Effects of Plant-Based Diets on Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Markers in Adults: An Umbrella Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
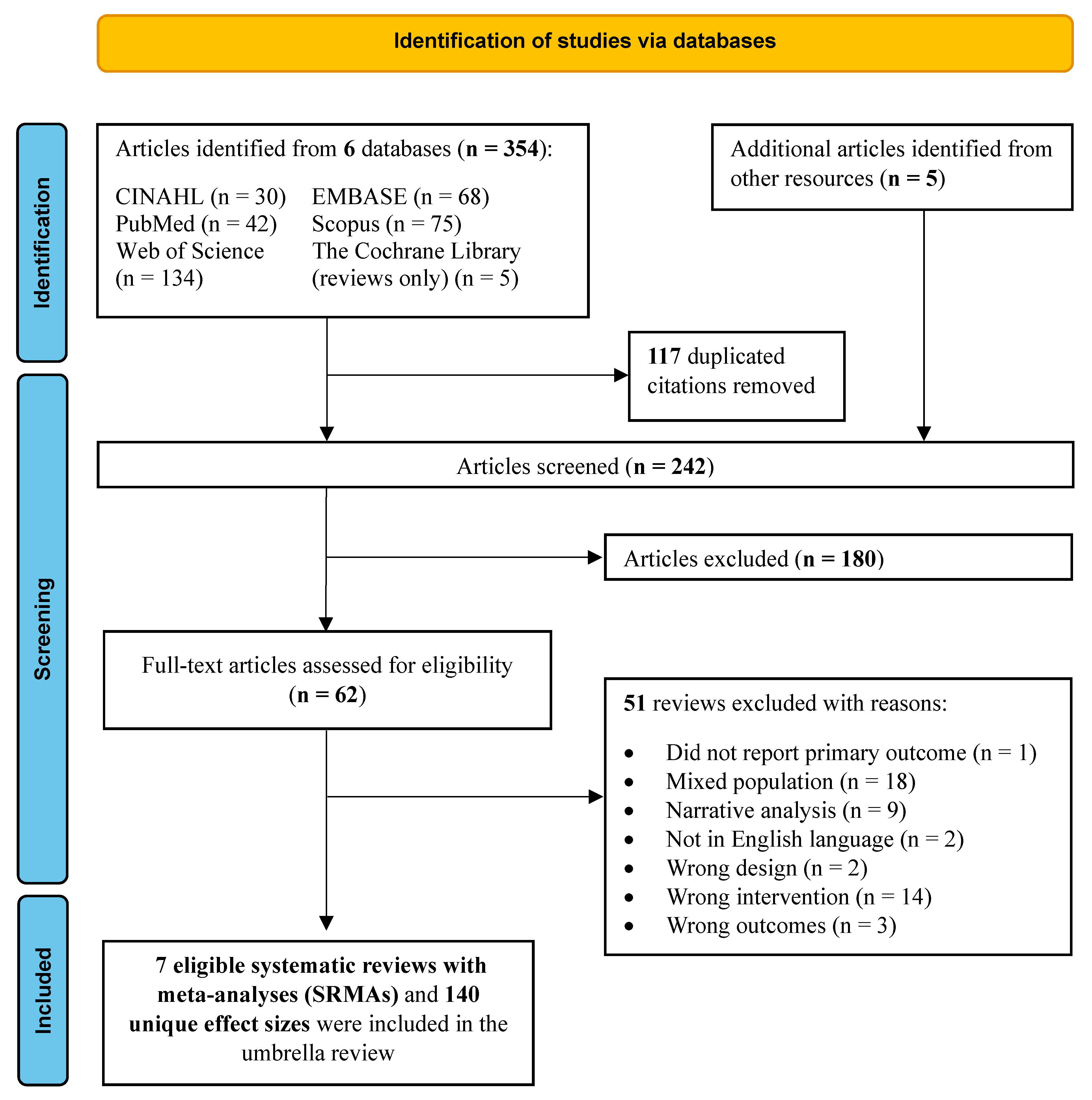
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Methodological Quality Appraisal
2.5. Certainty of Evidence
2.6. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Quality Assessment
3.3. Anthropometric Outcomes
| Outcomes and Subgroups | Meta-Analysis Level | Study Level | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Reviews | MD (95% CI) | t | p-Value | I2, % | Number of Study Arms | MD (95% CI) | t | p-Value | I2, % | Subgroup Differences Q, p-Value | |
| Weight, kg | |||||||||||
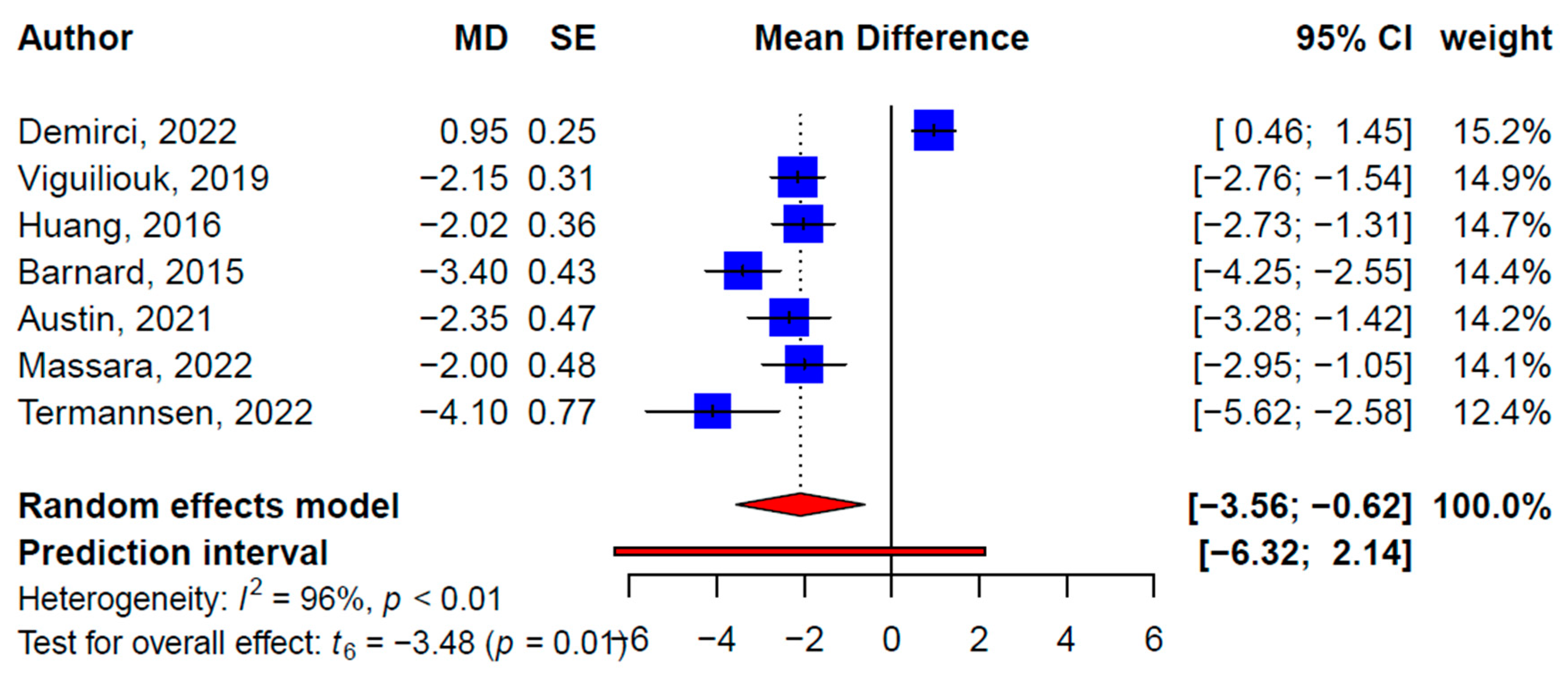
| Total | 7 | −2.09 (−3.56, −0.62) | −3.48 | * 0.01 | 95.6 | 35 | −2.90 (−3.62, −2.18) | −8.16 | *** <0.001 | 89.4 | |
| Subgroups | 4.63, 0.33 | ||||||||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 13 | −3.25 (−4.34, −2.17) | −6.53 | <0.01 | 87.4 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 9 | −3.54 (−5.89, −1.18) | −3.47 | <0.01 | 94.3 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 7 | −1.95 (−3.15, −0.76) | −4.00 | <0.01 | 83.1 | - |
| Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | −2.48 (−6.05, 1.09) | −1.93 | 0.13 | 68.7 | - |
| Lacto-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | −3.20 (−4.77, −1.63) | - | - | - | - |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | |||||||||||
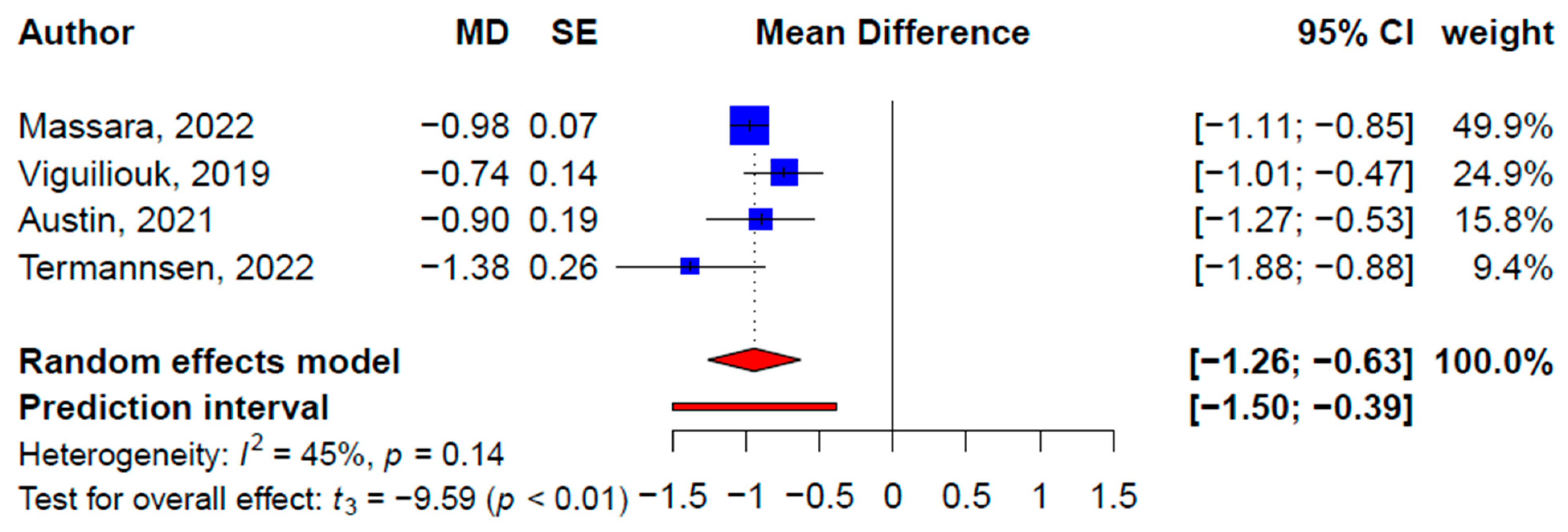
| Total | 4 | −0.95 (−1.26, −0.63) | −9.59 | ** 0.002 | 45.1 | 26 | −0.82 (−1.28, −0.37) | −3.71 | ** 0.001 | 82.6 | |
| Subgroups | - | - | - | - | - | 3.79, 0.15 | |||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 11 | −0.80 (−1.67, 0.06) | −2.07 | 0.06 | 86.3 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | −1.65 (−3.18, −0.11) | −2.98 | 0.04 | 73.3 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 7 | −0.55 (−1.04, −0.06) | −2.77 | 0.03 | 78.5 | - |
| Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | −1.63 (−22.43, 19.15) | −1.00 | 0.5 | 77.6 | - |
| Lacto-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 0.38 (−0.72, 1.48) | - | - | - | - |
| Waist circumference, cm | |||||||||||
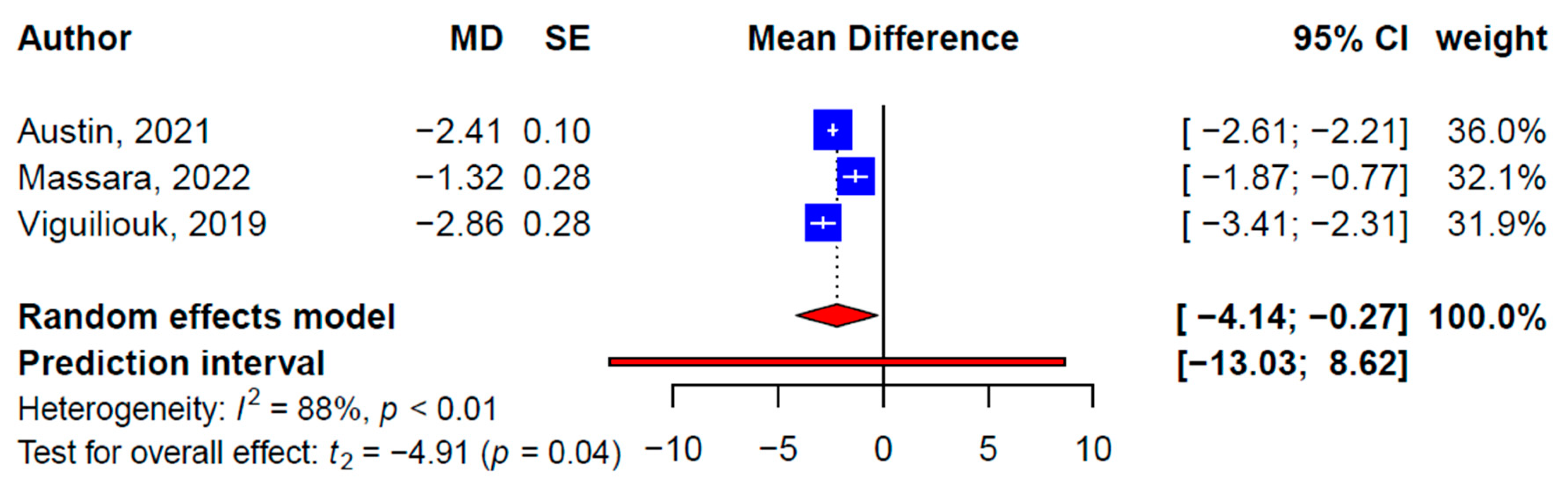
| Total | 3 | −2.20 (−4.14, −0.27) | −4.91 | * 0.04 | 88.4 | 14 | −2.16 (−4.07, −0.25) | −2.45 | * 0.03 | 92.9 | - |
| Subgroups | - | - | - | - | - | 1.79, 0.62 | |||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | −1.75 (−4.88, 1.38) | −1.55 | 0.2 | 89.4 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | −4.32 (−12.56, 3.91) | −1.67 | 0.19 | 95.2 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | −1.16 (−3.50, 1.18) | −1.58 | 0.21 | 64.9 | - |
