The Effects of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on the Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Function in Patients with Obesity: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
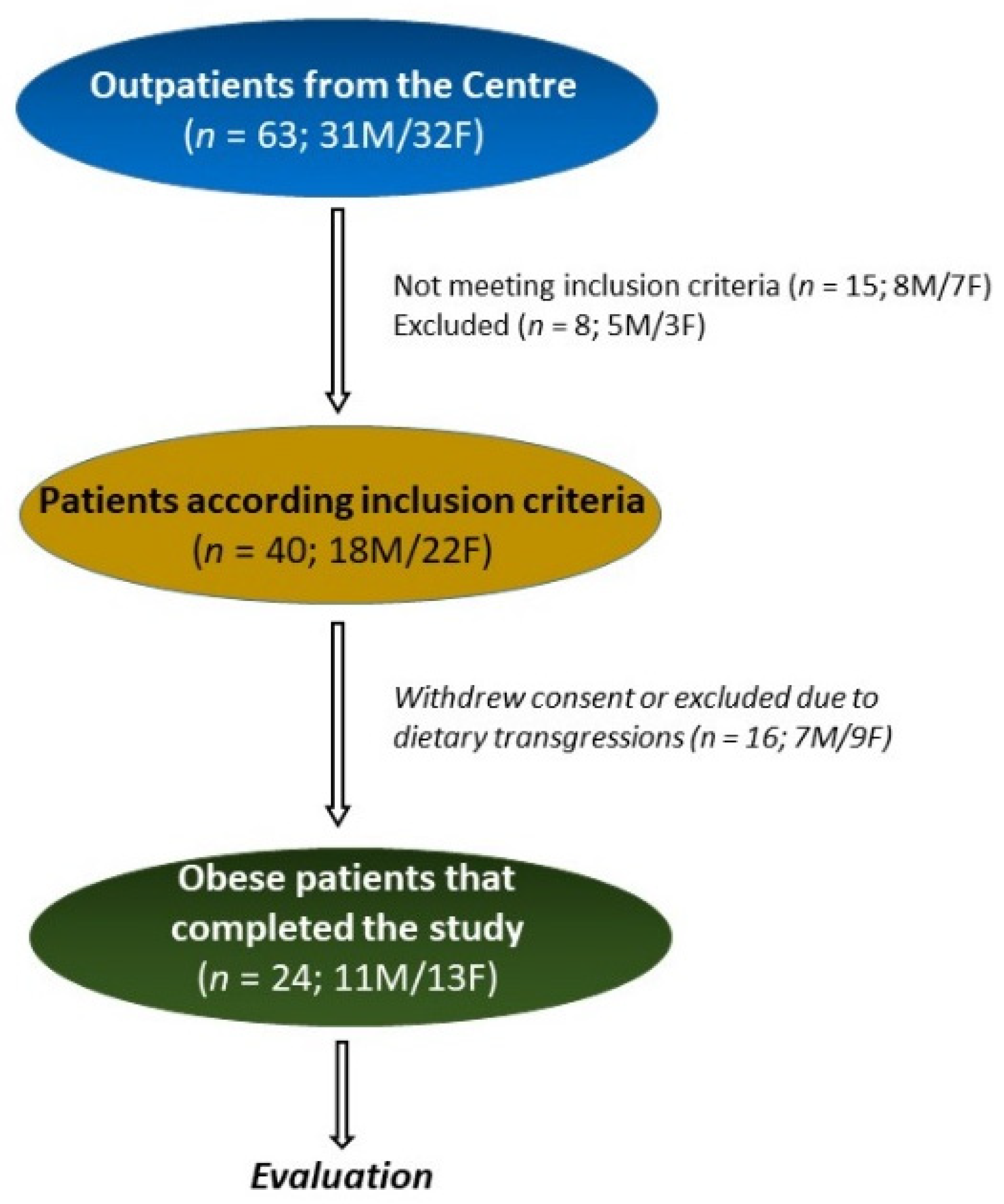
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Diet Protocol
2.3. Anthropometric Parameters and Biochemical Characteristics
2.4. Sugar Absorption Test
2.5. Serum and Fecal Zonulin, Serum I-FABP, and Serum DAO Concentrations
2.6. Indican and Skatole Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Number, Anthropometric, and Symptomatic Characteristics of the Patients, and Intervention Diet
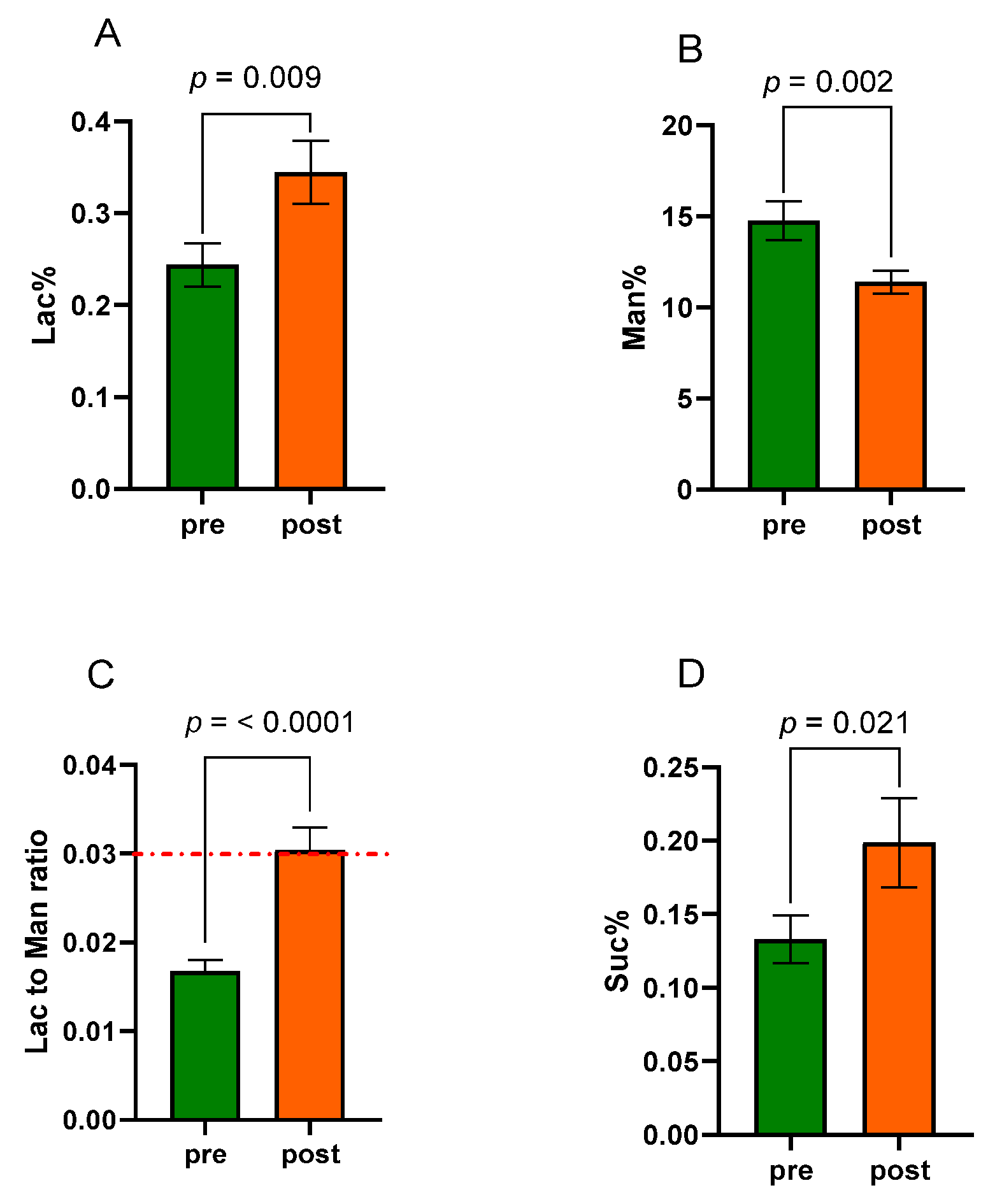
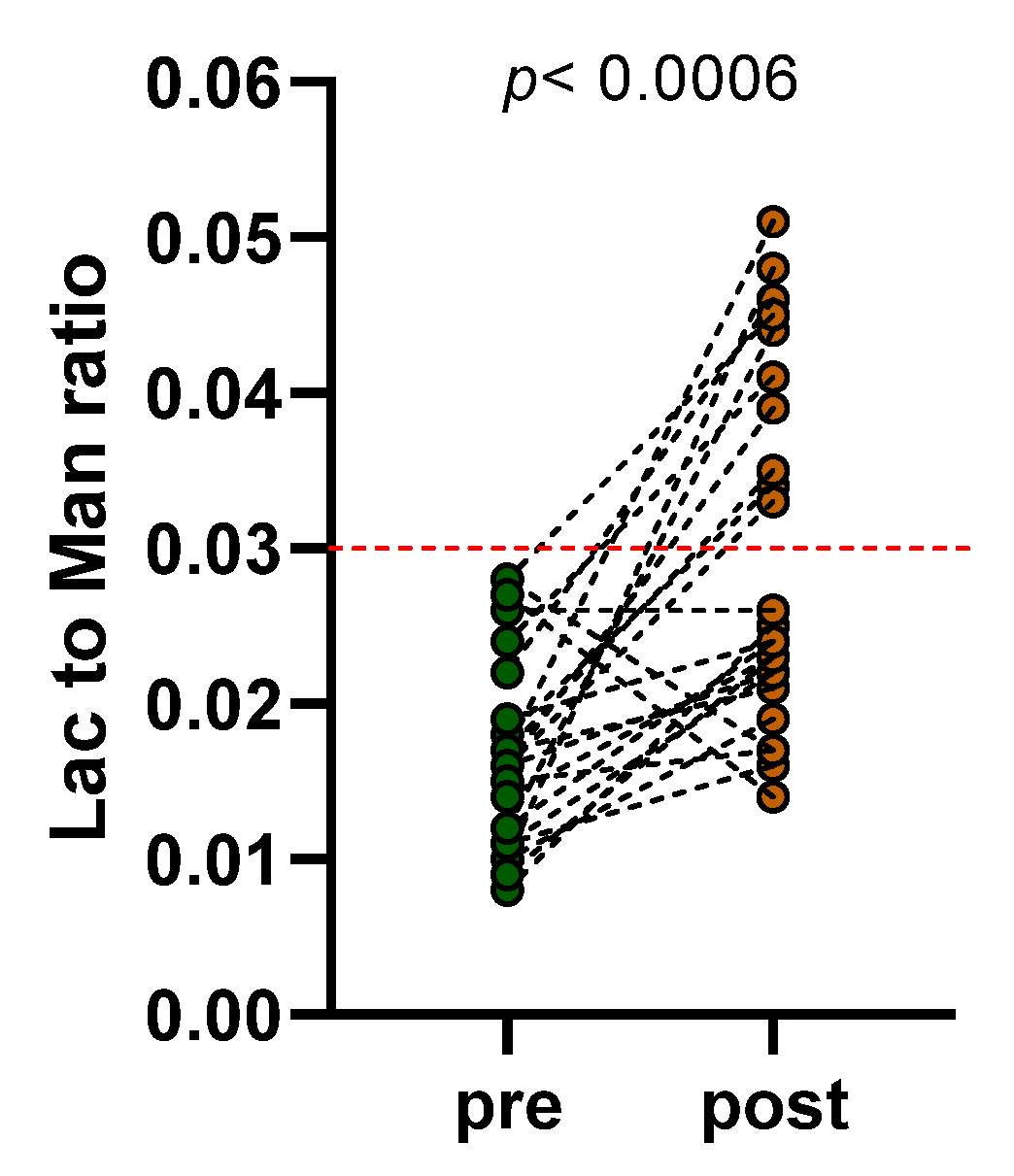
3.2. Sugar Absorption Test
3.3. Biomarkers Related to the Intestinal Barrier Function and Integrity
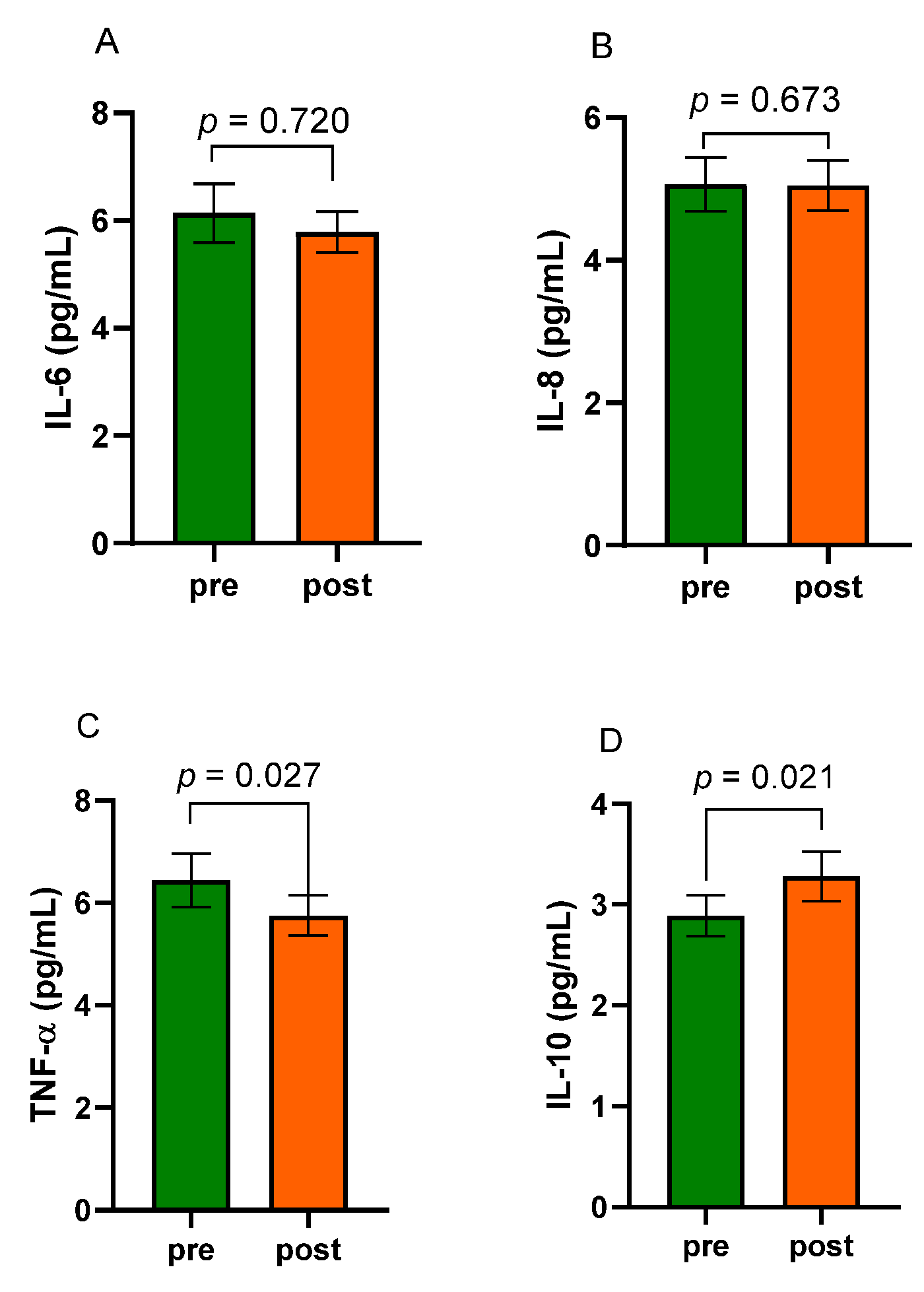
3.4. Levels of Inflammatory Factors
3.5. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Bacterial Translocation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lorenzo, A.; Romano, L.; Di Renzo, L.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Cenname, G.; Gualtieri, P. Obesity: A preventable, treatable, but relapsing disease. Nutrition 2020, 71, 110615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muehler, A.; Slizgi, J.R.; Kohlhof, H.; Groeppel, M.; Peelen, E.; Vitt, D. Clinical relevance of intestinal barrier dysfunction in common gastrointestinal diseases. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2020, 11, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bona, M.D.; Torres, C.H.d.M.; Lima, S.C.V.C.; Lima, A.A.M.; Maciel, B.L.L. Intestinal barrier function in obesity with or without metabolic syndrome: A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e043959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gummesson, A.; Carlsson, L.M.; Storlien, L.H.; Bäckhed, F.; Lundin, P.; Löfgren, L.; Stenlöf, K.; Lam, Y.Y.; Fagerberg, B.; Carlsson, B. Intestinal Permeability Is Associated with Visceral Adiposity in Healthy Women. Obesity 2011, 19, 2280–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajoka, M.S.R.; Shi, J.; Mehwish, H.M.