Exploring Caloric Restriction in Inpatients with Eating Disorders: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations with Body Dissatisfaction, Body Avoidance, Clinical Factors, and Psychopathology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Provide an assessment of the degree of caloric restriction (CR) in a population of individuals with ED at their first access to inpatient treatment, and investigate the associations between CR and a comprehensive battery of psychopathological variables.
- (2)
- Explore the relationship linking body image questionnaires, CR, weight suppression, and other clinical variables.
- (3)
- Explore the predictors of caloric intake and restriction at the end of inpatient treatment for underweight individuals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Questionnaires
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Caloric Restriction and Correlations
3.2. Body Dissatisfaction, Caloric Restriction, and Weight Suppression
3.3. Predictors of Caloric Intake/Restriction at End of Inpatient Treatment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stewart, T.M.; Martin, C.K.; Williamson, D.A. The Complicated Relationship Between Dieting, Dietary Restraint, Caloric Restriction, and Eating Disorders: Is a Shift in Public Health Messaging Warranted? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magkos, F. Is Calorie Restriction Beneficial for Normal-Weight Individuals? A Narrative Review of the Effects of Weight Loss in the Presence and Absence of Obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 1811–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.M.; Gardner, A.M.; Handley, C.E.; Smith, M.W.; Christensen, W.F.; Hancock, C.R.; Joseph, P.V.; Larson, M.J.; Martin, C.K.; LeCheminant, J.D. Body Shape Perception in Men and Women Without Obesity During Caloric Restriction: A Secondary Analysis from the CALERIE Study. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2023, 28, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, D.A.; Martin, C.K.; Anton, S.D.; York-Crowe, E.; Han, H.; Redman, L.; Ravussin, E. Is Caloric Restriction Associated with Development of Eating-Disorder Symptoms? Results from the CALERIE Trial. Health Psychol. 2008, 27, S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Guideline Alliance (UK). Eating Disorders: Recognition and Treatment; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2017.
- Marzola, E.; Martini, M.; Brustolin, A.; Abbate-Daga, G. Inpatients with Severe-Enduring Anorexia Nervosa: Understanding the “Enduringness” Specifier. Eur. Psychiatry 2021, 64, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissileff, H.; Brunstrom, J.; Tesser, R.; Bellace, D.; Berthod, S.; Thornton, J.; Halmi, K. Computerized Measurement of Anticipated Anxiety from Eating Increasing Portions of Food in Adolescents with and Without Anorexia Nervosa: Pilot Studies. Appetite 2016, 97, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzola, E.; Porliod, A.; Panero, M.; De-Bacco, C.; Abbate-Daga, G. Affective Temperaments and Eating Psychopathology in Anorexia Nervosa: Which Role for Anxious and Depressive Traits? J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 266, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limburg, K.; Watson, H.J.; Hagger, M.S.; Egan, S.J. The Relationship Between Perfectionism and Psychopathology: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Psychol. 2017, 73, 1301–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodgers, R.F.; Smith, K.; Murray, S.B. Cognitive Rigidity and Restrictive Eating Disorders: Delineating the Impact of Low Weight, Low Fat, Weight Suppression, Acute Negative Energy Balance, and Chronic Restriction. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 56, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, K.A.; Heron, K.E.; Ebener, D. Associations Among Weight Suppression, Self-Acceptance, Negative Body Image, and Eating Disorder Behaviors Among Women with Eating Disorder Symptoms. Women Health 2021, 61, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meule, A.; Kolar, D.R.; Voderholzer, U. Weight Suppression and Body Mass Index at Admission Interactively Predict Weight Trajectories During Inpatient Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa. J. Psychosom. Res. 2022, 158, 110924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessler, J.B.; Diedrich, A.; Greetfeld, M.; Schlegl, S.; Schwartz, C.; Voderholzer, U. Weight Suppression but Not Symptom Improvement Predicts Weight Gain During Inpatient Treatment for Bulimia Nervosa. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2018, 26, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.R.; Marti, C.N.; Lesser, E.L.; Stice, E. Weight Suppression Uniquely Predicts Body Fat Gain in First-Year Female College Students. Eat. Behav. 2019, 32, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.R.; Piers, A.D.; Benson, L. Weight Suppression in Eating Disorders: A Research and Conceptual Update. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uniacke, B.; Attia, E.; Kaplan, A.; Walsh, B.T. Weight Suppression and Weight Maintenance Following Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lock, J.; Litt, I. What Predicts Maintenance of Weight for Adolescents Medically Hospitalized for Anorexia Nervosa? Eat. Disord. 2003, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegl, S.; Quadflieg, N.; Löwe, B.; Cuntz, U.; Voderholzer, U. Specialized Inpatient Treatment of Adult Anorexia Nervosa: Effectiveness and Clinical Significance of Changes. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zawada, A.; Machowiak, A.; Rychter, A.M.; Ratajczak, A.E.; Szymczak-Tomczak, A.; Dobrowolska, A.; Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. Accumulation of Advanced Glycation End-Products in the Body and Dietary Habits. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettiga, A.; Fiorio, F.; Di Marco, F.; Trevisani, F.; Romani, A.; Porrini, E.; Salonia, A.; Montorsi, F.; Vago, R. The Modern Western Diet Rich in Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs): An Overview of Its Impact on Obesity and Early Progression of Renal Pathology. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misra, M.; Tsai, P.; Anderson, E.J.; Hubbard, J.L.; Gallagher, K.; Soyka, L.A.; Miller, K.K.; Herzog, D.B.; Klibanski, A. Nutrient Intake in Community-Dwelling Adolescent Girls with Anorexia Nervosa and in Healthy Adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovalčíková, A.G.; Tichá, L.; Šebeková, K.; Celec, P.; Čagalová, A.; Sogutlu, F.; Podracká, L. Oxidative Status in Plasma, Urine and Saliva of Girls with Anorexia Nervosa and Healthy Controls: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.J.; Yilmaz, Z.; Thornton, L.M.; Hübel, C.; Coleman, J.R.; Gaspar, H.A.; Bryois, J.; Hinney, A.; Leppä, V.M.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Eight Risk Loci and Implicates Metabo-Psychiatric Origins for Anorexia Nervosa. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Seitz, J.; Baines, J. Food Matters: How the Microbiome and Gut–Brain Interaction Might Impact the Development and Course of Anorexia Nervosa. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, M.J.; Perrini, A.A.; Eckel, L.A. The Role of the Gut Microbiome, Immunity, and Neuroinflammation in the Pathophysiology of Eating Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, B.; Campbell, I.C.; Chung, R.; Breen, G.; Schmidt, U.; Himmerich, H. Inflammatory Markers in Anorexia Nervosa: An Exploratory Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettersson, C.; Svedlund, A.; Wallengren, O.; Swolin-Eide, D.; Karlsson, G.P.; Ellegård, L. Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status in Adolescents and Young Adults with Anorexia Nervosa: A 3-Year Follow-up Study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5391–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucoin, M.; LaChance, L.; Naidoo, U.; Remy, D.; Shekdar, T.; Sayar, N.; Cardozo, V.; Rawana, T.; Chan, I.; Cooley, K. Diet and Anxiety: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calugi, S.; Milanese, C.; Sartirana, M.; El Ghoch, M.; Sartori, F.; Geccherle, E.; Coppini, A.; Franchini, C.; Dalle Grave, R. The Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire: Reliability and Validity of the Italian Version. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2017, 22, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzola, E.; Martini, M.; Longo, P.; Toppino, F.; Bevione, F.; Delsedime, N.; Abbate-Daga, G.; Preti, A. Psychometric Properties of the Italian Body Shape Questionnaire: An Investigation of Its Reliability, Factorial, Concurrent, and Criterion Validity. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2022, 27, 3637–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, G.; Molinari, E. Replicated Factor Analysis of the Italian Version of the Body Image Avoidance Questionnaire. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1998, 86, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Longo, P.; Delsedime, N.; Abbate-Daga, G.; Panero, M. Increased General, Eating, and Body-Related Psychopathology in Inpatients in a Specialized Eating Disorders Unit After the Beginning of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Comparison with the Pre-Pandemic Period. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, R.; Pancheri, P. Questionario di Valutazione Dell’ansia di Stato e di Tratto [State-Trait Anxiety Inventory]; Organizzazioni Speciali: Firenze, Italy, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Baggio, A.; Ferrari, R.; Partinico, M.; Vidotto, G.; Visentin, M. Il Beck Depression Inventory Per La Valutazione Della Depressione Nel Dolore Cronico. Il Contributo Degli “Item” Somatici. Int. J. Pain Ther. 1997, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, C. Adattamento Italiano Della Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale (MPS). Psicoter. Cogn. Comport. 2008, 14, 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- First, M.B.; Williams, J.B.; Karg, R.S.; Spitzer, R.L. User’s Guide for the SCID-5-CV Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Disorders: Clinical Version; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- El Ghoch, M.; Alberti, M.; Capelli, C.; Calugi, S.; Dalle Grave, R. Resting Energy Expenditure in Anorexia Nervosa: Measured Versus Estimated. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 652932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Polito, A.; De Filippo, E.; Cuzzolaro, M.; Ciarapica, D.; Contaldo, F.; Scalfi, L. Are the General Equations to Predict BMR Applicable to Patients with Anorexia Nervosa? Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2002, 7, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, A.; Fabbri, A.; Ferro-Luzzi, A.; Cuzzolaro, M.; Censi, L.; Ciarapica, D.; Fabbrini, E.; Giannini, D. Basal Metabolic Rate in Anorexia Nervosa: Relation to Body Composition and Leptin Concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scalfi, L.; Marra, M.; De Filippo, E.; Caso, G.; Pasanisi, F.; Contaldo, F. The Prediction of Basal Metabolic Rate in Female Patients with Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Obes. 2001, 25, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forman-Hoffman, V.L.; Ruffin, T.; Schultz, S.K. Basal Metabolic Rate in Anorexia Nervosa Patients: Using Appropriate Predictive Equations During the Refeeding Process. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 2006, 18, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifflin, M.D.; St Jeor, S.T.; Hill, L.A.; Scott, B.J.; Daugherty, S.A.; Koh, Y.O. A New Predictive Equation for Resting Energy Expenditure in Healthy Individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fife, D.A.; D’Onofrio, J. Common, Uncommon, and Novel Applications of Random Forest in Psychological Research. Behav. Res. Methods 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lüdecke, D.; Ben-Shachar, M.S.; Patil, I.; Wiernik, B.M.; Makowski, D. Easystats: Framework for Easy Statistical Modeling, Visualization, and Reporting. CRAN 2022. Available online: https://easystats.github.io/easystats/ (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Hothorn, T.; Hornik, K.; Zeileis, A. Unbiased Recursive Partitioning: A Conditional Inference Framework. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2006, 15, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leisch, F. FlexMix: A General Framework for Finite Mixture Models and Latent Class Regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2004, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fife, D. Flexplot: Graphically Based Data Analysis Using ‘Flexplot’. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/dustinfife/flexplot (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteleone, A.M.; Cascino, G. A Systematic Review of Network Analysis Studies in Eating Disorders: Is Time to Broaden the Core Psychopathology to Non Specific Symptoms. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2021, 29, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toppino, F.; Longo, P.; Martini, M.; Abbate-Daga, G.; Marzola, E. Body Mass Index Specifiers in Anorexia Nervosa: Anything Below the “Extreme”? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavender, J.M.; Shaw, J.A.; Crosby, R.D.; Feig, E.H.; Mitchell, J.E.; Crow, S.J.; Hill, L.; Le Grange, D.; Powers, P.; Lowe, M.R. Associations Between Weight Suppression and Dimensions of Eating Disorder Psychopathology in a Multisite Sample. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 69, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulik, C.M.; Tozzi, F.; Anderson, C.; Mazzeo, S.E.; Aggen, S.; Sullivan, P.F. The Relation Between Eating Disorders and Components of Perfectionism. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Marzola, E.; Brustolin, A.; Abbate-Daga, G. Feeling Imperfect and Imperfectly Feeling: A Network Analysis on Perfectionism, Interoceptive Sensibility, and Eating Symptomatology in Anorexia Nervosa. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2021, 29, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kaap-Deeder, J.; Smets, J.; Boone, L. The Impeding Role of Self-Critical Perfectionism on Therapeutic Alliance During Treatment and Eating Disorder Symptoms at Follow-up in Patients with an Eating Disorder. Psychol. Belg. 2016, 56, 101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaumberg, K.; Reilly, E.E.; Gorrell, S.; Levinson, C.A.; Farrell, N.R.; Brown, T.A.; Smith, K.M.; Schaefer, L.M.; Essayli, J.H.; Haynos, A.F.; et al. Conceptualizing Eating Disorder Psychopathology Using an Anxiety Disorders Framework: Evidence and Implications for Exposure-Based Clinical Research. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 83, 101952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S.; Schmidt, U.; Khondoker, M.; Tchanturia, K. Can Psychological Interventions Reduce Perfectionism? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2015, 43, 705–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dalle Grave, R.; Sartirana, M.; Calugi, S.; Dalle Grave, R.; Sartirana, M.; Calugi, S. Coexisting Psychological Problems. In Complex Cases and Comorbidity in Eating Disorders: Assessment and Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 59–77. [Google Scholar]
- Langlet, B.; Vestermark, F.; Stolt, J.; Zandian, M.; Södersten, P.; Bergh, C. Physical Activity and Sleep During the First Week of Anorexia Nervosa Inpatient Care. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
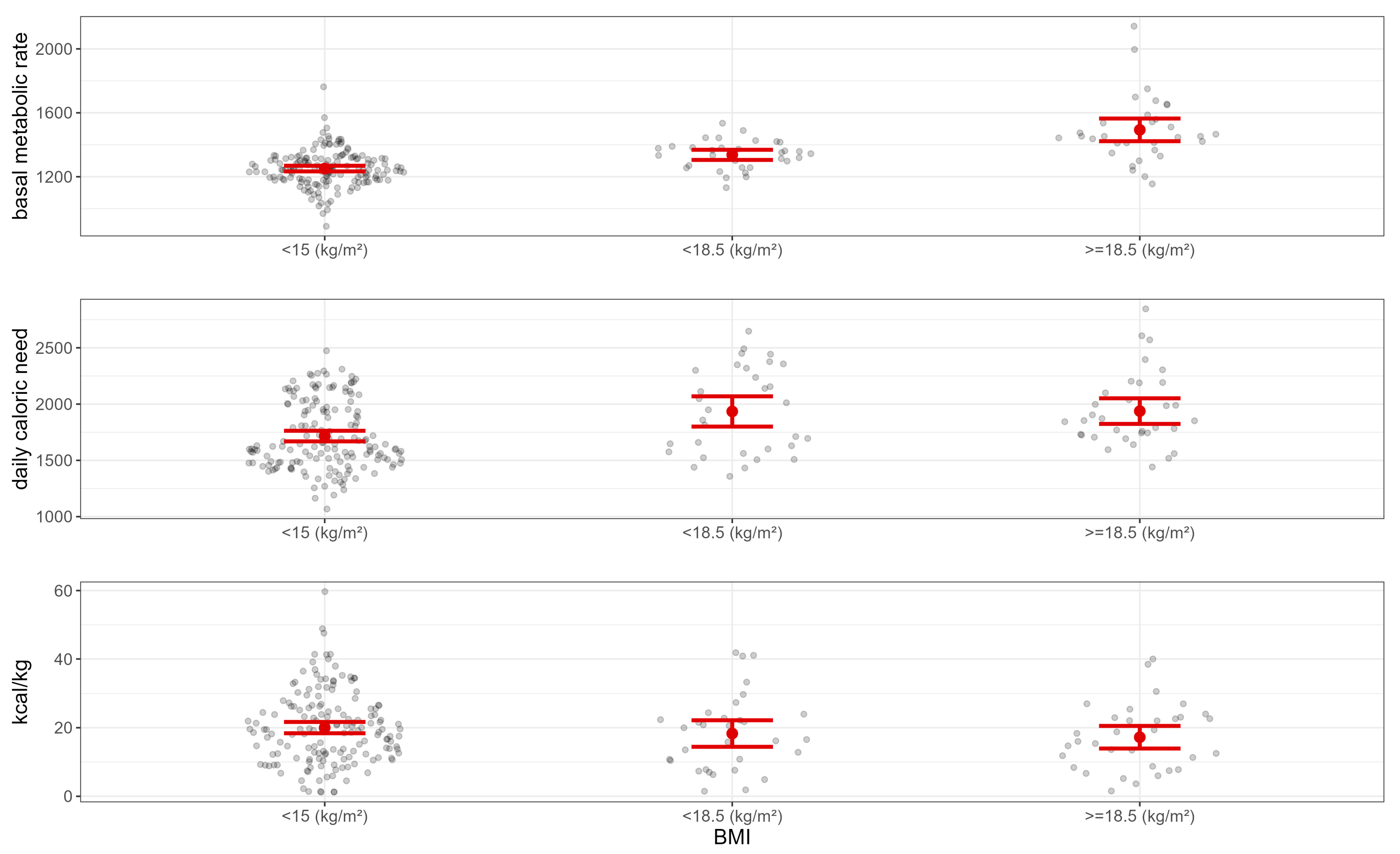


| Characteristic | N = 225 1 |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 25 (10) |
| Sex | |
| Female | 210 (93%) |
| Male | 15 (6.7%) |
| Education (years) | 13.38 (2.90) |
| Student | 127 (56%) |
| Occupation | 150 (67%) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Hispanic | 1 (0.4%) |
| Other | 1 (0.4%) |
| White/Caucasian | 223 (99%) |
| BMI | 15.5 (4.5) |
| diagnosis | |
| AN-R | 134 (60%) |
| AN-BP | 51 (23%) |
| BN | 20 (8.9%) |
| BED | 3 (1.3%) |
| ARFID | 8 (3.6%) |
| OSFED | 8 (3.6%) |
| Duration of illness (years) | 7 (9) |
| Binge-purging symptoms | 84 (37%) |
| Psychiatric comorbidity | 122 (54%) |
| Weight category | |
| BMI < 15 | 126 (56%) |
| BMI 15–15.99 | 34 (15%) |
| BMI 16–16.99 | 21 (9.3%) |
| BMI 17–18.49 | 11 (4.9%) |
| BMI 18.5–25 | 26 (12%) |
| BMI > 25 | 7 (3.1%) |
| History of overweight/obesity | 40 (18%) |
| Weight suppression (kg/m2) | 7.4 (5.8) |
| kcal/kg | 19 (11) |
| BMR | 1299 (154) |
| Daily calorie need | 1779 (332) |
| Activity | |
| Sedentary | 119 (53%) |
| Light | 39 (17%) |
| Moderate | 20 (8.9%) |
| Strong | 47 (21%) |
| Caloric restriction 2 | 54 (28) |
| EDE-Q restraint | 3.42 (2.10) |
| EDE-Q eating concern | 3.17 (1.67) |
| EDE-Q shape concern | 4.22 (1.71) |
| EDE-Q weight concern | 3.74 (1.83) |
| EDE-Q global score | 3.64 (1.69) |
| BSQ | 127 (46) |
| BIAQ clothing | 20 (10) |
| BIAQ social activities | 9 (6) |
| BIAQ eating-related control behavior | 7.2 (4.6) |
| BIAQ grooming/weighing | 8.5 (3.6) |
| BIAQ total score | 45 (19) |
| FMPS concern over mistakes | 30 (10) |
| FMPS personal standards | 24 (7) |
| FMPS parental expectations | 11.0 (5.4) |
| FMPS parental criticism | 9.9 (4.4) |
| FMPS doubts about actions | 13.1 (4.1) |
| FMPS organization | 23.9 (5.1) |
| STAI state anxiety | 57 (14) |
| STAI trait anxiety | 59 (13) |
| BDI total score | 17 (8) |
| Characteristic | Admission, N = 192 1 | Discharge, N = 192 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 24 (10) | - | |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 180 (94%) | - | |
| Male | 12 (6.3%) | - | |
| Diagnosis | |||
| AN-R | 134 (70%) | - | |
| AN-BP | 51 (27%) | - | |
| ARFID | 7 (3.6%) | - | |
| Duration of illness (years) | 6 (9) | - | |
| Binge-purging symptoms | 60 (31%) | - | |
| History of overweight/obesity | 24 (13%) | - | |
