Umbelliferone Ameliorates Memory Impairment and Enhances Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Scopolamine-Induced Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
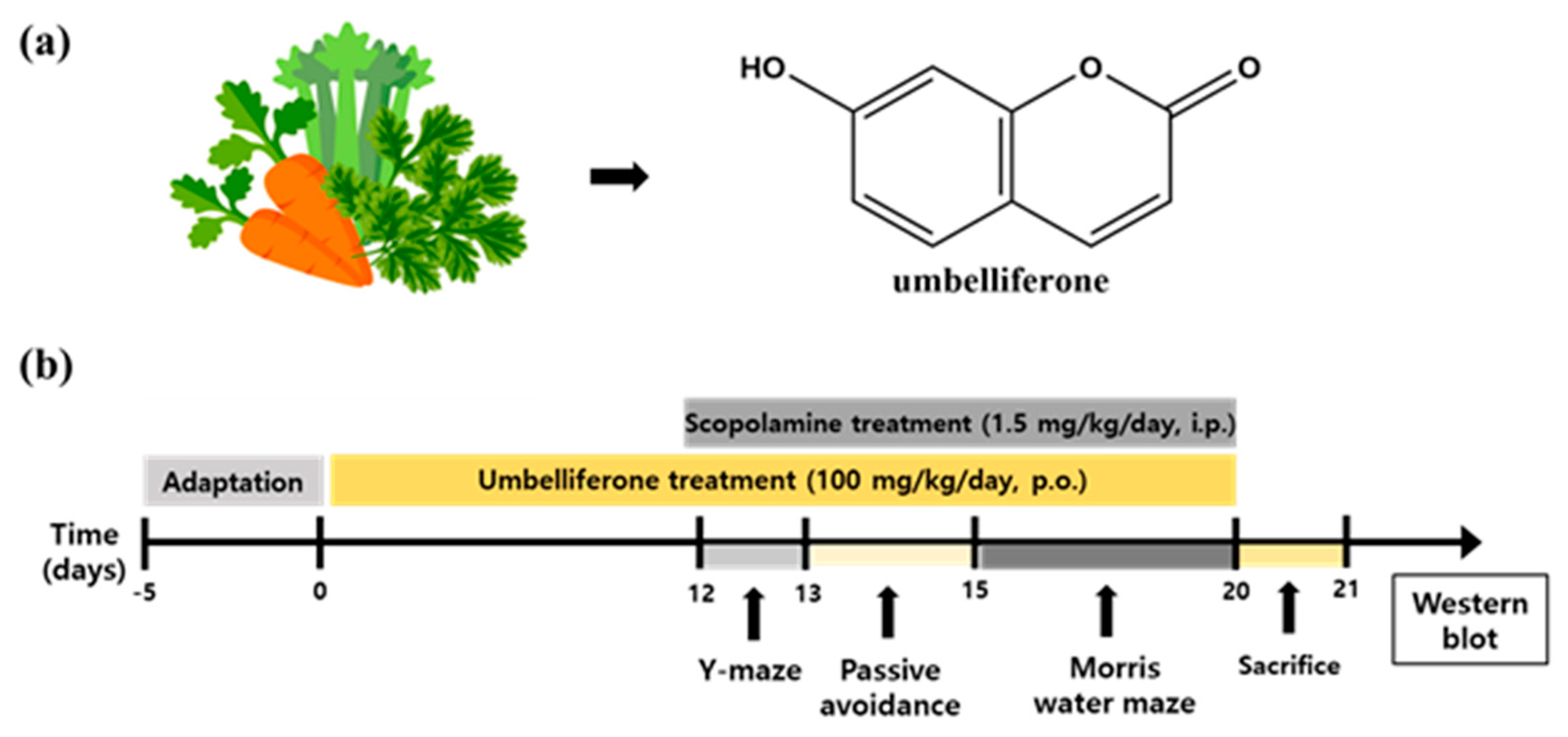
2.3. Experimental Design
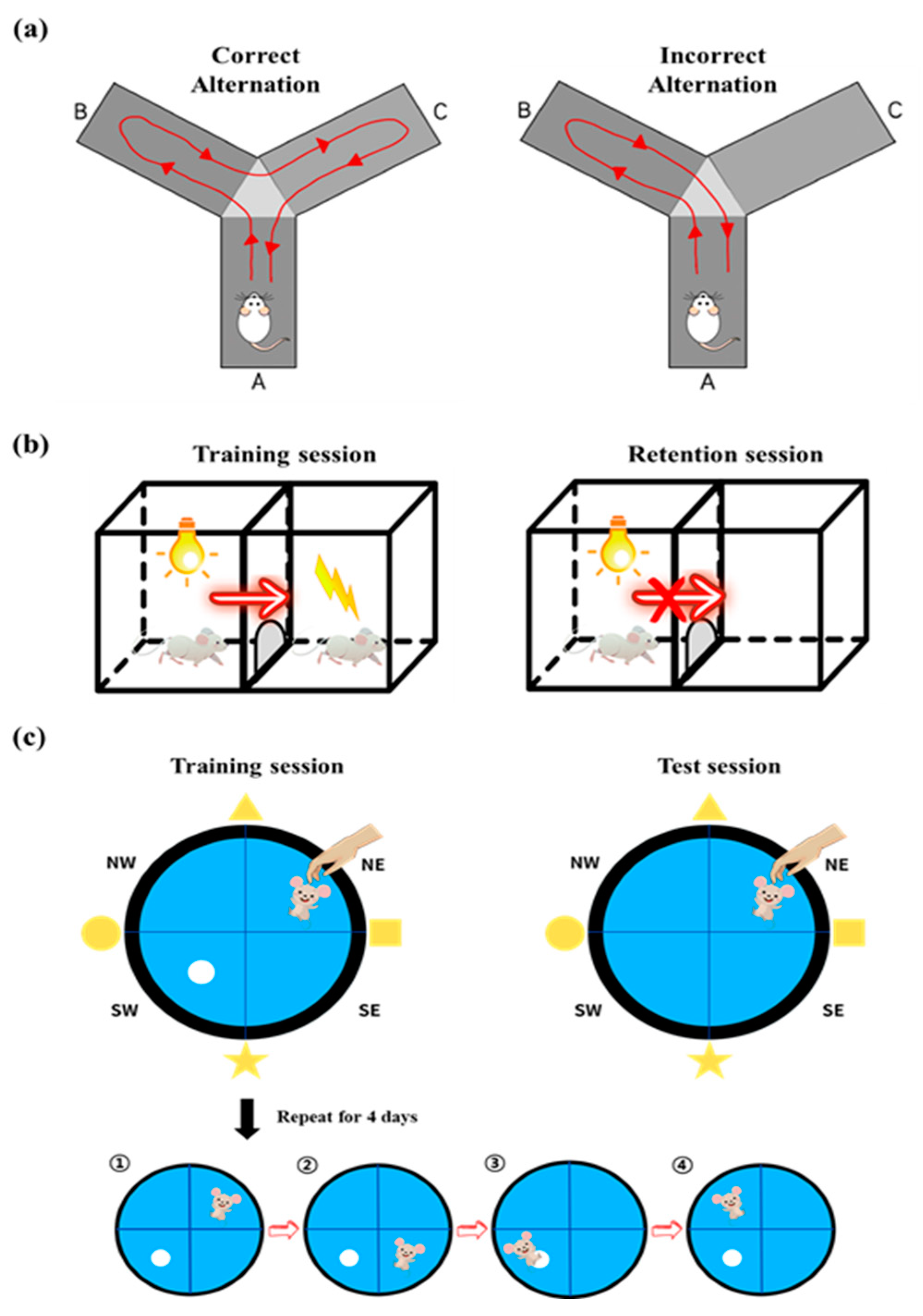
2.4. Y-Maze Test
2.5. Passive Avoidance Test
2.6. Morris Water Maze Test
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Measurement of Achtylcholinestarase (AChE) Activity
2.9. Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Cultures
2.10. Preparation of Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Tissue on Multi-Electrode Array (MEA) Probes
2.11. Induction of Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) in Hippocampal Slices
2.12. Electrophysiology Data Processing
2.13. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
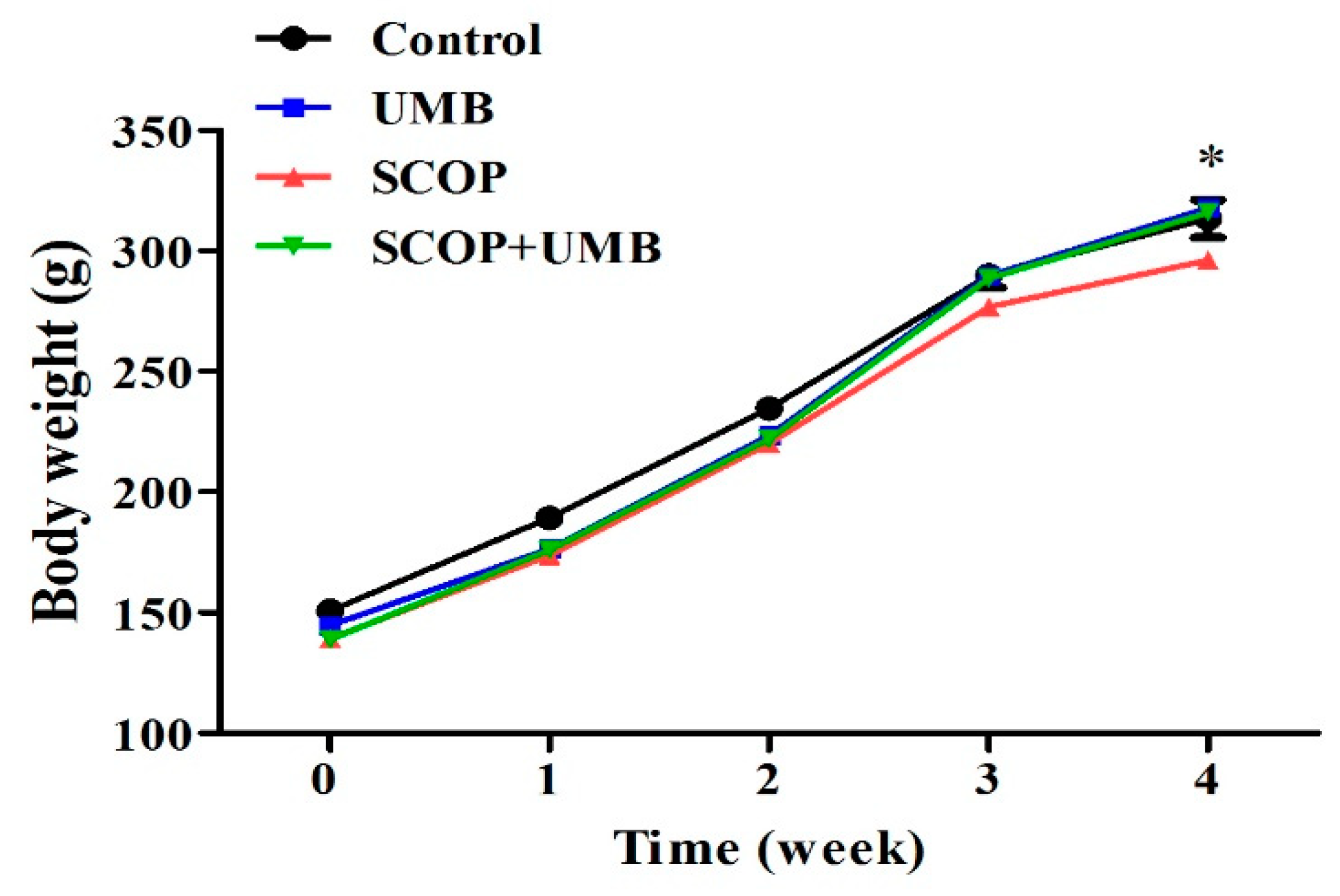
3.1. Change of Body Weight on the UMB-Treated Rats
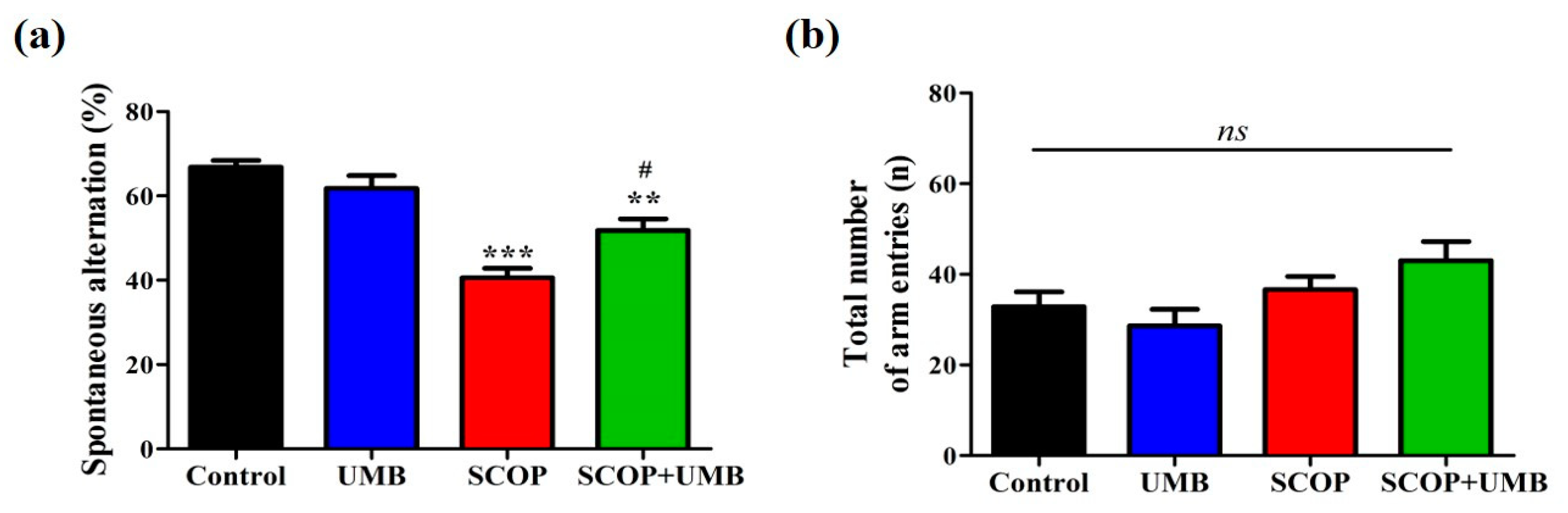
3.2. UMB Ameliorates Short-Term Spatial Learning and Memory Deficits in the Y-Maze Test
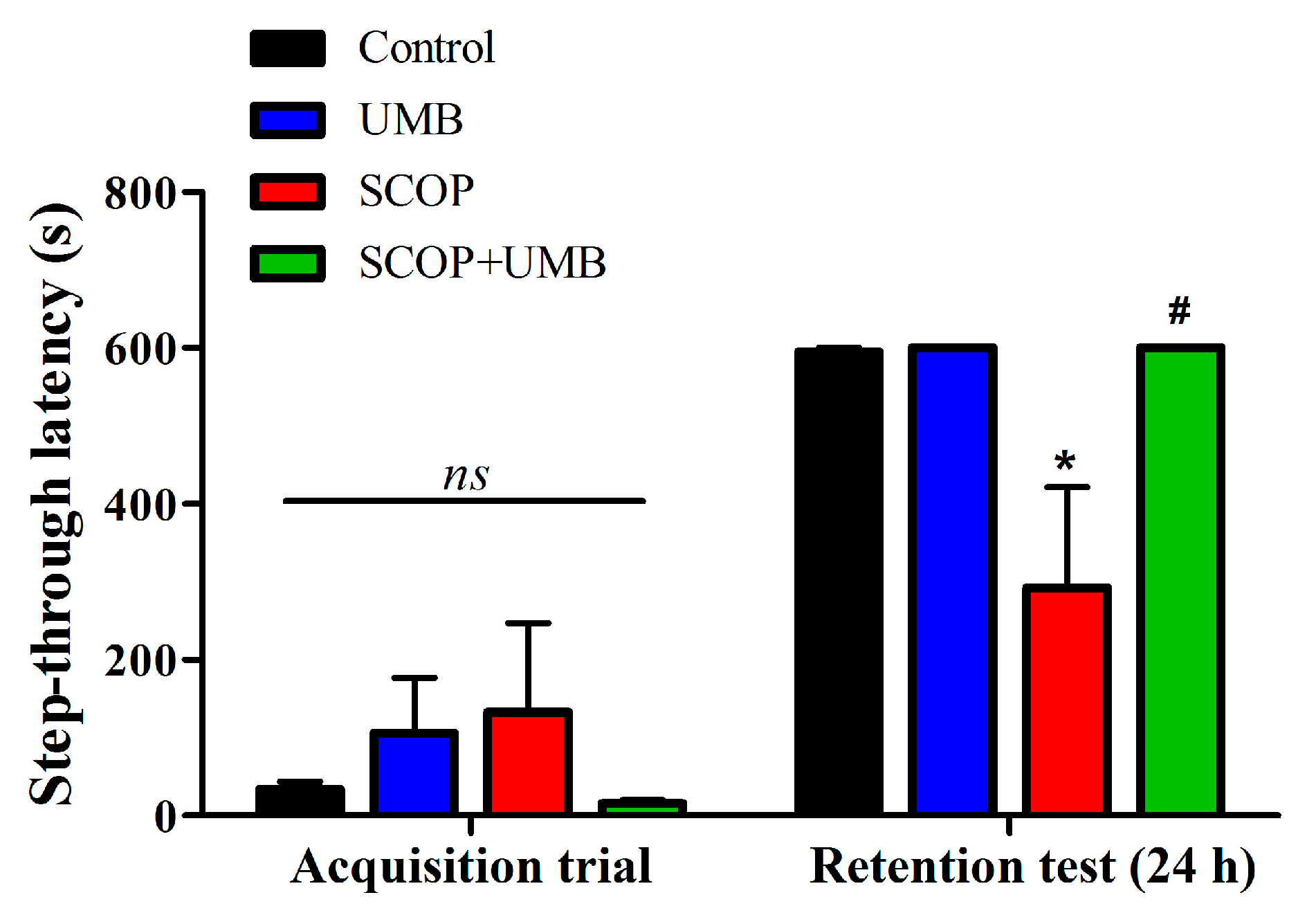
3.3. UMB Ameliorates Fear-Avoidance Learning and Memory Deficits in the PA Test
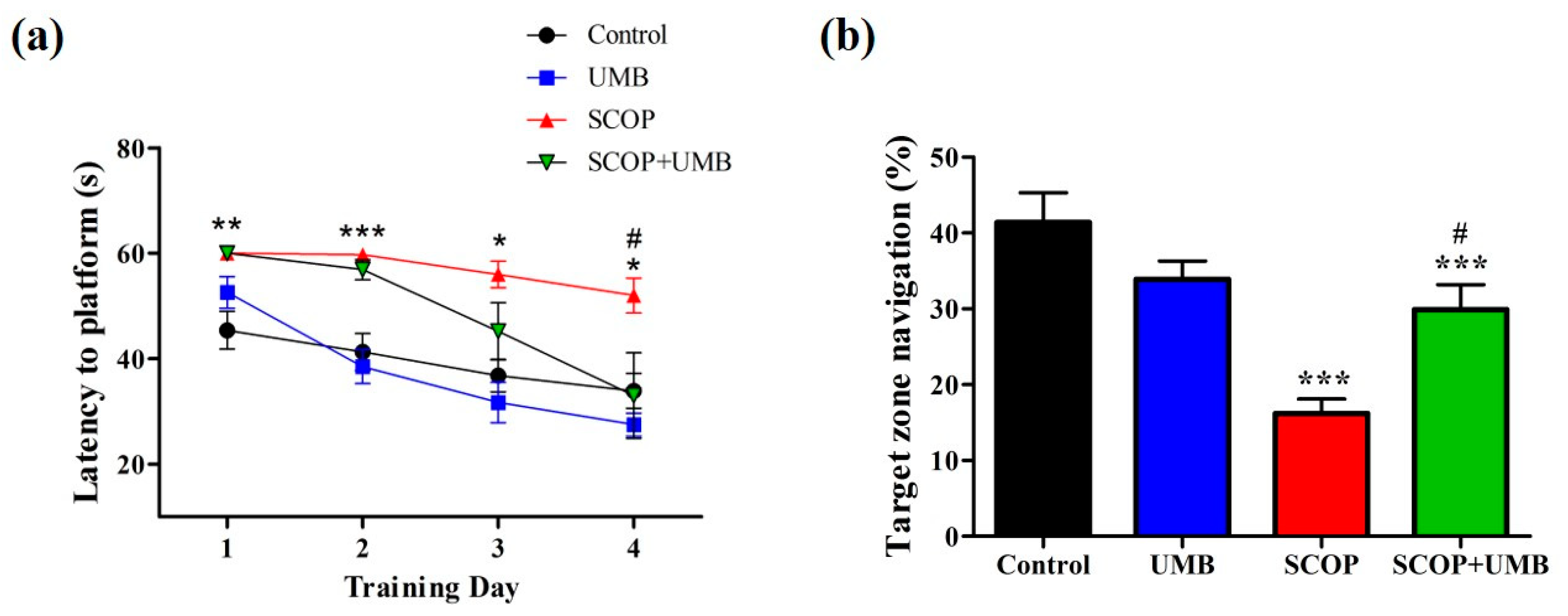
3.4. UMB Ameliorates Long-Term Spatial Learning and Memory Deficits in the MWM Test
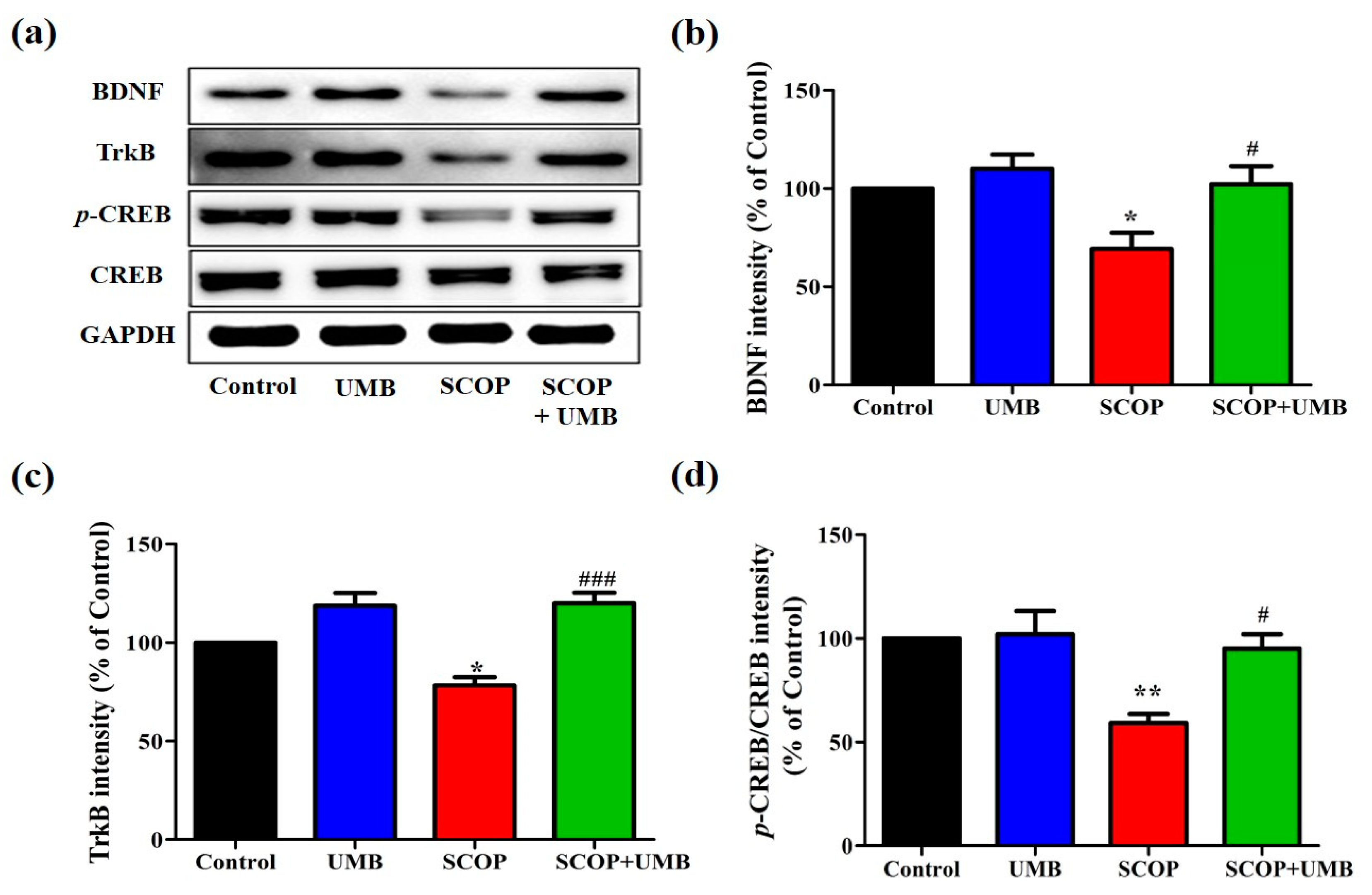
3.5. UMB Upregulates the Expressions of BDNF, TrkB, and p-CREB in the Hippocampus of SCOP-Induced Rat
3.6. UMB Attenuates the Increase in AChE Activity Induced by SCOP in Hippocampus
3.7. UMB Enhances fEPSP Activity of LTP in the CA1 Region of Hippocampal Slice
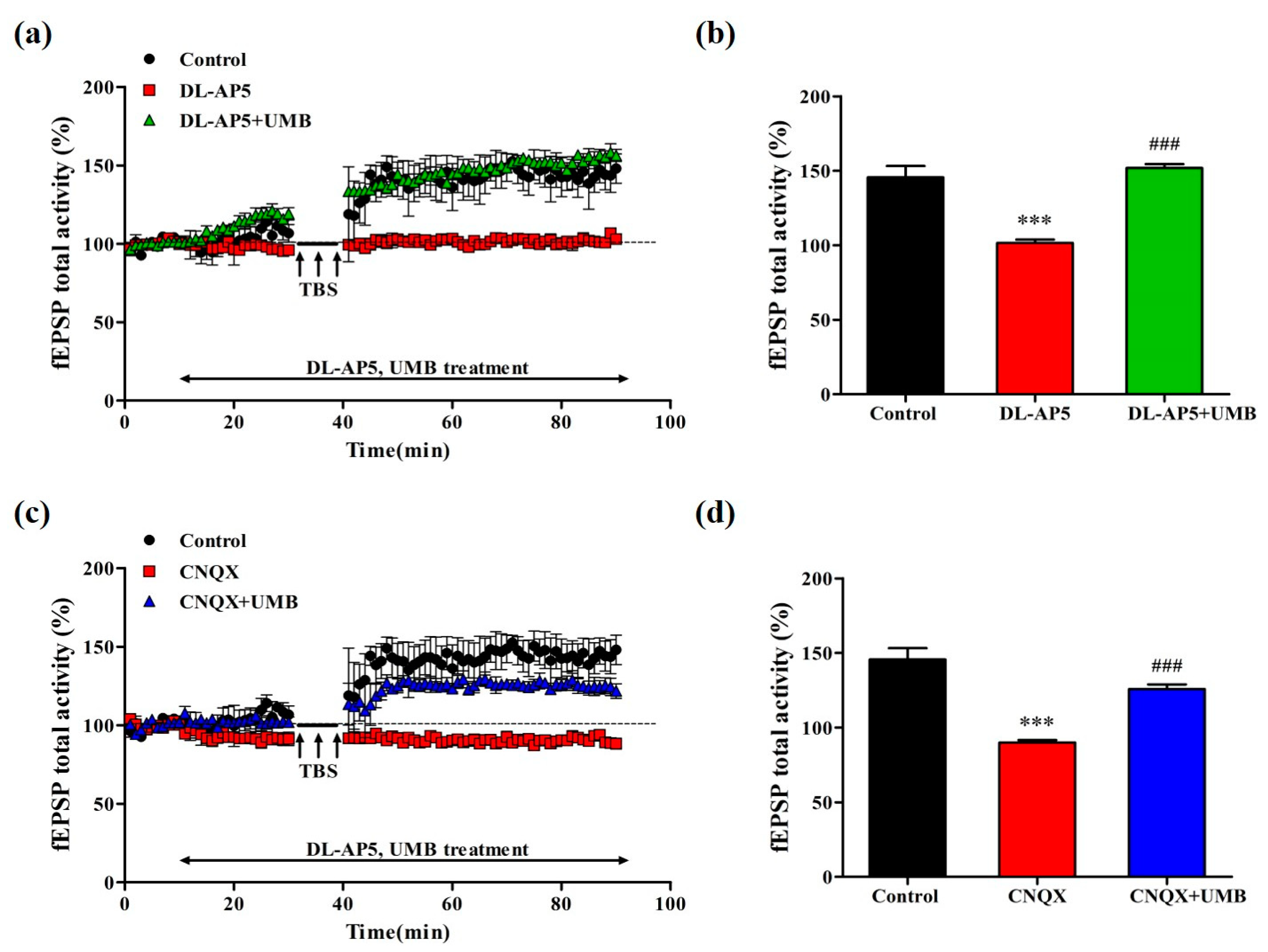
3.8. UMB Ameliorates fEPSP Activity Impairment of LTP Induction by SCOP in CA1 Region of Hippocampal Slices
3.9. UMB Ameliorates fEPSP Activity Impairment of LTP by NMDA Receptor Antagonist and AMPA Receptor Antagonist in CA1 Region of Hippocampal Slices
3.10. UMB Enhanced the Synaptic Vesicle Density on Synaptic Ultrastructure of the SCOP-Treated OHSC Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maltsev, A.V.; Bystryak, S.; Galzitskaya, O.V. The role of beta-amyloid peptide in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2011, 10, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquer-Alicea, J.; Diamond, M.I. Propagation of Protein Aggregation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 785–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugger, B.N.; Dickson, D.W. Pathology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a028035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Y.; Jannat, S.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, R.J.; Roy, A.; Choi, J.S. Anti-Alzheimer’s disease potential of coumarins from Angelica decursiva and Artemisia capillaris and structure-activity analysis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giridharan, V.V.