The Circadian Nobiletin-ROR Axis Suppresses Adipogenic Differentiation and IκBα/NF-κB Signaling in Adipocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Bioluminescence Measurement Using 3T3-L1 Cells
2.3. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
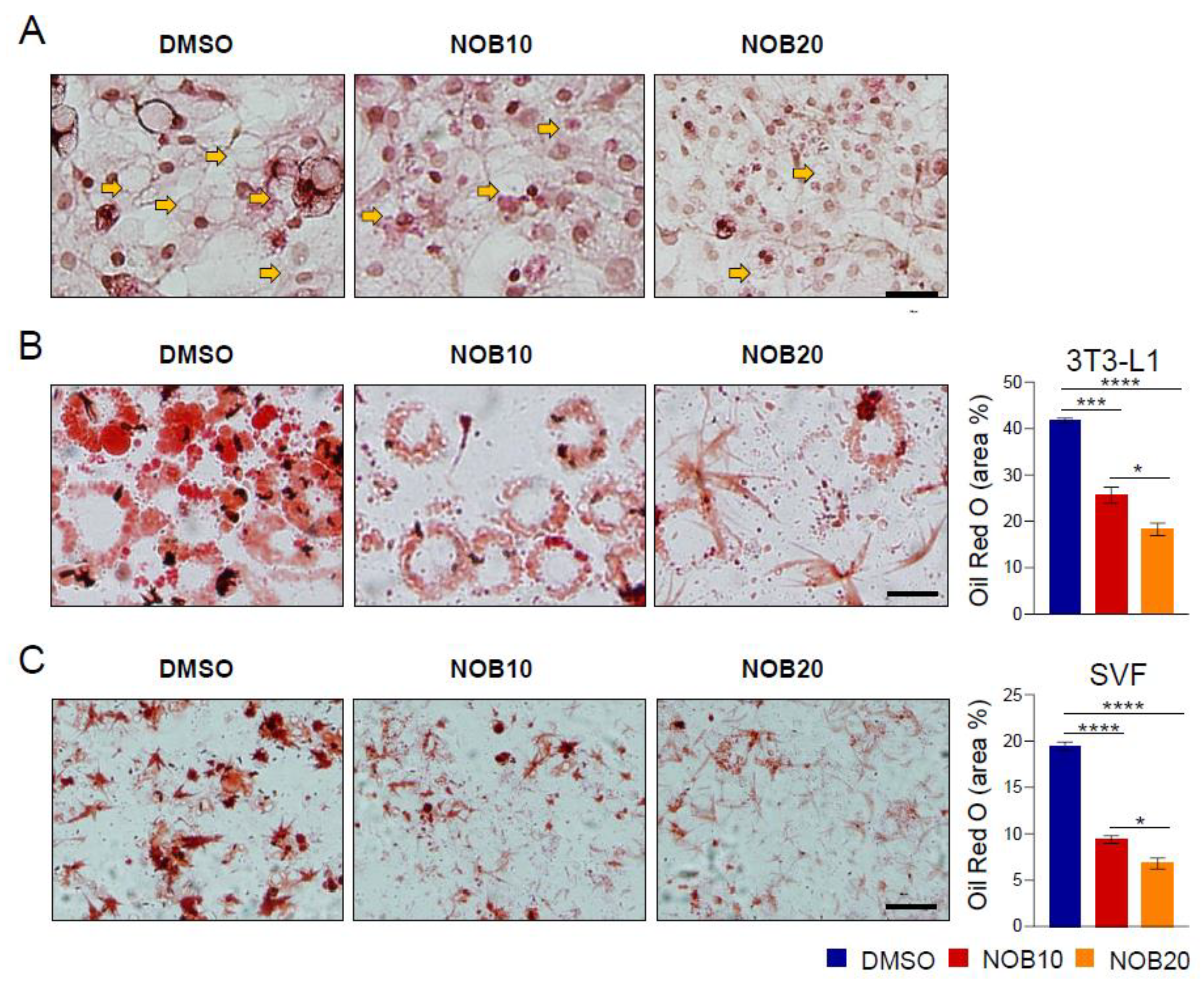
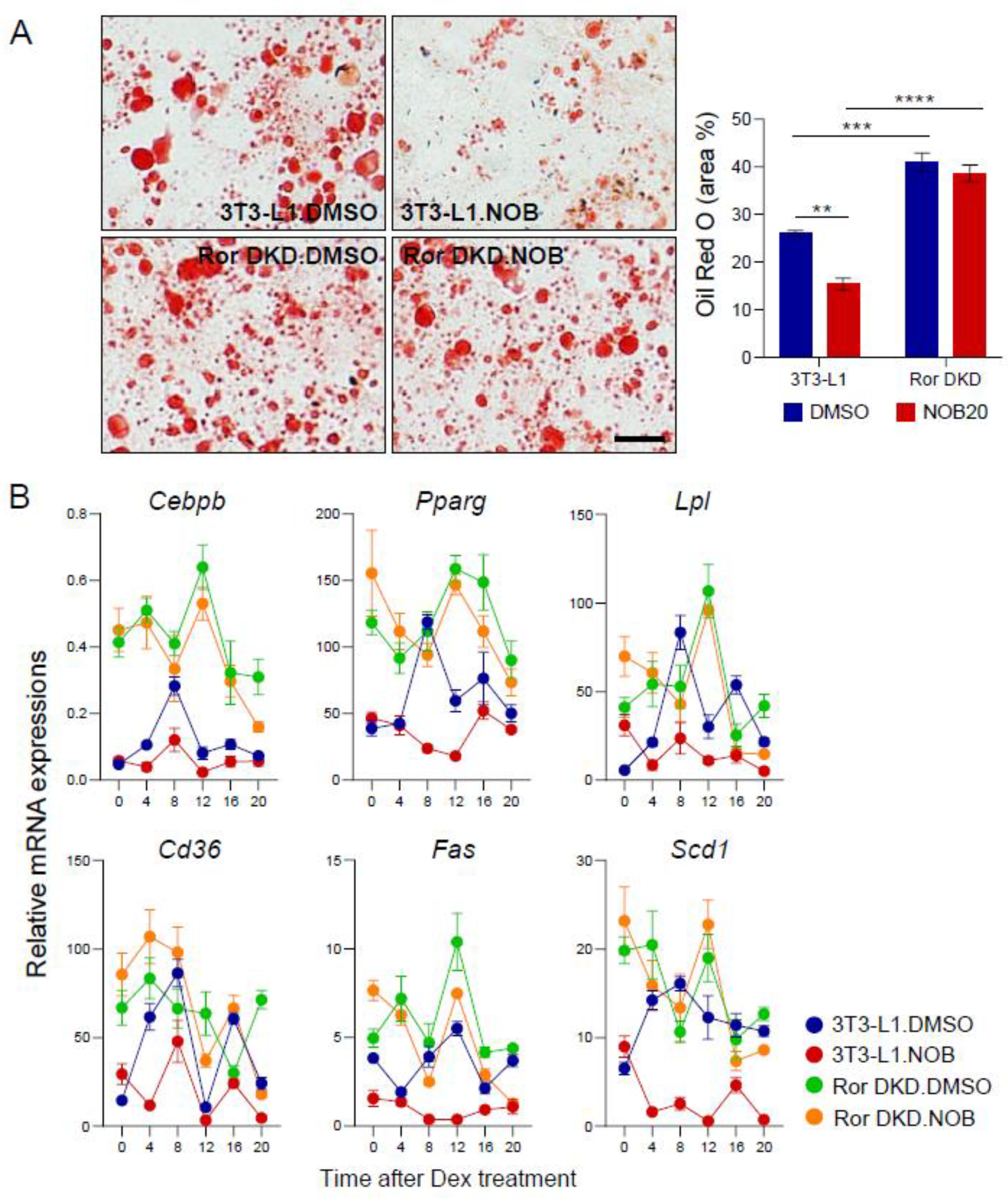
2.4. Oil Red O Staining
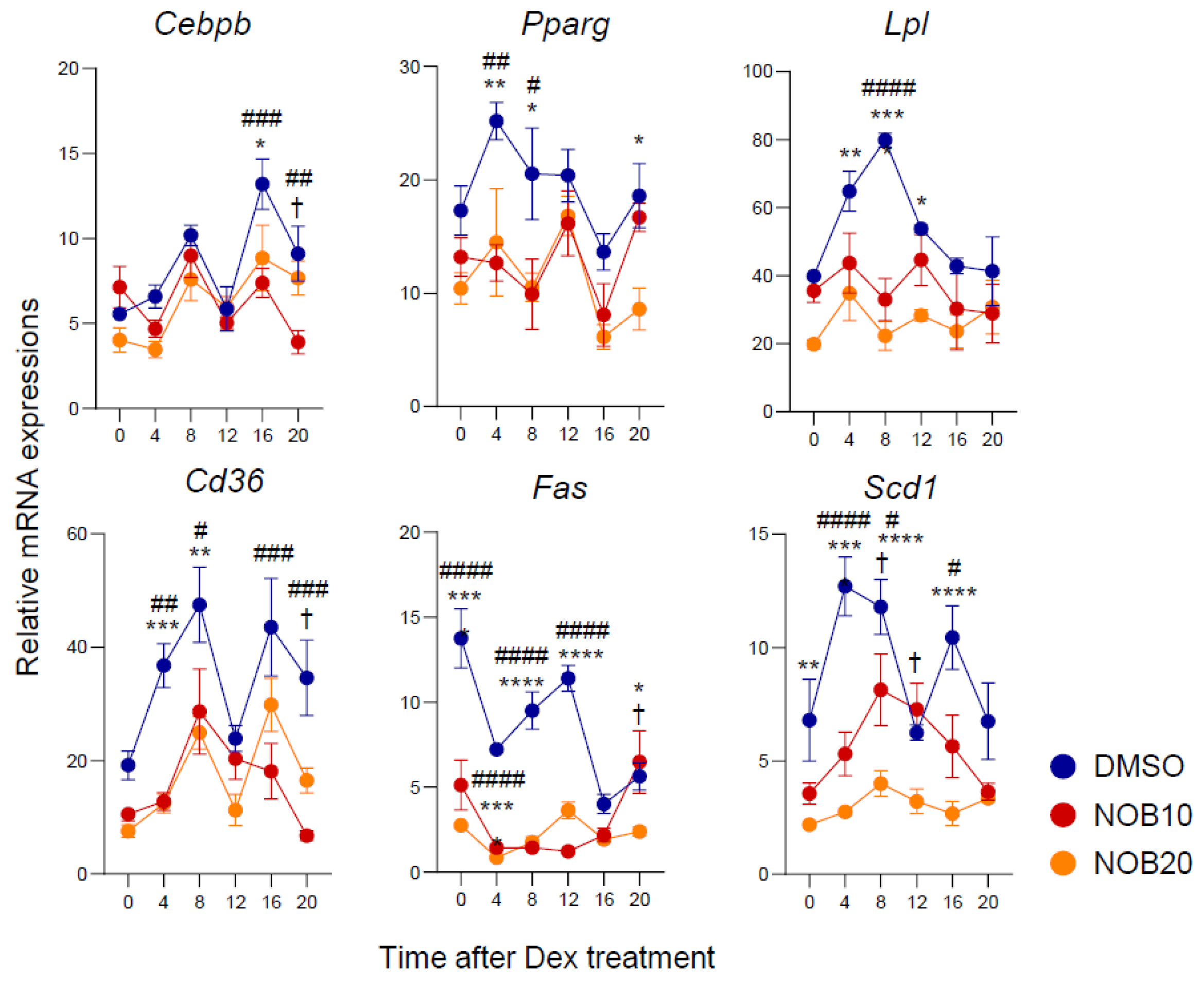
2.5. Real-Time PCR Analysis
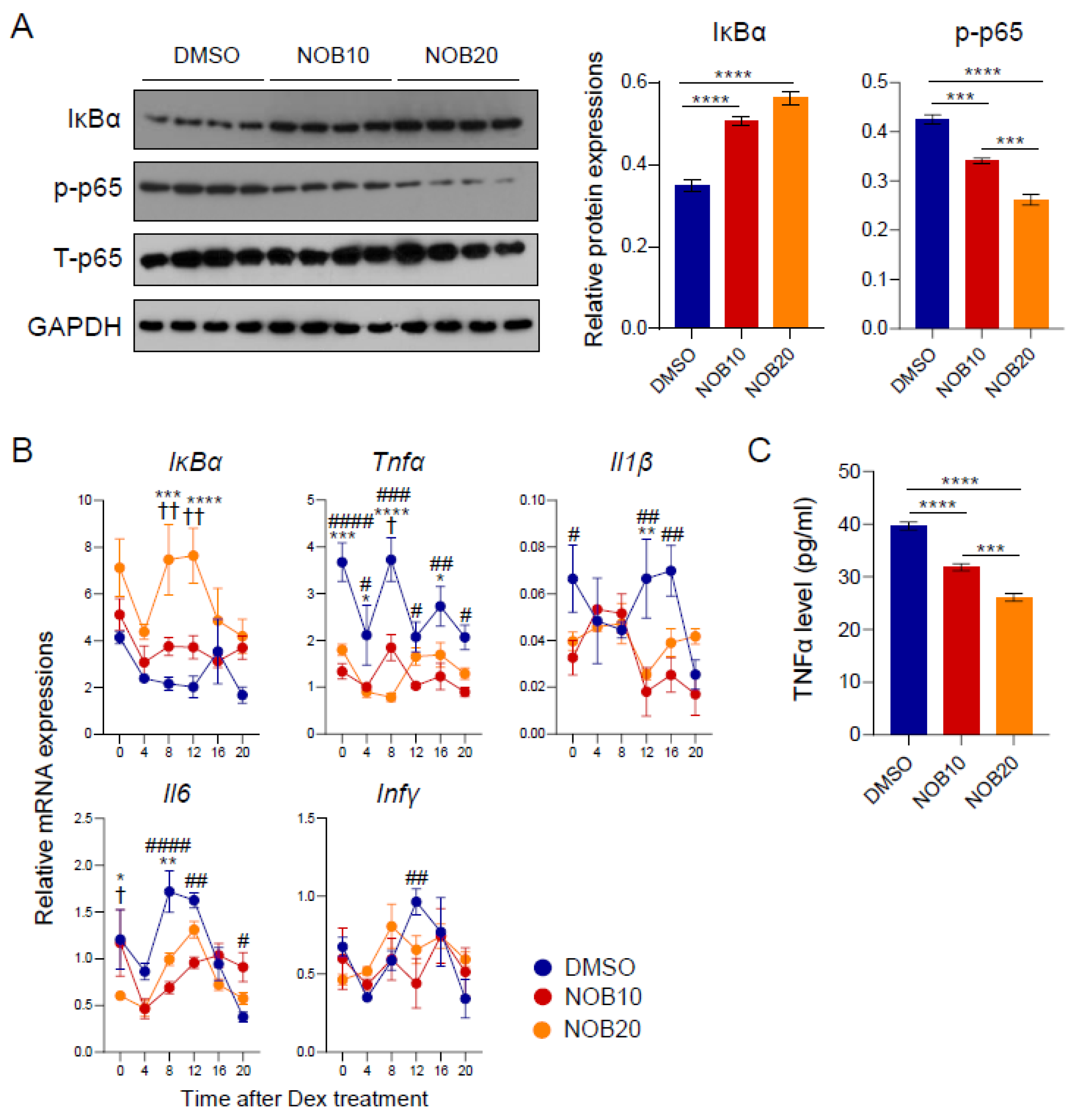
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. TNFα Measurement
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. NOB Modulates Circadian Rhythms of Core Clock Gene Expression
3.2. NOB Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Differentiated 3T3-L1 and SVF Cells
3.3. NOB Decreases Transcription of Adipogenesis-Related Genes
3.4. NOB Regulates the IκBα/NF-κB Pathway and Inflammatory Cytokines
3.5. ROR-Dependent Circadian Gene Regulation Is Enhanced by NOB
3.6. RORs Are Required for NOB Efficacy to Mitigate Lipid Accumulation
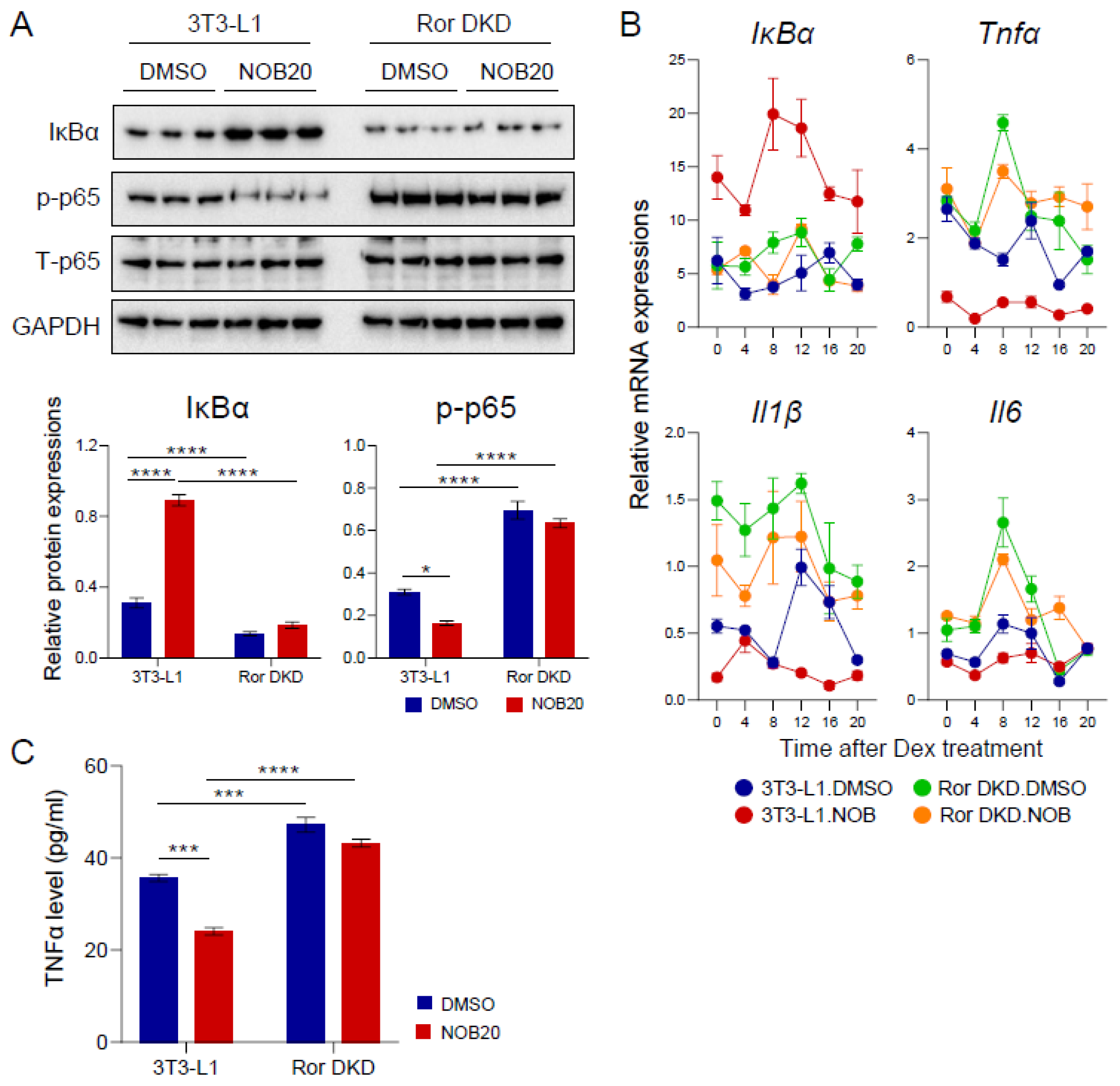
3.7. The ROR–NOB Axis Targets the IκBα/NF-κB Pathway
4. Discussions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarma, S.; Sockalingam, S.; Dash, S. Obesity as a multisystem disease: Trends in obesity rates and obesity-related complications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kahn, C.R.; Wang, G.; Lee, K.Y. Altered adipose tissue and adipocyte function in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3990–4000. [Google Scholar]
- Guru, A.; Issac, P.K.; Velayutham, M.; Saraswathi, N.; Arshad, A.; Arockiaraj, J. Molecular mechanism of down-regulating adipogenic transcription factors in 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells by bioactive anti-adipogenic compounds. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; MacDougald, O.A. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoire, F.M.; Smas, C.M.; Sul, H.S. Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 783–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, F.; Gomez, R.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Dieguez, C.; Gualillo, O. Adipokines as novel modulators of lipid metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moseti, D.; Regassa, A.; Kim, W.-K. Molecular regulation of adipogenesis and potential anti-adipogenic bioactive molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Burn, P. Lipid metabolic enzymes: Emerging drug targets for the treatment of obesity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 695–710. [Google Scholar]
