Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Lactation-Stage-Matched Human and Bovine Milk Samples at 2 Weeks Postnatal
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk Collection and Handling
2.2. Metabolite Extraction
2.3. Analytical Instrumentation
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
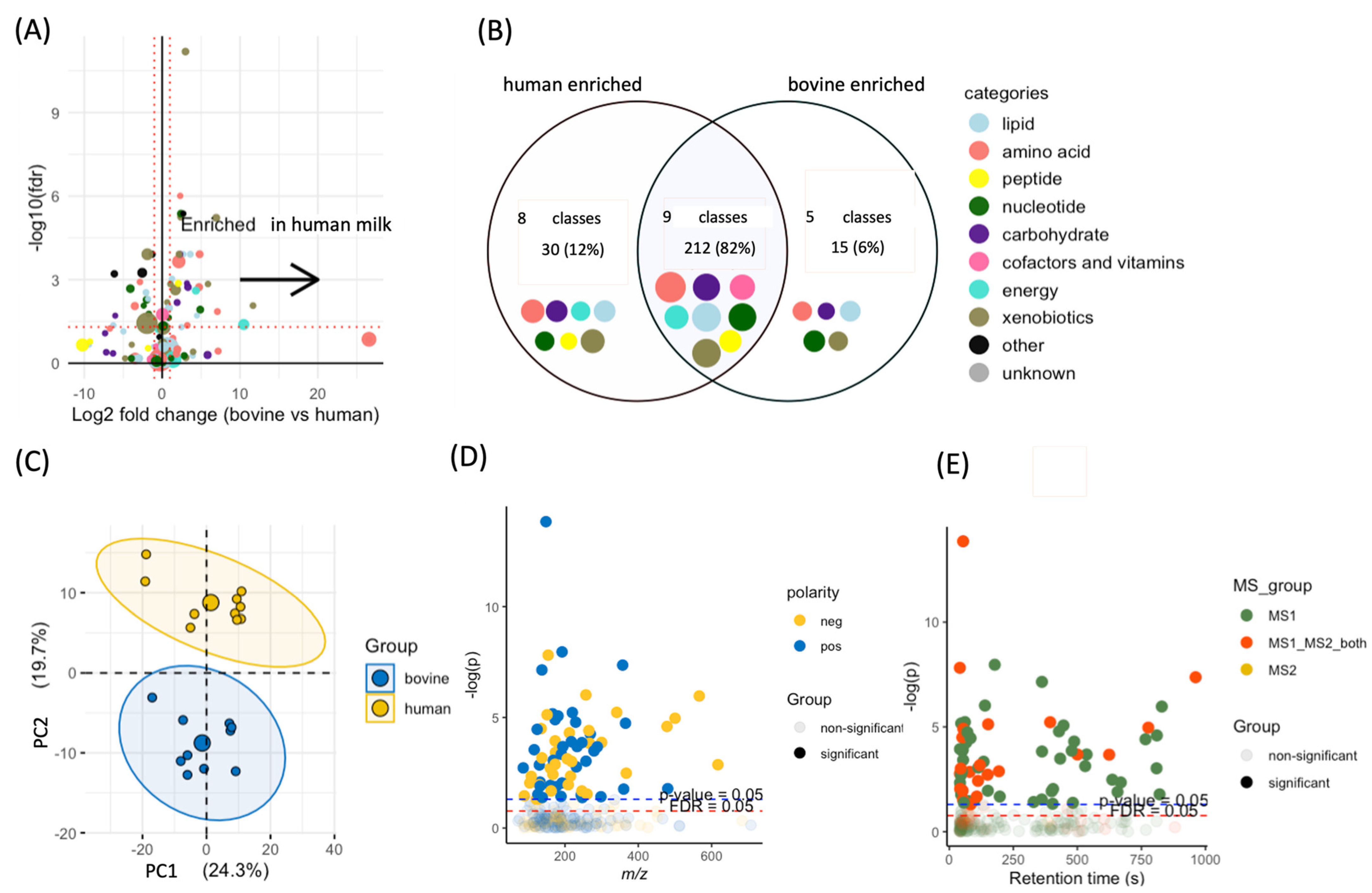
3. Results
3.1. Data Processing
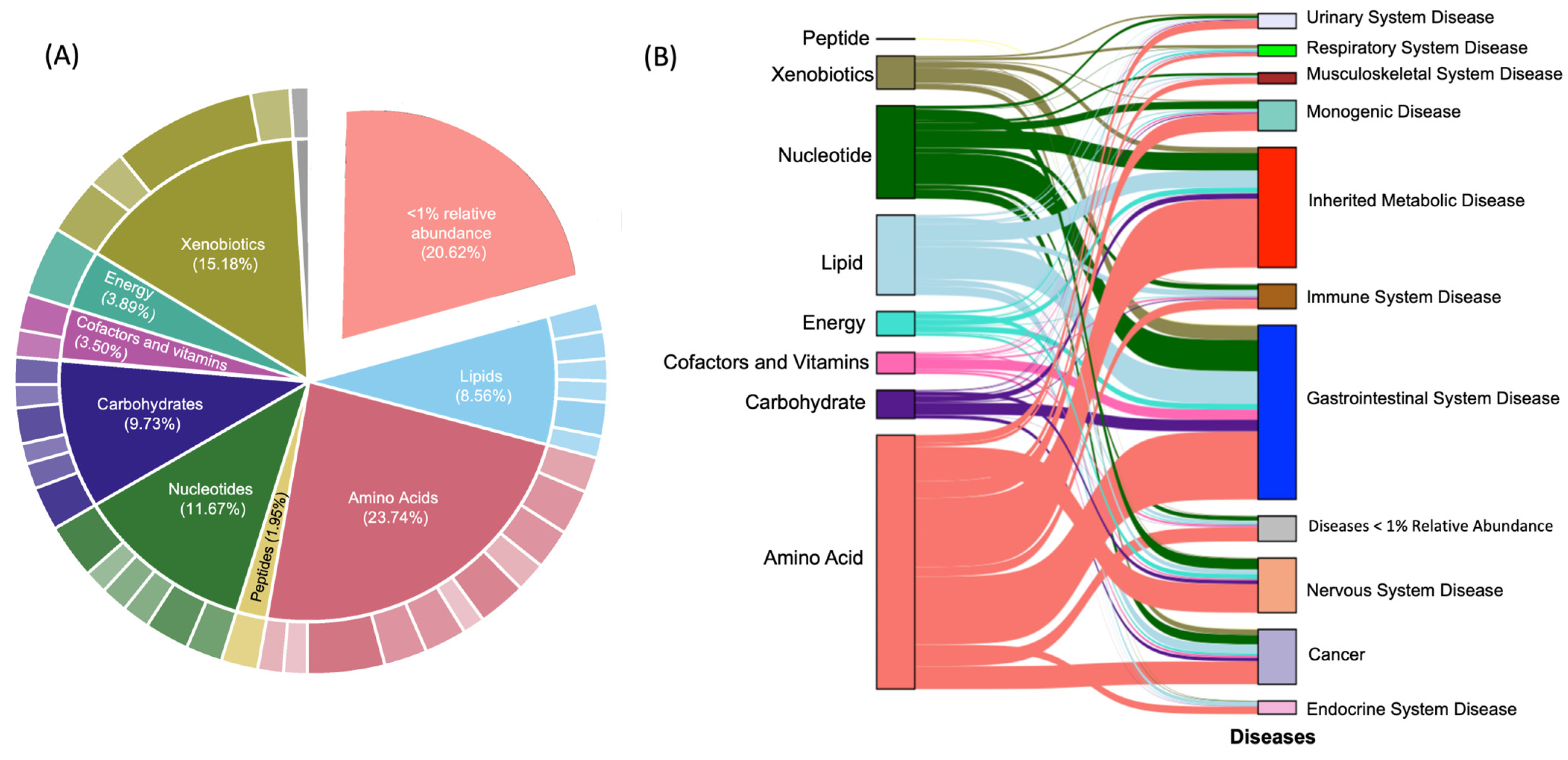
3.2. Differences between Human and Bovine Milk Metabolites
4. Discussion
4.1. Overview
4.2. Previous Work
4.3. Microbe–Host Interactions
4.4. Strengths, Limitations, and Future Works
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koletzko, B. Interindividual variation of human milk metabolome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, N.M.; Lynch, K.F.; Uusitalo, U.; Yang, J.; Lönnrot, M.; Virtanen, S.M.; Hyöty, H.; Norris, J.M. The relationship between breastfeeding and reported respiratory and gastrointestinal infection rates in young children. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.D.; Franca, G.V.A.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joannes-Boyau, R.; Adams, J.W.; Austin, C.; Arora, M.; Moffat, I.; Herries, A.I.R.; Tonge, M.P.; Benazzi, S.; Evans, A.R.; Kullmer, O.; et al. Elemental signatures of Australopithecus africanus teeth reveal seasonal dietary stress. Nature 2019, 572, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastavrou, M.; Genitsaridi, S.M.; Komodiki, E.; Paliatsou, S.; Midw, R.; Kontogeorgou, A.; Iacovidou, N. Breastfeeding in the Course of History. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Care 2015, 2, 00096. [Google Scholar]
- Results: Breastfeeding Rates. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/data/nis_data/results.html (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Maryniak, N.Z.; Sancho, A.I.; Hansen, E.B.; Bøgh, K.L. Alternatives to Cow’s Milk-Based Infant Formulas in the Prevention and Management of Cow’s Milk Allergy. Foods 2022, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, A.; Guo, A.C.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Lipfert, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Badran, H.; Budinski, Z.; Mandal, R.; Ametaj, B.M.; et al. Chemical Composition of Commercial Cow’s Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4897–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, W.L.; Cardoen, S.; Daube, G.; De Block, J.; Dewettinck, K.; Dierick, K.; De Zutter, L.; Huyghebaert, A.; Imberechts, H.; Thiange, P.; et al. Raw or heated cow milk consumption: Review of risks and benefits. Food Control 2013, 31, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Downey, E.; O’Mahony, J.A.; O’Shea, C.A.; Ryan, C.A.; Kelly, A.L.; Bertam, H.C. The Effect of Gestational and Lactational Age on the Human Milk Metabolome. Nutrients 2016, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulaviciene, I.J.; Liubsys, A.; Molyte, A.; Eidukaite, A.; Usonis, V. Circadian changes in the composition of human milk macronutrients depending on pregnancy duration: A cross-sectional study. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2020, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.W.; Yang, G.Q.; Wang, L.F.; Fu, T.; Lian, H.X.; Sun, Y.; Han, L.Q.; Zhang, L.Y.; Gao, T.Y. Effects of the circadian rhythm on milk composition in dairy cows: Does day milk differ from night milk? J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8301–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, K.O.; Meng, F.; Lanfranchi, E.; Young, J.F.; Stanton, C.; Ryan, C.A.; Kelly, A.L.; Sundekilde, U.K. Dynamic Changes in the Human Milk Metabolome over 25 Weeks of Lactation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 917659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human Milk Composition: Nutrients and Bioactive Factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innis, S.M. Impact of maternal diet on human milk composition and neurological development of infants123. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 734S–741S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, M.C.L.; Koleva, P.T.; Slupsky, C.M.; du Toit, E.; Eggesbo, M.; Johnson, C.C.; Wegienka, G.; Shimojo, N.; Campbell, D.E.; Prescott, S.L.; et al. Worldwide Variation in Human Milk Metabolome: Indicators of Breast Physiology and Maternal Lifestyle? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahdenperä, M.; Galante, L.; Gonzales-Inca, C.; Vahtera, J.; Pentti, J.; Rautava, S.; Käyhkö, N.; Yonemitsu, C.; Gupta, J.; Bode, L.; et al. Residential green environments are associated with human milk oligosaccharide diversity and composition. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastmalchi, F.; Xu, K.; Jones, H.N.; Lemas, D.J. Assessment of human milk in the era of precision health. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2022, 25, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Dastmalchi, F.; Ye, H.; Garrett, T.J.; Diller, M.A.; Liu, M.; Hogan, W.R.; Brochhausen, M.; Lemas, D.J. Evaluating LC-HRMS metabolomics data processing software using FAIR principles for research software. Metabolomics Off. J. Metabolomic Soc. 2023, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.M.; da Costa, K.A.; Galanko, J.; Sha, W.; Stephenson, B.; Vick, J.; Zeisel, S.H. Choline intake and genetic polymorphisms influence choline metabolite concentrations in human breast milk and plasma. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Knox, C.; Guo, A.C.; Eisner, R.; Young, N.; Gautam, B.; Hau, D.D.; Psychogios, N.; Dong, E.; Bouatra, S.; et al. HMDB: A knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D603–D610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. HMDB 3.0—The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.C.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemas, D.J.; Young, B.E.; Baker II, P.R.; Tomczik, A.C.; Soderborg, T.K.; Hernandez, T.L.; de la Houssaye, B.A.; Robertson, C.E.; Rudolph, M.C.; Ir, D.; et al. Alterations in human milk leptin and insulin are associated with early changes in the infant intestinal microbiome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R. Taking and storing biological samples for longitudinal birth cohorts. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2009, 23, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, C.A.; Rubio, V.Y.; Garrett, T.J. Impact of matrix effects and ionization efficiency in non-quantitative untargeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemas, D.J.; Loop, M.S.; Duong, M.; Schleffer, A.; Collins, C.; Bowden, J.A.; Du, X.; Patel, K.; Ciesielski, A.L.; Ridge, Z.; et al. Estimating drug consumption during a college sporting event from wastewater using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 143963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adusumilli, R.; Mallick, P. Data Conversion with ProteoWizard msConvert. In Proteomics: Methods and Protocols; Comai, L., Katz, J.E., Mallick, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 339–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpich, A.S.; Ibarra, M.; Moskalenko, O.; Fear, J.M.; Gerken, J.; Mi, X.; Ashrafi, A.; Morse, A.M.; McIntyre, L.M. SECIMTools: A suite of metabolomics data analysis tools. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K.; et al. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B. Steps for Building an Open Source EI-MS Mass Spectral Library for GC-MS-Based Metabolomics; protocols.io: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFelice, B.C.; Mehta, S.S.; Samra, S.; Čajka, T.; Wancewicz, B.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Fiehn, O. Mass Spectral Feature List Optimizer (MS-FLO): A Tool To Minimize False Positive Peak Reports in Untargeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectroscopy (LC-MS) Data Processing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3250–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAleer, P.; Nordmann, E. D Citing R and RStudio|Fundamentals of Quantitative Analysis. Available online: https://psyteachr.github.io/quant-fun-v2/citing-r-rstudio.html (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Lemas, D.J.; Griffin, E.K.; Costa, K.A.; Camacho, C.; Bowden, J.A. Metabolomic Profiling of Biological Reference Materials using a Multiplatform High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Approach. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 32, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriml, L.M.; Munro, J.B.; Schor, M.; Olley, D.; McCracken, C.; Felix, V.; Baron, J.A.; Jackson, R.; Bello, S.M.; Bearer, C.; et al. The Human Disease Ontology 2022 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1255–D1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Chemical Similarity Enrichment Analysis (ChemRICH) as alternative to biochemical pathway mapping for metabolomic datasets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodhan, U.K.; Milan, A.M.; Shrestha, A.; Vickers, M.H.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Barnett, M.P.G. Circulatory amino acid responses to milk consumption in dairy and lactose intolerant individuals. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldan, P.C.; Venancio, S.I.; Saldiva, S.R.D.M.; Vieira, D.G.; de Mello, D.F. Milk consumption in infants under one year of age and variables associated with non-maternal milk consumption. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2017, 35, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deming, D.M.; Afeiche, M.C.; Reidy, K.C.; Eldridge, A.L.; Villalpando-Carrión, S. Early feeding patterns among Mexican babies: Findings from the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey and implications for health and obesity prevention. BMC Nutr. 2015, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zeisel, S.H.; Jia, W.; Cai, W. Metabolomic Approaches to Explore Chemical Diversity of Human Breast-Milk, Formula Milk and Bovine Milk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartel, K.; Stevens, M.; Vijayakumar, N.; Saint Fleur, A.; Prescott, S.; Groer, M. The Human Milk Metabolome: A Scoping Literature Review. J. Hum. Lact. Off. J. Int. Lact. Consult. Assoc. 