| Lacto-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | −0.50 (−3.67, 2.67) | - | - | - | - |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), mmol/L | |||||||||||
| Total | 3 | −0.04 (−0.08, 0.00) | −4.11 | 0.05 | 0 | 30 | −0.03 (−0.15, 0.08) | −0.55 | 0.59 | 94.2 | |
| Subgroups | - | - | - | - | - | 5.95, 0.20 | |||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 12 | 0.05 (−0.24, 0.34) | 0.37 | 0.72 | 97.1 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 7 | −0.06 (−0.19, 0.08) | −1.05 | 0.33 | 90.7 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 7 | −0.07 (−0.11, −0.03) | −4.16 | <0.01 | 6.2 | - |
| Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | 3 | −0.16 (−0.82, 0.50) | −1.05 | 0.04 | 78.7 | - | |||||
| Lacto-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | −0.01 (−0.05, 0.03) | - | - | - | - |
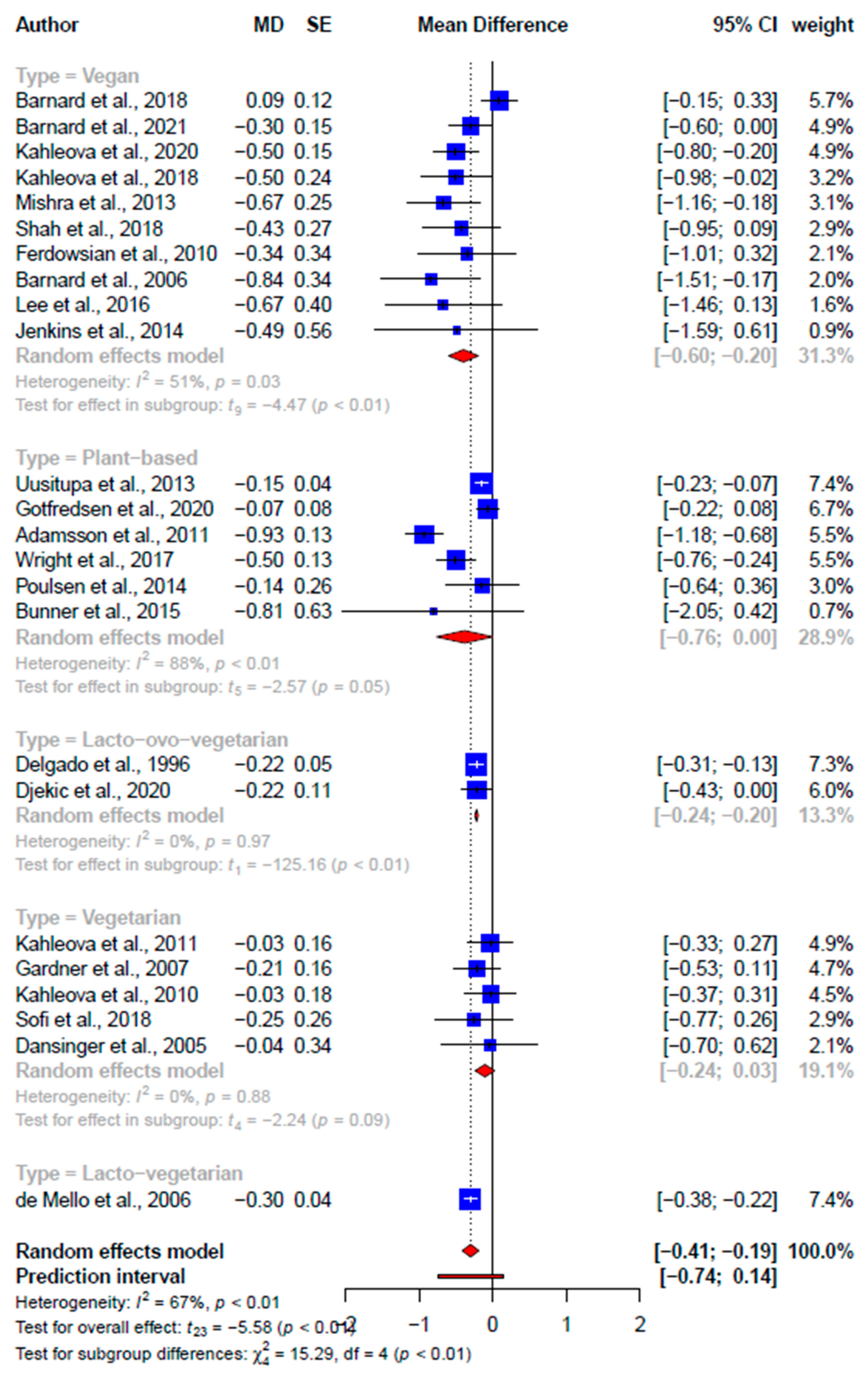
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) a, mmol/L | |||||||||||
| Total | 3 | −0.18 (−0.38, 0.01) | −4.00 | 0.06 | 49.7 | 24 | −0.30 (−0.41, −0.19) | −5.58 | *** <0.001 | 66.5 | |
| Subgroups | - | - | - | - | - | † 15.29, 0.004 | |||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 10 | −0.40 (−0.60, −0.20) | −4.47 | <0.01 | 50.7 | - |
| Non-specific | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | −0.38 (−0.76, −0.00) | −2.57 | 0.05 | 88.2 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | −0.11 (−0.24, 0.03) | −2.24 | 0.09 | 0 | - |
| Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | −0.22 (−0.24, −0.20) | −125.16 | <0.01 | 0 | - |
| Lacto-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | −0.30 (−0.38, −0.22) | - | - | - | - |
| Triglyceride, mmol/L | |||||||||||
| Total | 3 | 0.04 (−0.22, 0.31) | 0.71 | 0.55 | 66.3 | 26 | 0.39 (−0.06, 0.85) | 1.77 | 0.09 | 91.4 | |
| Subgroups | † 11.9, 0.04 | ||||||||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 11 | 0.82 (−0.17, 1.81) | 1.84 | 0.10 | 95.5 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | 0.09 (−0.12, 0.30) | 1.12 | 0.31 | 52.6 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | −0.18 (−0.41, 0.05) | −2.16 | 0.10 | 19.7 | - |
| Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | 3 | 0.00 (−0.20, 0.20) | 0.02 | 0.98 | 0.0 | - | |||||
| Lacto-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 0.86 (−0.18, 1.90) | - | - | 0.0 | - |
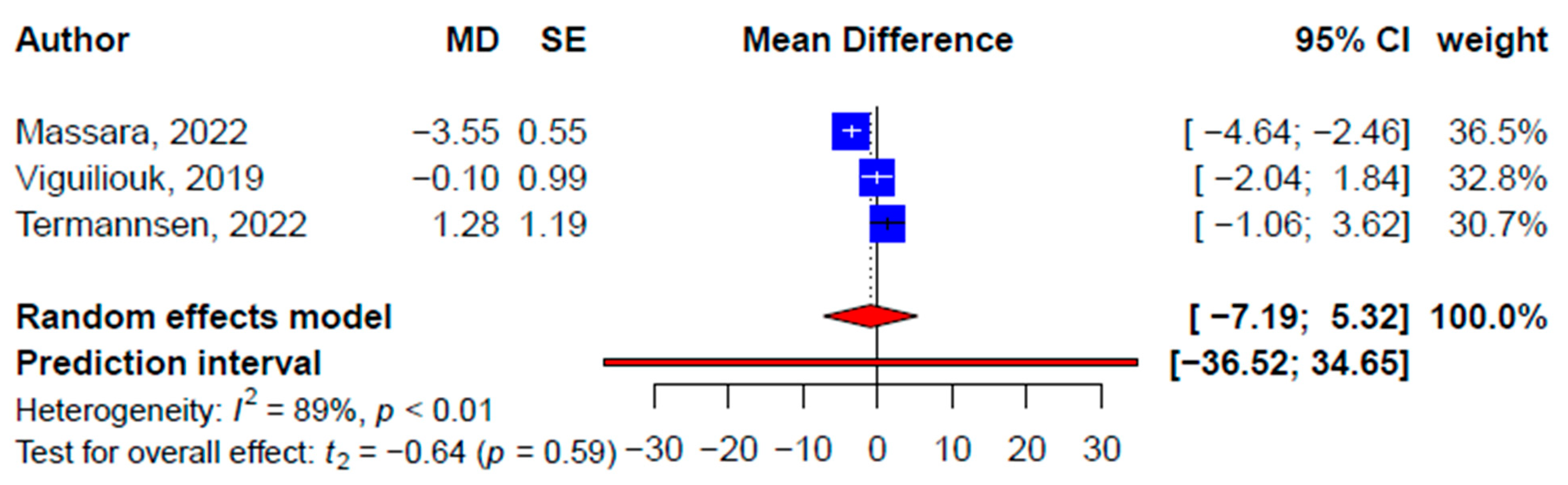
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | |||||||||||
| Total | 3 | −0.93 (−7.19, 5.32) | −0.64 | 0.59 | 89.4 | 21 | 0.07 (−1.97, 2.10) | 0.07 | 0.95 | 91.9 | - |