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Shao, D.; Huang, Q.; Yang, H. Interaction between diet composition and gut microbiota and its impact on gastrointestinal tract health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2017, 6, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, R.; Fiorani, M.; Rahiman, S.A.; Matteoli, G. Intestinal Permeability, Inflammation and the Role of Nutrients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbrink, J.; Bernards, N.; Mujagic, Z.; Van Avesaat, M.; Pijls, K.; Klaassen, T.; Van Eijk, H.; Nienhuijs, S.; Stronkhorst, A.; Wilms, E.; et al. Intestinal barrier function in morbid obesity: Results of a prospective study on the effect of sleeve gastrectomy. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; El Ghoch, M.; Colao, A.; Hassapidou, M.; Yumuk, V.; Busetto, L. Obesity Management Task Force (OMTF) of the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Facts 2021, 14, 222–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Vetrani, C.; Marino, F.; Aprano, S.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. VLCKD: A real time safety study in obesity. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruci, A.; Tuccinardi, D.; Tozzi, R.; Balena, A.; Santucci, S.; Frontani, R.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Gnessi, L.; et al. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Safe and Effective Tool for Weight Loss in Patients with Obesity and Mild Kidney Failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, M.; Moriconi, E.; Armani, A.; Fabbri, A.; Mantovani, G.; Mariani, S.; Lubrano, C.; Poggiogalle, E.; Migliaccio, S.; Donini, L.M.; et al. Very-low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in the management of metabolic diseases: Systematic review and consensus statement from the Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 1365–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, R.; De Nucci, S.; Castellana, F.; Di Chito, M.; Giannuzzi, V.; Shahini, E.; Zupo, R.; Lampignano, L.; Piazzolla, G.; Triggiani, V.; et al. The Effects of Eight