Dandelion Polysaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat-Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities
Abstract
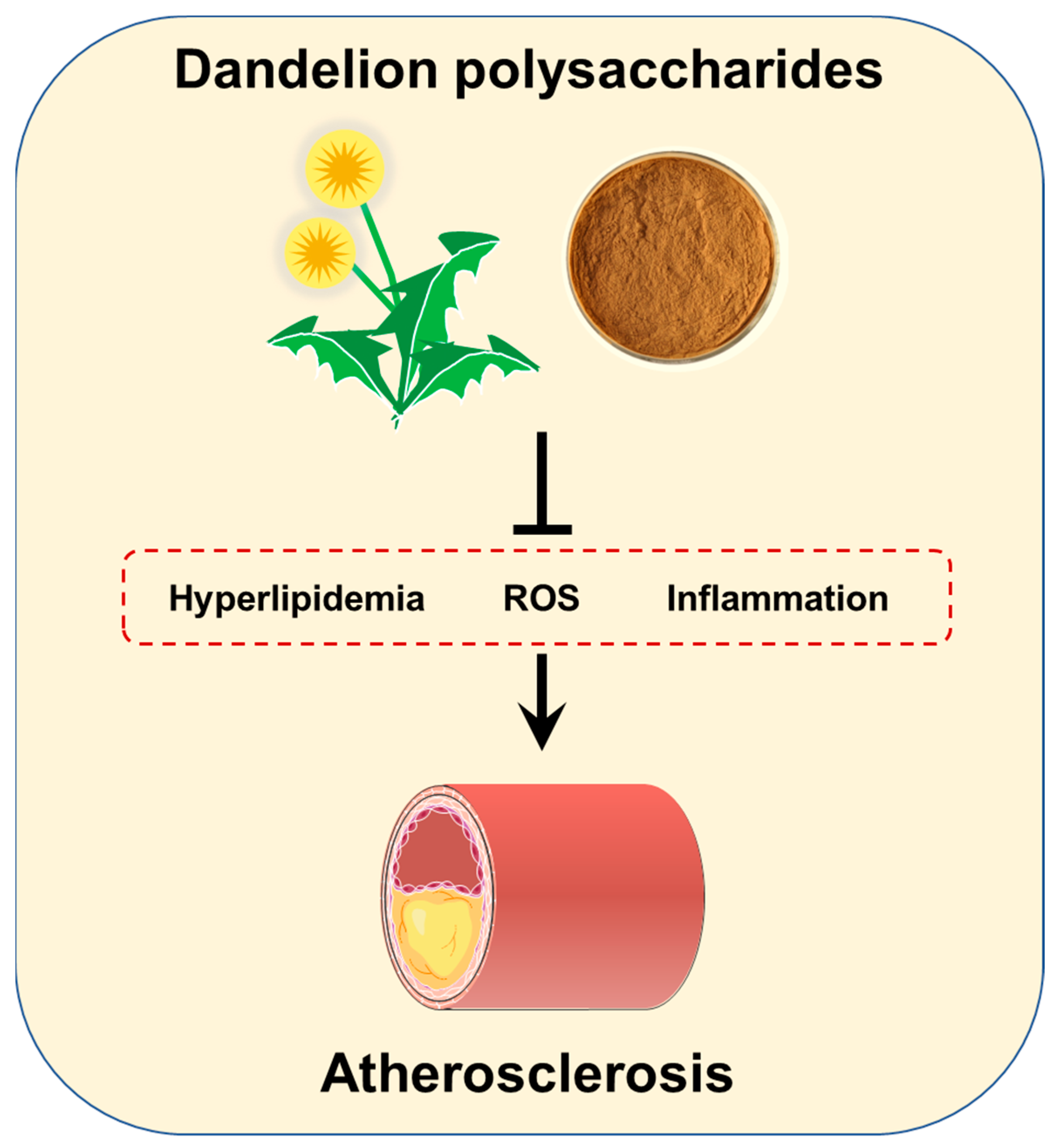
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
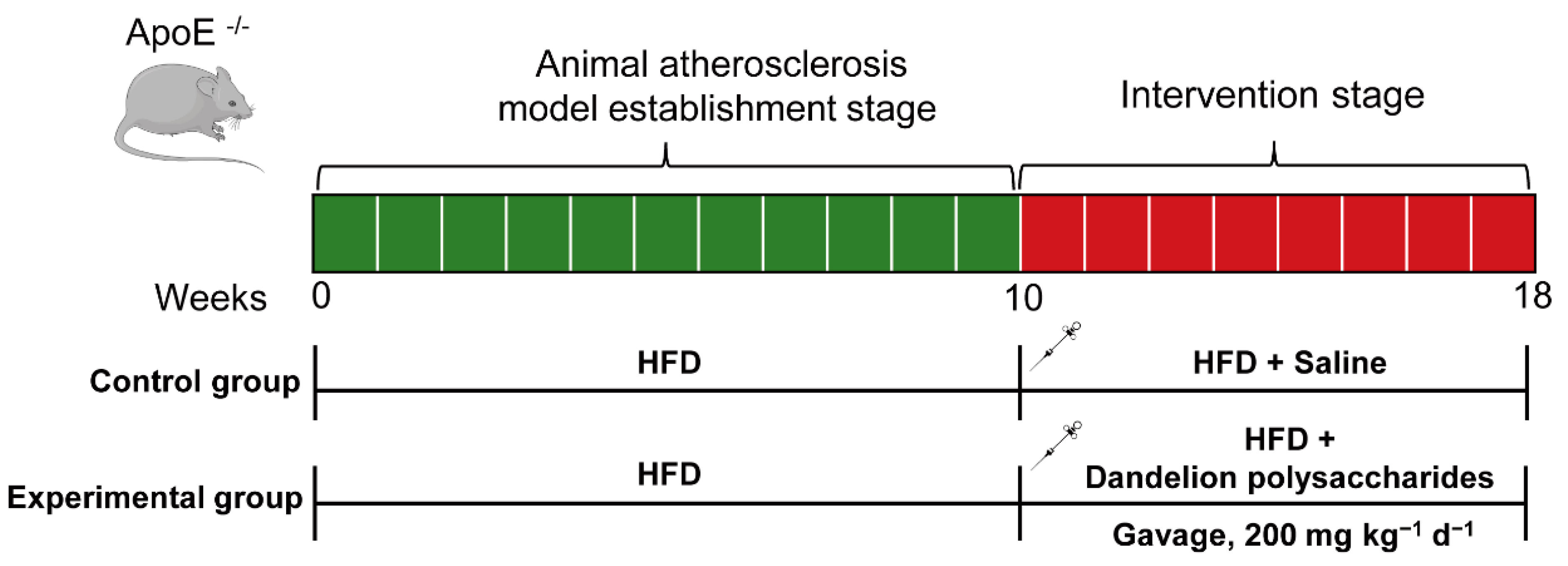
2.1. Animals
2.2. Characterization of Dandelion Polysaccharides
2.3. Analysis of Serum Lipid Profiles
2.4. Hematoxylin–Eosin (HE) Staining for Aorta
2.5. Oil Red O Staining for Lesions in Aorta
2.6. Masson’s Trichrome Stain
2.7. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.8. Analysis of MDA, SOD, and GSH-PX Levels in Serum
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.10. Immunoblotting Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Dandelion Polysaccharides
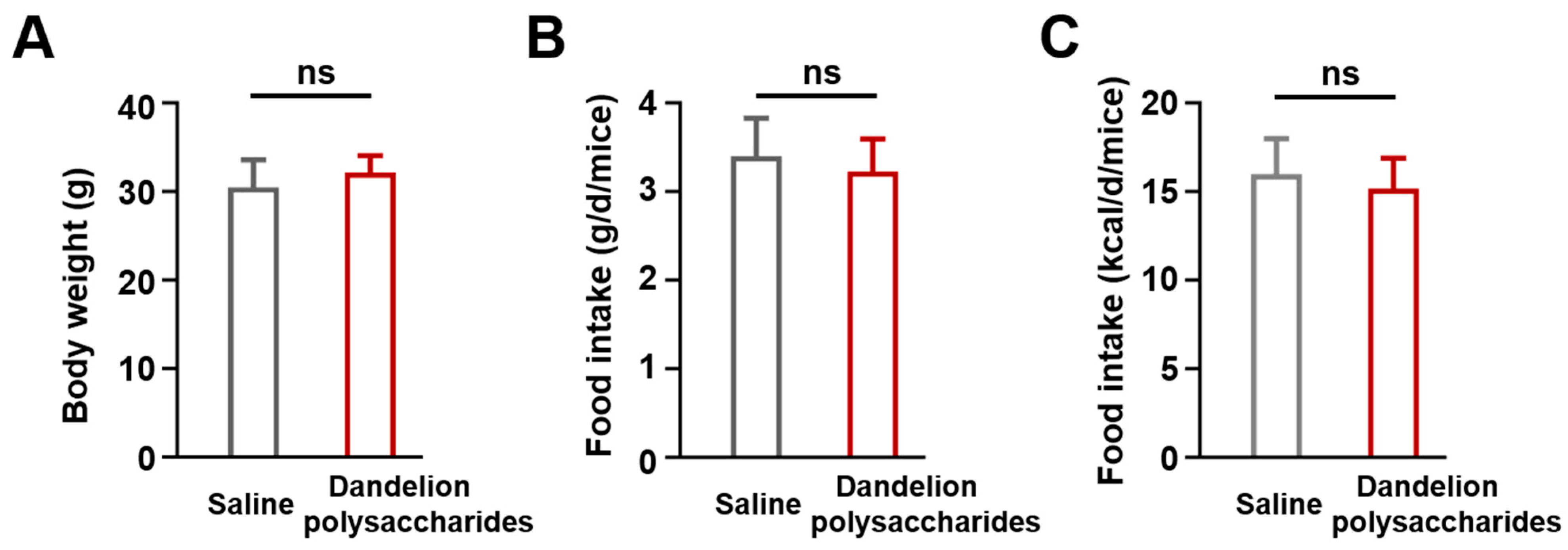
3.2. The Establishement of Atherosclerotic Animal Model
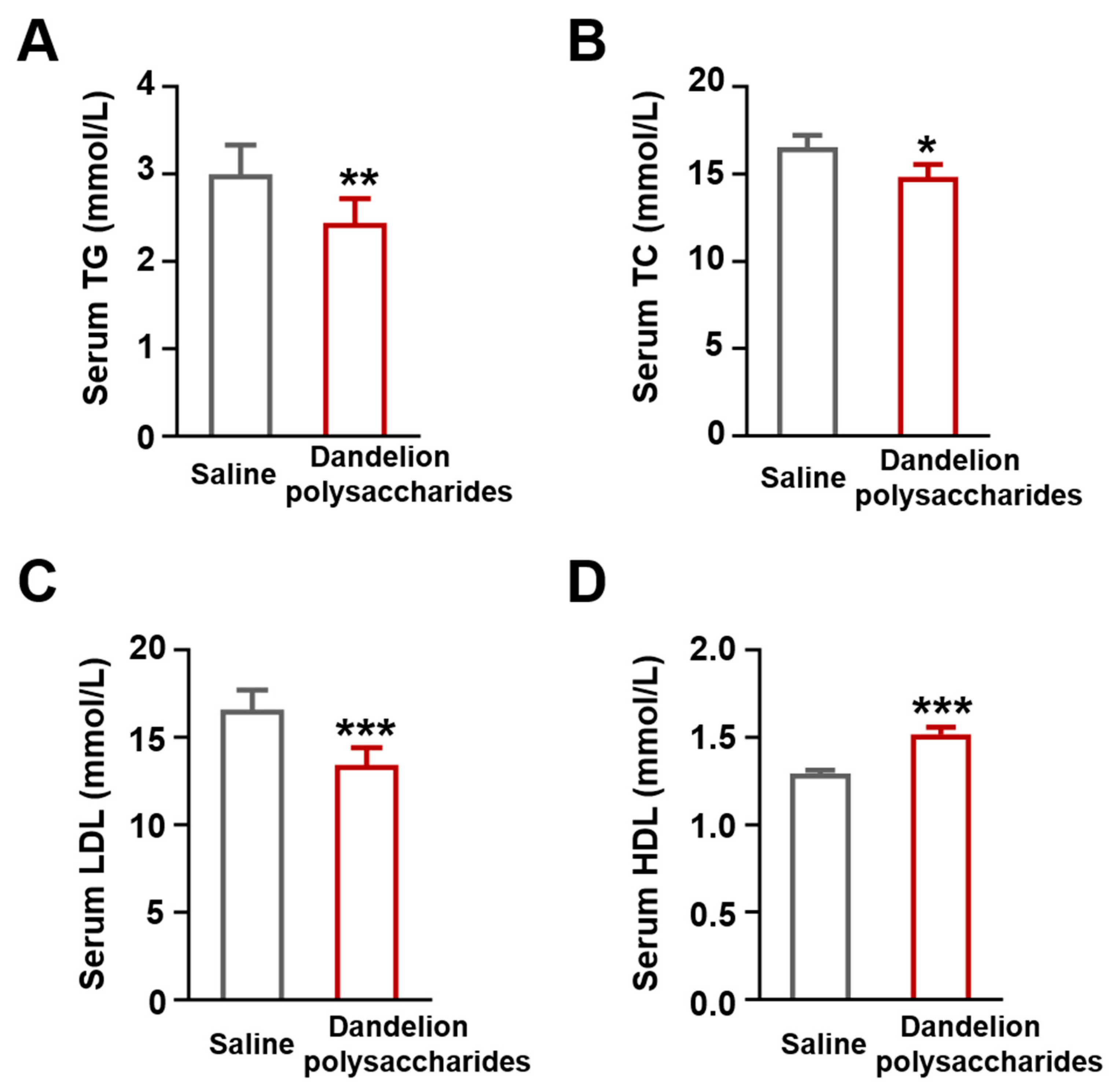
3.3. Dandelion Polysaccharides Improved Lipid Profiles
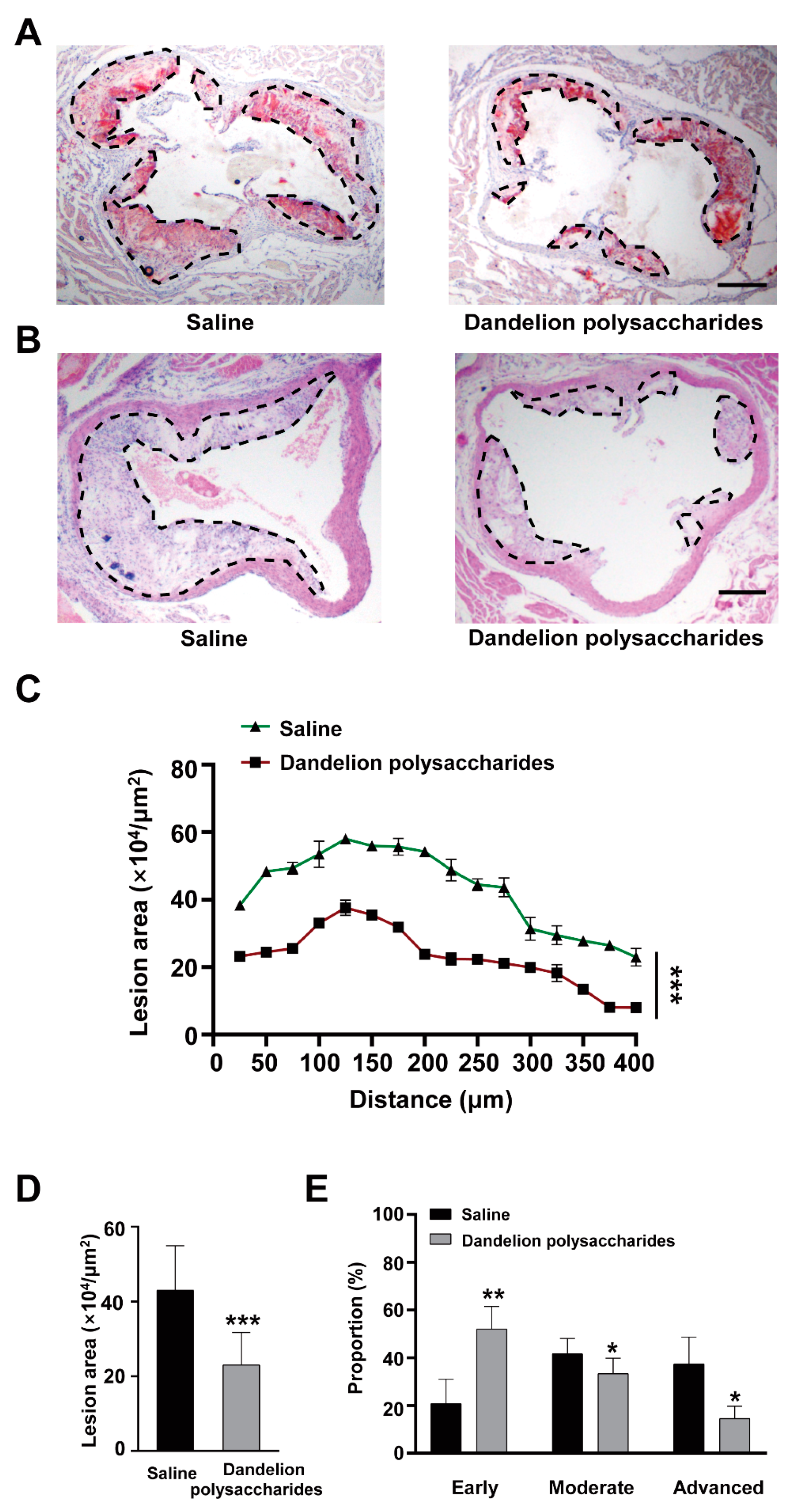
3.4. Dandelion Polysaccharides Reduce Atherosclerotic Plaques in Aortic Roots
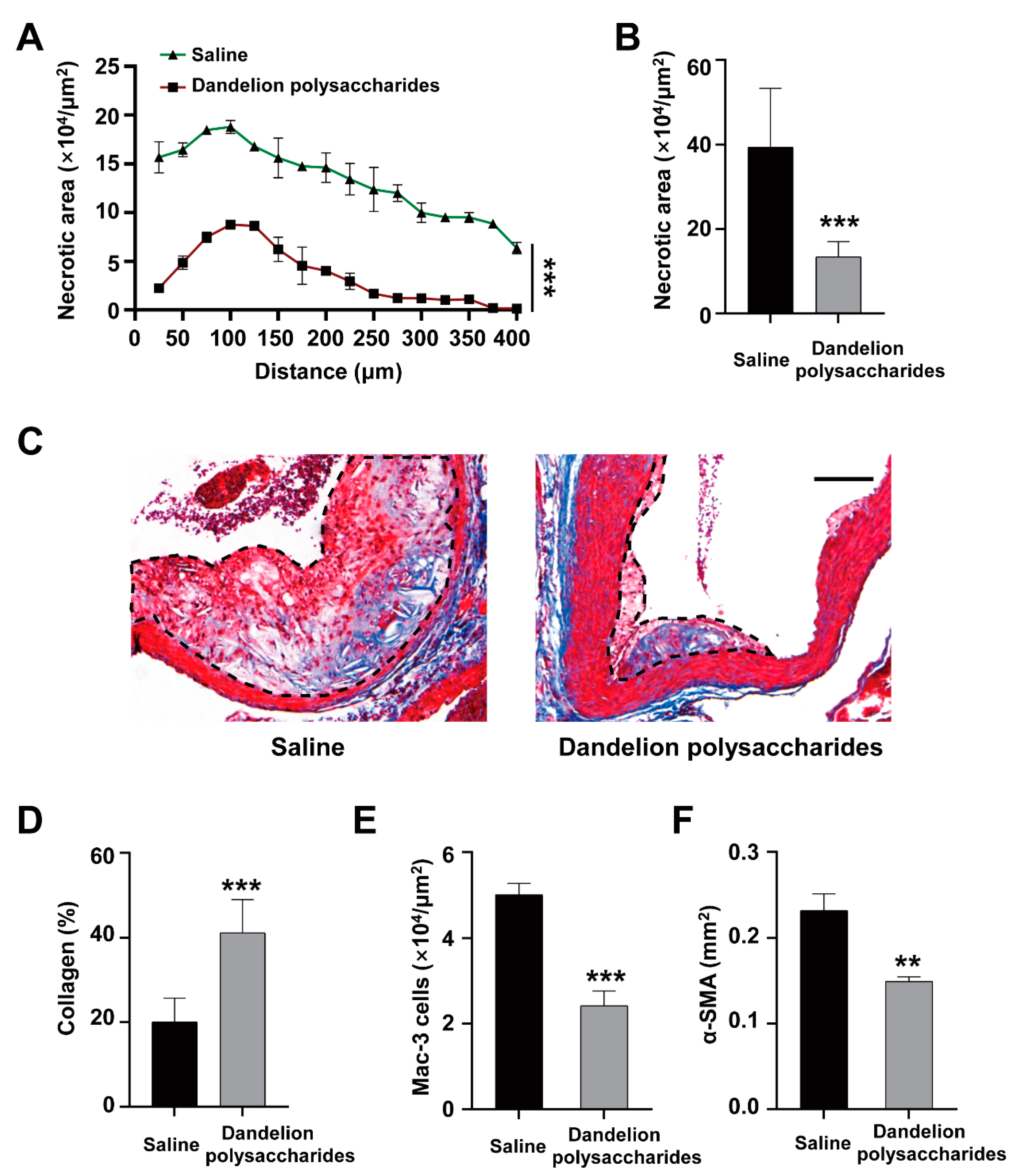
3.5. Dandelion Polysaccharides Reduce Necrotic Core Area and Elevated Collagen Content of Plaques
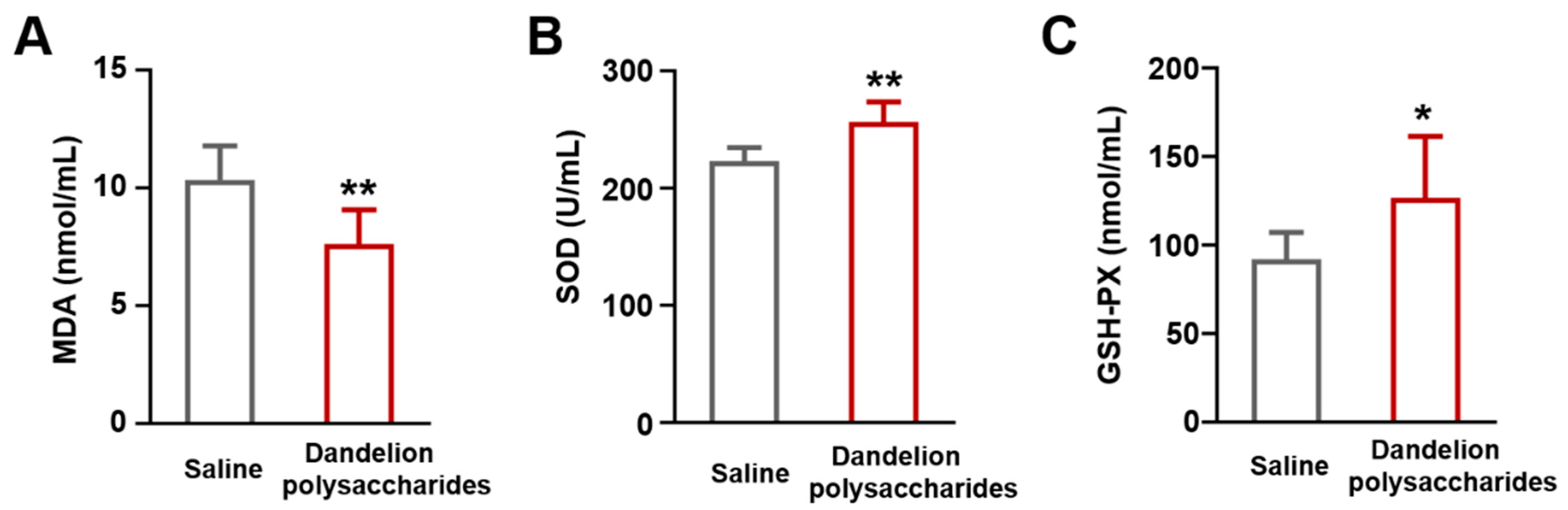
3.6. Dandelion Polysaccharides Reduce the Levels of Oxidant-Related Markers in Serum Samples
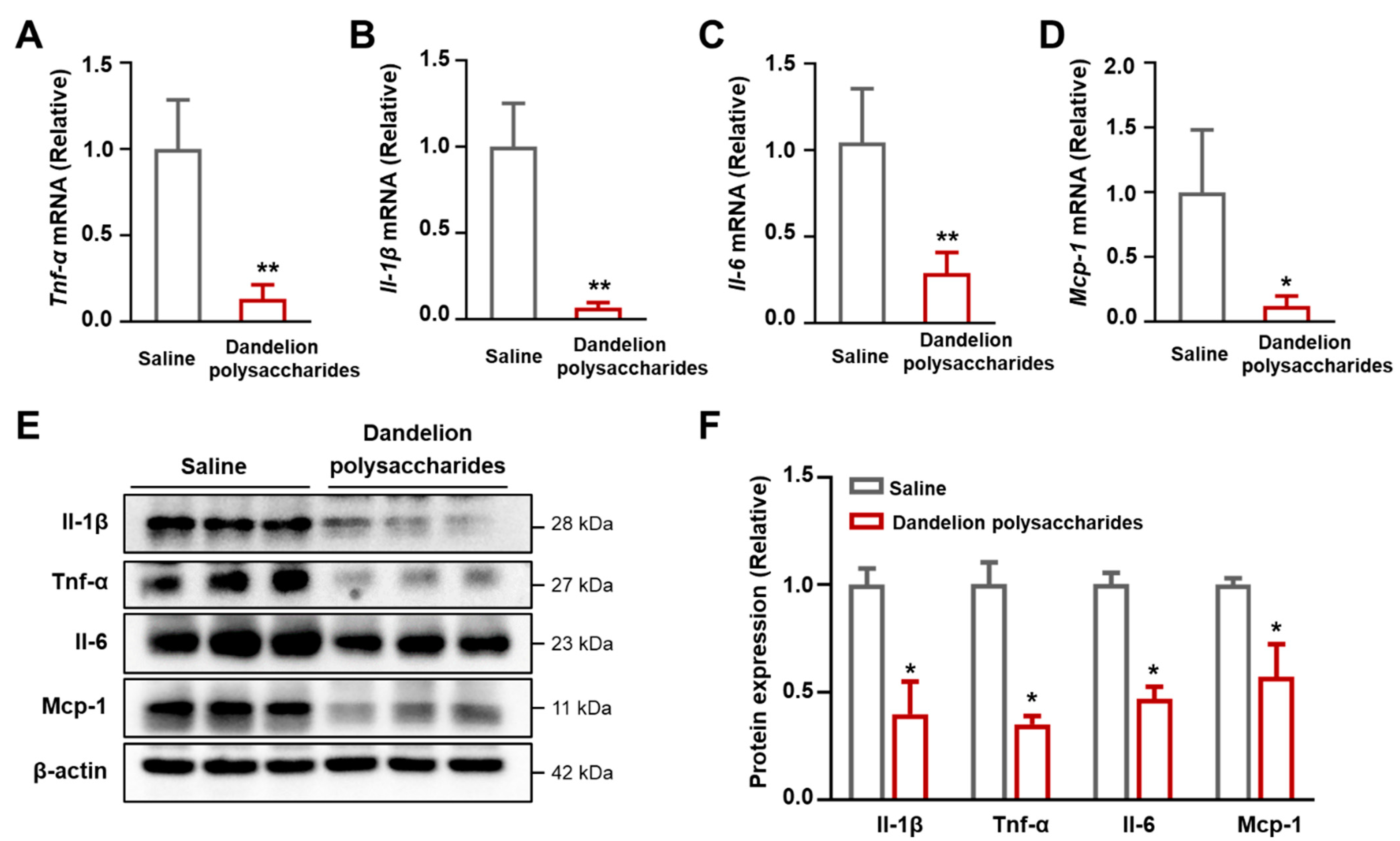
3.7. Dandelion Polysaccharides Reduce the Expression of Inflammatory Factors in Aorta
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Weber, C.; Noels, H. Atherosclerosis: Current Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Options. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Shan, S.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Hao, R.; Yang, R.; Li, Z. Millet Shell Polyphenols Prevent Atherosclerosis by Protecting the Gut Barrier and Remodeling the Gut Microbiota in ApoE−/− Mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7298–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, X.-Q.; Xiao, J.-J.; Zhang, H.-N.; Wang, J.-H.; Pan, L.