
| Micronutrients | Low | [51] |
| Sodium | High | [41,51,53] |
| Phosphorus | Low | [45] |
| Potassium | Low | [45] |
| Niacin | Low | [45] |
| Calcium | Low | [27,54] |
| Vitamin C | Low | [27,45] |
| Beverages intake | ||
| Dairy, milk | Low | [16,24,52] |
| Soft drinks | High | [11,16,52] |
| Fruit juice | High | [11,52] |
| Sugar-sweetened beverages | High | [25] |
| Beer | High | [53] |
| Alcohol | High | [50,52] |
| Food intake | ||
| Sugar | High | [5,27,48] |
| Starch | High | [27] |
| Fruit | Low | [5,16,51,52,53,55] |
| Vegetables | Low | [5,52,55] |
| Cereal | Low | [53] |
| Legumes | Low | [52] |
| Olive oil | Low | [53] |
| Nuts | High | [53] |
| Meat | High | [16,36,52,53] |
| Fish | High | [11] |
| Bakery | High | [11] |
| Food | ||
| Diet quality | Poor | [15,25,26,32,41] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gesteiro, E.; García-Carro, A.; Aparicio-Ugarriza, R.; González-Gross, M. Eating out of Home: Influence on Nutrition, Health, and Policies: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061265
Gesteiro E, García-Carro A, Aparicio-Ugarriza R, González-Gross M. Eating out of Home: Influence on Nutrition, Health, and Policies: A Scoping Review. Nutrients. 2022; 14(6):1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061265
Chicago/Turabian StyleGesteiro, Eva, Alberto García-Carro, Raquel Aparicio-Ugarriza, and Marcela González-Gross. 2022. "Eating out of Home: Influence on Nutrition, Health, and Policies: A Scoping Review" Nutrients 14, no. 6: 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061265
APA StyleGesteiro, E., García-Carro, A., Aparicio-Ugarriza, R., & González-Gross, M. (2022). Eating out of Home: Influence on Nutrition, Health, and Policies: A Scoping Review. Nutrients, 14(6), 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061265







