Pilot Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial: Effects of Jejunal Nutrition on Postprandial Distress in Diabetic Gastropathy (J4G Trial)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Screening
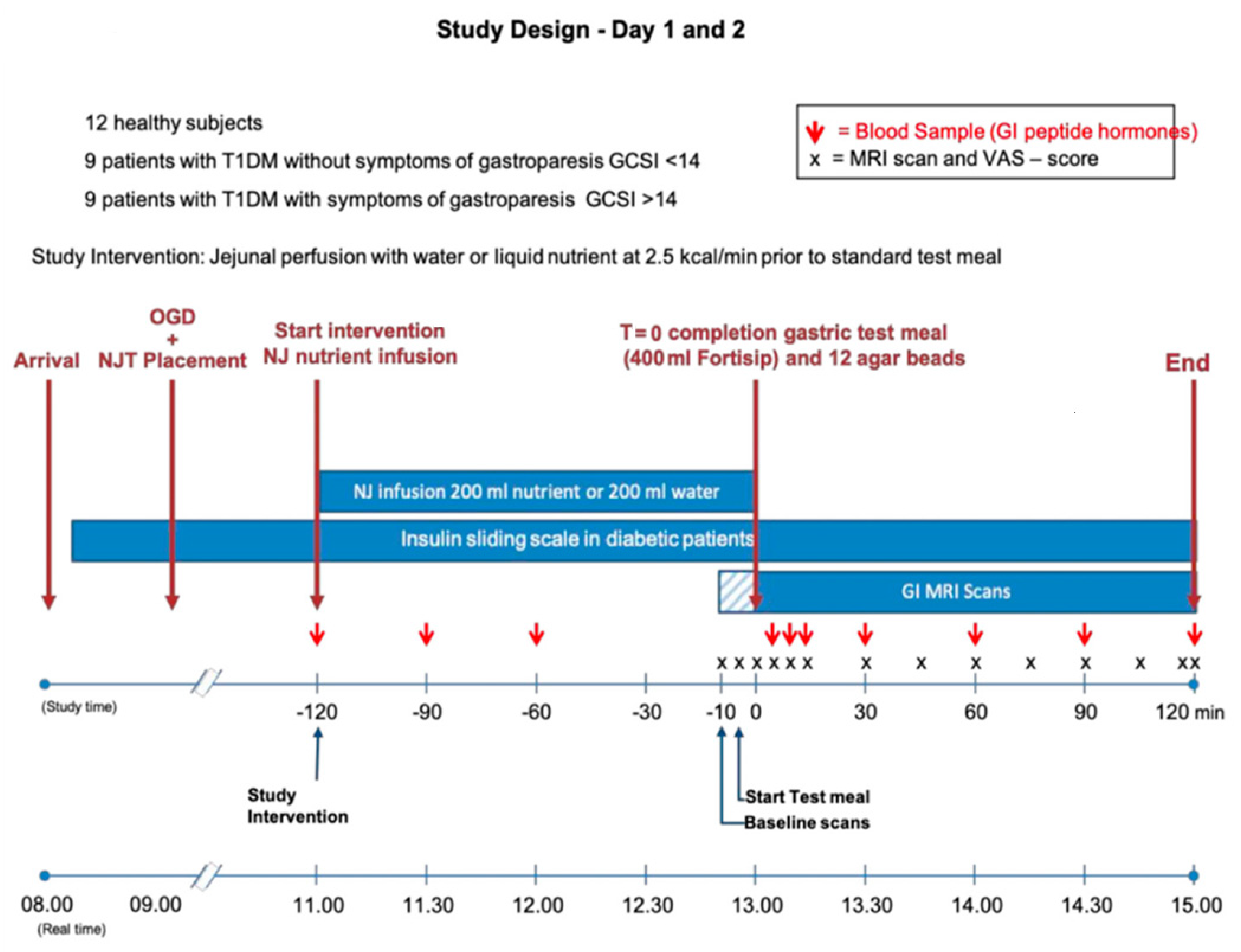
3. Randomisation and Study Procedures
3.1. Endoscopy and Histology
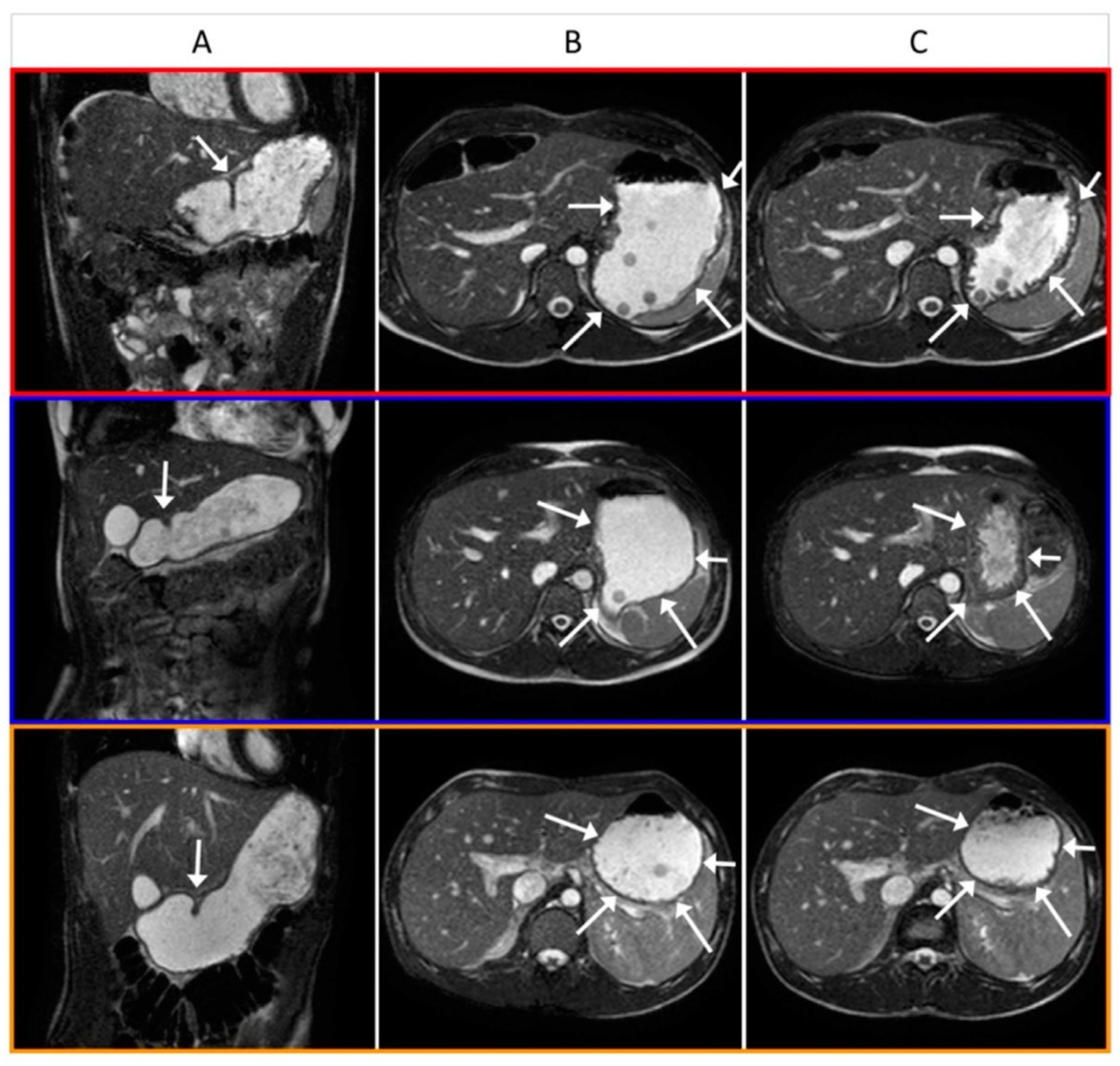
3.2. Gastric Magnetic Resonance Imaging
3.3. Symptom Assessment
3.4. Image Analysis
3.5. GI–Peptide Hormone Assay
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Study Participants
4.2. Endoscopic and Histological Findings
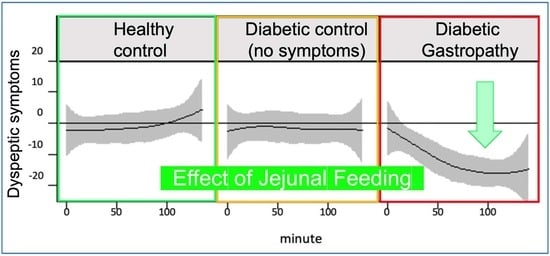
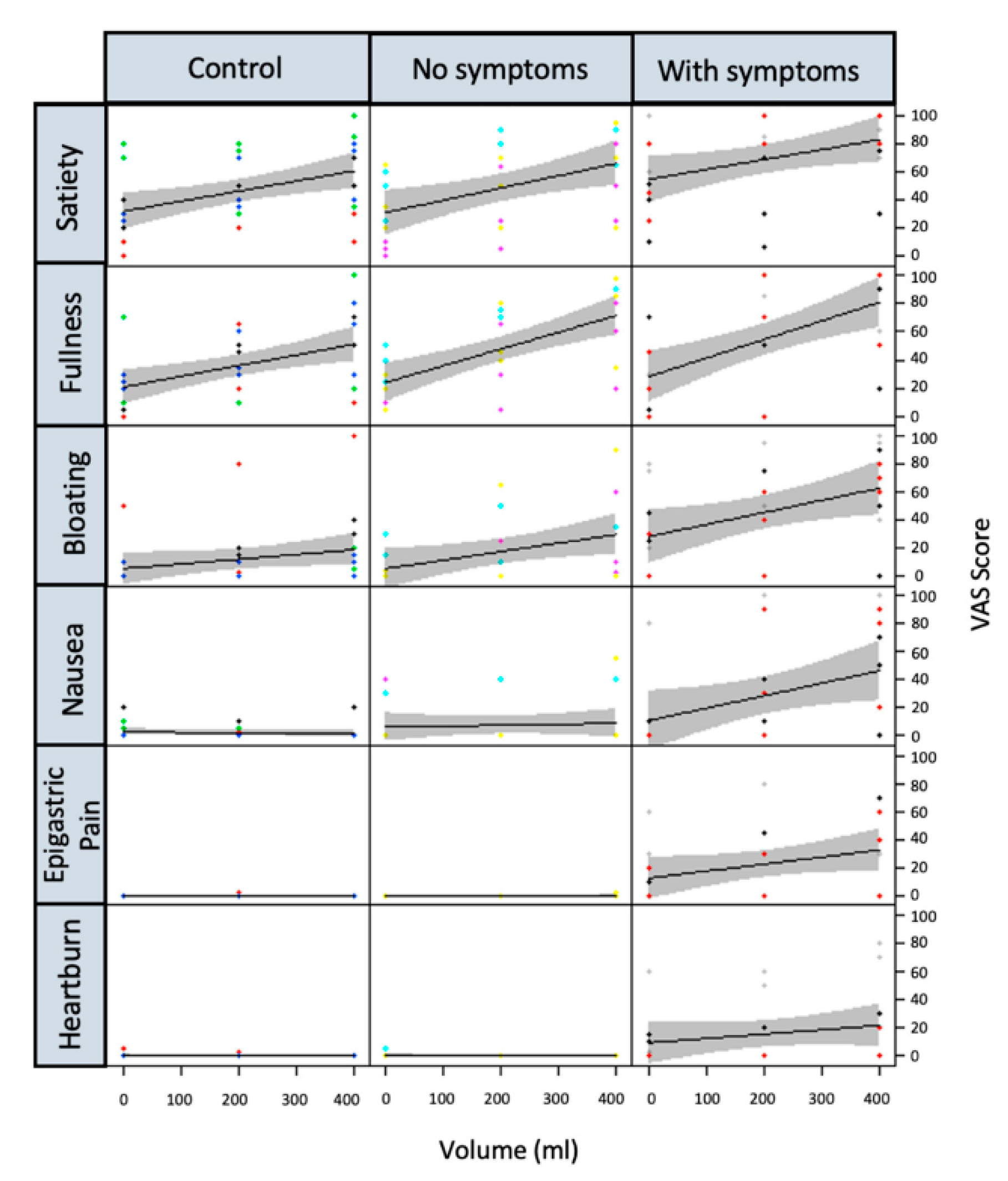
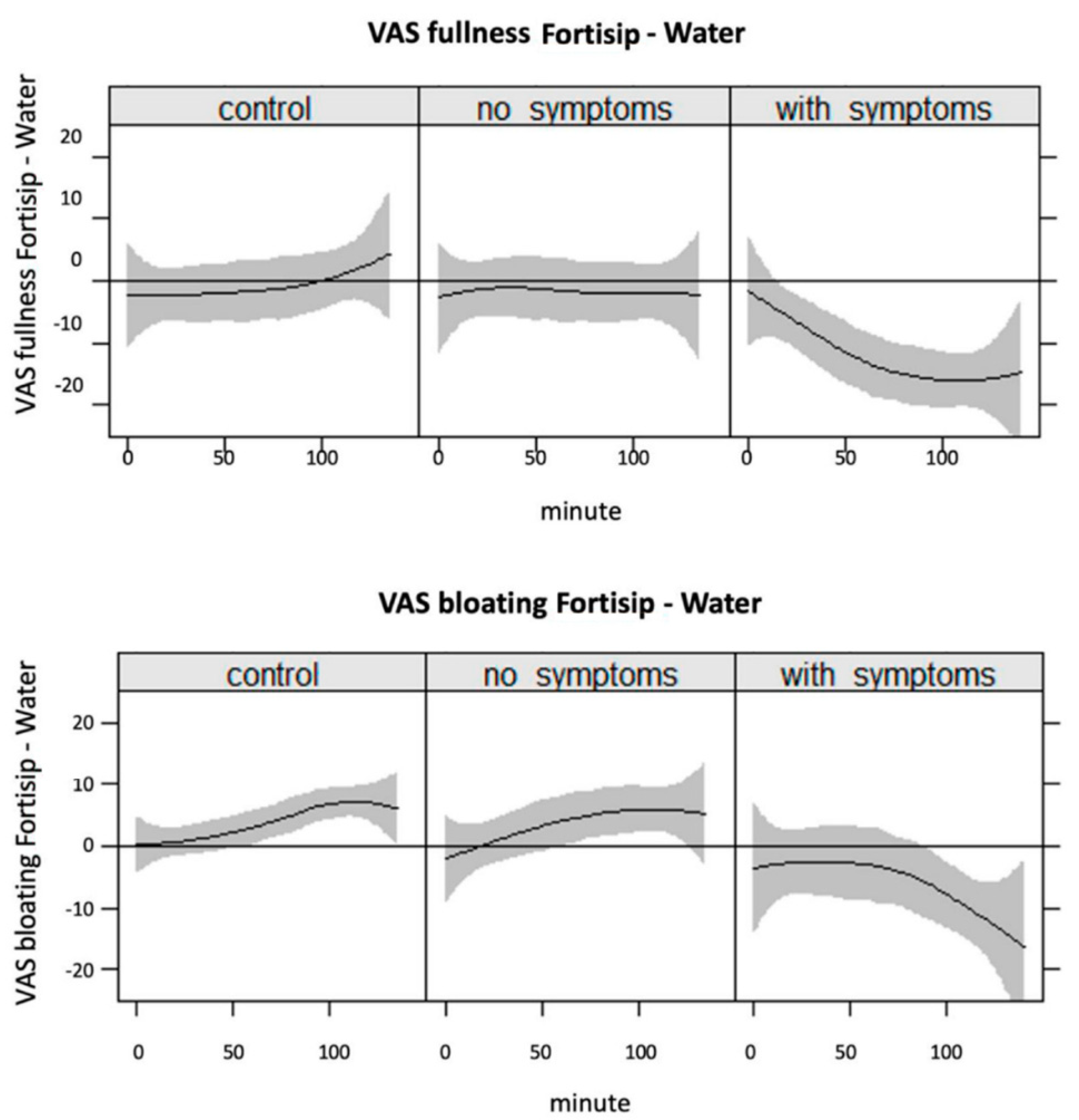
4.3. Effect of JN on Postprandial Symptoms
4.4. Gastric Volume, Motility and Emptying
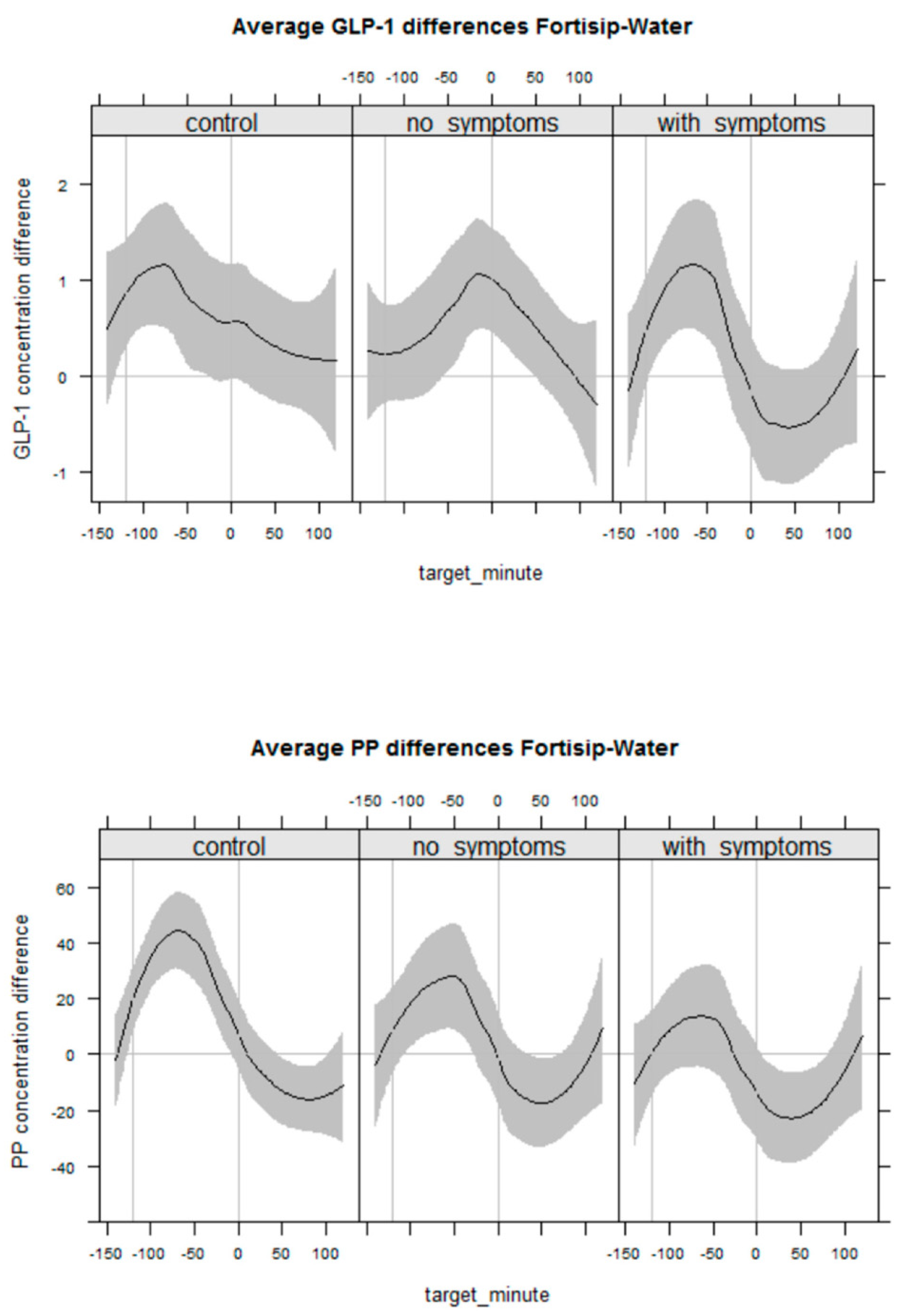
4.5. GI Neuroendocrine Response
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Coating (Capture Ab.: HYB 147-06) 96-well-Nunc-Maxisorp-Platte (weiß; je 100 μL) in diluted 1:2000 in 0.1 M NH4HCO3, min. 20–24 h; 4 °C
- 50 μL GLP-1-Assay-Puffer; 1 h block at room temperature; 3 times wash
