Effect of Nut Consumption on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
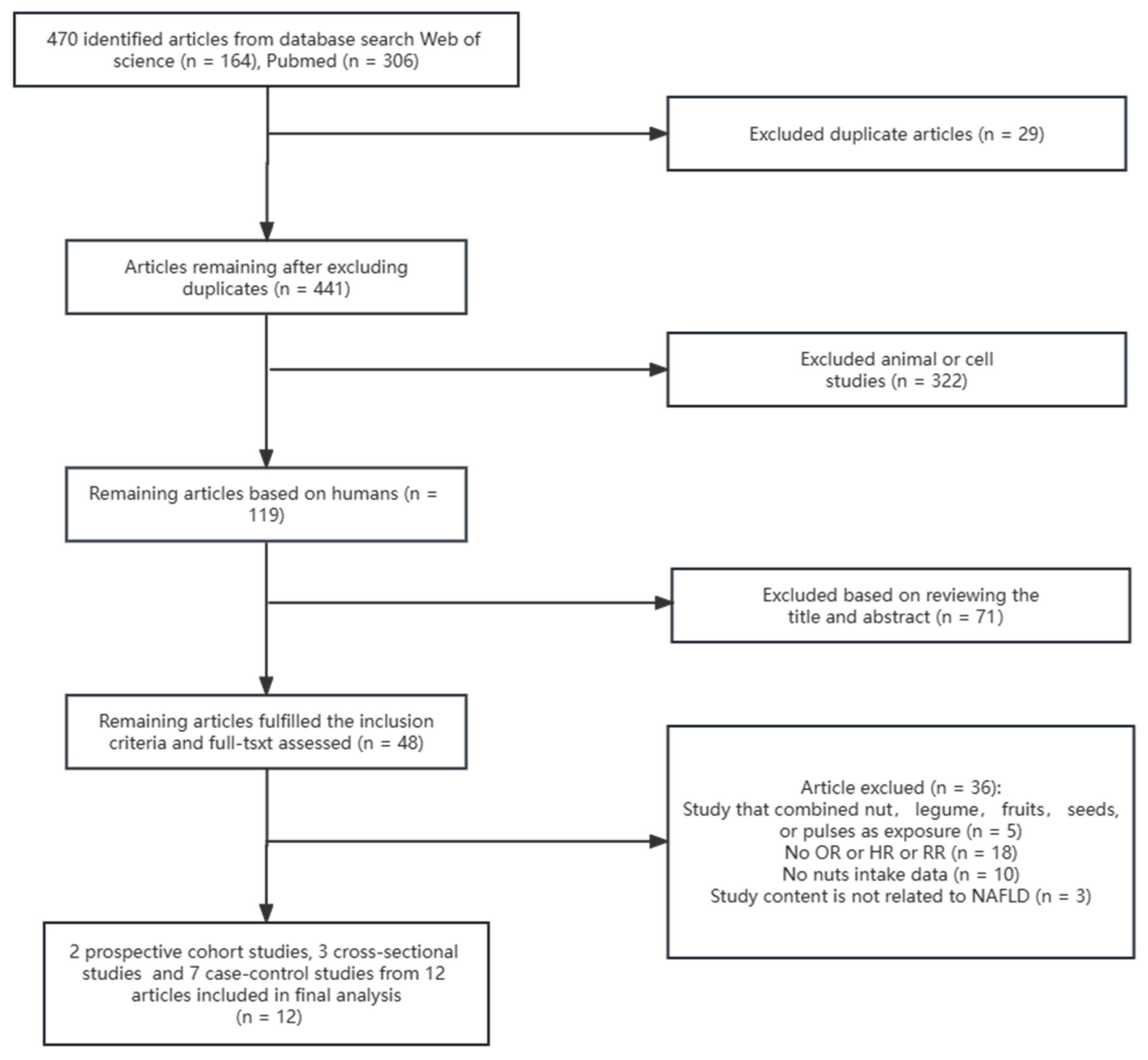
3. Results
3.1. Eligible Studies
3.2. Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis
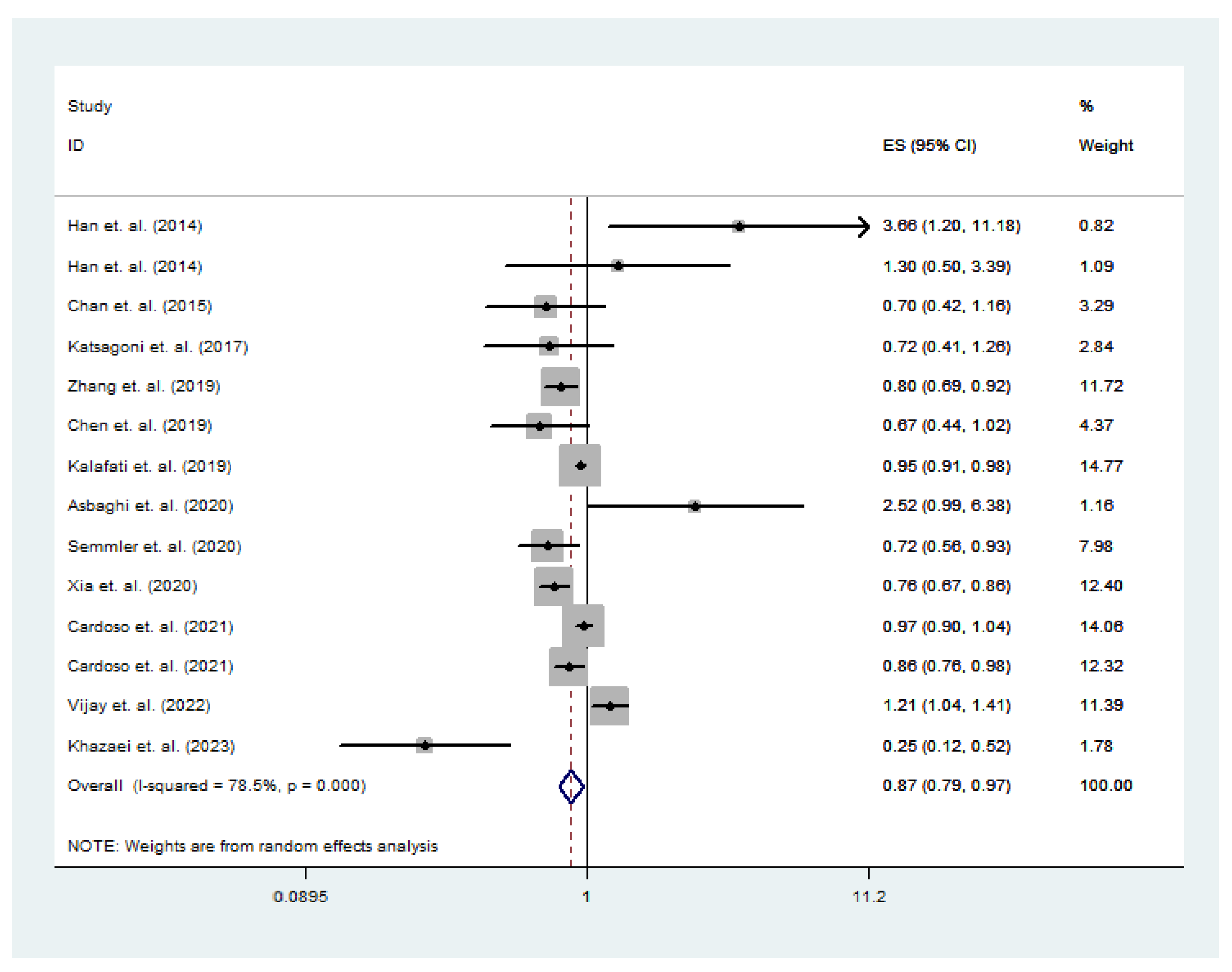
3.3. Nut Intake and Total NAFLD Risk
3.4. Subgroup Analysis of the Effect of Total Nut Intake on the Risk of NAFLD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maestri, M.; Santopaolo, F.; Pompili, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Gut microbiota modulation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Effects of current treatments and future strategies. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Meng, G.; Wu, H.; Bao, X.; Gu, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Insoluble dietary fibre intake is associated with lower prevalence of newly-diagnosed non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese men: A large population-based cross-sectional study. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmler, G.; Datz, C.; Trauner, M. Eating, diet, and nutrition for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S244–S260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anania, C.; Perla, F.M.; Olivero, F.; Pacifico, L.; Chiesa, C. Mediterranean diet and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventriglio, A.; Sancassiani, F.; Contu, M.P.; Latorre, M.; Di Slavatore, M.; Fornaro, M.; Bhugra, D. Mediterranean Diet and its Benefits on Health and Mental Health: A Literature Review. Clin. Pract. Epidemiology Ment. Health 2020, 16, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, J.; Gilani, A.-U.; Jamshed, H.; Khan, S.F.; Kamal, M.A. Edible Nuts for Memory. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4712–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, E.; Singh, A.; O’keefe, J.H. Nuts: Natural Pleiotropic Nutraceuticals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, D.A.; Martin, R.J.; Adams, S.H. Impact of Dietary Fibers on Nutrient Management and Detoxification Organs: Gut, Liver, and Kidneys. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2016, 7, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-M.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, L.; Nie, D.; Li, X.-A. Dietary fiber regulates intestinal flora and suppresses liver and systemic inflammation to alleviate liver fibrosis in mice. Nutrition 2020, 81, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarue, J.; Lallès, J.-P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Roles of the gut and the liver and metabolic modulation by some dietary factors and especially long-chain n-3 PUFA. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, H.; Leblanc, N.; Papineau, R.; Richard, D.; Côté, C.H. Peanut protein reduces body protein mass and alters skeletal muscle contractile properties and lipid metabolism in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, C.; Pohrt, A.; Pletsch-Borba, L.; Apostolopoulou, K.; Hornemann, S.; Meyer, N.; Machann, J.; Gerbracht, C.; Tacke, F.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; et al. Effect of unsaturated fat and protein intake on liver fat in people at risk of unhealthy aging: 1-year results of a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashimada, M.; Ota, T. Role of vitamin E in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüngreiff, K.; Reinhold, D.; Wedemeyer, H. The role of zinc in liver cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Zhan, T.