Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Supplementation of Preterm Infants on Growth, Body Composition, and Blood Pressure at 7-Years Corrected Age: Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The DINO Trial
2.2. DINO 7y Follow-Up Study
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
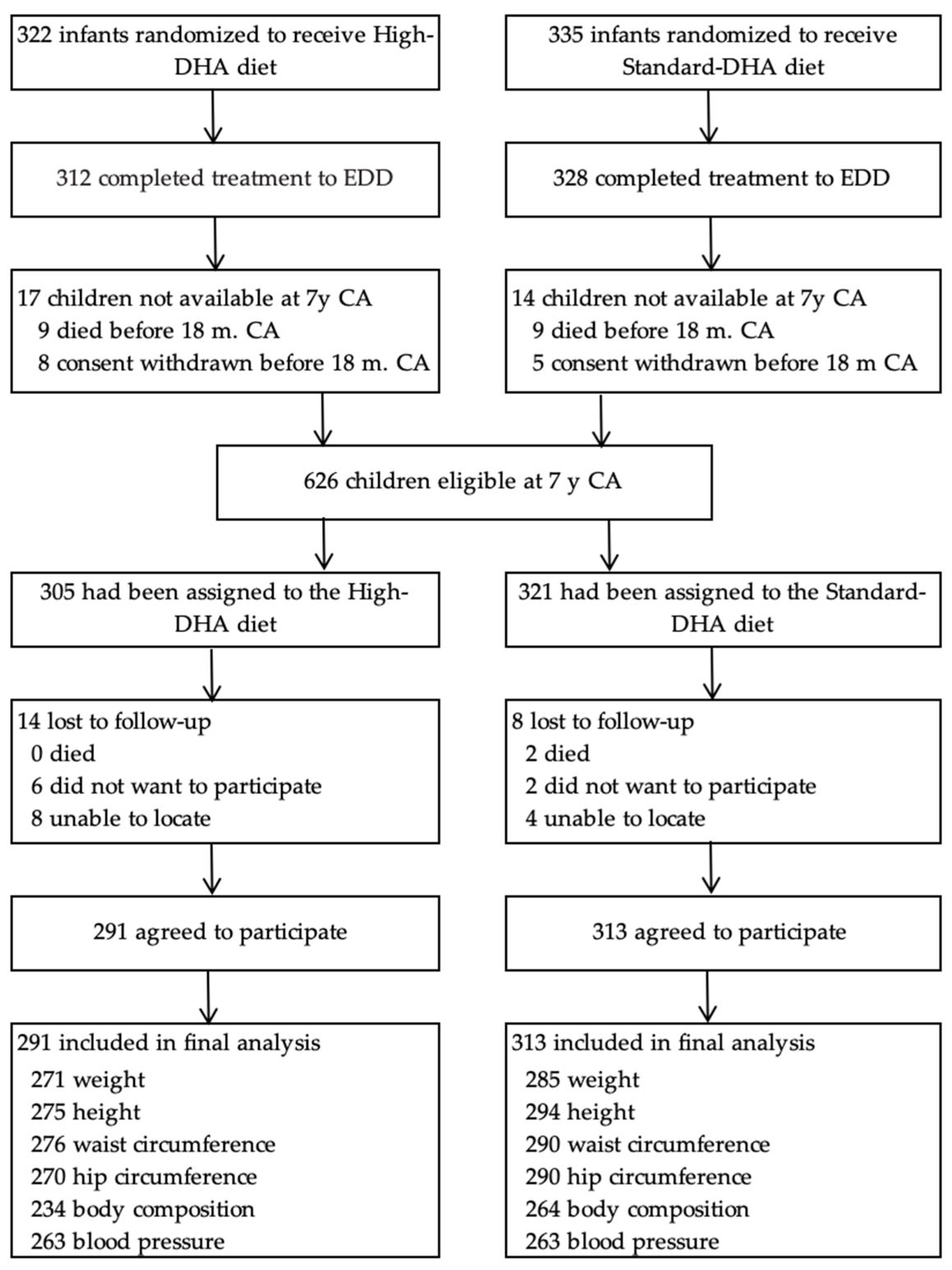
3.1. Participant Flow and Loss to Follow-Up
3.2. Baseline and Follow-Up Characteristics
3.3. Anthropometric Outcomes
3.4. Weight Status
3.5. Blood Pressure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Innis, S.M. Dietary (n-3) fatty acids and brain development. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, R.E.; Bazan, N.G. Changing fatty acid content of growth cone lipids prior to synaptogenesis. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M. Tissue levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids during early human development. J. Pediatr. 1992, 120, S129–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auestad, N.; Innis, S.M. Dietary n-3 fatty acid restriction during gestation in rats: Neuronal cell body and growth-cone fatty acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 312s–314s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lapillonne, A.; Groh-Wargo, S.; Gonzalez, C.H.; Uauy, R. Lipid needs of preterm infants: Updated recommendations. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, S37–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrides, M.; Gibson, R.A.; McPhee, A.J.; Collins, C.T.; Davis, P.G.; Doyle, L.W.; Simmer, K.; Colditz, P.B.; Morris, S.; Smithers, L.G.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants fed high-dose docosahexaenoic acid: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, C.T.; Makrides, M.; McPhee, A.J.; Sullivan, T.R.; Davis, P.G.; Thio, M.; Simmer, K.; Rajadurai, V.S.; Travadi, J.; Berry, M.J.; et al. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, C.; Haugholt, K.; Lindgren, M.; Aurvåg, A.K.; Rønnestad, A.; Grønn, M.; Solberg, R.; Moen, A.; Nakstad, B.; Berge, R.K.; et al. Improved cognitive development among preterm infants attributable to early supplementation of human milk with docosahexaenoic acid and arachidonic acid. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaas, A.N.; Tamnes, C.K.; Nakstad, B.; Henriksen, C.; Walhovd, K.B.; Fjell, A.M.; Due-Tønnessen, P.; Drevon, C.A.; Iversen, P.O. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and cognition in VLBW infants at 8 years: An RCT. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillot, M.; Synnes, A.; Pronovost, E.; Qureshi, M.; Daboval, T.; Caouette, G.; Olivier, F.; Bartholomew, J.; Mohamed, I.; Massé, E.; et al. Maternal High-Dose DHA Supplementation and Neurodevelopment at 18-22 Months of Preterm Children. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2021055819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.F.; Makrides, M.; Gibson, R.A.; Sullivan, T.R.; McPhee, A.J.; Anderson, P.J.; Best, K.P.; Sharp, M.; Cheong, J.L.Y.; Opie, G.F.; et al. Neonatal Docosahexaenoic Acid in Preterm Infants and Intelligence at 5 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, S.E.; Werkman, S.H.; Tolley, E.A. Effect of long-chain n-3 fatty acid supplementation on visual acuity and growth of preterm infants with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, A.S.; Montalto, M.B.; Groh-Wargo, S.; Mimouni, F.; Sentipal-Walerius, J.; Doyle, J.; Siegman, J.S.; Thomas, A.J. Effect of DHA-containing formula on growth of preterm infants to 59 weeks postmenstrual age. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 1999, 11, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.T.; Makrides, M.; Gibson, R.A.; McPhee, A.J.; Davis, P.G.; Doyle, L.W.; Simmer, K.; Colditz, P.B.; Morris, S.; Sullivan, T.R.; et al. Pre- and post-term growth in pre-term infants supplemented with higher-dose DHA: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fewtrell, M.S.; Abbott, R.A.; Kennedy, K.; Singhal, A.; Morley, R.; Caine, E.; Jamieson, C.; Cockburn, F.; Lucas, A. Randomized, Double-Blind Trial Of Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation with Fish Oil And Borage Oil In Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. 2004, 144, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, K.; Ross, S.; Isaacs, E.B.; Weaver, L.T.; Singhal, A.; Lucas, A.; Fewtrell, M.S. The 10-year follow-up of a randomised trial of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in preterm infants: Effects on growth and blood pressure. Arch. Dis. Child 2010, 95, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casirati, A.; Somaschini, A.; Perrone, M.; Vandoni, G.; Sebastiani, F.; Montagna, E.; Somaschini, M.; Caccialanza, R. Preterm birth and metabolic implications on later life: A narrative review focused on body composition. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, e978271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, A.W.; Makrides, M.; Collins, C.T.; Gibson, R.A.; McPhee, A.J.; Sullivan, T.R.; Gould, J.F.; Green, T.J.; Doyle, L.W.; Davis, P.G.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid supplementation of preterm infants and parent-reported symptoms of allergic disease at 7 years corrected age: Follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Child Growth Standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2006, 450, 76–85. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, K.J.; Shypailo, R.J.; Wong, W.W. Measurement of body water by multifrequency bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy in a multiethnic pediatric population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.R.; White, I.R.; Salter, A.B.; Ryan, P.; Lee, K.J. Should multiple imputation be the method of choice for handling missing data in randomized trials? Stat. Methods. Med. Res. 2018, 27, 2610–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, S.E.; Cooke, R.J.; Werkman, S.H.; Tolley, E.A. First year growth of preterm infants fed standard compared to marine oil n-3 supplemented formula. Lipids 1992, 27, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geleijnse, J.M.; Giltay, E.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Donders, A.R.; Kok, F.J. Blood pressure response to fish oil supplementation: Metaregression analysis of randomized trials. J. Hypertens. 2002, 20, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.C.; Sacks, F.; Rosner, B. Does fish oil lower blood pressure? A meta-analysis of controlled trials. Circulation. 1993, 88, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markopoulou, P.; Papanikolaou, E.; Analytis, A.; Zoumakis, E.; Siahanidou, T. Preterm Birth as a Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease in Adult Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. 2019, 210, 69–80.e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voortman, T.; van den Hooven, E.H.; Braun, K.V.E.; van den Broek, M.; Bramer, W.M.; Chowdhurry, R.; Franco, O.H. Effects of polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and status during pregnancy, lactation, and early childhood on cardiometabolic health: A systematic review. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2015, 59, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| High-DHA (n = 291) | Standard-DHA (n = 313) | |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | ||
| Gestational age, weeks | 30.0 (28.0, 31.0) | 30.0 (28.0, 31.0) |
| Birth weight, g | 1307 ± 420 | 1320 ± 410 |
| Male, n (%) | 152 (52.2) | 172 (55.0) |
| Singleton birth, n (%) | 208 (71.5) | 195 (62.3) |
| Birth weight <1250 g | 132 (45.4) | 139 (44.4) |
| Birth weight <5th percentile | 33 (11.3) | 37 (11.8) |
| Birth length 2, cm | 38.2 ± 3.9 | 38.2 ± 4.1 |
| Maternal age, y | 29.9 ± 5.7 | 30.5 ± 5.2 |
| Smoked during pregnancy | 77 (26.5) | 76 (24.3) |
| Infant breastmilk at trial entry | 271 (93.1) | 291 (93.0) |
| 7-Year Follow-up | ||
| Corrected age at follow-up 3, y | 7.2 ± 0.4 | 7.2 ± 0.3 |
| Fish in the previous month 4 | 248 (87.0) | 267 (89.6) |
| -no. fish meals in the previous month | 5.0 ± 3.8 | 5.1 ± 3.6 |
| DHA-enriched food in the previous month 4 | 172 (60.4) | 181 (60.7) |
| DHA supplements in the previous month 5 | 73 (25.8) | 57 (19.5) |
| High-DHA (n = 291) | Standard-DHA (n = 313) | Adjusted Difference 2 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight, kg | 24.3 ± 5.4 | 23.9 ± 5.0 | 0.5 (−0.4, 1.4) | 0.28 |
