Combined Ingestion of Tea Catechin and Citrus β-Cryptoxanthin Improves Liver Function via Adipokines in Chronic Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Generation of Obese Mice
2.3. Weight Measurement and Measurement of Food and Water Intake
2.4. Administration of Green Tea Catechins and/or Β-Cryptoxanthin
2.5. Blood Biochemistry Analysis
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
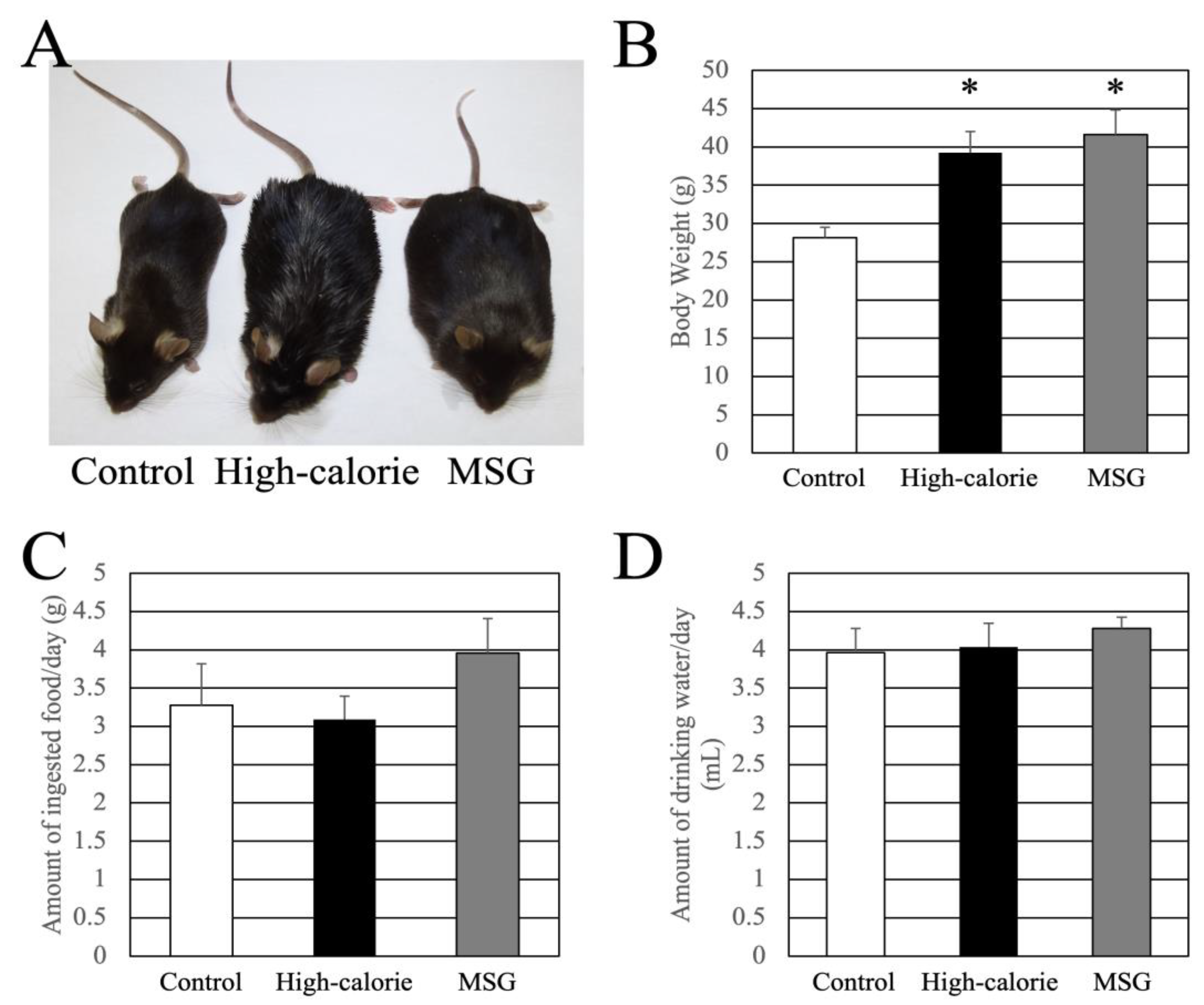
3.1. Body Weight and Food and Water Intake at 15 Weeks of Age
3.2. Changes in Body Weight and Blood Biochemistry
3.3. Changes in Adipocyte Size and Adipocyte Inflammatory Response
3.4. Reactions to Adipocytes in the Liver and Changes in Liver Structure and Function
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, J.; Pei, Z.; Sun, C.; He, J.; Qian, T.; Luo, F.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z. Nationwide Trends of Pediatric Obesity and BMI z-Score From 2017-2021 in China: Comparable Findings from Real-World Mobile- and Hospital-Based Data. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 859245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, G.; Elbaz-Greener, G.; Margolis, G.; Marai, I.; Heist, E.K.; Ruskin, J.N.; Carasso, S.; Roguin, A.; Birati, E.Y.; Amir, O. The Obesity Paradox in Real-World Nation-Wide Cohort of Patients Admitted for a Stroke in the U.S. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Huayllani, M.T.; Lu, X.; Boczar, D.; Cinotto, G.; Avila, F.R.; Guliyeva, G.; Forte, A.J. Effects of diet-induced obesity in the development of lymphedema in the animal model: A literature review. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 16, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovat, N.E.J.; Legare, D.J.; Lautt, W.W. An animal model of gestational obesity and prediabetes: HISS-dependent insulin resistance induced by a high-sucrose diet in Sprague Dawley rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Farias, B.X.; Costa, A.B.; Engel, N.A.; de Souza Goldim, M.P.; da Rosa Turatti, C.; Cargnin-Cavalho, A.; Fortunato, J.J.; Petronilho, F.; Jeremias, I.C.; Rezin, G.T. Donepezil Prevents Inhibition of Cerebral Energetic Metabolism Without Altering Behavioral Parameters in Animal Model of Obesity. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parfait, B.; Galba Jean, B.; Roger, P.; Hervé Hervé, N.A.; Balbine, K.K.; Guillaume, C.W.; Simon Desire, G.N.; Linda, D.K.J.; Lea Blondelle, K.D.; Germain, S.T. Antioxidant and Anticholinesterase Properties of the Aqueous Extract of Balanites aegyptiaca L. Delile Fruit Pulp on Monosodium Glutamate-Induced Excitotoxicity in Swiss Mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 7576132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, J.I.H.N.; Zazula, M.F.; Rodrigues, D.F.S.; Boaro, C.D.T.; Boaretto, M.L.; de Andrade, B.Z.; Schneider, S.C.S.; Naliwaiko, K.; Torrejais, M.M.; Costa, R.M.; et al. Whole-Body Vibration Promotes Skeletal Muscle Restructuring and Reduced Obesogenic Effect of MSG in Wistar Rats. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 3594–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luqman, E.M.; Ananda, A.T.; Widjiati, W.; Hendrawan, V.F. Protective Effect of Apis dorsata Honey on Chronic Monosodium Glutamate-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Mus musculus Mice. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 19, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnano, M.A.; Chafel, T.L.; Pilcher, W.H.; Joseph, S.A. The distribution of enkephalin in the mediobasal hypothalamus of the mouse brain: Effects of neonatal administration of MSG. Brain Res. 1982, 236, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olney, J.W. Brain Lesions, Obesity, and Other Disturbances in Mice Treated with Monosodium Glutamate. Science 1969, 164, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakadate, K.; Hirakawa, T.; Tanaka-Nakadate, S. Small intestine barrier function failure induces systemic inflammation in monosodium glutamate-induced chronically obese mice. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakadate, K.; Motojima, K.; Tanaka-Nakadate, S. Dilatation of Sinusoidal Capillary and Swelling of Sinusoidal Fenestration in Obesity: An Ultrastructural Study. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2015, 39, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakadate, K.; Motojima, K.; Kamata, S.; Yoshida, T.; Hikita, M.; Wakamatsu, H. Pathological Changes in Hepatocytes of Mice with Obesity-induced Type 2 Diabetes by Monosodium Glutamate. Yakugaku Zasshi 2014, 134, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogodziński, D.; Ostrowska, L.; Smarkusz-Zarzecka, J.; Zyśk, B. Secretome of Adipose Tissue as the Key to Understanding the Endocrine Function of Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumminia, A.; Vinciguerra, F.; Parisi, M.; Graziano, M.; Sciacca, L.; Baratta, R.; Frittitta, L. Adipose Tissue, Obesity and Adiponectin: Role in Endocrine Cancer Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froy, O.; Garaulet, M. The Circadian Clock in White and Brown Adipose Tissue: Mechanistic, Endocrine, and Clinical Aspects. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Ceccarini, G.; Scabia, G.; Barone, I.; Pelosini, C.; Ferrari, F.; Magno, S.; Dattilo, A.; Chiovato, L.; Vitti, P.; et al. Lipodystrophy and obesity are associated with decreased number of T cells with regulatory function and pro-inflammatory macrophage phenotype. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylikova, J.; Dvorackova, J.; Tauber, Z.; Kamarad, V. M1/M2 macrophage polarization in human obese adipose tissue. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2018, 162, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Imai, Y.; Shimozawa, N.; Hioki, K.; Uchida, S.; Ito, Y.; Takakuwa, K.; Matsui, J.; et al. Globular Adiponectin Protected ob/ob Mice from Diabetes and ApoE-deficient Mice from Atherosclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Nio, Y.; Maki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takazawa, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; et al. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, O.; Funaba, M.; Sekiyama, K.; Doi, S.; Shindo, D.; Satoh, R.; Itoi, H.; Oiwa, H.; Morita, M.; Suzuki, C.; et al. Activin E Controls Energy Homeostasis in Both Brown and White Adipose Tissues as a Hepatokine. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolin, J.; Ødegård, R.A.; Amundsen, V.V.; Köpp, U.M.S.; Kokkvoll, A.; Júlíusson, P.B.; Hjelmesæth, J. Supplementary drug treatment to reduce weight in adolescents with severe obesity. Tidsskr. Den Nor. Legeforening 2022, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, C.J.; Hu, L.; Kharmats, A.Y.; Curran, M.; Berube, L.; Wang, C.; Pompeii, M.L.; Illiano, P.; St-Jules, D.E.; Mottern, M.; et al. Effect of a Personalized Diet to Reduce Postprandial Glycemic Response vs a Low-fat Diet on Weight Loss in Adults with Abnormal Glucose Metabolism and Obesity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2233760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, T.; Meguro, S.; Hase, T.; Otsuka, K.; Komikado, M.; Tokimitsu, I.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamamoto, K. A Catechin-rich Beverage Improves Obesity and Blood Glucose Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Obesity 2009, 17, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, K.C.; Reeves, M.S.; Farmer, M.; Yasunaga, K.; Matsuo, N.; Katsuragi, Y.; Komikado, M.; Tokimitsu, I.; Wilder, D.; Jones, F.; et al. Green Tea Catechin Consumption Enhances Exercise-Induced Abdominal Fat Loss in Overweight and Obese Adults. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, T.; Nagasawa, A.; Suzuki, J.; Hase, T.; Tokimitsu, I. Beneficial effects of tea catechins on diet-induced obesity: Stimulation of lipid catabolism in the liver. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakadate, K.; Kawakami, K.; Yamazaki, N. Anti-Obesity and Anti-Inflammatory Synergistic Effects of Green Tea Catechins and Citrus β-Cryptoxanthin Ingestion in Obese Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakadate, K.; Motojima, K.; Hirakawa, T.; Tanaka-Nakadate, S. Progressive Depletion of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum in Epithelial Cells of the Small Intestine in Monosodium Glutamate Mice Model of Obesity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5251738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, R.; Kawakami, K.; Nakadate, K. Effects of Smart Drugs on Cholinergic System and Non-Neuronal Acetylcholine in the Mouse Hippocampus: Histopathological Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakadate, K.; Kamata, S. Severe Acute Hepatic Dysfunction Induced by Ammonium Acetate Treatment Results in Choroid Plexus Swelling and Ventricle Enlargement in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneshiro, T.; Matsushita, M.; Hibi, M.; Tone, H.; Takeshita, M.; Yasunaga, K.; Katsuragi, Y.; Kameya, T.; Sugie, H.; Saito, M. Tea catechin and caffeine activate brown adipose tissue and increase cold-induced thermogenic capacity in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirengi, S.; Amagasa, S.; Homma, T.; Yoneshiro, T.; Matsumiya, S.; Kurosawa, Y.; Sakane, N.; Ebi, K.; Saito, M.; Hamaoka, T. Daily ingestion of catechin-rich beverage increases brown adipose tissue density and decreases extramyocellular lipids in healthy young women. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikita, M.; Motojima, K.; Kamata, S.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka-Nakadate, S.; Nakadate, K. Protective Efficacy of the Ingestion of Mandarin Orange Containing β-Cryptoxanthin on Lipopolysaccharide-induced Acute Nephritis. Yakugaku Zasshi 2016, 136, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sene-Fiorese, M.; Duarte, F.O.; de Aquino Junior, A.E.; Campos, R.M.; Masquio, D.C.L.; Tock, L.; de Oliveira Duarte, A.C.; Dâmaso, A.R.; Parizotto, N.A.; Bagnato, V.S. The potential of phototherapy to reduce body fat, insulin resistance and “metabolic inflexibility” related to obesity in women undergoing weight loss treatment. Lasers Surg. Med. 2015, 47, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadde, K.M.; Yancy, W.S. Obesity medications reduce total body weight by 3–9% compared with placebo, when combined with lifestyle changes. Evid. Based Nurs. 2015, 18, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ikeda, I.; Tsuda, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Unno, T.; Tomoyori, H.; Goto, H.; Kawata, Y.; Imaizumi, K.; Nozawa, A.; et al. Tea Catechins with a Galloyl Moiety Suppress Postprandial Hypertriacylglycerolemia by Delaying Lymphatic Transport of Dietary Fat in Rats. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.S.; Bharadwaj, P.; Bilal, M.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Taboada, P.; Bungau, S.; Kyzas, G.Z. Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery, Imaging, and Theragnosis. Polymers 2020, 12, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchacki, K.J.; Stimson, R.H. Nutritional Regulation of Human Brown Adipose Tissue. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armani, A.; Feraco, A.; Camajani, E.; Gorini, S.; Lombardo, M.; Caprio, M. Nutraceuticals in Brown Adipose Tissue Activation. Cells 2022, 11, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, I.; Kobayashi, M.; Hamada, T.; Tsuda, K.; Goto, H.; Imaizumi, K.; Nozawa, A.; Sugimoto, A.; Kakuda, T. Heat-Epimerized Tea Catechins Rich in Gallocatechin Gallate and Catechin Gallate Are More Effective to Inhibit Cholesterol Absorption than Tea Catechins Rich in Epigallocatechin Gallate and Epicatechin Gallate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7303–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, I.; Imasato, Y.; Sasaki, E.; Nakayama, M.; Nagao, H.; Takeo, T.; Yayabe, F.; Sugano, M. Tea catechins decrease micellar solubility and intestinal absorption of cholesterol in rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Lipids Lipid Metab. 