- 50 μL Standards (0, 4, 9 pg/mL–5000 pg/ml 1.5–1516.2 pM; 500 ng/mL—>1:100 = 5000 pg/mL = 1516.2 pM) + 50 μL GLP-1-Assay-Puffer; 20–24 h 4 °C—>3 times wash
- Samples dissolved in 100 μL GLP-1-Assay-Puffer, 90 μL Sample volume; 20–24 h 4 °C—>3 times wash
- 100 μL Detection-Antibody ABS 033-10-biot. (1:10,000) in GLP-1-Assay-Puffer; 20–24 h 4 °C—>3 times wash
- 100 μL Streptavidin-Poly-HRP (1:500,000; 1:100 prediluted—>10 μL/50 mL) in 2% Tween20 in TBS—2 h—>5 times wash + dry (paper towels)
- 50 μL SuperSignal® ELISA Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (1:5; PIERCE #37075)—>Substrate addition in 6-min-Rhythmus in Orion II with 5 min Delay)
- -
- Coating of Luminunc-Platten with coating antibody; 1:5000 in NH4HCO3, day; 4 °C
- -
- Blocking: adding 50 μL 2%NFM; 1 h, room temperature—>3 times wash
- -
- Incubation with PP-Standard (10 μL) and serum (10 μL) + 100 μL 2%NFM; 2 h room temperature + overnight, 4 °C—>3 times wash
- -
- Incubation with 100 μL Anti Pancreatic polypeptide-biot. (13.1.2010) 1:2000 in 2% Tween20 in TBS, 3 h room temperature—>3 times wash