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Konishi, T. Amelioration of scopolamine induced cognitive dysfunction and oxidative stress by Inonotus obliquus—A medicinal mushroom. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkenberg, I.; Blokland, A. The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: A review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 1307–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, T.K.; Song, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Kang, I.J.; et al. Melatonin attenuates scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment via protecting against demyelination through BDNF-TrkB signaling in the mouse dentate gyrus. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 285, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, A.Y.; Doo, C.N.; Son, E.J.; Sung, N.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Sok, D.E.; Kim, M.R. N-palmitoyl serotonin alleviates scopolamine-induced memory impairment via regulation of cholinergic and antioxidant systems, and expression of BDNF and p-CREB in mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 242, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopelman, M.; Corn, T. Cholinergic ‘blockade’as a model for cholinergic depletion: A comparison of the memory deficits with those of Alzheimer-type dementia and the alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome. Brain 1988, 111, 1079–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejar, C.; Wang, R.-H.; Weinstock, M. Effect of rivastigmine on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 383, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.S.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.O.; Han, S.M.; Maeng, S.; Park, J.H. Loganin enhances long-term potentiation and recovers scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairments. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 171, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, G.; Zhang, J.; Gao, S.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Gao, Q. SKF83959 has protective effects in the scopolamine model of dementia. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, S. Cholinergic adverse effects of cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs Aging 2001, 18, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Seo, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Goo, N.; Jeong, Y.; Bae, H.J.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Ryu, J.H. Casticin ameliorates scopolamine-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeja Malar, D.; Beema Shafreen, R.; Karutha Pandian, S.; Pandima Devi, K. Cholinesterase inhibitory, anti-amyloidogenic and neuroprotective effect of the medicinal plant Grewia tiliaefolia—An in vitro and in silico study. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, Z.; Celik, M.; Bilen, A.; Halici, Z.; Yildirim, S.; Karabulut, S.; Karakaya, S.; Bostanlik, D.F.; Aydin, P. Effects of umbelliferone isolated from the Ferulago pauciradiata Boiss. & Heldr. Plant on cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis model in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, S.; Yilmaz-Oral, D.; Kilic, C.S.; Gur, S. Umbelliferone isolated from Zosima absinthifolia roots partially restored erectile dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazimba, O. Umbelliferone: Sources, chemistry and bioactivities review. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2017, 55, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Fang, F.; Song, M.; Li, R.; Ma, Z.; Ma, S. Umbelliferone reverses depression-like behavior in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced rats by attenuating neuronal apoptosis via regulating ROCK/Akt pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 317, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Tao, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, G. Umbelliferone attenuates unpredictable chronic mild stress induced-insulin resistance in rats. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindam, M.O.; Sayed, R.H.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Budzynska, B.; El Sayed, N.S. Xanthotoxin and umbelliferone attenuate cognitive dysfunction in a streptozotocin-induced rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: The role of JAK2/STAT3 and Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway modulation. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 2351–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.R.; Ellis, E.M. Neuroprotective effects of umbelliferone and esculetin in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 91, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S. Umbelliferone ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via upregulating the PPAR gamma expression and suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 600, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.Z.; Zhu, B.Q.; Xu, X.N.; Zeng, H.C. Role of the BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling pathway in the cytotoxicity of bisphenol S in SK-N-SH cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, C.Y.; Hyun, S.A.; Ko, M.Y.; Lee, B.S.; Hwang, D.Y.; Ka, M. 2-Phenylethylamine (PEA) Ameliorates Corticosterone-Induced Depression-Like Phenotype via the BDNF/TrkB/CREB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Fang, M.S.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Mahaman, Y.A.R.; Zeng, K.; Xia, Y.; Ke, D.; Liu, R.; et al. omega-3PUFAs Improve Cognitive Impairments Through Ser133 Phosphorylation of CREB Upregulating BDNF/TrkB Signal in Schizophrenia. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1271–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Xie, Q.; Yu, X.; Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Chen, X.; Yue, J.; Zhou, K.; Tu, W.; Jiang, S. Water treadmill training protects the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier following SCI via the BDNF/TrkB-CREB signalling pathway. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 143, 104945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, A.; Du, G. DL0410 attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via BDNF/TrkB/ERK/CREB and Nrf2/HO-1 activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 86, 106729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi, H.; Djazayery, A.; Javanbakht, M.H.; Dehpour, A.; Ghaedi, E.; Derakhshanian, H.; Mohammadi, H.; Mousavi, S.N.; Djalali, M. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on CREB-TrkB-BDNF pathway in the hippocampus of diabetic rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Mi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Huang, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Neuroprotective action of tea polyphenols on oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of the TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in SH-SY5Y cells and mice brain. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4421–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.L.; Zhong, K.; Liu, D.D.; Xu, J.; Pan, B.B.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.P.; Zhang, Q. Huanglian-Jie-Du-Tang Extract Ameliorates Depression-Like Behaviors through BDNF-TrkB-CREB Pathway in Rats with Chronic Unpredictable Stress. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 7903918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manji, H.K.; Quiroz, J.A.; Sporn, J.; Payne, J.L.; Denicoff, K.; Gray, N.A.; Zarate, C.A.; Charney, D.S. Enhancing neuronal plasticity and cellular resilience to develop novel, improved therapeutics for Difficult-to-Treat depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 53, 707–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Xing, C.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y. L-3-n-Butylphthalide Regulates Proliferation, Migration, and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cell In Vitro and Promotes Neurogenesis in APP/PS1 Mouse Model by Regulating BDNF/TrkB/CREB/Akt Pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 34, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, S.; Mirshekar, M.A. Diosmin is neuroprotective in a rat model of scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliss, T.V.; Lømo, T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. 1973, 232, 331–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dringenberg, H.C. The history of long-term potentiation as a memory mechanism: Controversies, confirmation, and some lessons to remember. Hippocampus 2020, 30, 987–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Katz, L.; LaMantia, A.; McNamara, J.; Williams, S. Types of Eye Movements and Their Functions. In Neuroscience, 2nd ed.; Sunderland (ma) Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Luscher, C.; Malenka, R.C. NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation and long-term depression (LTP/LTD). Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a005710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnaou, A.; White, E.; Biermans, R.; Manyakov, N.V.; Drinkenburg, W. In Vivo Plasticity at Hippocampal Schaffer Collateral-CA1 Synapses: Replicability of the LTP Response and Pharmacology in the Long-Evans Rat. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 6249375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Hwang, E.S.; Choi, G.Y.; Kim, H.B.; Park, K.S.; Sul, J.Y.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, G.W.; Kim, B.I.; Park, H.; et al. Sulforaphane enhances long-term potentiation and ameliorate scopolamine-induced memory impairment. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 238, 113467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Figurov, A. Role of neurotrophins in synapse development and plasticity. Rev. Neurosci. 1997, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volknandt, W. The synaptic vesicle and its targets. Neuroscience 1995, 64, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icoglu Aksakal, F.; Koc, K.; Geyikoglu, F.; Karakaya, S. Ameliorative effect of umbelliferone in remote organ injury induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Germoush, M.O.; Alotaibi, M.F.; Hussein, O.E. Possible involvement of Nrf2 and PPARgamma up-regulation in the protective effect of umbelliferone against cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudapati, K.; Singh, A.; Clarkson-Townsend, D.; Feola, A.J.; Allen, R.S. Behavioral assessment of visual function via optomotor response and cognitive function via Y-maze in diabetic rats. JoVE (J. Vis. Exp.) 2020, e61806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Dong, J.; Lu, W.; Song, Z.; Zhou, W. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide induces cognitive dysfunction, mediated by neuronal inflammation via activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhong, X.; Du, K.; Qian, P.; Yao, W.F.; Gao, H.; Wei, M.J. Baicalin mitigates cognitive impairment and protects neurons from microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasomes and TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppini, L.; Buchs, P.A.; Muller, D. A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J. Neurosci. Methods 1991, 37, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.B.; Kwon, B.J.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Chon, J.W.; Do, M.H.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Maeng, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; et al. Long-term Treatment with Oriental Medicinal Herb Artemisia princeps Alters Neuroplasticity in a Rat Model of Ovarian Hormone Deficiency. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.F.; Bellavance, L.L. Induction of long-term potentiation in the basolateral amygdala does not depend on NMDA receptor activation. Synapse 1992, 11, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Garcia, S.Z.; de Almeida, A.G.; Ortiz-Villatoro, N.N.; Scorza, F.