1992, 1127, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, O.; Kajimoto, Y.; Yabune, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kotani, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Nozawa, A.; Nagata, K.; Unno, T.; Sagesaka, Y.M.; et al. Tea Catechins with a Galloyl Moiety Reduce Body Weight and Fat. J. Health Sci. 2005, 51, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Horlad, H.; Shiraishi, D.; Tsuboki, J.; Kudo, R.; Ikeda, T.; Nohara, T.; Takeya, M.; Komohara, Y. Onionin A, a sulfur-containing compound isolated from onions, impairs tumor development and lung metastasis by inhibiting the protumoral and immunosuppressive functions of myeloid cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2467–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wang, D.; Yu, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Jiao, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Feng, J. Activated M1 macrophages suppress c-kit expression via TNF-α-mediated upregulation of miR-222 in Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, T.; Inoue, M.; Kubota, N.; Takamoto, I.; Mineyama, T.; Iwayama, K.; Tokuyama, K.; Moroi, M.; Ueki, K.; Yamauchi, T.; et al. Downregulation of macrophage Irs2 by hyperinsulinemia impairs IL-4-indeuced M2a-subtype macrophage activation in obesity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, M.; Stępień, A.; Wlazeł, R.N.; Paradowski, M.; Banach, M.; Rysz, M.; Rysz, J. Obesity indices and adipokines in non-diabetic obese patients with early stages of chronic kidney disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2013, 19, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, F.; Margaritis, M.; Antoniades, C. Perivascular Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ: The Role of Statins. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 7055–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, F.; Maldonado, M.; Chen, J.; Duan, H.; Zhou, S.; Yang, L.; Raja, M.A.; Huang, T.; Jiang, G.; Zhong, Y. Effects of caloric overload before caloric restriction in the murine heart. Aging 2022, 14, 2695–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, T.-Y.; Hong, J.-Y.; Kim, G.-J.; Oh, J.-B.; Kim, M.-J.; Apostolidis, E.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kwon, Y.-I. Anti-Obesity and Anti-Adipogenic Effects of Administration of Arginyl-Fructose-Enriched Jeju Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Extract in C57BL/6 Mice and in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes Models. Molecules 2022, 27, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshitomi, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Kumazoe, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Yonekura, M.; Shimamoto, Y.; Nakasone, A.; Kondo, S.; Hattori, H.; Haseda, A.; et al. The combined effect of green tea and α-glucosyl hesperidin in preventing obesity: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakadate, K.; Kawakami, K.; Yamazaki, N. Combined Ingestion of Tea Catechin and Citrus β-Cryptoxanthin Improves Liver Function via Adipokines in Chronic Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153345
Nakadate K, Kawakami K, Yamazaki N. Combined Ingestion of Tea Catechin and Citrus β-Cryptoxanthin Improves Liver Function via Adipokines in Chronic Obesity. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153345
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakadate, Kazuhiko, Kiyoharu Kawakami, and Noriko Yamazaki. 2023. "Combined Ingestion of Tea Catechin and Citrus β-Cryptoxanthin Improves Liver Function via Adipokines in Chronic Obesity" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153345
APA StyleNakadate, K., Kawakami, K., & Yamazaki, N. (2023). Combined Ingestion of Tea Catechin and Citrus β-Cryptoxanthin Improves Liver Function via Adipokines in Chronic Obesity. Nutrients, 15(15), 3345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153345