Weeks’ Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) on Liver Health in Subjects Affected by Overweight and Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, I.; Tutino, V.; Russo, F.; De Nunzio, V.; Coletta, S.; Armentano, R.; Crovace, A.; Caruso, M.G.; Orlando, A.; Notarnicola, M. Cannabinoid Receptors Overexpression in a Rat Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) after Treatment with a Ketogenic Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seethaler, B.; Basrai, M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Nazare, J.-A.; Walter, J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Bischoff, S.C. Biomarkers for assessment of intestinal permeability in clinical practice. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G11–G17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: Role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Research 2020, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.S.C.; Keenan, J.I.; Day, A.S. The Role of Gastrointestinal-Related Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins as Biomarkers in Gastrointestinal Diseases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honzawa, Y.; Nakase, H.; Matsuura, M.; Chiba, T. Clinical significance of serum diamine oxidase activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, E23–E25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsalata, M.; Riezzo, G.; Orlando, A.; D’attoma, B.; Prospero, L.; Tutino, V.; Notarnicola, M.; Russo, F. The Relationship between Low Serum Vitamin D Levels and Altered Intestinal Barrier Function in Patients with IBS Diarrhoea Undergoing a Long-Term Low-FODMAP Diet: Novel Observations from a Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, G.; Petta, S.; Grave, R.D. Diet, weight loss, and liver health in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathophysiology, evidence, and practice. Hepatology 2015, 63, 2032–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulich, K.R.; Madisch, A.; Pacini, F.; Piqué, J.M.; Regula, J.; Van Rensburg, C.J.; Újszászy, L.; Carlsson, J.; Halling, K.; Wiklund, I.K. Reliability and validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) questionnaire