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Selenium deficiency-induced redox imbalance leads to metabolic reprogramming and inflammation in the liver. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodore, L.E.; Kellow, N.J.; McNeil, E.A.; Close, E.O.; Coad, E.G.; Cardoso, B.R. Nut Consumption for Cognitive Performance: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2021, 12, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghshi, S.; Sadeghian, M.; Nasiri, M.; Mobarak, S.; Asadi, M.; Sadeghi, O. Association of Total Nut, Tree Nut, Peanut, and Peanut Butter Consumption with Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2021, 12, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, T.F.; Kim, E.; Buring, J.E.; Lee, I.-M.; Gaziano, J.M.; Djousse, L. Nut consumption, risk of cardiovascular mortality, and potential mediating mechanisms: The Women’s Health Study. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2021, 15, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Tan, S.-Y.; Daly, R.M.; Via, J.D.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; George, E.S. Intake of Nuts and Seeds Is Associated with a Lower Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in US Adults: Findings from 2005–2018 NHANES. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3507–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, G.; Bachmayer, S.; Wernly, S.; Wernly, B.; Niederseer, D.; Huber-Schönauer, U.; Stickel, F.; Aigner, E.; Datz, C. Nut consumption and the prevalence and severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Meng, G.; Yao, Z.; Wu, H.; Bao, X.; Gu, Y.; Lu, M.; et al. Association between nut consumption and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalafati, I.P.; Dimitriou, M.; Borsa, D.; Vlachogiannakos, J.; Revenas, K.; Kokkinos, A.; Ladas, S.D.; Dedoussis, G.V. Fish intake interacts with TM6SF2 gene variant to affect NAFLD risk: Results of a case–control study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Jo, A.N.; Lee, S.M.; Bae, H.S.; Jun, D.W.; Cho, Y.K.; Suk, K.T.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, S.B.; Cho, Y.J.; et al. Associations between intakes of individual nutrients or whole food groups and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among Korean adults. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, O.; Emamat, H.; Kelishadi, M.R.; Hekmatdoost, A. The Association between Nuts Intake and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Risk: A Case-Control Study. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2020, 9, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Al-Awadi, A.; Chalmers, J.; Balakumaran, L.; Grove, J.I.; Valdes, A.M.; Taylor, M.A.; Shenoy, K.T.; Aithal, G.P. Development of Food Group Tree-Based Analysis and Its Association with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Co-Morbidities in a South Indian Population: A Large Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslami, O.; Khorramrouz, F.; Sohouli, M.; Bagheri, N.; Shidfar, F.; Fernandez, M.L. Effect of nuts on components of metabolic syndrome in healthy adults with overweight/obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 2459–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Field, D.; Chen, V.; Ahmad, S.; Mejia, S.B.; Kahleová, H.; Rahelić, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Leiter, L.A.; Uusitupa, M.; et al. Combination of Multiple Low-Risk Lifestyle Behaviors and Incident Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Gan, X.; He, Y.; Nong, S.