-H.; Yang, X.-F.; Luo, J.-P. Polysaccharides in Laminaria Japonica (LP): Extraction, Physicochemical Properties and Their Hypolipidemic Activities in Diet-Induced Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Voyles, S.V.; Armstrong, E.J.; Fuller, E.N.; Rutledge, J.C. Angiogenesis and Oxidative Stress: Common Mechanisms Linking Psoriasis with Atherosclerosis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanet, A.; Milenkovic, D.; Deval, C.; Potier, M.; Constans, J.; Mazur, A.; Bennetau-Pelissero, C.; Morand, C.; Bérard, A.M. Naringin, the Major Grapefruit Flavonoid, Specifically Affects Atherosclerosis Development in Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia in Mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, C.; Tian, G.; Wei, X.; Ma, Z.; Cui, J.; Wei, R.; Bao, Y.; Kong, W.; Zheng, J. Naringin Alleviates Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− Mice by Regulating Cholesterol Metabolism Involved in Gut Microbiota Remodeling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12651–12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Coupland, C. Unintended Effects of Statins in Men and Women in England and Wales: Population Based Cohort Study Using the QResearch Database. BMJ 2010, 340, c2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Cui, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, T.; Hu, J.; Tian, J.; Yu, B.; Liu, F.; Kou, J.; et al. Ginsenoside Rd Promotes Omentin Secretion in Adipose through TBK1-AMPK to Improve Mitochondrial Biogenesis via WNT5A/Ca2+ Pathways in Heart Failure. Redox Biol. 2023, 60, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, R.; Jiang, H.; Yin, Q.; Gu, J.; Chen, J.; Ji, X.; Wu, X.; Fu, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Autophagy Enhanced by Curcumin Ameliorates Inflammation in Atherogenesis via the TFEB-P300-BRD4 Axis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2280–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Su, W.; Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, F.