in dyspepsia: A six-country study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2008, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsalata, M.; D’attoma, B.; Orlando, A.; Guerra, V.; Russo, F. Comparison of an enzymatic assay with liquid chromatography-pulsed amperometric detection for the determination of lactulose and mannitol in urine of healthy subjects and patients with active celiac disease. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, e61–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsalata, M.; Riezzo, G.; D’attoma, B.; Clemente, C.; Orlando, A.; Russo, F. Noninvasive biomarkers of gut barrier function identify two subtypes of patients suffering from diarrhoea predominant-IBS: A case-control study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeoni, M.; Citraro, M.L.; Cerantonio, A.; Deodato, F.; Provenzano, M.; Cianfrone, P.; Capria, M.; Corrado, S.; Libri, E.; Comi, A.; et al. An open-label, randomized, placebo-controlled study on the effectiveness of a novel probiotics administration protocol (ProbiotiCKD) in patients with mild renal insufficiency (stage 3a of CKD). Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescigno, M. The intestinal epithelial barrier in the control of homeostasis and immunity. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations in obesity and after weight-loss intervention. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.; He, J.; Gao, R.; Kalady, M.F.; Goel, A.; Qin, H.; et al. Ketogenic diet alleviates colitis by reduction of colonic group 3 innate lymphoid cells through altering gut microbiome. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhuge, A.; Wang, K.; Lv, L.; Bian, X.; Yang, L.; Xia, J.; Jiang, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, S.; et al. Ketogenic diet aggravates colitis, impairs intestinal barrier and alters gut microbiota and metabolism in DSS-induced mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10210–10225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, T.F.S.; Collado, M.C.; Ferreira, C.L.L.F.; Bressan, J.; do Carmo, G.; Peluzio, M. Potential mechanisms for the emerging link between obesity and increased intestinal permeability. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Is intestinal permeability increased in obesity? A review including the effects of dietary, pharmacological and surgical interventions on permeability and the microbiome. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hałasa, M.; Maciejewska, D.; Ryterska, K.; Baśkiewicz-Hałasa, M.; Safranow, K.; Stachowska, E. Assessing the Association of Elevated Zonulin Concentration in Stool with Increased Intestinal Permeability in Active Professional Athletes. Medicina 2019, 55, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignardello, J.; Morales, P.; Diaz, E.; Romero, J.; Brunser, O.; Gotteland, M. Pilot study: Alterations of intestinal microbiota in obese humans are not associated with colonic inflammation or disturbances of barrier function. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutoukidis, D.A.; Jebb, S.A.; Zimmerman, M.; Otunla, A.; Henry, J.A.; Ferrey, A.; Schofielda, E.; Kintona, J.; Paul, A.; Marchesi, J.R. The association of weight loss with changes in the gut microbiota diversity, composition, and intestinal permea-bility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, e2020068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Tuccinardi, D.; Moriconi, E.; Di Renzo, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Could ketogenic diet “starve” cancer? Emerging evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1800–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Rubini, A.; Volek, J.S.; Grimaldi, K.A. Beyond weight loss: A review of the therapeutic uses of very-low-carbohydrate (ketogenic) diets. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Watanabe, M.; Cammarata, G.; Feraco, A.; Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Could very low-calorie ketogenic diets turn off low grade inflammation in obesity? Emerging evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pulcini, G.