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Peng, X. Association between nut consumption and cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2023, 75, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Kumar, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of MAFLD and NAFLD diagnostic criteria in real world. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Ji, Z.; Yuan, P.; Long, T.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Cheng, L. Nut Consumption and Risk of Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Prospective Studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crovesy, L.; Masterson, D.; Rosado, E.L. Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Chu, W.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Li, L.S.; Leung, J.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Yeung, D.K.-W.; Sea, M.M.-M.; Woo, J.; et al. Diet-Quality Scores and Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population Study Using Proton-Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsagoni, C.N.; Georgoulis, M.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Fragopoulou, E.; Ioannidou, P.; Papageorgiou, M.; Alexopoulou, A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Deutsch, M.; Kontogianni, M.D. Associations Between Lifestyle Characteristics and the Presence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Case–Control Study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2017, 15, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Han, Y.; Pan, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Xu, S.; Peng, X.-E. Association between nut intake and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk: A retrospective case-control study in a sample of Chinese Han adults. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, Y.; Dehghanseresht, N.; Mousavi, S.E.; Nazari, M.; Salamat, S.; Asbaghi, O.; Mansoori, A. Association Between Protein Intake From Different Animal and Plant Origins and the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Case-Control Study. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2023, 12, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Keum, N.; Giovannucci, E.; Fadnes, L.T.; Boffetta, P.; Greenwood, D.C.; Tonstad, S.; Vatten, L.J.; Riboli, E.; Norat, T. Nut consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.C.P.; Bodini, G.; Furnari, M.; Marabotto, E.; Zentilin, P.; Giannini, E.G. Nuts and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Are Nuts Safe for Patients with Fatty Liver Disease? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.G.M.; Schincaglia, R.M.; Pimentel, G.D.; Mota, J.F. Nuts and Human Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasalvar, C.; Salvadó, J.-S.; Ros, E. Bioactives and health benefits of nuts and dried fruits. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, D.; Godos, J.; Marventano, S.; Tieri, M.; Ghelfi, F.; Titta, L.; Lafranconi, A.; Trigueiro, H.; Gambera, A.; Alonzo, E.; et al. Nut and legume consumption and human health: An umbrella review of observational studies. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolling, B.W.; Chen, C.-Y.O.; McKay, D.L.; Blumberg, J.B. Tree nut phytochemicals: Composition, antioxidant capacity, bioactivity, impact factors. A systematic review of almonds, Brazils, cashews, hazelnuts, macadamias, pecans, pine nuts, pistachios and walnuts. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2011, 24, 244–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belardo, D.; Michos, E.D.; Blankstein, R.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Ferdinand, K.C.; Hall, K.; Klatt, K.; Natajaran, P.; Ostfeld, R.J.; Reddy, K.; et al. Practical, Evidence-Based Approaches to Nutritional Modifications to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: An American Society for Preventive Cardiology Clinical Practice Statement. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 10, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinpour-Niazi, S.; Bakhshi, B.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F. Socioeconomic and lifestyle factors modifies the association between nut consumption and metabolic syndrome incidence. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4055–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.J.; Shadbolt, B.; Teoh, N.; Blunn, A.; To, C.; Rodriguez-Morales, I.; Chitturi, S.; Kaye, G.; Rodrigo, K.; Farrell, G. Influence of psychiatric diagnosis on treatment uptake and interferon side effects in patients with hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMacken, M.; Shah, S. A plant-based diet for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Name, M.A.; Savoye, M.; Chick, J.M.; Galuppo, B.T.; Feldstein, A.E.; Pierpont, B.; Johnson, C.; Shabanova, V.; Ekong, U.; Valentino, P.L.; et al. A Low ω-6 to ω-3 PUFA Ratio (n–6:n–3 PUFA) Diet to Treat Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Youth. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjermo, H.; Iggman, D.; Kullberg, J.; Dahlman, I.; Johansson, L.; Persson, L.; Berglund, J.; Pulkki, K.; Basu, S.; Uusitupa, M.; et al. Effects of n-6 PUFAs compared with SFAs on liver fat, lipoproteins, and inflammation in abdominal obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M. Benefits of Nut Consumption on Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Multiple Potential Mechanisms of Actions. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzon dos Santos, J.; Quadros, A.S.; Weschenfelder, C.; Garofallo, S.B.; Marcadenti, A. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers, Nut-Related Antioxidants, and Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasi, T.; Barreca, D.; Laganà, G.; Mandalari, G. Health Benefits Related to Tree Nut Consumption and Their Bioactive Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Larussa, T.; Corea, A.; Procopio, A.C.; Boccuto, L.; Dallio, M.; Federico, A.; Luzza, F. Dietary Polyphenols and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Mah, X.-J.; Garcia, M.C.; Antonypillai, C.; Van Der Poorten, D. Oily fish, coffee and walnuts: Dietary treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10621–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, D.W.; Stewart, W.D.P. Proline inhibits N2-fixation in Anabaena 7120. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 139, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Alejandre, B.A.; Abete, I.; Cantero, I.; Monreal, J.I.; Elorz, M.; Herrero, J.I.; Benito-Boillos, A.; Quiroga, J.; Martinez-Echeverria, A.; Uriz-Otano, J.I.; et al. The Metabolic and Hepatic Impact of Two Personalized Dietary Strategies in Subjects with Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Fatty Liver in Obesity (FLiO) Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, N.; Ishigami, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Sumi, H.; Doisaki, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ito, T.; Ishizu, Y.; Kuzuya, T.; Honda, T.; et al. Effect of weight change and lifestyle modifications on the development or remission of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Sex-specific analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivel, V.; Kunyanga, C.N.; Biesalski, H.K. Health benefits of nut consumption with special reference to body weight control. Nutrition 2012, 28, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, C.L.; Zunshine, E.; Nguyen, H.T.; Perez, A.O.; Zoumas, C.; Pakiz, B.; White, M.M. Effects of Pistachio Consumption in a Behavioral Weight Loss Intervention on Weight Change, Cardiometabolic Factors, and Dietary Intake. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tindall, A.M.; Petersen, K.S.; Lamendella, R.; Shearer, G.C.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; Proctor, D.N.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Tree Nut Consumption and Adipose Tissue Mass: Mechanisms of Action. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2018, 2, nzy069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour-Niazi, S.; Bakhshi, B.; Zahedi, A.-S.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Daneshpour, M.S.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F. TCF7L2 polymorphisms, nut consumption, and the risk of metabolic syndrome: A prospective population based study. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.-Z. Relationship between Nut Consumption and Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Fogelholm, M.; Poppitt, S.D.; Silvestre, M.P.; Møller, G.; Huttunen-Lenz, M.; Stratton, G.; Sundvall, J.; Råman, L.; Jalo, E.; et al. Adherence to a Plant-Based Diet and Consumption of Specific Plant Foods—Associations with 3-Year Weight-Loss Maintenance and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Secondary Analysis of the PREVIEW Intervention Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, S.; Rajak, S.; Upadhyay, A.; Tewari, A.; Anthony Sinha, R. Current treatment paradigms and emerging therapies for NAFLD/NASH. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Tsukamoto, H. Inflammation in Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Friend or Foe? Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, J.H.D.A.; de Moor, M.H.; de Geus, E.J.; Lubke, G.H.; Vink, J.M.; Willemsen, G.; Boomsma, D.I. The Genetic Architecture of Liver Enzyme Levels: GGT, ALT and AST. Behav. Genet. 2013, 43, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H.; Ahad, A.; Iqbal, J.; Siddiqui, W.A. Pharmacological potential of tocotrienols: A review. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Espín, J.C.; Carr, T.P.