An Updated Review Summarizing the Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin from Bee Venom in Several Models of Human Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Melittin and Its Analogs
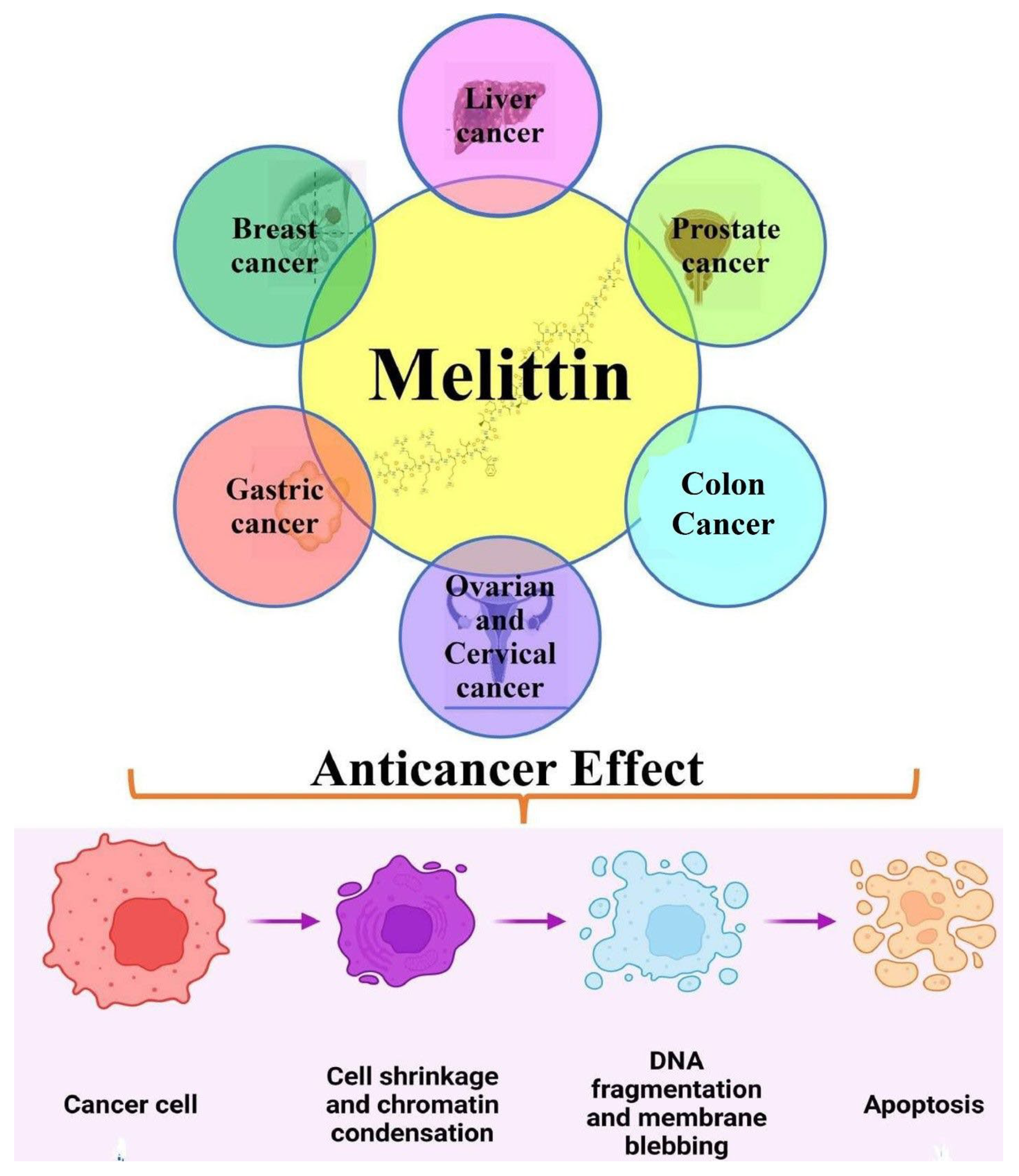
3. Molecular Interaction of Melittin (Honeybee Venom) in Cancer
3.1. Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin in Liver Cancer
3.2. Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin in Breast Cancer
3.3. Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin in Gastrointestinal Cancers
3.4. Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin in Gynecological Cancers
3.5. Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin in Other Human Cancers (Hepatocellular; HNSCC; Lung)
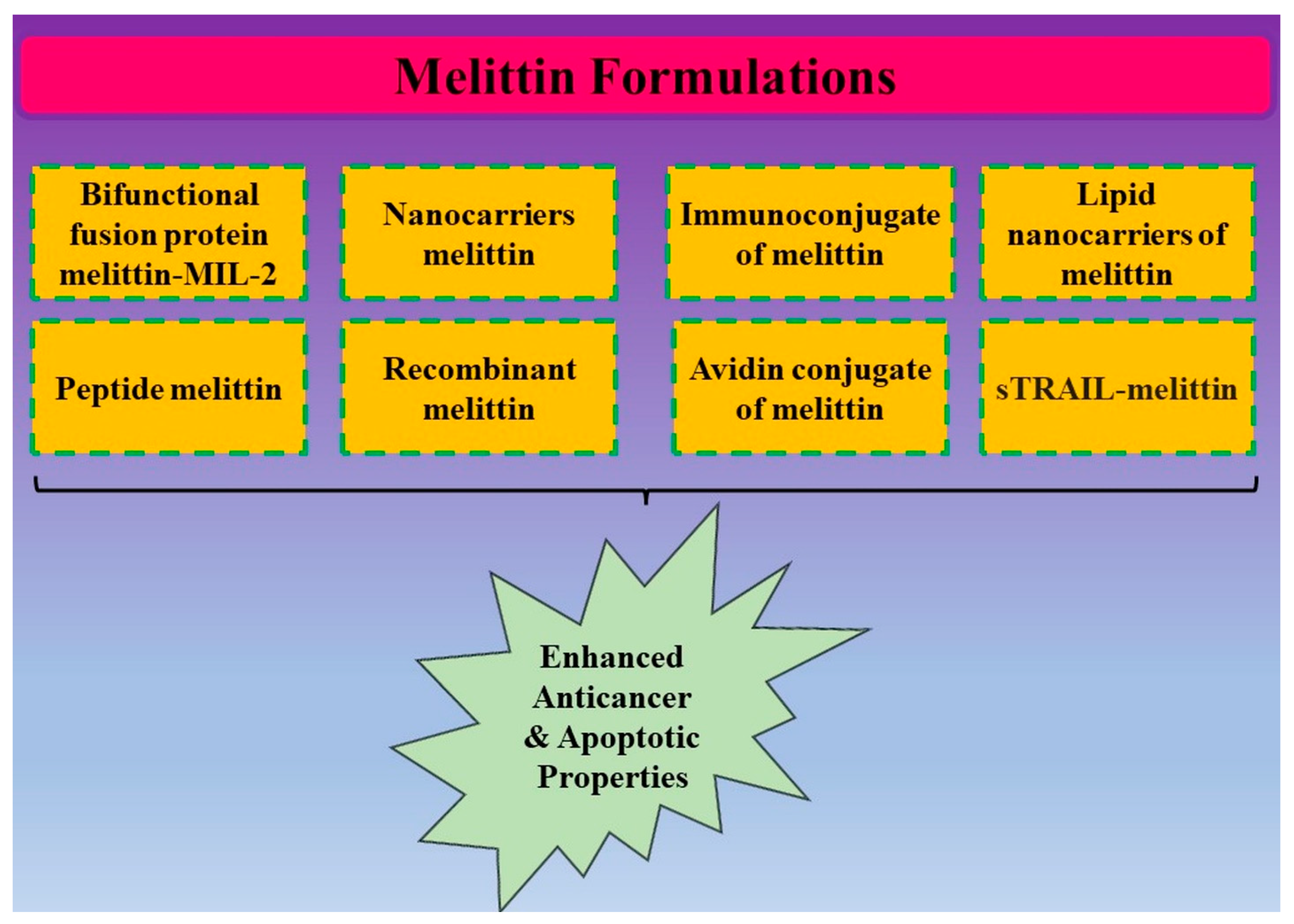
4. Conjugates of Melittin and Its Anticancer Potential
| MEL Conjugates | In Vitro/In Vivo | Modes of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melittin–MIL-2 fusion protein | SKOV3 cells |
| [56] |
| Non-viral vector (pSURV–Mel) |
|
| [57] |
| Dual secured nano-melittin |
|
| [58] |
| Ad-rAFP–Mel (Recombinant adenoviruses carrying the Mel gene and α-fetoprotein) |
|
| [72] |
| Melittin/Avidin conjugate |
|
| [73] |
| Ad-rAFP–Mel | BEL-7042 cells |
| [74] |
| Immunoconjugates having melittin-like peptide 101 | Mouse MAbs, J591 and BLCA-38 |
| [75] |
| Ad-rAFP–Mel | Bel-7402 |
| [76] |
| Melittin into perfluorocarbon nanoparticle | Murine tumors |
| [77] |
| Immunoliposomes having trastuzumab and melittin | SKBr3 cells |
| [78] |
| α-melittin-NP | Melanoma-bearing mice |
| [79] |
| AM-2 (peptide)+melittin | HepG2 cells |
| [80] |
| sTRAIL–melittin | K562 cells HepG2 cells |
| [81] |
| Melittin–MhIL-2 fusion protein |
|
| [82] |
| M-IL-2(88Arg, 125Ala) fusion protein | SKOV3 cells |
| [83] |
| Mel–N (asparagine-substituted melittin) and Mel–S (serine-substituted melittin) | BV-2 cells |
| [84] |
| 5-Fu + melittin | BGC-823 |
| [85] |
| QG511-HA–melittin |
|
| [86] |
| RhuPA1-43–melittin |
|
| [87] |
| rATF–mellitin |
|
| [88] |
5. Nanoformulations of Melittin and Its Anticancer Potential
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debela, D.T.; Muzazu, S.G.; Heraro, K.D.; Ndalama, M.T.; Mesele, B.W.; Haile, D.C.; Kitui, S.K.; Manyazewal, T. New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211034366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y. Biotoxins for cancer therapy. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 4753–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulraziq, N. Bee Venom and Its Potential to Treat Cancer; Libyan International Medical University: Banghazi, Libia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Şengül, F.; Vatansev, H. Overview of apitherapy products: Anticancer effects of bee venom used in apitherapy. Int. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. Res. 2021, 2, 36–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, X.-R.; Lin, L.-T.; Xiao, L.-Y.; Zhou, P.; Shi, G.-X.; Liu, C.-Z. Bee venom therapy: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Toxicon 2018, 148, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, A.; Sezen, S.; Evcimen, D.; Zarepour, A.; Ulus, G.; Zarrabi, A.; Badr, G.; Daştan, S.D.; Orbayoğlu, A.G.; Selamoğlu, Z.; et al. Cellular targets and molecular activity mechanisms of bee venom in cancer: Recent trends and developments. Toxin Rev. 2022, 41, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkoc, P.; von Reumont, B.M.; Lüddecke, T.; Henke, M.; Ulshöfer, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Fürst, R.; Schiffmann, S. The Pharmacological Potential of Novel Melittin Variants from the Honeybee and Solitary Bees against Inflammation and Cancer. Toxins 2022, 14, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Tiwari, G.; Lahiri, A.; Ramachandran, V.; Rai, A. Melittin: A Natural Peptide with Expanded Therapeutic Applications. Nat. Prod. J. 2022, 12, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, L.S.; Pande, J.; Shekhtman, A. Helical structure of recombinant melittin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 123, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceremuga, M.; Stela, M.; Janik, E.; Gorniak, L.; Synowiec, E.; Sliwinski, T.; Sitarek, P.