- Scheja, L.; Heeren, J. The endocrine function of adipose tissues in health and cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 507–524. [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, L.; Mittenbühler, M.J.; Vesting, A.J.; Ostermann, A.L.; Wunderlich, C.M.; Wunderlich, F.T. Obesity-Induced TNFα and IL-6 Signaling: The Missing Link between Obesity and Inflammation-Driven Liver and Colorectal Cancers. Cancers 2018, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, T. Methoxylated flavones, a superior cancer chemopreventive flavonoid subclass? In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 354–362. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.; Sharma, P.; Guthrie, N. Bioavailability of citrus polymethoxylated flavones and their biological role in metabolic syndrome and hyperlipidemia. In Readings in Advanced Pharmacokinetics-Theory, Methods and Applications; Intech: London, UK, 2012; pp. 267–284. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Burke, A.C.; Huff, M.W. Citrus flavonoids as regulators of lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Li, L.; Shi, W.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L. The multifunctional effects of nobiletin and its metabolites in vivo and in vitro. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 2918796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Qiu, P.; Xu, G.; Wu, X.; Dong, P.; Yang, G.; Zheng, J.; McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of nobiletin and sulforaphane in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Sato, T.; Takayama, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Yano, M.; Ito, A. Novel anti-inflammatory actions of nobiletin, a citrus polymethoxy flavonoid, on human synovial fibroblasts and mouse macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Cha, B.-Y.; Saito, K.; Yamakawa, H.; Choi, S.-S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Teruya, T.; Nagai, K.; Woo, J.-T. Nobiletin improves hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in obese diabetic ob/ob mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Cha, B.-Y.; Choi, S.-S.; Choi, B.-K.; Yonezawa, T.; Teruya, T.; Nagai, K.; Woo, J.-T. Nobiletin improves obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kim, Y.J.; Ji, Z.; Kang, J.M.; Wirianto, M.; Paudel, K.R.; Smith, J.A.; Ono, K.; Kim, J.A.; Eckel-Mahan, K.; et al. ROR activation by Nobiletin enhances antitumor efficacy via suppression of IκB/NF-κB signaling in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, Y.; Ham, H.; Park, Y.; Jeong, H.