- -
- 100 μL Streptavidin-Poly-HRP (1:500,000; 1:100 prediluted—>10 μL/50 mL) in 2% Tween20 in PBS—1,5 h room temperature (shake)—>3 times wash
- -
- 50 μL Super sensitive (PIERCE) in dilution 1:5—> Orion II Plate luminometer (5 min delay)
References
- Camilleri, M.; Parkman, H.P.; Shafi, M.A.; Abell, T.L.; Gerson, L. Clinical guideline: Management of gastroparesis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayvargiya, P.; Jameie-Oskooei, S.; Camilleri, M.; Chedid, V.; Erwin, P.J.; Murad, M.H. Association between delayed gastric emptying and upper gastrointestinal symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2019, 68, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasricha, P.J.; Grover, M.; Yates, K.P.; Abell, T.L.; Bernard, C.E.; Koch, K.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; Kuo, B.; Bulat, R.; et al. Functional Dyspepsia and Gastroparesis in Tertiary Care are Interchangeable Syndromes With Common Clinical and Pathologic Features. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, J.; Holvoet, L.; Caenepeel, P.; Bisschops, R.; Sifrim, D.; Verbeke, K.; Janssens, J.; Tack, J. Clinical trial: A randomized-controlled crossover study of intrapyloric injection of botulinum toxin in gastroparesis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehetner, J.; Ravari, F.; Ayazi, S.; Skibba, A.; Darehzereshki, A.; Pelipad, D.; Mason, R.J.; Katkhouda, N.; Lipham, J.C. Minimally invasive surgical approach for the treatment of gastroparesis. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Malagelada, J.R. Abnormal intestinal motility in diabetics with the gastroparesis syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 14, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziessman, H.A.; Fahey, F.H.; Collen, M.J. Biphasic solid and liquid gastric emptying in normal controls and diabetics using continuous acquisition in LAO view. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1992, 37, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsom, M.; Roelofs, J.M.; Akkermans, L.M.; van Berge Henegouwen, G.P.; Smout, A.J. Proximal gastric motor activity in response to a liquid meal in type I diabetes mellitus with autonomic