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Scorza, C.A. Robust Network Inhibition and Decay of Early-Phase LTP in the Hippocampal CA1 Subfield of the Amazon Rodent Proechimys. Front. Neural Circuits 2018, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, P.J.; Watson, J.; Lund, J.; Davies, C.H.; Peters, G.; Dodds, C.M.; Swirski, B.; Lawrence, P.; Bentley, G.D.; O’Neill, B.V.; et al. The potent M1 receptor allosteric agonist GSK1034702 improves episodic memory in humans in the nicotine abstinence model of cognitive dysfunction. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, T.J.; Morrill, A.; Lucas, K.; Gallup, J.; Harris, M.; Healey, M.; Pitman, T.; Schalomon, M.; Digweed, S.; Tresguerres, M. Establishing zebrafish as a model to study the anxiolytic effects of scopolamine. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabadu, D.; Sharma, M. Eugenol Attenuates Scopolamine-Induced Hippocampal Cholinergic, Glutamatergic, and Mitochondrial Toxicity in Experimental Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2019, 35, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, X.; Chen, J.; Yi, X.; Nie, D.; Sun, X.; Qin, J.; Tian, M.; Jin, G.; Zhang, X. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides prevent memory and neurogenesis impairments in scopolamine-treated rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeuter, A.-K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Y-maze for assessment of spatial working and reference memory in mice. In Pre-Clinical Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; He, B.; Wan, S.; Xu, M.; Yang, H.; Xiao, F.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Antidepressant-like effects and cognitive enhancement of Schisandra chinensis in chronic unpredictable mild stress mice and its related mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, S.; Segerstrom, L.; Roman, E. Supplier-dependent differences in intermittent voluntary alcohol intake and response to naltrexone in Wistar rats. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovic, J.; Tronson, N.C. Molecular specificity of multiple hippocampal processes governing fear extinction. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänicke, B.; Coper, H. Tests in Rodents for Assessing Sensorimotor Performance During Aging. Adv. Psychol. 1996, 114, 201–233. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, R.G.; Garrud, P.; Rawlins, J.a.; O’Keefe, J. Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 1982, 297, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; He, B.; Xiao, F.; Yan, T.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z. Neuroprotective Effects of Spinosin on Recovery of Learning and Memory in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomol. Ther. 2019, 27, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.X.; Zhang, K.