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Specifically Mediates the Anti-Hypercholesterolemic Effect of Berberine (BBR) and Facilitates to Predict BBR’s Cholesterol-Decreasing Efficacy in Patients. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 37, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, M.; Lis, B.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Ognik, K.; Jedrejek, D.; Stochmal, A.; Olas, B. The Composition and Vascular/Antioxidant Properties of Taraxacum Officinale Flower Water Syrup in a Normal-Fat Diet Using an Obese Rat Model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 265, 113393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.; Poirrier, P.; Chamy, R.; Prüfer, D.; Schulze-Gronover, C.; Jorquera, L.; Ruiz, G. Taraxacum Officinale and Related Species-An Ethnopharmacological Review and Its Potential as a Commercial Medicinal Plant. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 169, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, K.; Carle, R.; Schieber, A. Taraxacum—A Review on Its Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davaatseren, M.; Hur, H.J.; Yang, H.J.; Hwang, J.-T.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, M.J.; Kwon, D.Y.; Sung, M.J. Taraxacum Official (Dandelion) Leaf Extract Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.-K.; Lee, O.-H.; Yim, J.H.; Cho, C.-W.; Rhee, Y.K.; Lim, S.-I.; Kim, Y.-C. Hypolipidemic and Antioxidant Effects of Dandelion (Taraxacum Officinale) Root and Leaf on Cholesterol-Fed Rabbits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Gao, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, W. Characterization, Antioxidant and Immunomodulatory Effects of Selenized Polysaccharides from Dandelion Roots. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-B. Effect of Dandelion Polysaccharides on the Retardation of the Quality Changes of White Shrimp. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.M.; Youn, H.J.; Chang, H.K.; Song, Y.S. TOP1 and 2, Polysaccharides from Taraxacum Officinale, Attenuate CCl4-Induced Hepatic Damage through the Modulation of NF-kappaB and Its Regulatory Mediators. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.-J.; Cha, D.-S.; Ko, J.-S.; Park, H.-J.; Choi, H.-D. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Taraxacum Officinale Leaves on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW 264.7 Cells. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Yoo, S.; Yoon, H.-G.; Park, J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, S.; Oh, K.-T.; Lee, J.; Cho, H.-Y.; Jun, W. In Vitro and in Vivo Hepatoprotective Effects of the Aqueous Extract from Taraxacum Officinale (Dandelion) Root against Alcohol-Induced Oxidative Stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahesh, A.; Jeyachandran, R.; Cindrella, L.; Thangadurai, D.; Veerapur, V.P.; Muralidhara Rao, D. Hepatocurative Potential of Sesquiterpene Lactones of Taraxacum Officinale on Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Liver Toxicity in Mice. Acta Biol. Hung. 2010, 61, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Castejón, M.; Visioli, F.; Rodriguez-Casado, A. Diverse Biological Activities of Dandelion. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäck, M.; Yurdagul, A.; Tabas, I.; Öörni, K.; Kovanen, P.T. Inflammation and Its Resolution in Atherosclerosis: Mediators and Therapeutic Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Duan, H.; Qian, Y.; Feng, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, F.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Qin, Z.; Yan, X. Macrophagic CD146 Promotes Foam Cell Formation and Retention during Atherosclerosis. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Tabas, I. Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Cell 2011, 145, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.R.; Sinha, S.; Owens, G.K. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Luo, J.; Qi, J.; Zhao, X.; An, P.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G. The Role and Mechanism of Polysaccharides in Anti-Aging. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycan, I.