neuropathy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen, M.A.; Rayner, C.K.; Andrews, J.M.; Hebbard, G.S.; Doran, S.M.; Samsom, M.; Horowitz, M. Physiological changes in blood glucose do not affect gastric compliance and perception in normal subjects. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, G761–G766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendra, D.; Millward, B.A.; Travis, S.P. Diabetic gastroparesis improved by percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Revicki, D.A.; Rentz, A.M.; Dubois, D.; Kahrilas, P.; Stanghellini, V.; Talley, N.J.; Tack, J. Development and validation of a patient-assessed gastroparesis symptom severity measure: The Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, H.L.; Tucker, E.; Hoad, C.L.; Pal, A.; Costigan, C.; Hudders, N.; Perkins, A.; Blackshaw, E.; Gowland, P.; Marciani, L.; et al. Development and validation of a large, modular test meal with liquid and solid components for assessment of gastric motor and sensory function by non-invasive imaging. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revicki, D.A.; Camilleri, M.; Kuo, B.; Norton, N.J.; Murray, L.; Palsgrove, A.; Parkman, H.P. Development and content validity of a gastroparesis cardinal symptom index daily diary. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciani, L.; Gowland, P.A.; Fillery-Travis, A.; Manoj, P.; Wright, J.; Smith, A.; Young, P.; Moore, R.; Spiller, R.C. Assessment of antral grinding of a model solid meal with echo-planar imaging. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 280, G844–G849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, H.; Hoad, C.L.; Tucker, E.; Costigan, C.; Marciani, L.; Gowland, P.; Fox, M. Gastric motor and sensory function in health assessed by magnetic resonance imaging: Establishment of reference intervals for the Nottingham test meal in healthy subjects. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoad, C.L.; Parker, H.; Hudders, N.; Costigan, C.; Cox, E.F.; Perkins, A.C.; Blackshaw, P.E.; Marciani, L.; Spiller, R.C.; Fox, M.R.; et al. Measurement of gastric meal and secretion volumes using magnetic resonance imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 1367–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscalzo, J. Pilot trials in clinical research: Of what value are they? Circulation 2009, 119, 1694–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazziari, E.; Bytzer, P.; Delvaux, M.; Holtmann, G.; Malagelada, J.R.; Morris, J.; Muller-Lissner, S.; Spiller, R.C.; Tack, J.; Whorwell, P.J. Clinical trial guidelines for pharmacological treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2016. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Xie, Y. Dynamic Documents with R and Knitr; Chapman & Hall/CRC, Taylor and Frances: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.C.; Bates, D.M. Mixed-Effects Models in S and S-Plus; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabry, J.; Goodrich, B. Rstanarm: Bayesian Applied Regression Modeling via Stan, Version 2.10.1. 2016. Available online: https://mc-stan.org/rstanarm (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Stan Development Team. Stan: A C++ Library for Probability and Sampling, Version 2.7.0. 2015. Available online: http://mc-stan.org (accessed on 18 February 2022).