2023, 39, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mung, D.; Li, L. Development of Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS for Milk Metabolomics: Comprehensive and Quantitative Profiling of the Amine/Phenol Submetabolome. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4435–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrez Lamberti, M.F.; DeBose-Scarlett, E.; Garret, T.; Parker, L.A.; Neu, J.; Lorca, G.L. Metabolomic Profile of Personalized Donor Human Milk. Molecules 2020, 25, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokan, M.; Ramesha, K.P.; Hallur, S.; Karthikkeyan, G.; Rana, E.; Azharuddin, N.; Raj, S.R.; Jeyakumar, S.; Kumaresan, A.; Kataktalware, M.A.; et al. Differences in milk metabolites in Malnad Gidda (Bos indicus) cows reared under pasture-based feeding system. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, X.; Kwok, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Mi, Z.; Zhang, H. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry MSE-based untargeted milk metabolomics in dairy cows with subclinical or clinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4884–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Xie, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, W.; Huang, K.; Xu, W.; Lin, X. Untargeted Metabonomics of Genetically Modified Cows Expressing Lactoferrin Based on Serum and Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caboni, P.; Murgia, A.; Porcu, A.; Manis, C.; Ibba, I.; Contu, M.; Scano, P. A metabolomics comparison between sheep’s and goat’s milk. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-Z.; Shi, K.; Wu, X.-H.; Xue, M.-Y.; Wei, Z.-H.; Liu, J.-X.; Liu, H.-Y. Lactation-related metabolic mechanism investigated based on mammary gland metabolomics and 4 biofluids’ metabolomics relationships in dairy cows. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhai, Z.; Ni, X.; Wang, H.; Ji, Y.; Tang, T.; Ren, W.; Long, H.; Deng, B.; Deng, J.; et al. Metabolomic Profiles Reveal Potential Factors that Correlate with Lactation Performance in Sow Milk. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwierzchowski, G.; Zhang, G.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S.; Ametaj, B.N. Milk Metabotyping Identifies Metabolite Alterations in the Whole Raw Milk of Dairy Cows with Lameness. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4507–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecocci, S.; Gevi, F.; Pietrucci, D.; Cavinato, L.; Luly, F.R.; Pascucci, L.; Petrini, S.; Ascenzioni, F.; Zolla, L.; Chillemi, G.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Cow, Donkey and Goat Milk Extracellular Vesicles as Revealed by Metabolomic Profile. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Huang, D.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Hu, H.; Cheng, G. Exploration of the Relationship between Intestinal Colostrum or Milk, and Serum Metabolites in Neonatal Calves by Metabolomics Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7200–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Yu, J.; Mi, Z.; Mo, L.; Jin, H.; Yao, C.; Ren, D.; Menghe, B. A Metabolomics Approach Uncovers Differences between Traditional and Commercial Dairy Products in Buryatia (Russian Federation). Mol. J. Synth. Chem. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2018, 23, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Zhang, X.; Su, M.; Jia, M.; Zhu, D.; Kebede, B.; Wu, H.; Chen, G. Establishing an untargeted-to-MRM liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for discriminating reconstituted milk from ultra-high temperature milk. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiang, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, K.; Qi, C.; Sun, J.; Li, D. Changes in the metabolite profile of breast milk over lactation stages and their relationship with dietary intake in Chinese women: HPLC-QTOFMS based metabolomic analysis. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5189–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gastelen, S.; Antunes-Fernandes, E.C.; Hettinga, K.A.; Dijkstra, J. The relationship between milk metabolome and methane emission of Holstein Friesian dairy cows: Metabolic interpretation and prediction potential. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2110–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isganaitis, E.; Venditti, S.; Matthews, T.J.; Lerin, C.; Demerath, E.W.; Fields, D.A. Maternal obesity and the human milk metabolome: Associations with infant body composition and postnatal weight gain. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Bie, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, L.; Lin, S.-H.; Zhou, X. Omics study reveals abnormal alterations of breastmilk proteins and metabolites in puerperant women with COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, F.; Xue, F.; Hua, D.; Li, K.; et al. Coupling 16S rDNA Sequencing and Untargeted Mass Spectrometry for Milk Microbial Composition and Metabolites from Dairy Cows with Clinical and Subclinical Mastitis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8496–8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Kebede, B.; Chen, G.; McComb, K.; Frew, R. Effects of the vat pasteurization process and refrigerated storage on the bovine milk metabolome. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.D.; Dodder, N.G.; Quintana, P.J.E.; Wantanabe, K.; Kim, J.H.; Hovell, M.F.; Chambers, C.D.; Hoh, E. Organic contaminants in human breast milk identified by non-targeted analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Bi, H.; Yu, R.; Wei, W.; Wang, X. Short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) and medium-chain fatty acid (MCFA) concentrations in human milk consumed by infants born at different gestational ages and the variations in concentration during lactation stages. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörmannsperger, G.; Clavel, T.; Haller, D. Gut matters: Microbe-host interactions in allergic diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, H.C.; Herrmann, B.; Wiredu, D.; Thaiss, C.A. The path toward using microbial metabolites as therapies. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinson, L.F.; Geddes, D.T. Microbial metabolites: The next frontier in human milk. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, N.; Tytgat, H.L.P.; Binia, A.; Austin, S.; Singhal, A. Biology of human milk oligosaccharides: From basic science to clinical evidence. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. Off. J. Br. Diet. Assoc. 2022, 35, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzior, D.V.; Quinn, R.A. Review: Microbial transformations of human bile acids. Microbiome 2021, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Ohishi, K.; Suzuki, H.; Hatanaka, Y.; Kamisako, H.; Minatogawa, Y.; Uemura, S.; Koike, M. The High Concentration of Biopterin In Breast Milk and It’s Absorption During the Neonatal Period. Pteridines 1995, 6, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribo, S.; Sánchez-Infantes, D.; Martinez-Guino, L.; García-Mantrana, I.; Ramon-Krauel, M.; Tondo, M.; Arning, E.; Nofrarías, M.; Osorio-Conles, O.; Fernández-Pérez, A.; et al. Increasing breast milk betaine modulates Akkermansia abundance in mammalian neonates and improves long-term metabolic health. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb0322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesare Marincola, F.; Corbu, S.; Lussu, M.; Noto, A.; Dessi, A.; Longo, S.; Civardi, E.; Garofoli, F.; Grenci, B.; Mongini, E.; et al. Impact of Early Postnatal Nutrition on the NMR Urinary Metabolic Profile of Infant. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 3712–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, F.; Matazel, K.S.; Elolimy, A.A.; Adams, S.H.; Bowlin, A.; Williams, K.D.; Bode, L.; Yeruva, L. Human Milk-Fed Piglets Have a Distinct Small Intestine and Circulatory Metabolome Profile Relative to That of Milk Formula-Fed Piglets. mSystems 2021, 6, e01376-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Garrett, T.J.; Brochhausen, M.; Hogan, W.R.; Lemas, D.J. A Checklist for Reproducible Computational Analysis in Clinical Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2022, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lemas, D.J.; Du, X.; Dado-Senn, B.; Xu, K.; Dobrowolski, A.; Magalhães, M.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Young, B.E.; Francois, M.; Thompson, L.A.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Lactation-Stage-Matched Human and Bovine Milk Samples at 2 Weeks Postnatal. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173768
Lemas DJ, Du X, Dado-Senn B, Xu K, Dobrowolski A, Magalhães M, Aristizabal-Henao JJ, Young BE, Francois M, Thompson LA, et al. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Lactation-Stage-Matched Human and Bovine Milk Samples at 2 Weeks Postnatal. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173768
Chicago/Turabian StyleLemas, Dominick J., Xinsong Du, Bethany Dado-Senn, Ke Xu, Amanda Dobrowolski, Marina Magalhães, Juan J. Aristizabal-Henao, Bridget E. Young, Magda Francois, Lindsay A. Thompson, and et al. 2023. "Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Lactation-Stage-Matched Human and Bovine Milk Samples at 2 Weeks Postnatal" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173768
APA StyleLemas, D. J., Du, X., Dado-Senn, B., Xu, K., Dobrowolski, A., Magalhães, M., Aristizabal-Henao, J. J., Young, B. E., Francois, M., Thompson, L. A., Parker, L. A., Neu, J., Laporta, J., Misra, B. B., Wane, I., Samaan, S., & Garrett, T. J. (2023). Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Lactation-Stage-Matched Human and Bovine Milk Samples at 2 Weeks Postnatal. Nutrients, 15(17), 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173768