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Yue, Y.S.; Xia, S.Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.H.; Jing, H.L.; Cao, Y.J. Imperatorin ameliorates learning and memory deficits through BDNF/TrkB and ERK/CaMKIIalpha/CREB signaling in prenatally-stressed female offspring. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 2408–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Gong, Q. Icariside II, a Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitor, Attenuates Beta-Amyloid-Induced Cognitive Deficits via BDNF/TrkB/CREB Signaling. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.Y.; Li, F.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.R. Enteromorpha prolifera Extract Improves Memory in Scopolamine-Treated Mice via Downregulating Amyloid-beta Expression and Upregulating BDNF/TrkB Pathway. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagib, M.M.; Tadros, M.G.; Rahmo, R.M.; Sabri, N.A.; Khalifa, A.E.; Masoud, S.I. Ameliorative Effects of alpha-Tocopherol and/or Coenzyme Q10 on Phenytoin-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Rats: Role of VEGF and BDNF-TrkB-CREB Pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2019, 35, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, X.Q.; Ding, C.; Du, X.L. Genistein attenuates isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity and improves impaired spatial learning and memory by regulating cAMP/CREB and BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 21, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Xie, D.J.; Zhou, P.; Gao, H.W.; Zhang, M.T.; Chen, D.B.; Qin, Y.P.; Lei, X.; Li, X.Q.; Liu, J.; et al. Huang-Pu-Tong-Qiao Formula Ameliorates the Hippocampus Apoptosis in Diabetic Cognitive Dysfunction Mice by Activating CREB/BDNF/TrkB Signaling Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 5514175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.A. Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 87–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdsson, T.; Doyere, V.; Cain, C.K.; LeDoux, J.E. Long-term potentiation in the amygdala: A cellular mechanism of fear learning and memory. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, G.; Reymann, K. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in hippocampal long-term potentiation and learning and memory. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1996, 157, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleshchevnikov, A. Long-term potentiation of the NMDA-dependent component of the EPSP in the hippocampus. Uspekhi Fiziol. Nauk. 1998, 29, 6–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.H.; Wei, M.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Y.S. The amino-terminal domain of GluA1 mediates LTP maintenance via interaction with neuroplastin-65. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2019194118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, Q.L.; Niu, Q. Effects of exposure to aluminum on long-term potentiation and AMPA receptor subunits in rats in vivo. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, P.J.; Rancz, E.A.; Roth, A.; Hausser, M. Dendritic excitability and synaptic plasticity. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 769–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamji, S.X.; Rico, B.; Kimes, N.; Reichardt, L.F. BDNF mobilizes synaptic vesicles and enhances synapse formation by disrupting cadherin-beta-catenin interactions. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzo-Miller, L.D.; Gottschalk, W.; Zhang, L.; McDermott, K.; Du, J.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Oho, C.; Sheng, Z.H.; Lu, B. Impairments in high-frequency transmission, synaptic vesicle docking, and synaptic protein distribution in the hippocampus of BDNF knockout mice. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 4972–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otal, R.; Martinez, A.; Soriano, E. Lack of TrkB and TrkC signaling alters the synaptogenesis and maturation of mossy fiber terminals in the hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 319, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luikart, B.W.; Nef, S.; Virmani, T.; Lush, M.E.; Liu, Y.; Kavalali, E.T.; Parada, L.F. TrkB has a cell-autonomous role in the establishment of hippocampal Schaffer collateral synapses. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3774–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, G.-Y.; Kim, H.-B.; Cho, J.-M.; Sreelatha, I.; Lee, I.-S.; Kweon, H.-S.; Sul, S.; Kim, S.A.; Maeng, S.; Park, J.-H. Umbelliferone Ameliorates Memory Impairment and Enhances Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Scopolamine-Induced Rat Model. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102351
Choi G-Y, Kim H-B, Cho J-M, Sreelatha I, Lee I-S, Kweon H-S, Sul S, Kim SA, Maeng S, Park J-H. Umbelliferone Ameliorates Memory Impairment and Enhances Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Scopolamine-Induced Rat Model. Nutrients. 2023; 15(10):2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102351
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Ga-Young, Hyun-Bum Kim, Jae-Min Cho, Inturu Sreelatha, In-Seo Lee, Hee-Seok Kweon, Sehyun Sul, Sun Ae Kim, Sungho Maeng, and Ji-Ho Park. 2023. "Umbelliferone Ameliorates Memory Impairment and Enhances Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Scopolamine-Induced Rat Model" Nutrients 15, no. 10: 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102351
APA StyleChoi, G.-Y., Kim, H.-B., Cho, J.-M., Sreelatha, I., Lee, I.-S., Kweon, H.-S., Sul, S., Kim, S. A., Maeng, S., & Park, J.-H. (2023). Umbelliferone Ameliorates Memory Impairment and Enhances Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Scopolamine-Induced Rat Model. Nutrients, 15(10), 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102351