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L. TT-1, an analog of melittin, triggers apoptosis in human thyroid cancer TT cells via regulating caspase, Bcl-2 and Bax. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Wu, R. MEL-pep, an analog of melittin, disrupts cell membranes and reverses 5-fluorouracil resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 101, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Cai, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Hong, X.; Shi, B. Construction and Characterization of a CTLA-4-Targeted scFv–Melittin Fusion Protein as a Potential Immunosuppressive Agent for Organ Transplant. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 67, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangboonruang, S.; Kitidee, K.; Chantawannakul, P.; Tragoolpua, K.; Tragoolpua, Y. Melittin from Apis florea venom is a promising therapeutic agent for skin cancer treatment. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdian-Robati, R.; Arab, A.; Ramezani, M.; Rafatpanah, H.; Bahreyni, A.; Nabavinia, M.S.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. Smart aptamer-modified calcium carbonate nanoparticles for controlled release and targeted delivery of epirubicin and melittin into cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, M.; Salesi, Z.; Derakhti, A.; Azimzadeh, S.; Varpaei, H.A.; Esmaeili, H.; Jafari, M. Melittin and breast cancer: A brief review of the evidence. J. Nurs. Patient Saf. 2020, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Guha, S.; Ferrie, R.P.; Ghimire, J.; Ventura, C.R.; Wu, E.; Sun, L.; Kim, S.Y.; Weidman, G.R.; Hristova, K.; Wimley, W.C. Applications and evolution of melittin, the quintessential membrane-active peptide. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 193, 114769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danijela, N.D.; Milena, M.G.; Danijela, C.M.; Maja, Ć.Đ.; Milena, J.M.; Ivan, M.V.; Marija, J.-G.Đ.; Snežana, M.D. Impact of bee venom and melittin on apoptosis and biotransformation in colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufschnaiter, A.; Kohler, V.; Khalifa, S.; El-Wahed, A.A.; Du, M.; El-Seedi, H.; Büttner, S. Apitoxin and Its Components against Cancer, Neurodegeneration and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Limitations and Possibilities. Toxins 2020, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memariani, H.; Memariani, M.; Shahidi-Dadras, M.; Nasiri, S.; Akhavan, M.M.; Moravvej, H. Melittin: From honeybees to superbugs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3265–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tender, T.; Rahangdale, R.R.; Balireddy, S.; Nampoothiri, M.; Sharma, K.K.; Raghu Chandrashekar, H. Melittin, a honeybee venom-derived peptide for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Med. Oncol. 2021, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, C.; Fang, F.; Li, B. Antitumor effects of melittin and its potential applications in the clinic. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, G.M.; Tao, W.H.; Diao, Y.L.; Fang, P.H.; Wang, J.J.; Bo, P.; Qian, F. Melittin induces human gastric cancer cell apoptosis via activation of mitochondrial pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yu, M.; He, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wang, F.; Song, C.; Sun, S.; Ling, C.; Xu, Z. Melittin prevents liver cancer cell metastasis through inhibition of the Rac1-dependent pathway. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Qi, Y.; Diao, Q.; Wu, L.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, L. Cytotoxicity of melittin and apamin in human hepatic L02 and HepG2 cells in vitro. Toxin Rev. 2013, 32, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lin, W.; Yin, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liang, S.; Ruan, S.; Chen, P.; Li, S.; Shu, Q.; Ling, C.; et al. Melittin Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through Suppression of HIF-1/Akt Pathway in Liver Cancer. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 9602935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, G.H.; El-Magd, M.A.; Mahfouz, D.H.; Abdelhamid, I.A.; Mohamed, M.F.; Ibrahim, N.S.; Wahab, A.H.A.A.; Elzayat, E.M. Bee venom and its active component Melittin synergistically potentiate the anticancer effect of Sorafenib against HepG2 cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 116, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-J.; Choi, Y.; Shin, J.-M.; Cho, H.-J.; Kang, J.-H.; Park, K.-K.; Choe, J.-Y.; Bae, Y.-S.; Han, S.-M.; Kim, C.-H.; et al. Melittin suppresses EGF-induced cell motility and invasion by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, F.D.; Mortazavi, P.; Hamedi, S.; Nabiuni, M.; Roodbari, N.H. Apoptotic effects of melittin on the 4T1 breast cancer cell line are associated with upregulation of Mfn1 and Drp1 mRNA expression. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents) 2020, 20, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.; Sorolla, A.; Wang, E.; Golden, E.; Woodward, E.; Davern, K.; Ho, D.; Johnstone, E.; Pfleger, K.; Redfern, A.; et al. Honeybee venom and melittin suppress growth factor receptor activation in HER2-enriched and triple-negative breast cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, Z.M.; Nabiuni, M.; Parivar, K.; Abdirad, S.; Karimzadeh, L. Melittin inhibits the expression of key genes involved in tumor microenvironment formation by suppressing HIF-1α signaling in breast cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2021, 38, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-N.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, K.C. In Vitro and In Vivo Investigation of the Radiation-Sensitizing Effects of Melittin in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2022, 28, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Zarrinnahad, H.; Bagheri, K.P.; Moradia, A.; Shahbazzadeh, D. First report on the isolation of melittin from Iranian honey bee venom and evaluation of its toxicity on gastric cancer AGS cells. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2015, 78, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, S.; McClean, S. Melittin exhibits necrotic cytotoxicity in gastrointestinal cells which is attenuated by cholesterol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Peng, S.F.; Chueh, F.S.; Chen, P.Y.; Huang, Y.P.; Huang, W.W.; Chung, J.G. Melittin suppresses epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metastasis in human gastric cancer AGS cells via regulating Wnt/BMP-associated pathways. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 2250–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, C.; Rifi, M.; El-Obeid, D.; Mawlawi, H.; Sabatier, J.M.; Coutard, B.; Fajloun, Z. The cytotoxic effect of Apis mellifera venom with a synergistic potential of its two main components—Melittin and PLA2—On colon cancer HCT116 cell lines. Molecules 2021, 26, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, C.-M.; Luo, B.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Q. Melittin treatment prevents colorectal cancer from progressing in mice through ER stress-mediated apoptosis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2023, 75, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghi, H.; Mirzavi, F.; Afshari, A.R.; Jalili-Nik, M.; Mashkani, B.; Soukhtanloo, M. Bee venom induces anti-tumor effects in HT-29 colon cancer cells through regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Biologia 2022, 77, 3595–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Park, M.H.; Kollipara, P.S.; An, B.J.; Song, H.S.; Han, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Song, M.J.; Hong, J.T. Anticancer effect of bee venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, O.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Althagafi, A.A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Rizg, W.Y.; Mahdi, W.A.; Caruso, G.; et al. Cytotoxic and proapoptotic effects of a sub-toxic concentration of fluvastatin on OVCAR3 ovarian cancer cells after its optimized formulation to melittin nano-conjugates. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 642171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinnahad, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Hamidi, M.P.; Mahdavi, M.; Moradi, A.; Bagheri, K.P.; Shahbazzadeh, D. Apoptotic effect of melittin purified from Iranian honey bee venom on human cervical cancer HeLa cell line. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2018, 24, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.W.; Park, H.W.; Lee, H.W.; Chun, K.H. Bee venom inhibits the proliferation and migration of cervical-cancer cells in an HPV E6/E7-dependent manner. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elrefay, M.I.; Elfiky, A.A.; Sayed, R.H.; Zaki, H.F. Snake venom, bee venom, and their components exert an anticancer effect by triggering apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in prostate cancer. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2019, 57, 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.H.; Choi, M.S.; Kwak, D.H.; Oh, K.-W.; Yoon, D.Y.; Han, S.B.; Song, H.S.; Song, M.J.; Hong, J.T. Anti-cancer effect of bee venom in prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase pathway via inactivation of NF-κB. Prostate 2011, 71, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Bian, E.B.; Li, J. Melittin restores PTEN expression by down-regulating HDAC2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95520. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, H.; Ge, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, J.; Qin, Q.; Zhan, L.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Melittin enhances the radiosensitivity of hypoxic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing HIF-1α. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 10443–10448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Bae, S.-J.S.; Joo, H.; Bae, H. Melittin suppresses tumor progression by regulating tumor-associated macrophages in a Lewis lung carcinoma mouse model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 54951–54965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Lu, X.; Li, H.; Wen, C.; Huo, Z.; Xie, J.; Shi, M.; Tang, X.; Chen, H.; et al. Melittin inhibits tumor growth and decreases resistance to gemcitabine by downregulating cholesterol pathway gene CLU in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2017, 399, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-F.; Chen, Z. Melittin exerts an antitumor effect on non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipgomut, C.; Wongprommoon, A.; Takeo, E.; Ittiudomrak, T.; Puthong, S.; Chanchao, C. Melittin induced G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in chago-K1 human bronchogenic carcinoma cells and inhibited the differentiation of THP-1 cells into tumor-associated macrophages. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2018, 19, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, C.; Eastwood, S.; Truong, V.K.; Ramsland, P.A.; Elbourne, A. The membrane effects of melittin on gastric and colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jeong, H.; Bae, Y.; Shin, K.; Kang, S.; Kim, H.; Oh, J.; Bae, H. Targeting of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages with a melittin-based pro-apoptotic peptide. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Han, L. Melittin suppresses growth and induces apoptosis of non-small-cell lung cancer cells via down-regulation of TGF-β-mediated ERK signal pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 54, e9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Bae, H. Anti-inflammatory applications of melittin, a major component of bee venom: Detailed mechanism of action and adverse effects. Molecules 2016, 21, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Sun, G. Melittin-MIL-2 fusion protein as a candidate for cancer immunotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Jiang, M.; Li, Z.; Pu, F.; Gong, L.; Sun, L.; Gong, R.; Ji, G.; Si, J. Inhibitory Effect of Biosynthetic Nanoscale Peptide Melittin on Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Driven by Survivin Promoter. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Thapa, B.; Remant, K.C.; Xu, P. Dual secured nano-melittin for the safe and effective eradication of cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, B.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.; Wu, B.