Resveratrol Food Supplement Products and the Challenges of Accurate Label Information to Ensure Food Safety for Consumers
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Food Supplements: Safety and Labels
1.2. Mandatory and Voluntary Food Information
1.3. Health and Nutrition Claims
1.4. Food Supplements and Novel Foods
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
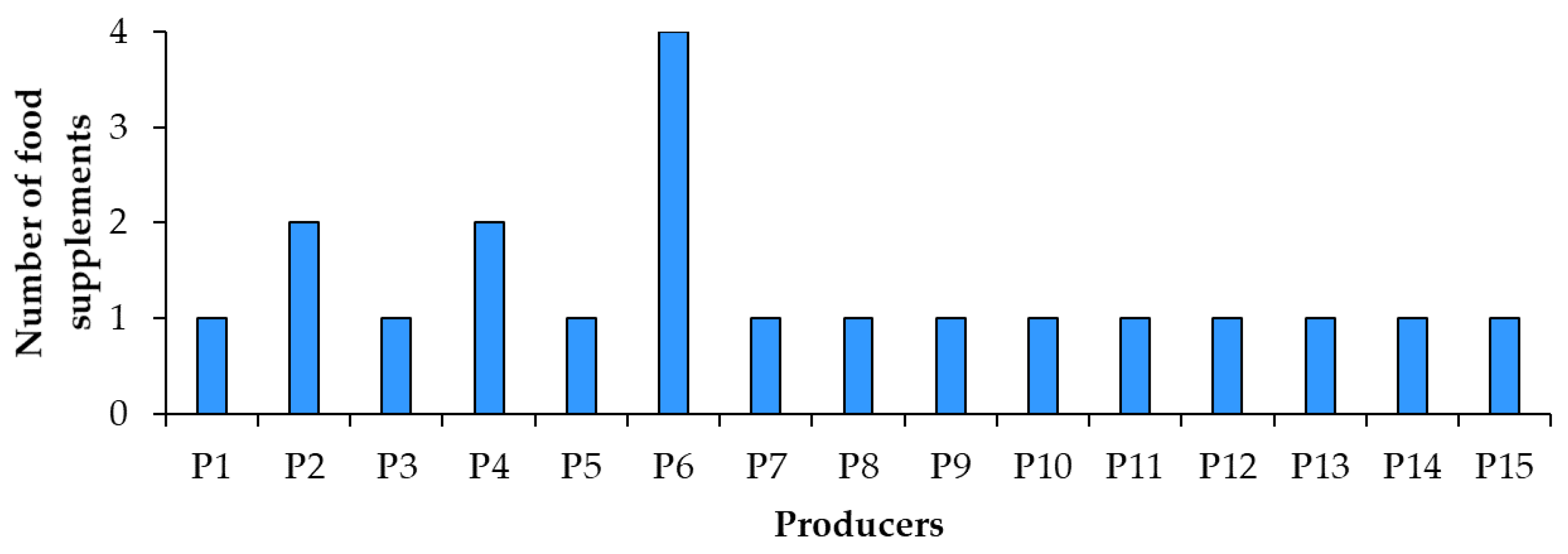
2.2. Food Supplements with Resveratrol
2.3. Preparation of Standard Solutions
2.4. Preparation of Sample Test Solutions (STSs) of Food Supplements
2.5. HPTLC Analyses
2.6. Validation of HPTLC Method
2.7. Label Regulatory Compliance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HPTLC Quantification of Resveratrol and Assessment of Compliance of Declared and Determined Resveratrol Contents
| Sample | Average Determined Resveratrol Content (mg/unit ± SD) 1 | RSD (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 205.92 ± 6.36 | 3.09 |
| 2 | 203.10 ± 1.56 | 0.77 |
| 3 | 31.35 ± 0.52 | 1.67 |
| 4 | 215.00 ± 0.89 | 0.41 |
| 5 | 1.52 ± 0.03 | 2.23 |
| 6 | 1.54 ± 0.05 | 3.15 |
| 7 | 189.85 ± 4.63 | 2.44 |
| 8 | 164.28 ± 1.92 | 1.17 |
| 9 | 2.34 ± 0.01 | 0.34 |
| 10 | 176.29 ± 4.37 | 2.48 |
| 11 | 6.78 ± 0.09 | 1.28 |
| 12 | 124.27 ± 3.28 | 2.64 |
| 13 | 42.21 ± 1.22 | 2.88 |
| 14 | 1.94 ± 0.13 | 6.49 |
| 15 | 125.41 ± 0.63 | 0.50 |
| 16 | 3.33 ± 0.07 | 2.01 |
| 17 | 73.76 ± 2.84 | 3.85 |
| 18 | 28.92 ± 0.37 | 1.28 |
| 19 | 269.14 ± 4.70 | 1.75 |
| 20 | 182.80 ± 3.48 | 1.90 |
3.2. Label Regulatory Compliance
3.2.1. Mandatory Food Information
3.2.2. Voluntary Food Information
3.2.3. Nutrition and Health Claims
| Nutrients (Number of Products Using the Health Claim) | Health Claims (Summarized from Commission Regulation (EU) No 432/2012 [24] | |
|---|---|---|
| Copper (2), zinc (2), manganese (1), selenium (3), vitamin C (3), vitamin E (1) | [Nutrient] contributes to the “protection of cells from oxidative stress.” | |
| Magnesium (3), niacin (3), pantothenic acid (3), vitamin B2/riboflavin (3), vitamin B6 (3), vitamin B12 (3), vitamin C (2) | [Nutrient] contributes to the “reduction of tiredness and fatigue.” | |
| Calcium (1), potassium (1), magnesium (2), vitamin D (2) | Nutrient] contributes to “normal muscle function.” | |
| Thiamine (1) | [Nutrient] contributes to the “normal function of the heart.” | |
| Copper (1), zinc (2), folate (2), selenium (1), vitamin B6 (2), vitamin B12 (2), vitamin C (2), vitamin D (3) | [Nutrient] contributes to the “function of the immune system.” | |
| Copper (1), biotin (1), iodine (1), potassium (1), magnesium (2), niacin (1), vitamin B1/thiamine (1), vitamin B2/riboflavin (1), vitamin B6 (1), vitamin B12 (1), vitamin C (1) | [Nutrient] contributes to “normal functioning of the nervous system.” | |
| Zinc (1) | [Nutrient] contributes to the “maintenance of normal vision.” | |
| Calcium (1), vitamin D (1) | [Nutrient] contributes to the “maintenance of normal bones.” | |
| Magnesium (1), niacin (1), vitamin B2/riboflavin (1), vitamin B6 (1), vitamin B12 (1) | [Nutrient] contributes to “normal energy-yielding metabolism.” |
3.2.4. Food Supplements and Novel Foods
3.2.5. Other Label Noncompliances
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Directive 2002/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 10 June 2002 on the Approximation of the Laws of the Member States Relating to Food Supplements. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02002L0046-20220930 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- European Commission. 2021 Annual Report Alert and Cooperation Network; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02011R1169-20180101 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2470 of 20 December 2017 Establishing the Union List of Novel Foods in Accordance with Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Novel Foods. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02017R2470-20220829 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on Nutrition and Health Claims Made on Foods. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02006R1924-20141213 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 828/2014 of 30 July 2014 on the Requirements for the Provision of Information to Consumers on the Absence or Reduced Presence of Gluten in Food. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2014/828/oj (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- EU Register of Nutrition and Health Claims Made on Foods (v.3.6). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/safety/labelling_nutrition/claims/register/public/?event=register.home (accessed on 16 August 2022).