| Subgroups | - | - | - | - | - | † 4.41, 0.04 | |||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 9 | 1.56 (−2.41, 5.53) | 0.91 | 0.39 | 83.9 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 8 | −1.48 (−5.10, 2.14) | −0.97 | 0.36 | 91.4 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 0.96 (−10.50, 12.43) | 1.07 | 0.48 | 0 | - |
| Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | −1.51 (−8.76, 5.74) | −2.64 | 0.23 | 0 | - |
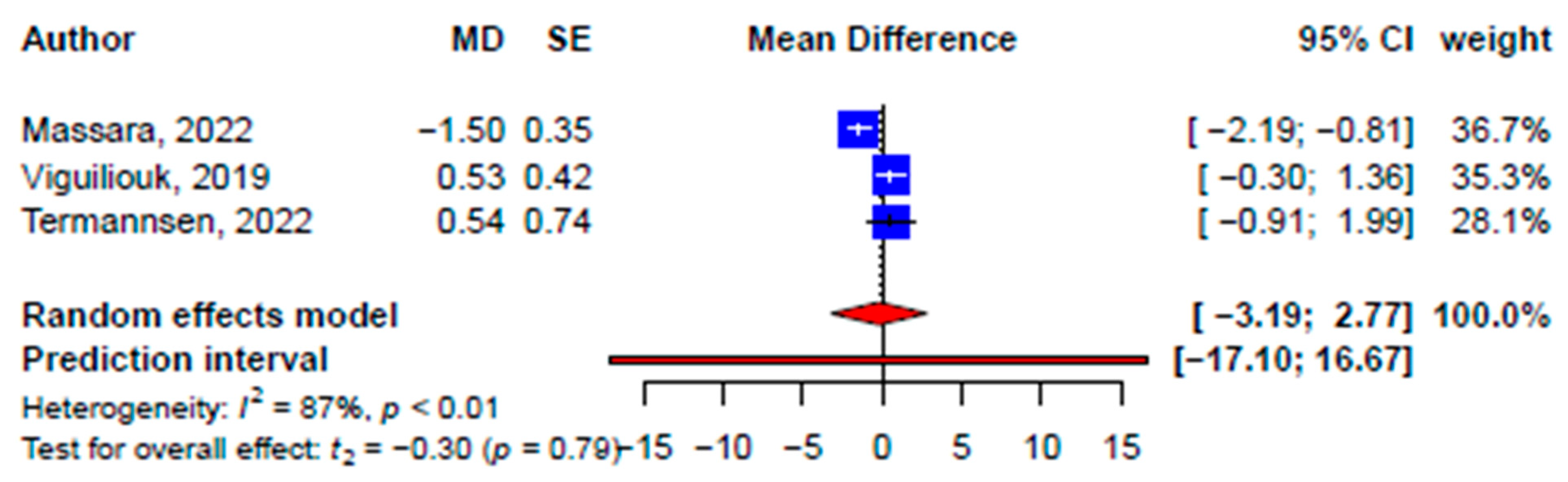
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | |||||||||||
| Total | 3 | −0.21 (−3.19, 2.77) | −0.3 | 0.79 | 87.4 | 21 | 0.01 (−1.41, 1.43) | 0.02 | 0.99 | 88.9 | - |
| Subgroups | - | - | - | - | - | - | † 131.2, <0.001 | ||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 9 | 0.61 (−2.10, 3.31) | 0.52 | 0.62 | 82.0 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 8 | −0.73 (−3.62, 2.16) | −0.60 | 0.57 | 89.1 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 1.16 (−1.34, 3.66) | 5.92 | 0.11 | 0 | - |
| Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | −1.35 (−2.78, 0.08) | −12.02 | 0.05 | 0 | - |
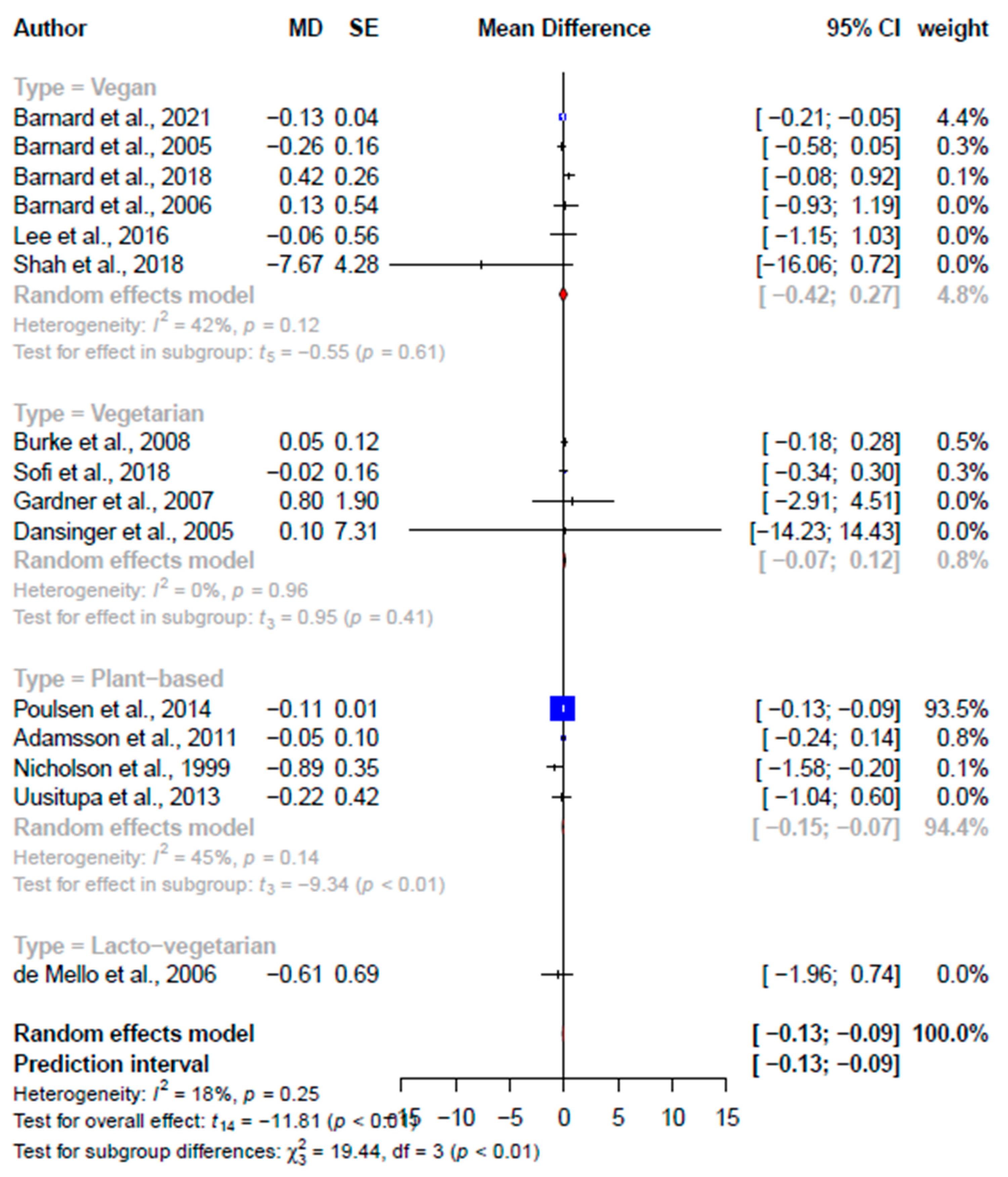
| Fasting blood glucose, mmol/L | |||||||||||
| Total | 3 | −0.06 (−0.33, 0.21) | −0.97 | 0.44 | 84.0 | 15 | −0.11 (−0.13, −0.09) | −11.8 | *** <0.001 | 18.2 | |
| Subgroups | - | - | - | - | - | † 26.9, <0.001 | |||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | −0.07 (−0.42, 0.27) | −0.55 | 0.61 | 42.1 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | −0.11 (−0.15, −0.07) | −9.34 | <0.01 | 44.8 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | 0.03 (−1.97, 0.75) | 0.95 | 0.41 | 0.0 | - |
| Lacto-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | −0.61 (−1.97, 0.95) | - | - | - | - |
| HbA1c b | |||||||||||
| Total | - | - | - | - | - | 13 | −0.03 (−0.06, 0.00) | −1.83 | 0.09 | 32.4 | - |
| Subgroups | - | - | - | - | - | † 43.3, <0.001 | |||||
| Vegan | - | - | - | - | - | 9 | −0.06 (−0.08, −0.04) | −5.83 | <0.01 | 0.0 | - |
| Plant-based | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 0.01 (0.00, 0.01) | 22.13 | 0.03 | 0.0 | - |
| Vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | −0.44 (−0.97, 0.09) | - | - | - | - |
| Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | −0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) | - | - | - | - |
Glucose Metabolism