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.; Li, J. Melittin induces PTCH1 expression by down-regulating MeCP2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 288, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarokh, Z.; Naderi-Manesh, H.; Nazari, M. Towards prostate cancer gene therapy: Development of a chlorotoxin-targeted nanovector for toxic (melittin) gene delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, F.; Tan, J.; Peng, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, P.; Jia, S.; Yu, Q.; Huo, H.; Zhao, H. Melittin inhibits the invasion of MCF-7 cells by downregulating CD147 and MMP-9 expression. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hematyar, M.; Soleimani, M.; Es-Haghi, A.; Rezaei Mokarram, A. Synergistic co-delivery of doxorubicin and melittin using functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for cancer treatment: Loading and in vitro release study by LC–MS/MS. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. S3), 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabnejad, S.H.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Razavi, B.M. Targeted delivery of melittin to cancer cells by AS1411 anti-nucleolin aptamer. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.; Kumar, N.; Hammerschmid, D.; Privat-Maldonado, A.; Dewilde, S.; Bogaerts, A. Synergistic effects of melittin and plasma treatment: A promising approach for cancer therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbagh Moghaddam, F.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Marzbankia, E.; Farid, M.; Khaledi, L.; Reihani, A.H.; Javidfar, M.; Mortazavi, P. Delivery of melittin-loaded niosomes for breast cancer treatment: An in vitro and in vivo evaluation of anticancer effect. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ma, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, B.; Lin, J.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiao, P.; et al. TERT promoter regulating melittin expression induces apoptosis and G 0/G 1 cell cycle arrest in esophageal carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ruan, S.; Wang, Z.; Feng, N.; Zhang, Y. Hyaluronic Acid Coating Reduces the Leakage of Melittin Encapsulated in Liposomes and Increases Targeted Delivery to Melanoma Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombredane, A.S.; Andrade, L.R.; Bonadio, R.S.; Pinheiro, W.O.; Azevedo, R.B.; Joanitti, G.A. Melittin sensitizes skin squamous carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil by affecting cell proliferation and survival. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.H.; Jeong, C.; Yang, J.; Park, S.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Bae, H. Therapeutic Effect of Melittin–dKLA Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaleh, M.A.; Fahmy, O.; Al-Rabia, M.W.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Alsulimani, H.H.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Aldhabi, B.M.; et al. Hybrid nanoparticulate system of Fluvastatin loaded phospholipid, alpha lipoic acid and melittin for the management of colon cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Shang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Mo, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; et al. Melittin Tryptophan Substitution with a Fluorescent Amino Acid Reveals the Structural Basis of Selective Antitumor Effect and Subcellular Localization in Tumor Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.-Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, D.-Z.; Huang, X.-Q.; Gu, W.; Li, S.-X. Inhibitory effect of recombinant adenovirus carrying melittin gene on hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holle, L.; Song, W.; Holle, E.; Wei, Y.; Wagner, T.; Yu, X. A matrix metalloproteinase 2 cleavable melittin/avidin conjugate specifically targets tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 22, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ling, C.Q.; Zhang, C.; Gu, W.; Li, S.X.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yu, C.Q. The induced apoptosis of recombinant adenovirus carrying melittin gene for hepatocellular carcinoma cell. Chin. J. Hepatol. 2004, 12, 453–455. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, P.J.; Hewish, D.; Carter, T.; Sterling-Levis, K.; Ow, K.; Hattarki, M.; Doughty, L.; Guthrie, R.; Shapira, D.; Molloy, P.L.; et al. Cytotoxic properties of immunoconjugates containing melittin-like peptide 101 against prostate cancer: In vitro and in vivo studies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2004, 53, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gu, W.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.-Q.; Han, K.-Q.; Ling, C.-Q. Growth Arrest and Apoptosis of the Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line Bel-7402 Induced by Melittin. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2006, 29, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, N.R.; Baldwin, S.L.; Hu, G.; Marsh, J.N.; Lanza, G.M.; Heuser, J.E.; Arbeit, J.M.; Wickline, S.A.; Schlesinger, P.H. Molecularly targeted nanocarriers deliver the cytolytic peptide melittin specifically to tumor cells in mice, reducing tumor growth. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2830–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Menéndez-Gutiérrez, M.P.; Falco, A.; Carrato, A.; Saceda, M.; Micol, V. Selective death of human breast cancer cells by lytic immunoliposomes: Correlation with their HER2 expression level. Cancer Lett. 2010, 290, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Jin, H.; Qian, Y.; Qi, S.; Luo, H.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Z. Hybrid Melittin Cytolytic Peptide-Driven Ultrasmall Lipid Nanoparticles Block Melanoma Growth in Vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5791–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, X.; Han, W.; Diao, Y.; Han, D.; Tian, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, S.; Lei, L.; et al. Enhanced binding to and killing of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro by melittin when linked with a novel targeting peptide screened from phage display. J. Pept. Sci. 2013, 19, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Han, Y.; Fu, H.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y. Construction and expression of sTRAIL–melittin combining enhanced anticancer activity with antibacterial activity in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 97, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zong, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, G. A novel melittin-MhIL-2 fusion protein inhibits the growth of human ovarian cancer SKOV 3 cells in vitro and in vivo tumor growth. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qian, D.; Shao, G.; Yan, Z.; Li, R.; Hua, X.; Song, X.; Wang, B. High-level expression, purification, and study of bioactivity of fusion protein M-IL-2 (88Arg, 125Ala) in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 101, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Jung, J.W.; Lee, M.O.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, B.; Jin, H.J.; Kim, J.; Ahn, Y.-J.; Lee, K.W.; Song, Y.S.; et al. Functional characterization of naturally occurring melittin peptide isoforms in two honey bee species, Apis mellifera and Apis cerana. Peptides 2014, 53, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.P.; Huang, S.R.; Zhou, J.Y.; Zou, X. Synergistic interaction between melittin and chemotherapeutic agents and their possible mechanisms: An experimental research. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2014, 34, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.-Y.; Wang, K.-L.; Fang, F.-F.; Gu, W.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.-Z.; Li, B.; Wang, L.-N. Triple-controlled oncolytic adenovirus expressing melittin to exert inhibitory efficacy on hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10403. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.; Chang, W.; Cui, M.; Lin, Y.; Wu, S.; Xu, T. Expression and anticancer activity analysis of recombinant human uPA1-43-melittin. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Chang, W.; Zhang, K.; Cui, M.; Wu, S.; Xu, T. Expression and purification of recombinant ATF-mellitin, a new type fusion protein targeting ovarian cancer cells, in P. pastoris. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Xia, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Xiao, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, G. Genetically engineered nano-melittin vesicles for multimodal synergetic cancer therapy. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, e10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Das, B.; Mote, C. In vivo and in vitro experimentation for scientific validation of the traditional use of Chromolaena odorata (L.) against envenomation of honey bee sting. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2023, 23, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.C.; Min, K.A.; Cheong, H.; Moon, C.; Huang, Y.; He, H.; Yang, V.C. Preparation and characterization of gelonin-melittin fusion biotoxin for synergistically enhanced anti-tumor activity. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Liu, S.; Ai, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Hu, K.; Gao, X.; Yang, Y. A novel melittin nano-liposome exerted excellent anti-hepatocellular carcinoma efficacy with better biological safety. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Chen, F.; Lu, M.; Stenzel, M.H.; Xiao, P. Polypeptide-grafted nanodiamonds for controlled release of melittin to treat breast cancer. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniluk, K.; Kutwin, M.; Grodzik, M.; Wierzbicki, M.; Strojny, B.; Szczepaniak, J.; Bałaban, J.; Sosnowska, M.; Chwalibog, A.; Sawosz, E.; et al. Use of Selected Carbon Nanoparticles as Melittin Carriers for MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Materials 2019, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, T.; Lin, Y.; Huang, S.; Cao, S.; Wang, X.; Su, Y.; Lin, Z. Graphene oxide-based magnetic nanocomposites for the delivery of melittin to cervical cancer HeLa cells. Nanotechnology 2019, 31, 065102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, S.; Liu, L.; Lu, L.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Z. Melittin-lipid nanoparticles target to lymph nodes and elicit a systemic anti-tumor immune response. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Sylvestre, M.; Song, K.; Pun, S.H. Development of D-melittin polymeric nanoparticles for anti-cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Shi, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wang, A.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; et al. Stable Loading and Delivery of Melittin with Lipid-Coated Polymeric Nanoparticles for Effective Tumor Therapy with Negligible Systemic Toxicity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55902–55912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, P.; Abnous, K.; Balarastaghi, S.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Saeedi, M.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Mahmoudi, M. Aptamer AS1411-functionalized gold nanoparticle-melittin complex for targeting MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Nanomed. J. 2022, 9, 164–169. [Google Scholar]


| Components of Bee Venom | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Melittin | Fructose | 2-nonanol | Tertiapin |
| Apamin | Glucose | n-decyl acetate | Melittin F |
| MCD Peptide | Isopentanol | Phosphorous | Acid phosphatase |
| Secarpin | Benzyl acetate | Calcium | Hyaluronidase |
| Minimise | Isopentyl acetate | Magnesium | Phospholipase B |
| Procamine A, B | n-butyl acetate | Noradrenaline | Phospholipase A2 |
| Protease inhibitor | n-octyl acetate | Histamine | a-Glucosidase |
| Cardiopep | Benzyl alcohol | Dopamine | Phospholipase |
| Cancer | Cancer Model | Anticancer Effect | Molecular Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver cancer | MHCC97L and MHCC97H cells; Nude mice | Antimetastatic, reduced cell migration, and motility | Rac1-dependent inhibition | [25] |
| HepG2 cells | Cell growth arrest and apoptotic induction | - | [26] | |
| SMMC-7721, Huh7, and Hep G2 cells; xenograft tumor model | Tumor growth inhibition, reduced cell migration, and motility | Reduced expression of HIF-1α, VEGF, p-Akt, and MMP-2/9 | [27] | |
| HepG2 cells | Cell growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest | Reduced expression of Bcl-2, VEGF, Nf-κB, HIF-1a, Cyclin-D1, Rac1, and MMP9 Increased expression of p53, Bax, PTEN, Cas7, and Cas3 | [28] | |