- European Commission Novel Food. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/safety/novel-food_en (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Gómez-Maqueo, A.; Escobedo-Avellaneda, Z.; Cano, M.P.; Welti-Chanes, J. Phenolic compounds in food. In Phenolic Compounds in Food: Characterization and Analysis; Nollet, M.L.L., Gutierrez-Uribe, J.A., Eds.; CRC Ptrss, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Angelis, M.; Della-Morte, D.; Buttinelli, G.; Di Martino, A.; Pacifici, F.; Checconi, P.; Ambrosio, L.; Stefanelli, P.; Palamara, A.T.; Garaci, E.; et al. Protective role of combined polyphenols and micronutrients against influenza a virus and SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, G.; Martínez Pinilla, E.; Ortiz, R.; Noé, V.; Ciudad, C.J.; Franco, R. Resveratrol and related stilbenoids, nutraceutical/dietary complements with health-promoting actions: Industrial production, safety, and the search for mode of action. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 808–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonovska, B.; Vovk, I.; Andrenšek, S.; Valentová, K.; Ulrichová, J. Investigation of phenolic acids in yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) leaves and tubers. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1016, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavnik, V.; Simonovska, B.; Albreht, A.; Vovk, I. TLC and HPLC screening of p-coumaric acid, trans-resveratrol, and pterostilbene in bacterial cultures, food supplements, and wine. J. Planar Chromatogr.-Mod. TLC 2012, 25, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jork, H.; Funk, W.; Fischer, W.R.; Wimmer, H. Dünnschicht-Chromatographie. Reagenzien und Nachweismethoden, Bd. 1a, Physikalishe und chemische Nach-weismethoden: Grundlagen, Reagenzien I; Thin-Layer Chromatography; VCH Verlagsgesellschaft: Weinheim, Germany, 1989; ISBN 9783527278343. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, J.M.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Marquardt, R.R.; Jones, P.J.H. Development of an improved reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous analyses of trans -/ cis-resveratrol, quercetin, and emodin in commercial resveratrol supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5812–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardelean, F.; Vlase, L.; Mocan, A.M.; Gheldiu, A.M.; Antal, D.S.; Trandafirescu, C.; Marginean, O.; Dragan, S. Dietary supplements with resveratrol, flavonoids and phenolic acids: In-depth HPLC profiling and antioxidant capacity as quality markers. Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattar, S.; Khan, S.A.; Zaidi, S.A.A.; Darvishikolour, M.; Farooq, U.; Naseef, P.P.; Kurunian, M.S.; Khan, M.Z.; Shamim, A.; Khan, M.M.U.; et al. Resveratrol from dietary supplement to a drug candidate: An assessment of potential. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnowska-Kujawska, M.; Klepacka, J.; Zielińska, O.; Samaniego-Vaesken, M. de L. Characteristics of dietary supplements with folic acid available on the Polish market. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe-Matsumoto, L.T.; Sampaio, G.R.; Bastos, D.H.M. Do the labels of vitamin A, C, and E supplements reflect actual vitamin content in commercial supplements? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 72, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Bartosiewicz, N.; Socha, K. Is the magnesium content in food supplements consistent with the manufacturers’ declarations? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, L.