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Chung, S. Raspberry seed flour attenuates high-sucrose diet-mediated hepatic stress and adipose tissue inflammation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 32, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Granda, M.B.M.; Sinclair, A.J. Fatty Acids and Obesity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 4117–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.S.; Galano, J.-M.; Yau, Y.F.; Oger, C.; Durand, T.; Lee, J.C.-Y. Walnut-Enriched Diet Elevated α-Linolenic Acid, Phytoprostanes, and Phytofurans in Rat Liver and Heart Tissues and Modulated Anti-inflammatory Lipid Mediators in the Liver. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9094–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Deng, W.-S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.-H.; Sun, L.-C.; Sun, X.-F.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, H. Ellagic acid protects Lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute hepatic injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, L.-Q.; Bai, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, G.-Y.; Fang, C.-W.; Wang, F.; Qin, X.-J. Exercise and dietary intervention ameliorate high-fat diet-induced NAFLD and liver aging by inducing lipophagy. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Vázquez, S.; Aragonès, G.; Del Bas, J.M.; Escoté, X. Diet, Gut Microbiota and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Three Parts of the Same Axis. Cells 2020, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moslehi, Z.; Nafchi, A.M.; Moslehi, M.; Jafarzadeh, S. Aflatoxin, microbial contamination, sensory attributes, and morphological analysis of pistachio nut coated with methylcellulose. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.-J.; Yang, H.-I.; Wu, H.-C.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.-Y.; Lu, S.-N.; Lee, M.-H.; Jen, C.-L.; You, S.-L.; Santella, R.M.; et al. Aflatoxin B1exposure increases the risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Studies | Study Design | Location | Years Enrolled | Age Range (Years) | Gender | Sample Size | Adjustment Variables | NOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Han et al. (2014) [23] | Case–control Study | Korea | 2014 | 20–69 | Male/female | 348 | Age group, current job, education level, exercise frequency group, smoking, and energy intake. | 6 |
| Chan et al. (2015) [33] | Cross-sectional Study | China | 2008–2010 | 19–72 | Male/female | 797 | BMI, smoker status, drinker status, central obesity, triglyceride > 1.7 mmol/L, reduced HDL cholesterol, hypertension, impaired fasting glucose or diabetes, and the PNPLA3 genotypes. | 8 |
| Katsagoni et al. (2017) [34] | Case–control Study | Greece | 2013–2015 | 18–67 | Male/female | 155 | Age, sex, waist circumference, HOMA-IR, adiponectin, and TNF-a. | 7 |
| Zhang et al. (2019) [21] | Prospective Cohort Study | China | 2013–2016 | ≥18 | Male/female | 33,150 | Age, gender, BMI, smoking status, alcohol drinking, education level, occupation, household income, physical activity, family history of disease, history of hypertension, total energy intake, eicosatetraenoic acid + docosahexaenoic acid intake, soft drink intake, three main dietary pattern scores, and potential intermediates of the nut–NAFLD association. | 9 |
| Kalafati et al. (2019) [22] | Case–control Study | Greece | 2012–2015 | ≤65 | Male/female | 351 | Age, sex, BMI or energy intake, smoking, and PAL. | 7 |