-S.; Lee, J. Nobiletin suppresses adipogenesis by regulating the expression of adipogenic transcription factors and the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12843–12849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, J.; Parray, H.A.; Yun, J.W. Nobiletin induces brown adipocyte-like phenotype and ameliorates stress in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochimie 2018, 146, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, K.; Nishi, K.; Kadota, A.; Nishimoto, S.; Liu, M.-C.; Sugahara, T. Nobiletin suppresses adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells by an insulin and IBMX mixture induction. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkoong, S.; Sung, J.; Yang, J.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, J. Nobiletin attenuates the inflammatory response through heme oxygenase-1 induction in the crosstalk between adipocytes and macrophages. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Nohara, K.; Park, N.; Park, Y.-S.; Guillory, B.; Zhao, Z.; Garcia, J.M.; Koike, N.; Lee, C.C.; Takahashi, J.S. The small molecule nobiletin targets the molecular oscillator to enhance circadian rhythms and protect against metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohara, K.; Mallampalli, V.; Nemkov, T.; Wirianto, M.; Yang, J.; Ye, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, L.; Esser, K.A.; Mileykovskaya, E. Nobiletin fortifies mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle to promote healthy aging against metabolic challenge. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, K.; Nemkov, T.; D’Alessandro, A.; Yoo, S.-H.; Chen, Z. Coordinate regulation of cholesterol and bile acid metabolism by the clock modifier nobiletin in metabolically challenged old mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirianto, M.; Wang, C.Y.; Kim, E.; Koike, N.; Gomez-Gutierrez, R.; Nohara, K.; Escobedo, G., Jr.; Choi, J.M.; Han, C.; Yagita, K. The clock modulator Nobiletin mitigates astrogliosis-associated neuroinflammation and disease hallmarks in an Alzheimer’s disease model. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Nohara, K.; Wirianto, M.; Escobedo, G., Jr.; Lim, J.Y.; Morales, R.; Yoo, S.-H.; Chen, Z. Effects of the clock modulator nobiletin on circadian rhythms and pathophysiology in female mice of an Alzheimer’s disease model. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, P.; Fitzsimmons, R.L.; Raichur, S.; Wang, S.