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Morales, P.; Sánchez-Mata, M.C.; Cámara, M. Assessment of health claims related to folic acid in food supplements for pregnant women according to the european regulation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation (EC) No 1334/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Flavourings and Certain Food Ingredients with Flavouring Properties for Use in and on Foods and Amending Council Regulation (EEC) No 1601/91, Regulations (EC) No 2232/96 and (EC) No 110/2008 and Directive 2000/13/EC. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02008R1334-20220926 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Directive 2011/91/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 December 2011 on Indications or Marks Identifying the Lot to Which a Foodstuff Belongs (Codification). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex%3A32011L0091 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 432/2012 of 16 May 2012 Establishing a List of Permitted Health Claims Made on Foods, Other than Those Referring to the Reduction of Disease Risk and to Children’s Development and Health. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02012R0432-20210517 (accessed on 14 December 2022).











| Regulatory Compliance Checklist for Food Supplement Labels | |
|---|---|
| Regulation Topic | Information |
| Mandatory food information | Name of the food |
| List of ingredients | |
| Allergens | |
| Quantity of certain ingredients or categories of ingredients | |
| Net quantity of the food | |
| Date of minimum durability | |
| Any special storage conditions and/or conditions of use | |
| Name or business name and address of the food business operator | |
| Country of origin or place of provenance | |
| Instructions for use | |
| Nutrition declaration * | |
| Voluntary food information | Absence or reduced presence of gluten in food |
| Reference intakes for specific population groups | |
| Suitability of a food for vegetarians or vegans | |
| Unintentional presence of allergens | |
| Nutrition and health claims | Nutrition claims |
| Health claims | |
| Warning for products that are likely to present a health risk if consumed to excess | |
| Persons who should avoid using the food | |
| Quantity of the food and pattern of consumption required to obtain the claimed beneficial effect | |
| Importance of a varied and balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle | |
| Nutrition declaration | |
| Food supplements | “Food supplement” |
| Names of the categories of nutrients | |
| Portion of product recommended for daily consumption | |
| Do not exceed the stated recommended daily dose | |
| Food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a varied diet | |
| Store out of the reach of young children | |
| Amount of the minerals/vitamins (in specified units and as a percentage of the reference values) | |
| Amount of nutrients/substances with nutritional/physiological effect present in the product & per daily dose | |
| Novel foods | “trans-resveratrol” |
| People using medicines should only consume the product under medical supervision | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bensa, M.; Vovk, I.; Glavnik, V. Resveratrol Food Supplement Products and the Challenges of Accurate Label Information to Ensure Food Safety for Consumers. Nutrients 2023, 15, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020474
Bensa M, Vovk I, Glavnik V. Resveratrol Food Supplement Products and the Challenges of Accurate Label Information to Ensure Food Safety for Consumers. Nutrients. 2023; 15(2):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020474
Chicago/Turabian StyleBensa, Maja, Irena Vovk, and Vesna Glavnik. 2023. "Resveratrol Food Supplement Products and the Challenges of Accurate Label Information to Ensure Food Safety for Consumers" Nutrients 15, no. 2: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020474
APA StyleBensa, M., Vovk, I., & Glavnik, V. (2023). Resveratrol Food Supplement Products and the Challenges of Accurate Label Information to Ensure Food Safety for Consumers. Nutrients, 15(2), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020474