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Food Components and Dietary Habits: Keys for a Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Gasparri, C.; Peroni, G.; Faliva, M.A.; Naso, M.; Perna, S.; Bazire, P.; Sajoux, I.; Maugeri, R.; Rigon, C. The Potential Roles of Very Low Calorie, Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diets and Very Low Carbohydrate Diets on the Gut Microbiota Composition. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 662591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Miao, Z. High-fat diet induces intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in ulcerative colitis: Emerging mechanisms and dietary intervention perspective. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 653–677. [Google Scholar]
- Zilberter, T.; Zilberter, Y. Ketogenic Ratio Determines Metabolic Effects of Macronutrients and Prevents Interpretive Bias. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Pre-VLCKD (n = 24) | Post-VLCKD (n = 24) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 42.58 ± 2.64 | 42.58 ± 2.64 | ns |
| Sex (M/F) | 11 M/13 F | 11 M/13 F | ns |
| Weight (Kg) | 101.80 ± 5.18 | 92.76 ± 4.95 | <0.0001 |
| Height (m) | 150.60 ± 11.85 | 150.60 ± 11.85 | ns |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 35.56 ± 1.12 | 31.56 ± 1.30 | <0.0001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 111.80 ± 3.48 | 102.80 ± 3.63 | <0.0001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 86.33 ± 2.47 | 79.29 ± 1.54 | <0.0001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 137.40 ± 3.19 | 127.00 ± 1.08 | 0.0002 |
| Pre-VLCKD (n = 24) | Post-VLCKD (n = 24) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSH (μU/mL) | 1.85 ± 0.26 | 1.90 ± 0.17 | ns |
| FT3 (pg/mL) | 3.38 ± 0.06 | 2.98 ± 0.09 | <0.0001 |
| FT4 (pg/mL) | 10.73 ± 0.41 | 11.90 ± 0.43 | 0.0002 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 98.63 ± 3.83 | 91.08 ± 2.85 | 0.0027 |
| Insulin (μU/mL) | 16.08 ± 2.15 | 10.54 ± 1.10 | <0.0001 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.55 ± 0.28 | 5.79 ± 0.27 | ns |
| 25-OH-Vitamin D (ng/mL) | 21.67 ± 1.76 | 25.71 ± 2.37 | 0.0002 |
| γGT (U/L) | 27.63 ± 4.20 | 19.08 ± 2.70 | <0.0001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 36.79 ± 5.75 | 31.79 ± 6.70 | 0.033 |