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner-McGrievy, G.; Mandes, T.; Crimarco, A. A plant-based diet for overweight and obesity prevention and treatment. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. JGC 2017, 14, 369. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, N.; Wilson, L.; Smith, M.; Duncan, B.; McHugh, P. The BROAD study: A randomised controlled trial using a whole food plant-based diet in the community for obesity, ischaemic heart disease or diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Caulfield, L.E.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; Steffen, L.M.; Coresh, J.; Rebholz, C.M. Plant-based diets are associated with a lower risk of incident cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular disease mortality, and all-cause mortality in a general population of middle-aged adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, S.; Delattre, C.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D.; Benbasat, N.; Nalbantova, V.; Ivanov, K. Plant-based diet as a strategy for weight control. Foods 2021, 10, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, V.; Vasudeva, N.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Rowley, D. Lead anti-obesity compounds from nature. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord.-Drug Targets 2020, 20, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, T.M.; Meyer, R.K.; Duca, F.A. Therapeutic potential of various plant-based fibers to improve energy homeostasis via the gut microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrelli, M.; Statti, G.; Conforti, F. A review of biologically active natural products from Mediterranean wild edible plants: Benefits in the treatment of obesity and its related disorders. Molecules 2020, 25, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahleova, H.; Rembert, E.; Alwarith, J.; Yonas, W.N.; Tura, A.; Holubkov, R.; Agnello, M.; Chutkan, R.; Barnard, N.D. Effects of a low-fat vegan diet on gut microbiota in overweight individuals and relationships with body weight, body composition, and insulin sensitivity. A randomized clinical trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.S.; Fernandez, M.L. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), diet and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, S.M.; Rosenfeld, D.L.; Moreira, A.V.B.; Zandonadi, R.P. Plant-based and vegetarian diets: An overview and definition of these dietary patterns. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chareonrungrueangchai, K.; Wongkawinwoot, K.; Anothaisintawee, T.; Reutrakul, S. Dietary factors and risks of cardiovascular diseases: An umbrella review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.S.; Umar, S.; Myint, P.K.; Mamas, M.A.; Loke, Y.K. Vegetarian diet, Seventh Day Adventists and risk of cardiovascular mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 176, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churuangsuk, C.; Hall, J.; Reynolds, A.; Griffin, S.J.; Combet, E.; Lean, M.E. Diets for weight management in adults with type 2 diabetes: An umbrella review of published meta-analyses and systematic review of trials of diets for diabetes remission. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguiliouk, E.; Glenn, A.J.; Nishi, S.K.; Chiavaroli, L.; Seider, M.; Khan, T.; Bonaccio, M.; Iacoviello, L.; Mejia, S.B.; A Jenkins, D.J.; et al. Associations between dietary pulses alone or with other legumes and cardiometabolic disease outcomes: An umbrella review and updated systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2019, 10 (Suppl. S4), S308–S319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, S.S. When to Trust a Meta-analysis or Systematic Review About a Surgical Treatment, and Why. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2022, 480, 437–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunny, C.; Pieper, D.; Thabet, P.; Kanji, S. Managing overlap of primary study results across systematic reviews: Practical considerations for authors of overviews of reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromataris, E.; Fernandez, R.; Godfrey, C.M.; Holly, C.; Khalil, H.; Tungpunkom, P. Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. JBI Evid. Implement. 2015, 13, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satija, A.; Hu, F.B. Plant-based diets and cardiovascular health. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 28, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusar-Poli, P.; Radua, J. Ten simple rules for conducting umbrella reviews. BMJ Ment. Health 2018, 21, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IntHout, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Rovers, M.M.; Goeman, J.J. Plea for routinely presenting prediction intervals in meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IntHout, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Borm, G.F. The Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method for random effects meta-analysis is straightforward and considerably outperforms the standard DerSimonian-Laird method. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieper, D.; Antoine, S.-L.; Mathes, T.; Neugebauer, E.A.; Eikermann, M. Systematic review finds overlapping reviews were not mentioned in every other overview. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Software Version 4.1.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Schwarzer, G. General Package for Meta-Analysis, Version 6.2-1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022.