| Weight suppression (kg/m2) | 7.8 (5.5) | - | |
| Length of stay (days) | 34 (16) | - | |
| Enteral therapy | 51 (28%) | - | |
| Delta kcal 3 | 808 (471) | - | |
| kcal/week 4 | 189 (143) | - | |
| Weight (kg)/week | 0.38 (0.47) | - | |
| BMI | 14.21 (1.78) | 14.84 (1.69) | <0.001 |
| BMR | 1265 (114) | 1283 (116) | 0.13 |
| Daily calorie need | 1752 (326) | 1679 (290) | 0.021 |
| kcal/kg | 20 (11) | 40 (10) | <0.001 |
| Caloric restriction 5 | 56 (25) | 6 (26) | <0.001 |
| Characteristic | Beta | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caloric restriction | 19 | 13, 25 | <0.001 |
| Weight suppression (kg/m2) | −0.38 | −6.0, 5.2 | 0.9 |
| BMI | 19 | 13, 26 | <0.001 |
| Binge-purging symptoms | 18 | 6.1, 30 | 0.003 |
| Age (years) | 4.4 | −5.9, 15 | 0.4 |
| Duration of illness (years) | −5.6 | −16, 4.5 | 0.3 |
| Caloric restriction × weight suppression (kg/m2) | −7.5 | −13, −1.8 | 0.010 |
| Characteristic | Beta | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caloric restriction | 7.3 | 4.8, 9.9 | <0.001 |
| Weight suppression (kg/m2) | −0.07 | −2.4, 2.3 | >0.9 |
| BMI | 6.2 | 3.5, 8.8 | <0.001 |
| Binge-purging symptoms | 4.2 | −1.0, 9.4 | 0.11 |
| Age (years) | 0.13 | −4.3, 4.5 | >0.9 |
| Duration of illness (years) | −1.3 | −5.6, 3.1 | 0.6 |
| Caloric restriction × weight suppression (kg/m2) | −3.1 | −5.5, −0.70 | 0.012 |
| Characteristic | Beta | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMR | −2.7 | −4.1, −1.3 | <0.001 |
| Length of stay (days) | 2.3 | 0.98, 3.7 | <0.001 |
| BMI | −1.1 | −2.4, 0.16 | 0.086 |
| Daily calorie need | −0.19 | −1.6, 1.2 | 0.8 |
| FMPS concern over mistakes | −2.6 | −3.8, −1.4 | <0.001 |
| Characteristic | Beta | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily calorie need | 5.2 | 1.1, 9.4 | 0.014 |
| FMPS concern over mistakes | 4.9 | 0.98, 8.8 | 0.014 |
| STAI state anxiety | 5.1 | 1.1, 9.0 | 0.012 |
| BMR | 3.2 | −0.40, 6.8 | 0.081 |
| EDE-Q global score | 1.7 | −2.6, 5.9 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martini, M.; Longo, P.; Tamarin, T.; Toppino, F.; Brustolin, A.; Abbate-Daga, G.; Panero, M. Exploring Caloric Restriction in Inpatients with Eating Disorders: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations with Body Dissatisfaction, Body Avoidance, Clinical Factors, and Psychopathology. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153409
Martini M, Longo P, Tamarin T, Toppino F, Brustolin A, Abbate-Daga G, Panero M. Exploring Caloric Restriction in Inpatients with Eating Disorders: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations with Body Dissatisfaction, Body Avoidance, Clinical Factors, and Psychopathology. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153409
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartini, Matteo, Paola Longo, Tiziano Tamarin, Federica Toppino, Annalisa Brustolin, Giovanni Abbate-Daga, and Matteo Panero. 2023. "Exploring Caloric Restriction in Inpatients with Eating Disorders: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations with Body Dissatisfaction, Body Avoidance, Clinical Factors, and Psychopathology" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153409
APA StyleMartini, M., Longo, P., Tamarin, T., Toppino, F., Brustolin, A., Abbate-Daga, G., & Panero, M. (2023). Exploring Caloric Restriction in Inpatients with Eating Disorders: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations with Body Dissatisfaction, Body Avoidance, Clinical Factors, and Psychopathology. Nutrients, 15(15), 3409. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153409