| Weight z-score | 0.15 ± 1.34 | 0.06 ± 1.28 | 0.09 (−0.13, 0.31) | 0.41 |
| Height, cm | 122.2 ± 6.6 | 122.2 ± 6.1 | 0.1 (−1.0, 1.2) | 0.86 |
| Height z-score | −0.01 ± 1.14 | −0.00 ± 1.10 | 0.00 (−0.19, 0.19) | 1.00 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 16.1 ± 2.4 | 15.9 ± 2.4 | 0.3 (−0.2, 0.7) | 0.21 |
| BMI z-scores | 0.19 ± 1.26 | 0.05 ± 1.26 | 0.15 (−0.07, 0.36) | 0.18 |
| WC, cm | 56.5 ± 6.6 | 56.0 ± 6.3 | 0.6 (−0.5, 1.7) | 0.28 |
| WC z-scores | 0.40 ± 1.45 | 0.29 ± 1.39 | 0.13 (−0.11, 0.37) | 0.29 |
| WHC | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 0.89 ± 0.06 | 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.60 |
| WHC z scores | 0.29 ± 0.87 | 0.33 ± 1.06 | −0.04 (−0.20, 0.13) | 0.68 |
| Lean body mass, kg | 19.3 ± 2.7 | 19.3 ± 2.6 | 0.0 (−0.4, 0.5) | 0.86 |
| Fat mass. kg | 4.8 ± 3.5 | 4.3 ± 3.3 | 0.4 (−0.2, 1.0) | 0.17 |
| High-DHA (n = 291) 2 | Standard-DHA (n = 313) 3 | Adjusted Difference 4 | P Interaction 5 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 0.41 | ||||
| Female | 24.6 ± 5.7 | 23.7 ± 5.1 | 0.9 (−0.5, 2.2) | 0.20 | |
| Male | 24.0 ± 5.2 | 23.9 ± 4.9 | 0.2 (−1.0, 1.3) | 0.79 | |
| Weight z-score | 0.40 | ||||
| Female | 0.3 ± 1.3 | 0.1 ± 1.2 | 0.2 (−0.1, 0.5) | 0.24 | |
| Male | 0.0 ± 1.3 | 0.0 ± 1.3 | 0.0 (−0.3, 0.3) | 0.98 | |
| Height (cm) | 0.65 | ||||
| Female | 122.1 ± 6.5 | 121.8 ± 5.7 | 0.4 (−1.1, 1.8) | 0.64 | |
| Male | 122.3 ± 6.6 | 122.5 ± 6.4 | −0.1 (−1.6, 1.4) | 0.87 | |
| Height z-score | 0.65 | ||||
| Female | 0.1 ± 1.1 | 0.0 ± 1.0 | 0.0 (−0.2, 0.3) | 0.75 | |
| Male | −0.1 ± 1.1 | −0.0 ± 1.2 | −0.0 (−0.3, 0.2) | 0.76 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.33 | ||||
| Female | 16.4 ± 2.7 | 15.9 ± 2.4 | 0.5 (−0.2, 1.1) | 0.14 | |
| Male | 15.9 ± 2.2 | 15.9 ± 2.4 | 0.1 (−0.4, 0.6) | 0.75 | |
| BMI z-score | 0.38 | ||||
| Female | 0.3 ± 1.3 | 0.1 ± 1.2 | 0.2 (−0.1, 0.5) | 0.12 | |
| Male | 0.1 ± 1.3 | 0.0 ± 1.3 | 0.1 (−0.2, 0.3) | 0.69 | |
| WC (cm) | 0.70 | ||||
| Female | 56.7 ± 7.0 | 56.0 ± 6.7 | 0.8 (−0.8, 2.5) | 0.33 | |
| Male | 56.4 ± 6.3 | 56.0 ± 6.0 | 0.4 (−1.0, 1.8) | 0.56 | |
| WC z-score | 0.70 | ||||
| Female | 0.5 ± 1.5 | 0.4 ± 1.4 | 0.2 (−0.2, 0.5) | 0.35 | |
| Male | 0.3 ± 1.4 | 0.2 ± 1.4 | 0.1 (−0.2, 0.4) | 0.60 | |
| WHC | 0.5 | ||||
| Female | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.0 (−0.0, 0.0) | 0.92 | |
| Male | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | −0.0 (−0.0, 0.0) | 0.43 | |
| WHC z-score | 0.92 | ||||
| Female | 0.3 ± 0.8 | 0.3 ± 1.0 | 0.0 (−0.2, 0.2) | 0.86 | |
| Male | 0.2 ± 0.9 | 0.3 ± 1.1 | −0.1 (−0.3, 0.1) | 0.47 | |
| Lean body mass, kg | 0.74 | ||||
| Female | 18.6 ± 2.5 | 18.5 ± 2.3 | 0.1 (−0.4, 0.7) | 0.60 | |
| Male | 20.0 ± 2.7 | 20.0 ± 2.6 | 0.0 (−0.6, 0.6) | 0.96 | |