-C.M.; Lechtken, A.; Muscat, G.E. The orphan nuclear receptor, RORα, regulates gene expression that controls lipid metabolism: Staggerer (SG/SG) mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18411–18421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetten, A.M.; Kang, H.S.; Takeda, Y. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptors α and γ: Key regulators of lipid/glucose metabolism, inflammation, and insulin sensitivity. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shostak, A.; Meyer-Kovac, J.; Oster, H. Circadian regulation of lipid mobilization in white adipose tissues. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, M.S.; Young, M.E. Circadian rhythms in the development of obesity: Potential role for the circadian clock within the adipocyte. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohara, K.; Kim, E.; Wirianto, M.; Mileykovskaya, E.; Dowhan, W.; Chen, Z.; Yoo, S.H. Cardiolipin Synthesis in Skeletal Muscle Is Rhythmic and Modifiable by Age and Diet. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5304768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjana, N.E.; Shalem, O.; Zhang, F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.C.; Tran, H.G.; Zhang, E.E.; Priest, A.A.; Welsh, D.K.; Kay, S.A. Redundant function of REV-ERBalpha and beta and non-essential role for Bmal1 cycling in transcriptional regulation of intracellular circadian rhythms. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.H.; Yamazaki, S.; Lowrey, P.L.; Shimomura, K.; Ko, C.H.; Buhr, E.D.; Siepka, S.M.; Hong, H.K.; Oh, W.J.; Yoo, O.J.; et al. PERIOD2::LUCIFERASE real-time reporting of circadian dynamics reveals persistent circadian oscillations in mouse peripheral tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5339–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, R.; Parsons, R.; Garner, N.; Oster, H.; Rawashdeh, O. CircaCompare: A method to estimate and statistically support differences in mesor, amplitude and phase, between circadian rhythms. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, N.; Noshiro, M.; Kawamoto, T.; Nakashima, A.; Honda, K.; Fukuzaki-Dohi, U.; Honma, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Tanimoto, K.; Tanne, K.; et al. Regulation of basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors Dec1 and Dec2 by RORα and their roles in adipogenesis. Genes Cells 2012, 17, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykstra, J.A.; Facile, T.; Patrick, R.J.; Francis, K.R.; Milanovich, S.; Weimer, J.M.; Kota, D.J. Concise review: Fat and furious: Harnessing the full potential of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Ribas-Latre, A.; Santos, R.B.; Fekry, B.; Tamim, Y.M.; Shivshankar, S.; Mohamed, A.M.T.; Baumgartner, C.; Kwok, C.; Gebhardt, C.; Rivera, A.; et al. Cellular and physiological circadian mechanisms drive diurnal cell proliferation and expansion of white adipose tissue. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, C.C.; Ramaswami, S.; Juvekar, A.; Vu, H.-Y.; Galdieri, L.; Davidson, D.; Vancurova, I. Gene-specific repression of proinflammatory cytokines in stimulated human macrophages by nuclear IκBα. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3685–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Ahsan, M.H.; Zhu, L.; Sambucetti, L.C.; Purchio, A.F.; West, D.B. Regulation of IκBα expression involves both NF-κB and the MAP kinase signaling pathways. J. Inflamm. 2005, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, M.L.; Baeuerle, P.A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 3805–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawthorn, W.P.; Sethi, J.K. TNF-α and adipocyte biology. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duez, H.; Duhem, C.; Laitinen, S.; Patole, P.S.; Abdelkarim, M.; Bois-Joyeux, B.; Danan, J.-L.; Staels, B. Inhibition of adipocyte differentiation by RORα. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohoka, N.; Kato, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Sato, R. The orphan nuclear receptor RORα restrains adipocyte differentiation through a reduction of C/EBPβ activity and perilipin gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiri, S.; Monnier, C.; Ganbold, M.; Ledent, T.; Capeau, J.; Antoine, B. The nuclear retinoid-related orphan receptor-α regulates adipose tissue glyceroneogenesis in addition to hepatic gluconeogenesis. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E105–E114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delerive, P.; Monté, D.; Dubois, G.; Trottein, F.; Fruchart-Najib, J.; Mariani, J.; Fruchart, J.C.; Staels, B. The orphan nuclear receptor ROR alpha is a negative regulator of the inflammatory response. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, H.; Yanagihara, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Obi, Y.; Tsuruoka, S.; Takamura, T.; Kaneko, S.; Fujimura, A. Rhythmic messenger ribonucleic acid expression of clock genes and adipocytokines in mouse visceral adipose tissue. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 5631–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojetin, D.J.; Burris, T.P. REV-ERB and ROR nuclear receptors as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Yoo, S.-H.; Chen, Z. Circadian stabilization loop: The regulatory hub and therapeutic target promoting circadian resilience and physiological health. F1000Research 2022, 11, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.N.; Kang, H.S.; Jetten, A.M. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptors (RORs): Regulatory functions in immunity, development, circadian rhythm, and metabolism. Nucl. Recept. Res. 2015, 2, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solt, L.A.; Kumar, N.; Nuhant, P.; Wang, Y.; Lauer, J.L.; Liu, J.; Istrate, M.A.; Kamenecka, T.M.; Roush, W.R.; Vidović, D. Suppression of TH17 differentiation and autoimmunity by a synthetic ROR ligand. Nature 2011, 472, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.R.; He, Y.; Khan, T.M.; Kuruvilla, D.S.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.; Corzo, C.A.; Unger, T.J.; White, D.W.; Khan, S.; Lin, L. Antiobesity effect of a small molecule repressor of RORγ. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloston, G.F.; Yoo, S.-H.; Chen, Z. Clock-enhancing small molecules and potential applications in chronic diseases and aging. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, A.; Misawa, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Haraguchi, A.; Kamagata, M.; Tahara, Y.; Shibata, S. Potent effects of flavonoid nobiletin on amplitude, period, and phase of the circadian clock rhythm in PER2:: LUCIFERASE mouse embryonic fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noshiro, M.; Kawamoto, T.; Nakashima, A.; Ozaki, N.; Saeki, M.; Honda, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Kato, Y. DEC1 regulates the rhythmic expression of PPARγ target genes involved in lipid metabolism in white adipose tissue. Genes Cells 2020, 25, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, U.-H.; Jeong, J.-C.; Jang, J.-S.; Sung, M.-R.; Youn, H.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, E.-J.; Um, S.-J. Negative regulation of adipogenesis by kaempferol, a component of Rhizoma Polygonati falcatum in 3T3-L1 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Flowers, M.T.; Sampath, H.; Chu, K.; Otzelberger, C.; Liu, X.; Ntambi, J.M. Hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 deficiency protects mice from carbohydrate-induced adiposity and hepatic steatosis. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Boo, K.; Yu, Y.S.; Oh, S.K.; Kim, H.; Jeon, Y.; Bhin, J.; Hwang, D.; Kim, K.I.; Lee, J.