| AST (U/L) | 24.67 ± 2.46 | 22.50 ± 2.48 | ns |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 207.10 ± 8.41 | 180.20 ± 5.85 | <0.0001 |
| HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 55.78 ± 3.52 | 50.74 ± 2.97 | 0.0060 |
| LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 141.40 ± 7.62 | 113.00 ± 5.93 | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 109.80 ± 14.06 | 93.46 ± 9.81 | 0.0010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linsalata, M.; Russo, F.; Riezzo, G.; D’Attoma, B.; Prospero, L.; Orlando, A.; Ignazzi, A.; Di Chito, M.; Sila, A.; De Nucci, S.; et al. The Effects of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on the Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Function in Patients with Obesity: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112561
Linsalata M, Russo F, Riezzo G, D’Attoma B, Prospero L, Orlando A, Ignazzi A, Di Chito M, Sila A, De Nucci S, et al. The Effects of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on the Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Function in Patients with Obesity: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112561
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinsalata, Michele, Francesco Russo, Giuseppe Riezzo, Benedetta D’Attoma, Laura Prospero, Antonella Orlando, Antonia Ignazzi, Martina Di Chito, Annamaria Sila, Sara De Nucci, and et al. 2023. "The Effects of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on the Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Function in Patients with Obesity: A Pilot Study" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112561
APA StyleLinsalata, M., Russo, F., Riezzo, G., D’Attoma, B., Prospero, L., Orlando, A., Ignazzi, A., Di Chito, M., Sila, A., De Nucci, S., Rinaldi, R., Giannelli, G., & De Pergola, G. (2023). The Effects of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on the Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Function in Patients with Obesity: A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 15(11), 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112561