Ö.; Tüfek, A.; Tokgöz, O.; Evliyaoğlu, O.; Fırat, U.; Kavak, G.Ö.; Turgut, H.; Yüksel, M.U. Thymoquinone Treatment against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, M.F.; Yancey, P.G.; Tao, H.; Davies, S.S. HDL Function and Atherosclerosis: Reactive Dicarbonyls as Promising Targets of Therapy. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 1521–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.L.; Baker, A.H.; Oka, K.; Chan, L.; Newby, A.C.; Jackson, C.L.; George, S.J. Suppression of Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression and Instability by Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2: Involvement of Macrophage Migration and Apoptosis. Circulation 2006, 113, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattoor, A.J.; Pothineni, N.V.K.; Palagiri, D.; Mehta, J.L. Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, S. Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 109, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Xie, W.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Dai, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Inhibitory Effects of Ginsenoside Rb1 on Early Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− Mice via Inhibition of Apoptosis and Enhancing Autophagy. Molecules 2018, 23, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-W.; Ma, X.; Huang, J.-L.; Mao, X.-R.; Yang, J.-Y.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Li, S.-F.; Qiu, Y.-R.; Yang, J.; Zheng, L.; et al. Dihydrocapsaicin Attenuates Plaque Formation through a PPARγ/LXRα Pathway in apoE−/− Mice Fed a High-Fat/High-Cholesterol Diet. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, C.; Huang, Z.; Tan, L.; Xun, P.; Huang, Q.; Lin, H.; Ye, C.; Wang, A. Effects of Dietary Dandelion Extract on Intestinal Morphology, Antioxidant Status, Immune Function and Physical Barrier Function of Juvenile Golden Pompano Trachinotus Ovatus. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 73, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. The Changing Landscape of Atherosclerosis. Nature 2021, 592, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramji, D.P.; Davies, T.S. Cytokines in Atherosclerosis: Key Players in All Stages of Disease and Promising Therapeutic Targets. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2015, 26, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, D.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.S. Anti-Inflammatory Evaluation of the Methanolic Extract of Taraxacum Officinale in LPS-Stimulated Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, J.; Ulfgren, A.K.; Nyberg, P.; Hedin, U.; Swedenborg, J.; Andersson, U.; Hansson, G.K. Cytokine Expression in Advanced Human Atherosclerotic Plaques: Dominance of pro-Inflammatory (Th1) and Macrophage-Stimulating Cytokines. Atherosclerosis 1999, 145, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Progress and Challenges in Translating the Biology of Atherosclerosis. Nature 2011, 473, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.-A.; Park, D.W.; Kwon, J.E.; Song, H.S.; Park, B.; Jeon, H.; Sohn, E.-H.; Koo, H.J.; Kang, S.C. Quinic Acid Inhibits Vascular Inflammation in TNF-α-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Carru, C.; Piga, M.; Erre, G.L. Protective Effects of Methotrexate against Proatherosclerotic Cytokines: A Review of the Evidence. Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9632846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Peng, Y.; Yan, S.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Lan, T. Andrographolide Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Pro-Inflammation and ROS Generation-Mediated Foam Cell Formation. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhi, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Zang, L.; Liu, F.; Niu, X. Cinnamaldehyde Attenuates Atherosclerosis via Targeting the IκB/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in High Fat Diet-Induced ApoE−/− Mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4001–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiopu, A.; Bengtsson, J.; Söderberg, I.; Janciauskiene, S.; Lindgren, S.; Ares, M.P.S.; Shah, P.K.; Carlsson, R.; Nilsson, J.; Fredrikson, G.N. Recombinant