| Fat mass, kg | 0.32 | ||||
| Female | 5.8 ± 3.7 | 5.0 ± 3.4 | 0.7 (−0.2, 1.6) | 0.12 | |
| Male | 3.8 ± 3.1 | 3.7 ± 3.1 | 0.1 (−0.6, 0.9) | 0.69 |
| High-DHA (n = 291) 2 | Standard-DHA (n = 313) 3 | Adjusted Difference 4 | P Interaction 5 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 0.22 | ||||
| <1250 g | 22.7 ± 5.3 | 22.9 ± 5.0 | −0.1 (−1.4, 1.2) | 0.88 | |
| ≥1250 g | 25.6 ± 5.2 | 24.6 ± 4.8 | 1.0 (−0.2, 2.1) | 0.10 | |
| Weight z-score | 0.28 | ||||
| <1250 g | −0.3 ± 1.4 | −0.2 ± 1.3 | −0.0 (−0.4, 0.3) | 0.83 | |
| ≥1250 g | 0.5 ± 1.2 | 0.3 ± 1.2 | 0.2 (−0.1, 0.5) | 0.15 | |
| Height ± cm | 0.03 | ||||
| <1250 g | 119.9 ± 6.6 | 121.1 ± 6.2 | −1.2 (−2.8, 0.5) | 0.16 | |
| ≥1250 g | 124.1 ± 5.9 | 123.0 ± 5.8 | 1.1 (−0.2, 2.5) | 0.10 | |
| Height z-score | 0.04 | ||||
| <1250 g | −0.4 ± 1.1 | −0.2 ± 1.1 | −0.2 (−0.5, 0.1) | 0.15 | |
| ≥1250 g | 0.3 ± 1.0 | 0.1 ± 1.0 | 0.2 (−0.1, 0.4) | 0.16 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.77 | ||||
| <1250 g | 15.7 ± 2.4 | 15.5 ± 2.4 | 0.2 (−0.4, 0.8) | 0.51 | |
| ≥1250 g | 16.5 ± 2.4 | 16.2 ± 2.3 | 0.3 (−0.2, 0.9) | 0.25 | |
| BMI z-score | 0.88 | ||||
| <1250 g | −0.1 ± 1.3 | −0.2 ± 1.2 | 0.1 (−0.2, 0.4) | 0.42 | |
| ≥1250 g | 0.4 ± 1.2 | 0.3 ± 1.2 | 0.2 (−0.1, 0.4) | 0.26 | |
| WC ± cm) | 0.63 | ||||
| <1250 g | 55.3 ± 6.5 | 55.1 ± 6.4 | 0.3 (−1.3, 1.9) | 0.69 | |
| ≥1250 g | 57.6 ± 6.6 | 56.8 ± 6.2 | 0.8 (−0.6, 2.2) | 0.25 | |
| WC z-score | 0.65 | ||||
| <1250 g | 0.1 ± 1.4 | 0.1 ± 1.4 | 0.1 (−0.3, 0.4) | 0.69 | |
| ≥1250 g | 0.6 ± 1.4 | 0.4 ± 1.4 | 0.2 (−0.1, 0.5) | 0.27 | |
| WHC | 0.12 | ||||
| <1250 g | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.0 (−0.0, 0.0) | 0.44 | |
| ≥1250 g | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | −0.0 (−0.0, 0.0) | 0.15 | |
| WHC z-score | 0.14 | ||||
| <1250 g | 0.4 ± 0.9 | 0.3 ± 1.1 | 0.1 (−0.1, 0.3) | 0.43 | |
| ≥1250 g | 0.2 ± 0.9 | 0.4 ± 1.0 | −0.1 (−0.4, 0.1) | 0.20 | |
| Lean body mass, kg | 0.45 | ||||
| <1250 g | 18.4 ± 2.6 | 18.6 ± 2.6 | −0.1 (−0.8, 0.5) | 0.67 | |
| ≥1250 g | 20.1 ± 2.6 | 19.9 ± 2.4 | 0.2 (−0.4, 0.8) | 0.52 | |
| Fat mass, kg | 0.22 | ||||
| <1250 g | 4.1 ± 3.4 | 4.1 ± 3.4 | 0.0 (−0.8, 0.9) | 0.93 | |
| ≥1250 g | 5.3 ± 3.5 | 4.5 ± 3.2 | 0.7 (0.0, 1.4) | 0.06 |
| High-DHA (n = 291) | Standard-DHA (n = 313) | Adjusted Relative Risk (95% CI) 2 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin 3 | 31 (10.5) | 36 (11.4) | 0.9 (0.6, 1.5) | 0.74 |
| Overweight (85th to 95th percentile) 4 | 20 (7.0) | 25 (8.0) | 0.9 (0.5, 1.6) | 0.68 |
| Obese (>95th percentile) 5 | 42 (14.4) | 28 (9.0) | 1.6 (1.0, 2.6) | 0.05 |
| High-DHA (n = 291) | Standard-DHA (n = 313) | Adjusted Difference | P Interaction 2 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic BP (mm/Hg) | 100.3 ± 10.0 | 101.0 ± 9.8 | −0.7 (−2.4, 1.0) 3 | 0.43 | |