| Chen et al. (2019) [35] | Case–control Study | China | 2015–2017 | 18–70 | Male/female | 1068 | Age, income, smoking, educational level, tea drinking, occupation, marital status, BMI, physical activity, diabetes, hypertension and hyperlipidemia, and MUFA and PUFA intake. | 8 |
| Asbaghi et al. (2020) [24] | Case–control Study | Iran | 2015 | 18–75 | Male/female | 999 | Age, gender, BMI, alcohol drinking, smoking, diabetes, physical activity, and energy intake. | 7 |
| Semmler et al. (2020) [20] | Prospective Cohort Study | Austria | 2010–2019 | 58.5 ± 9.8 | Male/female | 4655 | Age, sex, BMI, metabolic syndrome, hepatic steatosis, alcohol drinking, intake of fast food, vegetables, fruits, sweets, red and processed meat, white meat, fish, coffee, and consumption of SSB. | 9 |
| Xia et al. (2020) [2] | Prospective Cohort Study | China | 2013–2016 | Na | Male/female | 23,529 | Age, sex, BMI, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, physical activity, educational level, income, smoking, drinking, employment status, energy intake, total carbohydrate intake, total fat intake, sweet food intake, red meat intake, white meat intake, DHA + EPA intake, family history of CVD, hypertension, and diabetes. | 9 |
| Cardoso et al. (2021) [19] | Cross-sectional Study | USA | 2005–2018 | ≥18 | Male/female | 25,360 | Age, sex, smoking, HEI-2015, physical activity, history of CVD, and HbA1c. | 9 |
| Vijay et al. (2022) [25] | Case–control Study | India | 2013–2016 | ≥25 | Male/female | 1966 | Age, gender, and weight. | 7 |
| Khazaei et al. (2023) [36] | Case–control Study | Iran | 2018–2019 | average 42.7 | Male/female | 243 | Age, sex, energy intake, physical activity, marital status, education, supplement use, drug use, smoking status, fat intake, carbohydrate intake (continuous), and BMI. | 8 |
| Nuts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Study | OR (95% CI) | I2 | |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 5 | 0.77 (0.56, 1.08) | 84.5% |
| Female | 5 | 0.83 (0.75, 0.91) | 2.8% |
| All | 7 | 0.88 (0.72, 1.07) | 82.6% |
| Region | |||
| Asia | 9 | 0.88 (0.68, 1.13) | 83.7% |
| Europe | 3 | 0.84 (0.67, 1.05) | 62.4% |
| North America | 2 | 0.92 (0.82, 1.04) | 61.6% |
| Study design | |||
| Prospective cohort study | 2 | 0.78 (0.69, 0.88) | 0.0% |
| Cross-sectional study | 4 | 0.85 (0.74, 0.98) | 76.2% |
| Case–control study | 8 | 0.94 (0.73, 1.23) | 80.6% |
| Sample size | |||
| <1000 | 7 | 0.93 (0.61, 1.43) | 76.2% |
| ≥1000 | 7 | 0.87 (0.76, 0.99) | 82.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, L.; Sui, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q. Effect of Nut Consumption on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102394
Pan L, Sui J, Xu Y, Zhao Q. Effect of Nut Consumption on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(10):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102394
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Ling, Jing Sui, Ying Xu, and Qun Zhao. 2023. "Effect of Nut Consumption on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 15, no. 10: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102394
APA StylePan, L., Sui, J., Xu, Y., & Zhao, Q. (2023). Effect of Nut Consumption on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 15(10), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102394