- Spiller, R.C.; Trotman, I.F.; Adrian, T.E.; Bloom, S.R.; Misiewicz, J.J.; Silk, D.B. Further characterisation of the 'ileal brake' reflex in man--effect of ileal infusion of partial digests of fat, protein, and starch on jejunal motility and release of neurotensin, enteroglucagon, and peptide YY. Gut 1988, 29, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, T.V.; Johnson, C.P.; Kalbfleisch, J.H.; Roza, A.M.; Wood, C.M.; Weisbruch, J.P.; Soergel, K.H. Highly variable gastric emptying in patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Gut 1995, 37, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undeland, K.A.; Hausken, T.; Svebak, S.; Aanderud, S.; Berstad, A. Wide gastric antrum and low vagal tone in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 compared to patients with functional dyspepsia and healthy individuals. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undeland, K.A.; Hausken, T.; Gilja, O.H.; Aanderud, S.; Berstad, A. Gastric meal accommodation studied by ultrasound in diabetes. Relation to vagal tone. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 33, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chedid, V.; Brandler, J.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Park, S.Y.; Szarka, L.A.; Camilleri, M. Characterization of Upper Gastrointestinal Symptoms, Gastric Motor Functions, and Associations in Patients with Diabetes at a Referral Center. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, F.; Verschueren, S.; Rotondo, A.; Tack, J. Duodenal nutrient exposure contributes to enhancing gastric accommodation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatek, M.A.; Menne, D.; Steingoetter, A.; Goetze, O.; Forras-Kaufman, Z.; Kaufman, E.; Fruehauf, H.; Boesiger, P.; Fried, M.; Schwizer, W.; et al. Effect of meal volume and calorie load on postprandial gastric function and emptying: Studies under physiological conditions by combined fiber-optic pressure measurement and MRI. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G894–G901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronkainen, J.; Aro, P.; Walker, M.M.; Agreus, L.; Johansson, S.E.; Jones, M.; Talley, N.J. Duodenal eosinophilia is associated with functional dyspepsia and new onset gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| HV (GCSI < 14) | DC (GCSI < 14) | DG (GCSI > 27) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 12 | 9 | 9 | - |
| Male sex (Percentages) | 5 (41.7) | 3 (33.3) | 5 (55.6) | 0.629 |
| BMI | 26.70 (22.5–30.18) | 22.20 (21.5–25.1) | 22.40 (20.4–25.2) | 0.213 |
| Age (years, range) | 30.50 (24.75–41.25) | 32.00 (29–38) | 30.00 (27–34) | 0.724 |
| Anxiety score (range) | 2.50 (1–3.25) | 3.00 (1–4) | 5.00 (4–10) | 0.013 |
| Depression score | 0 (0–0.25) | 0 (0–1) | 4 (4–10) | 0.003 |
| PHQ 15 Score | 1.50 (0–2) | 2.00 (1–3) | 10.00 (7–13) | <0.001 |
| PHQ15 quantile | 37.40 (0.38–46.97) | 38.60 (23.9–58.40) | 96.70 (92.6–97.60) | 0.001 |
| Smoking | 0.156 | |||
| Current smoker (percentage) | 4 (33.3) | 2 (22.2) | 4 (44.4) | |
| Ex-smoker (percentage) | 1 (8.3) | 2 (22.2) | 4 (44.4) | |
| Never smoked (percentage) | 7 (58.3) | 5 (55.6) | 1 (11.1) | |
| Alcohol | 0.189 | |||
| <20 units per week (percentage) | 9 (75.0) | 9 (100.0) | 5 (55.5) | |
| Never (percentage) | 3 (25.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (44.4) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carneiro, L.; White, J.; Parker, H.; Hoad, C.; Tucker, E.; Marciani, L.; Gowland, P.; Gazis, T.; Walker, M.; Fox, M. Pilot Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial: Effects of Jejunal Nutrition on Postprandial Distress in Diabetic Gastropathy (J4G Trial). Nutrients 2022, 14, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071321
Carneiro L, White J, Parker H, Hoad C, Tucker E, Marciani L, Gowland P, Gazis T, Walker M, Fox M. Pilot Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial: Effects of Jejunal Nutrition on Postprandial Distress in Diabetic Gastropathy (J4G Trial). Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071321
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarneiro, Lucianno, Jonathan White, Helen Parker, Caroline Hoad, Emily Tucker, Luca Marciani, Penny Gowland, Tasso Gazis, Marjorie Walker, and Mark Fox. 2022. "Pilot Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial: Effects of Jejunal Nutrition on Postprandial Distress in Diabetic Gastropathy (J4G Trial)" Nutrients 14, no. 7: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071321
APA StyleCarneiro, L., White, J., Parker, H., Hoad, C., Tucker, E., Marciani, L., Gowland, P., Gazis, T., Walker, M., & Fox, M. (2022). Pilot Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial: Effects of Jejunal Nutrition on Postprandial Distress in Diabetic Gastropathy (J4G Trial). Nutrients, 14(7), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071321