- Viechtbauer, W.; Viechtbauer, M.W. Package ‘Metafor’ The Comprehesive R Archive Network. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/metafor/metafor.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Austin, G.; Ferguson, J.J.A.; Garg, M.L. Effects of Plant-Based Diets on Weight Status in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, N.D.; Levin, S.M.; Yokoyama, Y. A systematic review and meta-analysis of changes in body weight in clinical trials of vegetarian diets. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, Ü.; Kaptanoğlu, A. Adherence to Vegetarian Diet and Weight Loss: A Meta-Analysis. Prog. Nutr. 2022, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Hu, F.B.; Chavarro, J.E. Vegetarian Diets and Weight Reduction: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massara, P.; Zurbau, A.; Glenn, A.J.; Chiavaroli, L.; Khan, T.A.; Viguiliouk, E.; Mejia, S.B.; Comelli, E.M.; Chen, V.; Schwab, U.; et al. Nordic dietary patterns and cardiometabolic outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies and randomised controlled trials. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 2011–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termannsen, A.D.; Clemmensen, K.K.B.; Thomsen, J.M.; Norgaard, O.; Diaz, L.J.; Torekov, S.S.; Quist, J.S.; Faerch, K. Effects of vegan diets on cardiometabolic health: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viguiliouk, E.; Kendall, C.W.; Kahleová, H.; Rahelić, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Choo, V.L.; Mejia, S.B.; Stewart, S.E.; Leiter, L.A.; Jenkins, D.J.; et al. Effect of vegetarian dietary patterns on cardiometabolic risk factors in diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahleova, H.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I.; Alwarith, J.; Rembert, E.; Tura, A.; Hill, M.; Holubkov, R.; Barnard, N.D. Effect of a low-fat vegan diet on body weight, insulin sensitivity, postprandial metabolism, and intramyocellular and hepatocellular lipid levels in overweight adults: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2025454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, N.D.; Levin, S.M.; Gloede, L.; Flores, R. Turning the waiting room into a classroom: Weekly classes using a vegan or a portion-controlled eating plan improve diabetes control in a randomized translational study. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, N.D.; Alwarith, J.; Rembert, E.; Brandon, L.; Nguyen, M.; Goergen, A.; Horne, T.; do Nascimento, G.F.; Lakkadi, K.; Tura, A.; et al. A Mediterranean diet and low-fat vegan diet to improve body weight and cardiometabolic risk factors: A randomized, cross-over trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2021, 41, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahleova, H.; Tura, A.; Hill, M.; Holubkov, R.; Barnard, N.D. A Plant-Based Dietary Intervention Improves Beta-Cell Function and Insulin Resistance in Overweight Adults: A 16-Week Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Xu, J.; Agarwal, U.; Gonzales, J.; Levin, S.; Barnard, N.D. A multicenter randomized controlled trial of a plant-based nutrition program to reduce body weight and cardiovascular risk in the corporate setting: The GEICO study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 718.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Newman, J.D.; Woolf, K.; Ganguzza, L.; Guo, Y.; Allen, N.; Zhong, J.; Fisher, E.A.; Slater, J. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Vegan Diet Versus the American Heart Association–Recommended Diet in Coronary Artery Disease Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e011367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdowsian, H.; Barnard, N.D.; Hoover, V.J.; Katcher, H.I.; Levin, S.M.; Green, A.A.; Cohen, J.L. A Multicomponent Intervention Reduces Body Weight and Cardiovascular Risk at a GEICO Corporate Site. Am. J. Health Promot. 2010, 24, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, N.D.; Cohen, J.; Jenkins, D.J.; Turner-McGrievy, G.; Gloede, L.; Jaster, B.; Seidl, K.; Green, A.A.; Talpers, S. A Low-Fat Vegan Diet Improves Glycemic Control and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in a Randomized Clinical Trial in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1777–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, S.-A.; Lee, I.-K.; Kim, J.-G.; Park, K.-G.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Jeon, J.-H.; Shin, J.-Y.; Lee, D.-H. Effect of a Brown Rice Based Vegan Diet and Conventional Diabetic Diet on Glycemic Control of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A 12-Week Randomized Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Wong, J.M.W.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Esfahani, A.; Ng, V.W.Y.; Leong, T.C.K.; Faulkner, D.A.; Vidgen, E.; Paul, G.; Mukherjea, R.; et al. Effect of a 6-month vegan low-carbohydrate (‘Eco-Atkins’) diet on cardiovascular risk factors and body weight in hyperlipidaemic adults: A randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2014, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusitupa, M.; Hermansen, K.; Savolainen, M.J.; Schwab, U.; Kolehmainen, M.; Brader, L.; Mortensen, L.S.; Cloetens, L.; Johansson-Persson, A.; Onning, G.; et al. Effects of an isocaloric healthy Nordic diet on insulin sensitivity, lipid profile and inflammation markers in metabolic syndrome—A randomized study (SYSDIET). J. Int. Med. 2013, 274, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotfredsen, J.L.; Hoppe, C.; Andersen, R.; Andersen, E.W.; Landberg, R.; Overvad, K.; Tetens, I. Effects of substitution dietary guidelines targeted at prevention of IHD on dietary intake and risk factors in middle-aged Danish adults: The Diet and Prevention of Ischemic Heart Disease: A Translational Approach (DIPI) randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 126, 1179–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamsson, V.; Reumark, A.; Cederholm, T.; Vessby, B.; Risérus, U.; Johansson, G. What is a healthy Nordic diet? Foods and nutrients in the NORDIET study. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 56, 18189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, S.K.; Due, A.; Jordy, A.B.; Kiens, B.; Stark, K.D.; Stender, S.; Holst, C.; Astrup, A.; Larsen, T.M. Health effect of the new nordic diet in adults with increased waist circumference: A 6-mo randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunner, A.E.; Wells, C.L.; Gonzales, J.; Agarwal, U.; Bayat, E.; Barnard, N.D. A dietary intervention for chronic diabetic neuropathy pain: A randomized controlled pilot study. Nutr. Diabetes 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, M.; Gutierrez, A.; Cano, M.D.; Castillo, M.J. Elimination of meat, fish, and derived products from the Spanish-Mediterranean diet: Effect on the plasma lipid profile. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 1996, 40, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djekic, D.; Shi, L.; Brolin, H.; Carlsson, F.; Särnqvist, C.; Savolainen, O.; Cao, Y.; Bäckhed, F.; Tremaroli, V.; Landberg, R.; et al. Effects of a Vegetarian Diet on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, Gut Microbiota, and Plasma Metabolome in Subjects with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Randomized, Crossover Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahleova, H.; Matoulek, M.; Malinska, H.; Oliyarnik, O.; Kazdova, L.; Neskudla, T.; Skoch, A.; Hajek, M.; Hill, M.; Kahle, M.; et al. Vegetarian diet improves insulin resistance and oxidative stress markers more than conventional diet in subjects with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.D.; Kiazand, A.; Alhassan, S.; Kim, S.; Stafford, R.S.; Balise, R.R.; Kraemer, H.C.; King, A.C. Comparison of the Atkins, Zone, Ornish, and LEARN diets for change in weight and related risk factors among overweight premenopausal women: The A TO Z Weight Loss Study: A randomized trial. JAMA 2007, 297, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, F.; Dinu, M.; Pagliai, G.; Cesari, F.; Gori, A.M.; Sereni, A.; Becatti, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Marcucci, R.; Casini, A. Low-Calorie Vegetarian Versus Mediterranean Diets for Reducing Body Weight and Improving Cardiovascular Risk Profile CARDIVEG Study (Cardiovascular Prevention With Vegetarian Diet). Am. Heart J. 2018, 137, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Dansinger, M.L.; Gleason, J.A.; Griffith, J.L.; Selker, H.P.; Schaefer, E.J. Comparison of the Atkins, Ornish, Weight Watchers, and Zone diets for weight loss and heart disease risk reduction: A randomized trial. JAMA 2005, 293, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mello, V.D.; Zelmanovitz, T.; Perassolo, M.S.; Azevedo, M.J.; Gross, J.L. Withdrawal of red meat from the usual diet reduces albuminuria and improves serum fatty acid profile in type 2 diabetes patients with macroalbuminuria. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1032.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.E.; Warziski, M.; Styn, M.A.; Music, E.; Hudson, A.G.; Sereika, S.M. A randomized clinical trial of a standard versus vegetarian diet for weight loss: The impact of treatment preference. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, A.S.; Sklar, M.; Barnard, N.D.; Gore, S.; Sullivan, R.; Browning, S. Toward Improved Management of NIDDM: A Randomized, Controlled, Pilot Intervention Using a Lowfat, Vegetarian Diet. Prev. Med. 1999, 29, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahleova, H.; Matoulek, M.; Bratova, M.; Malinska, H.; Kazdova, L.; Hill, M.; Pelikanova, T. Vegetarian diet-induced increase in linoleic acid in serum phospholipids is associated with improved insulin sensitivity in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2013, 3, e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, A.K.; Flynn, M.G.; Stewart, L.K.; McFarlin, B.K.; Iglay, H.B.; Mattes, R.D.; Lyle, R.M.; Considine, R.V.; Campbell, W.W. Protein intake during energy restriction: Effects on body composition and markers of metabolic and cardiovascular health in postmenopausal women. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.; Pagliai, G.; Angelino, D.; Rosi, A.; Dall’Asta, M.; Bresciani, L.; Ferraris, C.; Guglielmetti, M.; Godos, J.; Del Bo’, C. Effects of popular diets on anthropometric and cardiometabolic parameters: An umbrella review of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borazjani, M.; Nouri, M.; Venkatakrishnane, K.; Najafi, M.; Faghih, S. Association of plant-based diets with lipid profile and anthropometric indices: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 52, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selinger, E.; Neuenschwander, M.; Koller, A.; Gojda, J.; Kühn, T.; Schwingshackl, L.; Barbaresko, J.; Schlesinger, S. Evidence of a vegan diet for health benefits and risks–an umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational and clinical studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J.; Liang, S. An Accurate Noninvasive Blood Glucose Measurement System Using Portable Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Transfer Learning Framework. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 3506–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhato, K.; Akksilp, K.; Dellow, A.; Vathesatogkit, P.; Anothaisintawee, T. Efficacy of different dietary patterns on lowering of blood pressure level: An umbrella review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1584–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, K. Cultural awareness of eating patterns in the health care setting. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 16, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year | No. of RCTs/Participant Characteristics/Age */Sample Size | Countries/Year Range | No. of Databases/Search Period | Types of Plant-Based Diet/Duration | Outcomes | Quality Assessment/Certainty of Evidence/Protocol Number | AMSTAR 2 Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austin, 2021 [29] | 7/participants with T2DM/57.1/269 | USA, Czech Republic, Republic of Korea/1999–2018 | 4 (Cochrane Library, CINAHL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE)/inception until April 2021 | Semi-vegetarian, pesco-vegetarian, lacto-ovo vegetarian, and vegan/6–22 weeks | Weight, BMI, waist circumference | Quality criteria checklist for primary research #/NR/CRD42021222987 | Moderate |
| Barnard, 2015 [30] | 15/general adults/NR/755 | Sweden, Norway, Spain, Finland, USA, Poland/1947–2013 | 3 (PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials)/until 31 December 2013 | Vegan or vegetarian diet/4 weeks > 2 years | Weight | ROB/NR/CRD42012003506 | Moderate |
| Demirci, 2022 [31] | 11/participants with T2 DM and overweight/NR/934 | USA, Sweden, Czechia, Republic of Korea, Italy, New Zealand/2007–2021 | 3 (PubMed, Science Direct, ResearchGate)/inception until 2021 | Vegetarian diet/4–72 weeks | Weight | Jadad score/NR | Low |
| Huang, 2016 [32] | 12/general adults/18 to 82 years/1151 | NR/1950 to 22 September 2014 | 3 (PubMed, Embase, and UpToDate databases)/inception until 2014 | Vegan or lacto-ovo-vegetarian diets/9–96 weeks | Weight | ROB/NR/NR | Low |
| Massara, 2022 [33] | 6/participants with risk factor(s) for diabetes/NR/706 | Denmark, Sweden, Iceland, Finland/2008–2020 | 3 (MEDLINE, Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials)/inception until 2021 | Nordic diet/NR | Weight, BMI, waist circumference, fasting blood glucose, blood pressure, lipid profiles | ROB/GRADE/NCT04094194 | Moderate |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | 11/participants with T2DM or overweight/48–61/796 | USA, Canada, Republic of Korea, New Zealand/1999–2021 | 4 (MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL))/inception until 2022 | Low-fat vegan, low-carbohydrate vegan diet/12–26 weeks | Weight, BMI, fasting blood glucose, blood pressure, lipid profiles | ROB2/GRADE/CRD42021233938 | Moderate |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | 9/participants with T1DM or T2DM/32–61/664 | USA, Greece, Brazil, Czech Republic, Korea/NR | 3 (MEDLINE, Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials)/inception until 2018 | Vegetarian protein diet, low-fat vegan diet, plant-based protein diet, lacto-vegetarian low-protein diet, low-fat vegan diet, vegetarian diet, low-fat low-glycemic index vegan diet/NR | Weight, BMI, waist circumference, fasting blood glucose, blood pressure, lipid profiles | NR/GRADE/NCT02600377 | High |
| Authors, Year | MD/SMD (95% CI) | Sample Size in Number of Studies | p-Value | 95% Prediction Interval Rule | Small-Study Effects or Excess Significance Bias | I2 | Credibility of Evidence (Class) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | ||||||||
| Austin, 2021 [29] | MD = −2.35 (−3.51, −1.19) | N < 1000 (N = 384 in 7 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | NR | 78.43% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Barnard, 2015 [30] | MD = −3.4 (−2.4, −4.4) | N < 1000 (N = 755 in 15 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (Egger’s test: p = 0.27) | 64.3% | Convincing (Class I) | |