| Breast cancer | MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 cells | Reduced tumor cell migration and invasion | Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR/Akt/ pathway and NF-κB Reduced MMP-9 expression | [29] |
| 4T1 cells | Decreased cell proliferation and apoptotic induction | Upregulated Drp1 and Mfn1 mRNA expression levels | [30] | |
| MCF 10A, MCF-12A cells; allograft TNBC model | Apoptotic induction decreased chemoresistance | Suppressed HER2, MAPK, and EGFR activation | [31] | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Inhibited cell growth, apoptotic induction, and modulation of tumor microenvironment | Deregulated VEGFA, LDHA, and NFκB expression levels Increased TNFA and BAX expression levels Inhibition of HIF-1α cell signaling pathway | [32] | |
| 4T1, MCF-7 cells; xenograft mouse model | Inhibited tumor growth, apoptotic induction, increased radiosensitivity and | Increased Bax Decreased Bcl-2 | [33] | |
| Gastric cancer | AGS cell line | Inhibited cell growth, and apoptotic induction | - | [34] |
| SGC-7901 cells | Inhibited cell growth, and apoptotic induction | Enhanced ROS, caspase-3, cyt C, AIF, Endo G | [24,35] | |
| AGS cell line | Reduced cell viability, antimetastatic effect, reduced cell migration and motility | Reduced expression of Wnt/BMP and MMP-2 signaling pathway proteins | [36] | |
| Colorectal cancer | HCT-116, SW-480 cells | Inhibited cell growth, apoptotic induction | Increased Fas receptors, caspase 9, and members of the Bcl-2 family | [19] |
| HCT-116 cells | Increased cytotoxic effect, apoptotic induction | Membrane disruption | [37] | |
| Colon cancer cells | SW480 cells; SW480 tumor-bearing mice | Suppressed cancer growth, apoptotic induction | Stimulated ER stress Imbalance in calcium homeostasis | [38] |
| HT-29 cells | Antitumor and anti-inflammatory effects | Reduced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin one beta (IL-1β) | [39] | |
| Ovarian cancer cells | SKOV3 and PA-1 cells | Inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis | Increased expression of death receptors (DR3 and DR6) Increased expression of caspase-3, 8, and Bax Increased expression of cleaved caspase-3 Inhibition of the STAT3 pathway | [40] |
| OVCAR3 cells | Increased cytotoxicity and cell cycle arrest significant proapoptotic and pro-necrotic activities | Modulated BAX/BCL-2 ratio | [41] | |
| Cervical cancer cells | HeLa | Induced apoptotic cell death, inhibited cell proliferation | - | [42] |
| C33A, Caski, HeLa cells | Induced apoptosis and inhibit wound healing and migration | Reduced expression of HPV E6 and E7, cyclin A and B, AKT, JNK, p38, and ERK | [43] | |
| Prostate cancer cells | PC-3 cells | Induced apoptotic cell death, inhibited cell proliferation | Decreased expression of Bcl-2, PCA3, upregulated Bax level | [44] |
| LNCaP, DU145, PC-3 cells | Inhibited cell growth, induced apoptotic cell death, | Suppression of NF-kB, Bcl-2, Cox-2, increased expression of caspase-3/9 | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandey, P.; Khan, F.; Khan, M.A.; Kumar, R.; Upadhyay, T.K. An Updated Review Summarizing the Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin from Bee Venom in Several Models of Human Cancers. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143111
Pandey P, Khan F, Khan MA, Kumar R, Upadhyay TK. An Updated Review Summarizing the Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin from Bee Venom in Several Models of Human Cancers. Nutrients. 2023; 15(14):3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143111
Chicago/Turabian StylePandey, Pratibha, Fahad Khan, Minhaj Ahmad Khan, Rajnish Kumar, and Tarun Kumar Upadhyay. 2023. "An Updated Review Summarizing the Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin from Bee Venom in Several Models of Human Cancers" Nutrients 15, no. 14: 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143111
APA StylePandey, P., Khan, F., Khan, M. A., Kumar, R., & Upadhyay, T. K. (2023). An Updated Review Summarizing the Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin from Bee Venom in Several Models of Human Cancers. Nutrients, 15(14), 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143111