-S. RORα controls hepatic lipid homeostasis via negative regulation of PPARγ transcriptional network. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, P.; Nixon, S.J.; Parton, R.G.; Muscat, G.E. RORα regulates the expression of genes involved in lipid homeostasis in skeletal muscle cells: Caveolin-3 and CPT-1 are direct targets of ROR. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36828–36840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raichur, S.; Fitzsimmons, R.; Myers, S.; Pearen, M.; Lau, P.; Eriksson, N.; Wang, S.; Muscat, G. Identification and validation of the pathways and functions regulated by the orphan nuclear receptor, ROR alpha1, in skeletal muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 4296–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, S.; Medvedev, A.; Yan, Z.-H.; Adachi, H.; Hirose, T.; Jetten, A.M. Induction of the nuclear orphan receptor RORgamma during adipocyte differentiation of D1 and 3T3-L1 cells. Cell Growth Differ. Mol. Biol. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1998, 9, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.S.; Angers, M.; Beak, J.Y.; Wu, X.; Gimble, J.M.; Wada, T.; Xie, W.; Collins, J.B.; Grissom, S.F.; Jetten, A.M. Gene expression profiling reveals a regulatory role for RORα and RORγ in phase I and phase II metabolism. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 31, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Sun, S.; Ye, J.; Li, Z.; Mao, L.; Ren, J. Enhancement of anti-inflammatory properties of nobiletin in macrophages by a nano-emulsion preparation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Ngo, C.; Salomon, C.; Quak, S.; Lai, A.; Willcox, J.C.; Lappas, M. Nobiletin exerts anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects in an in vitro human model and in vivo murine model of gestational diabetes. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunbupha, S.; Apaijit, K.; Maneesai, P.; Prasarttong, P.; Pakdeechote, P. Nobiletin ameliorates high-fat diet-induced vascular and renal changes by reducing inflammation with modulating AdipoR1 and TGF-β1 expression in rats. Life Sci. 2020, 260, 118398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci Ozkan, A.; Kaleli, S.; Onen, H.I.; Sarihan, M.; Guney Eskiler, G.; Kalayci Yigin, A.; Akdogan, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of nobiletin on TLR4/TRIF/IRF3 and TLR9/IRF7 signaling pathways in prostate cancer cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenlocher, Y.; Gommeringer, S.; Held, A.; Feilhauer, K.; Köninger, J.; Bischoff, S.C.; Lorentz, A. Nobiletin acts anti-inflammatory on murine IL-10−/− colitis and human intestinal fibroblasts. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, D.; Yu, C.; Lv, B.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y. Citrus nobiletin ameliorates experimental colitis by reducing inflammation and restoring impaired intestinal barrier function. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Bmal1 | CCACCTCAGAGCCATTGATACA | GAGCAGGTTTAGTTCCACTTTGTCT |
| Cry1 | CTGGCGTGGAAGTCATCGT | CTGTCCGCCATTGAGTTCTATG |
| Per2 | ATGCTCGCCATCCACAAGA | GCGGAATCGAATGGGAGAAT |
| Dbp | CTGGCCCGAGTCTTTTTGC | CCAGGTCCACGTATTCCACG |
| Nr1d1 | CATGGTGCTACTGTGTAAGGTGTGT | CACAGGCGTGCACTCCATAG |
| Dec1 | CATGAGAACACTCGGGACC | CCACACGATGGAGATGAGTG |
| Dec2 | AAACCTGCGCCAAAGAAGT | CTGGGTGTCCAGCTCTCAA |
| C/ebpβ | AAGCTGAGCGACGAGTACAAGA | GTCAGCTCCAGCACCTTGTG |
| Pparγ | GAAAGACAACGGACAAATCACC | GGGGGTGATATGTTTGAACTTG |
| Lpl | GGGAGTTTGGCTCCAGAGTTT | TGTGTCTTCAGGGGTCCTTAG |
| Cd36 | AAGCTATTGCGACATGATT | GATCCGAACACAGCGTAGAT |
| Fas | GCAAATGAATGGGGGTACA | CAGTGTTCACAGCCAGGAGA |
| Scd1 | CTGACCTGAAAGCCGCGAAG | GCGTTGAGCACCAGAGTGTA |
| IkBα | TCCTGAGCTCCGAGACTTTC | GCGTCAAGACTGCTACACTG |
| Tnfα | CACCACCATCAAGGACTCAA | TCCAGCCTCATTCTGAGACA |
| Il1β | TGTGGCAGCTACCTGTGTCT | TCATCTCGGAGCCTGTAGTG |
| Il6 | ACAACCACGGCCTTCCCTACTT | CACGATTTCCCAGAGAACATGTG |
| Infγ | TCAAGTGGCATAGATGTGGAAGAA | TGGCTCTGCAGGATTTTCATG |
| Gapdh | CAAGGTCATCCATGACAACTTTG | GGCCATCCACAGTCTTCTGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.; Mawatari, K.; Yoo, S.-H.; Chen, Z. The Circadian Nobiletin-ROR Axis Suppresses Adipogenic Differentiation and IκBα/NF-κB Signaling in Adipocytes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183919
Kim E, Mawatari K, Yoo S-H, Chen Z. The Circadian Nobiletin-ROR Axis Suppresses Adipogenic Differentiation and IκBα/NF-κB Signaling in Adipocytes. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183919
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eunju, Kazuaki Mawatari, Seung-Hee Yoo, and Zheng Chen. 2023. "The Circadian Nobiletin-ROR Axis Suppresses Adipogenic Differentiation and IκBα/NF-κB Signaling in Adipocytes" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183919
APA StyleKim, E., Mawatari, K., Yoo, S.-H., & Chen, Z. (2023). The Circadian Nobiletin-ROR Axis Suppresses Adipogenic Differentiation and IκBα/NF-κB Signaling in Adipocytes. Nutrients, 15(18), 3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183919