| Demirci, 2022 [31] | MD = 0.954 (1.515, 0.393) | N < 1000 (N = 934 in 11 studies) | p = 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (p = 0.425), no publication bias seen | 93.75% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Huang, 2016 [32] | MD = −2.02 (−1.23, −2.80) | N > 1000 (N = 1151 in 12 studies) | p = 0.001 | Including the null value | No publication bias seen (Begg’s test p = 0.32) | 62.3% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −2 (−3.24, −0.75) | N < 1000 (N = 706 in 6 studies) | p = 0.002 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 88% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | MD = −4.1 (−5.9, −2.4) | N < 1000 (N = 697 in 11 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 91% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = −2.15 (−2.95, −1.34) | N < 1000 (N = 532 in 9 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 21% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||||
| Austin, 2021 [29] | MD = −0.9 (−1.42, −0.38) | N < 1000 (N = 339 in 7 studies) | p = 0.001 | Including the null value | Statistically significant publication bias (Egger’s test: p < 0.005) | 85.32% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −0.98 (−1.19, −0.77) | N < 1000 (N = 393 in 6 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 19% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | MD = −1.38 (−1.96, −0.8) | N < 1000 (N = 780 in 11 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 89% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = −0.74 (−1.09, −0.39) | N < 1000 (N = 614 in 9 studies) | p < 0.001) | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 60% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Waist circumference (cm) | ||||||||
| Austin, 2021 [29] | MD = −2.41 (−3.72, −1.09) | N < 1000 (N = 191 in 7 studies) | p< 0.001 | Including the null value | NR | 81.01% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −1.32 (−2.2, −0.43) | N < 1000 (N = 454 in 6 studies) | p = 0.003 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 71% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = −2.86 (−3.76, −1.96) | N < 1000 (N = 283 in 9 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 48% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | ||||||||
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −0.26 (−0.52, 0) | N < 1000 (N = 606 in 6 studies) | p = 0.05 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 89% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | MD = −0.24 (−0.4, −0.07) | N < 1000 (N = 684 in 11 studies) | p = 0.005 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 58% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = −0.12 (−0.2, −0.04) | N < 1000 (N = 602 in 9 studies) | p = 0.002 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 0% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | ||||||||
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −0.03 (−0.1, 0.03) | N < 1000 (N = 606 in 6 studies) | p = 0.35 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 75% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | MD = −0.06 (−0.12, 0.01) | N < 1000 (N = 698 in 11 studies) | p = 0.08 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 67% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = −0.03 (−0.08, 0.02) | N < 1000 (N = 632 in 9 studies) | p = 0.19 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 66% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | ||||||||
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −0.05 (−0.14, 0.05) | N < 1000 (N = 606 in 6 studies) | p = 0.34 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 43% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | MD = 0.11 (−0.08, 0.29) | N < 1000 (N = 698 in 11 studies) | p = 0.26 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 65% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = 0.14 (−0.1, 0.38) | N < 1000 (N = 615 in 9 studies) | p = 0.26 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 71% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| HbA1c (%) | ||||||||
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = 0.01 (−0.06, 0.08) | N < 1000 (N = 145 in 6 studies) | p = 0.79 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | NR | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | MD = −0.18 (−0.29, −0.07) | N < 1000 (N = 687 in 11 studies) | p = 0.002 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 66% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = −0.29 (−0.45, −0.12) | N < 1000 (N = 378 in 9 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 14% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Fasting insulin (pmol/L) | ||||||||
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −7.83 (−12.26, −3.39) | N < 1000 (N = 393 in 6 studies) | p < 0.001 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 0% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = −7.92 (−27.92, 12.08) | N < 1000 (N = 74 in 9 studies) | p = 0.44 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | NR | Weak (Class IV) | |
| SBP (mmHg) | ||||||||
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −3.55 (−5.12, −1.59) | N < 1000 (N = 533 in 6 studies) | p = 0.002 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 50% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | MD = 1.28 (−1.54, 4.11) | N < 1000 (N = 466 in 11 studies) | p = 0.37 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 34% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = −0.1 (−2.33, 2.52) | N < 1000 (N = 606 in 9 studies) | p = 0.94 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 35% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| DBP (mmHg) | ||||||||
| Massara, 2022 [33] | MD = −1.5 (−2.62, −0.37) | N < 1000 (N = 533 in 6 studies) | p = 0.009 | Including the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 34% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Termannsen, 2022 [34] | MD = 0.54 (−1.21, 2.29) | N < 1000 (N = 466 in 11 studies) | p = 0.55 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 37% | Weak (Class IV) | |
| Viguiliouk, 2019 [35] | MD = 0.53 (−0.5, 1.57) | N < 1000 (N = 606 in 9 studies) | p = 0.31 | Excluding the null value | No small-study effects (no publication bias, no Egger’s result) | 0% | Weak (Class IV) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chew, H.S.J.; Heng, F.K.X.; Tien, S.A.; Thian, J.Y.; Chou, H.S.; Loong, S.S.E.; Ang, W.H.D.; Chew, N.W.S.; Lo, K.-H.K. Effects of Plant-Based Diets on Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Markers in Adults: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102331
Chew HSJ, Heng FKX, Tien SA, Thian JY, Chou HS, Loong SSE, Ang WHD, Chew NWS, Lo K-HK. Effects of Plant-Based Diets on Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Markers in Adults: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients. 2023; 15(10):2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102331
Chicago/Turabian StyleChew, Han Shi Jocelyn, Felicia Kai Xin Heng, Si Ai Tien, Jie Yun Thian, Hui Shan Chou, Shaun Seh Ern Loong, Wei How Darryl Ang, Nicholas W. S. Chew, and Ka-Hei Kenneth Lo. 2023. "Effects of Plant-Based Diets on Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Markers in Adults: An Umbrella Review" Nutrients 15, no. 10: 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102331
APA StyleChew, H. S. J., Heng, F. K. X., Tien, S. A., Thian, J. Y., Chou, H. S., Loong, S. S. E., Ang, W. H. D., Chew, N. W. S., & Lo, K.-H. K. (2023). Effects of Plant-Based Diets on Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Markers in Adults: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients, 15(10), 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102331