| Sex | 0.53 | ||||
| Female | 100.8 ± 10.8 4 | 101.1 ± 9.7 5 | −0.1 (−2.6, 2.4) 6 | 0.93 | |
| Male | 99.8 ± 9.2 4 | 101.0 ± 9.9 5 | −1.2 (−3.5, 1.1) 6 | 0.31 | |
| Birthweight | 0.24 | ||||
| <1250 g | 100.3 ± 9.8 7 | 100.0 ± 10.5 8 | 0.4 (−2.1, 2.9) 9 | 0.74 | |
| ≥1250 g | 100.2 ± 10.2 7 | 101.9 ± 9.2 8 | −1.6 (−3.9, 0.7) 9 | 0.17 | |
| Diastolic BP (mm/Hg) | 57.4 ± 8.4 | 57.2 ± 7.5 | 0.4 (−0.9, 1.7) 3 | 0.57 | |
| Sex | 0.53 | ||||
| Female | 58.3 ± 8.5 4 | 57.7 ± 7.4 5 | 0.8 (−1.0, 2.6) 6 | 0.40 | |
| Male | 56.6 ± 8.3 4 | 56.7 ± 7.6 5 | 0.0 (−1.8, 1.9) 6 | 0.97 | |
| Birthweight | 0.12 | ||||
| <1250 g | 56.0 ± 7.3 7 | 57.0 ± 7.2 8 | −0.7 (−2.5, 1.0) 9 | 0.42 | |
| ≥1250 g | 58.6 ± 9.0 7 | 57.3 ± 7.7 8 | 1.3 (−0.6, 3.1) 9 | 0.17 | |
| Mean arterial pressure (mm/Hg) | 71.7 ± 7.2 | 71.8 ± 7.1 | 0.0 (−1.2, 1.2) 3 | 0.97 | |
| Sex | 0.57 | ||||
| Female | 72.5 ± 7.2 4 | 72.2 ± 6.9 5 | 0.5 (−1.1, 2.0) 6 | 0.55 | |
| Male | 71.0 ± 7.1 4 | 71.4 ± 7.2 5 | −0.4 (−2.1, 1.3) 6 | 0.67 | |
| Birthweight | 0.57 | ||||
| <1250 g | 70.7 ± 7.0 7 | 71.3 ± 7.1 8 | −0.3 (−2.0, 1.3) 9 | 0.69 | |
| ≥1250 g | 72.5 ± 7.3 7 | 72.1 ± 7.0 8 | 0.3 (−1.3, 1.9) 9 | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Best, K.P.; Sullivan, T.R.; Gunaratne, A.W.; Gould, J.F.; Gibson, R.A.; Collins, C.T.; Makrides, M.; Green, T.J. Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Supplementation of Preterm Infants on Growth, Body Composition, and Blood Pressure at 7-Years Corrected Age: Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020335
Best KP, Sullivan TR, Gunaratne AW, Gould JF, Gibson RA, Collins CT, Makrides M, Green TJ. Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Supplementation of Preterm Infants on Growth, Body Composition, and Blood Pressure at 7-Years Corrected Age: Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2023; 15(2):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020335
Chicago/Turabian StyleBest, Karen P., Thomas R. Sullivan, Anoja W. Gunaratne, Jacqueline F. Gould, Robert A. Gibson, Carmel T. Collins, Maria Makrides, and Tim J. Green. 2023. "Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Supplementation of Preterm Infants on Growth, Body Composition, and Blood Pressure at 7-Years Corrected Age: Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 15, no. 2: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020335
APA StyleBest, K. P., Sullivan, T. R., Gunaratne, A. W., Gould, J. F., Gibson, R. A., Collins, C. T., Makrides, M., & Green, T. J. (2023). Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Supplementation of Preterm Infants on Growth, Body Composition, and Blood Pressure at 7-Years Corrected Age: Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 15(2), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020335