Human Antibodies against Aldehyde-Modified Apolipoprotein B-100 Peptide Sequences Inhibit Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004, 110, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskesund, R.; Su, J.; Bulatovic, I.; Vikström, M.; de Faire, U.; Frostegård, J. IgM Phosphorylcholine Antibodies Inhibit Cell Death and Constitute a Strong Protection Marker for Atherosclerosis Development, Particularly in Combination with Other Auto-Antibodies against Modified LDL. Results Immunol. 2012, 2, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, R.; Ketelhuth, D.F.J.; Strodthoff, D.; Gregori, S.; Hansson, G.K. Subcutaneous Immunization with Heat Shock Protein-65 Reduces Atherosclerosis in Apoe−/− Mice. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raish, M.; Ahmad, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Aljenoobi, F.I.; Jan, B.L.; Al-Mohizea, A.M.; Khan, A.; Ali, N. Momordica Charantia Polysaccharides Ameliorate Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Ethanol-Induced Gastritis in Mucosa through NF-kB Signaling Pathway Inhibition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Niu, H.; Liu, J.; Ruilian, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, J.; Dong, Y.; et al. Astragalus Polysaccharide from Astragalus Melittin Ameliorates Inflammation via Suppressing the Activation of TLR-4/NF-κB P65 Signal Pathway and Protects Mice from CVB3-Induced Virus Myocarditis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H. Structural Characteristics and Immunopotentiation Activity of Two Polysaccharides from the Petal of Crocus Sativus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, X.-X.; Pan, S.-N. Effects of Dandelion Extract on the Proliferation of Rat Skeletal Muscle Cells and the Inhibition of a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Reaction. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asha, K.; Singal, A.; Sharma, S.B.; Arora, V.K.; Aggarwal, A. Dyslipidaemia & Oxidative Stress in Patients of Psoriasis: Emerging Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Indian J. Med. Res. 2017, 146, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Xia, N.; Li, H. Roles of Vascular Oxidative Stress and Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Chen, B.; Yi, F.; Zou, S. Optimization of Extraction of Polysaccharide from Dandelion Root by Response Surface Methodology: Structural Characterization and Antioxidant Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
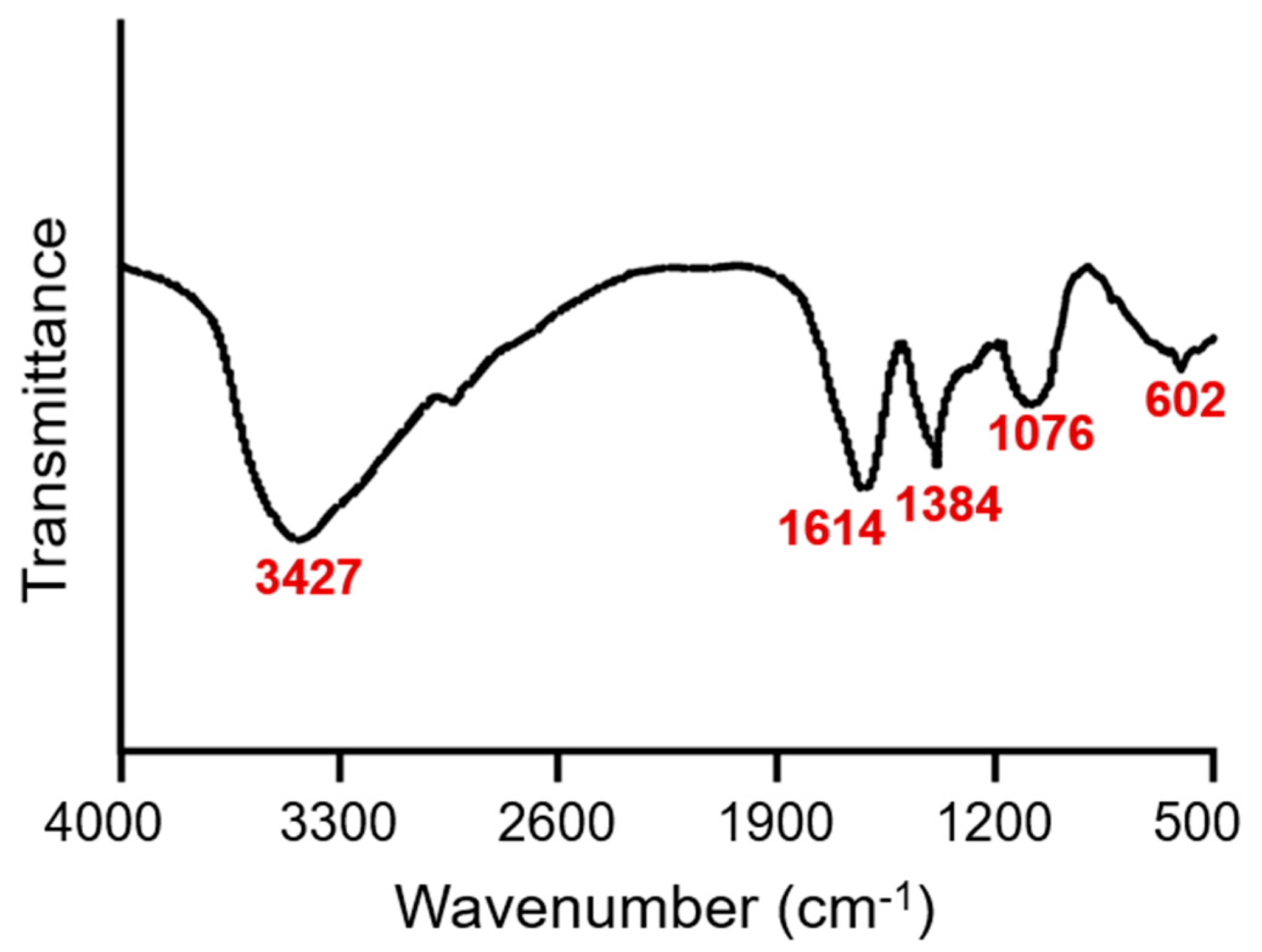
| Items | Amount |
|---|---|
| Number average molecular weight (Mn) | 533 |
| Weight average molecular weight (Mw) | 4293 |
| Z average molecular weight (Mz) | 129,668 |
| Glucose (μmol/L) | 9.2 |
| Galactose (μmol/L) | 5.3 |
| Ribose (μmol/L) | 1.3 |
| Fucose (μmol/L) | 0.4 |
| Xylose (μmol/L) | 4.3 |
| Arabinose (μmol/L) | 6.0 |
| Rhamnose (μmol/L) | 2.4 |
| Mannose (μmol/L) | 1.6 |
| Glucuronic acid (μmol/L) | 1.5 |
| Galacturonic acid (μmol/L) | 3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Wang, Z.; Hao, Y.; An, P.; Luo, J.; Luo, Y. Dandelion Polysaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat-Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194120
Zhou S, Wang Z, Hao Y, An P, Luo J, Luo Y. Dandelion Polysaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat-Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194120
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shuaishuai, Zi Wang, Yanling Hao, Peng An, Junjie Luo, and Yongting Luo. 2023. "Dandelion Polysaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat-Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities" Nutrients 15, no. 19: 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194120
APA StyleZhou, S., Wang, Z., Hao, Y., An, P., Luo, J., & Luo, Y. (2023). Dandelion Polysaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat-Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities. Nutrients, 15(19), 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194120









