The Design and Impact of a Clinic-Based Community Program on Food Insecurity, Healthy Eating Behaviors, and Mood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Intervention
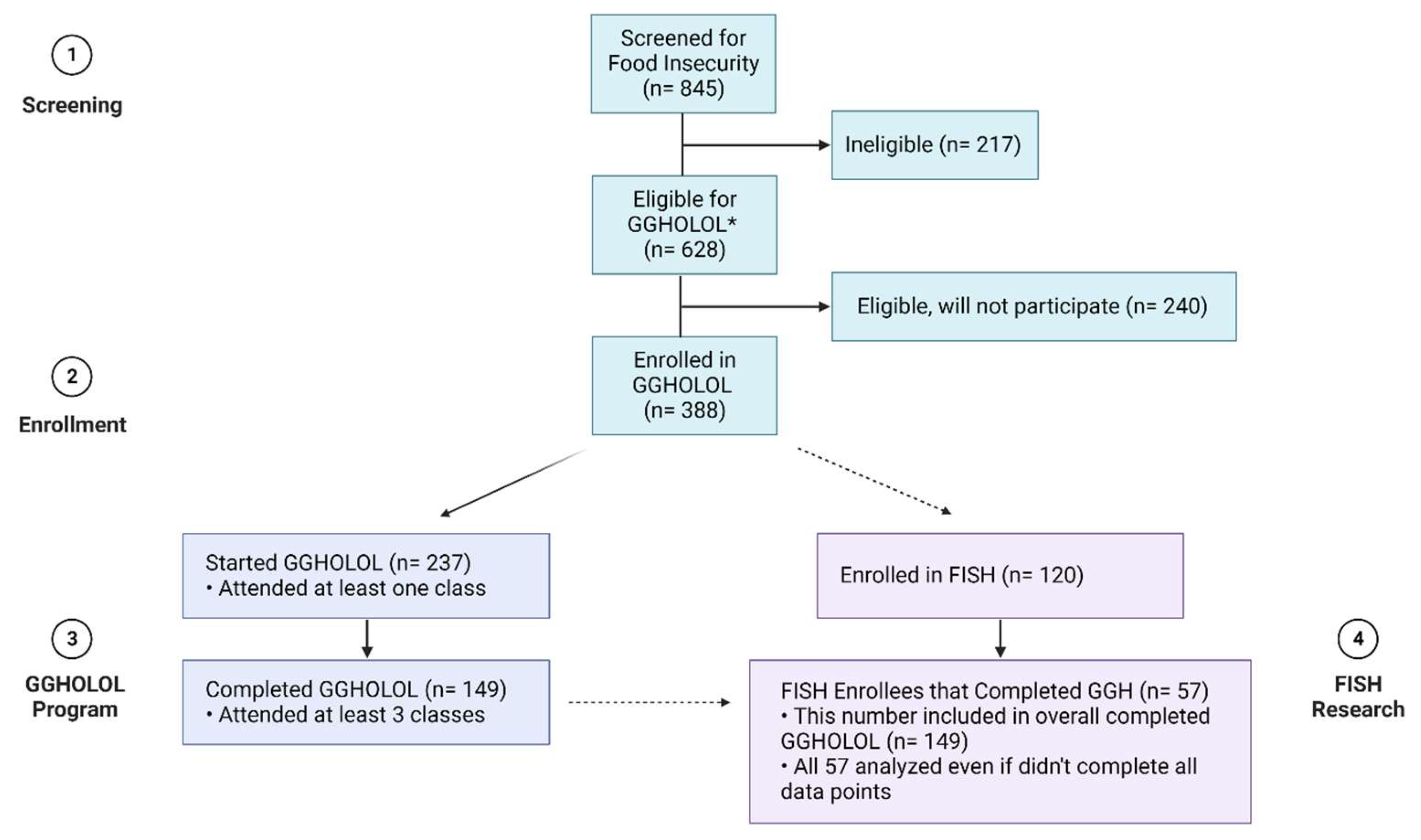
2.2. Study Procedures
2.3. Measures
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Food Insecurity
3.2. Food Serving Consumption
3.3. Other Nutrition Behaviors
3.4. Depression
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Implications for Research and Practice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seligman, H.K.; Laraia, B.A.; Kushel, M.B. Food Insecurity Is Associated with Chronic Disease among Low-Income NHANES Participants. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- America’s Health Rankings 2022 Annual Report. America’s Health Rankings, United Health Foundation. Available online: https://assets.americashealthrankings.org/app/uploads/2021_ahr_health-disparities-comprehensive-report_final.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Gundersen, C.; Ziliak, J.P. Food Insecurity And Health Outcomes. Health Aff. 2015, 34, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman-Jensen, A.; Rabbitt, M.P.; Hales, L.; Gregory, C. Food Security in the U.S. USDA ERS, USDA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/food-nutrition-assistance/food-security-in-the-us/key-statistics-graphics.aspx (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Myers, C.A.; Mire, E.F.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Trends in Adiposity and Food Insecurity Among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2012767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, C.; Coleman-Jensen, A. Food Insecurity, Chronic Disease, and Health among Working-Age Adults. USDA ERS, USDA, 2017. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/84467/err-235.pdf?v=5133.9 (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Phillips, C.; Billioux, A. 2019 Louisiana Health Report Card. LDH, Louisiana Department of Health. Available online: https://ldh.la.gov/assets/docs/LegisReports/RS401262019HealthRptCard72020.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Social Determinants of Health Literature Summaries. Social Determinants of Health Literature Summaries—Healthy People 2030, HHS. Available online: https://health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/social-determinants-health/literature-summaries (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Fraanje, W.; Lee-Gammage, S. What Is Food Security? (Foodsource: Building Blocks); Food Climate Research Network; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, K.S.; Wu, R.; Wolff, M.; Colantonio, A.G.; Grady, J. A Novel Food Pantry Program. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 45, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.E.; Berkowitz, S.A. The Relationship between Food Insecurity, Dietary Patterns, and Obesity. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2016, 5, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchis, E.H.; Torres, J.M.; Benesch, T.; Fichtenberg, C.; Allen, I.E.; Whitaker, E.M.; Gottlieb, L.M. Interventions Addressing Food Insecurity in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review. Ann. Fam. Med. 2019, 17, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyer, J.N.; Raber, M.; Bello, R.S.; Brewster, A.; Caballero, E.; Chennisi, C.; Durand, C.; Galindez, M.; Oestman, K.; Saifuddin, M.; et al. A pilot food prescription program promotes produce intake and decreases food insecurity. Transl. Behav. Med. 2019, 9, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oronce, C.I.A.; Miake-Lye, I.M.; Begashaw, M.M.; Booth, M.; Shrank, W.H.; Shekelle, P.G. Interventions to Address Food Insecurity Among Adults in Canada and the US: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Health Forum 2021, 2, e212001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economic Research Service; U.S. Department of Agriculture. U.S. Adult Food Security Survey Module—USDA ERS. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/media/8279/ad2012.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2020).
- Berkowitz, S.A.; Palakshappa, D.; Seligman, H.K.; Hanmer, J. Changes in Food Insecurity and Changes in Patient-Reported Outcomes: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 3638–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantor, J.; Ghosh-Dastidar, B.; Hunter, G.; Baird, M.; Richardson, A.S.; Siddiqi, S.; Dubowitz, T. What Is Associated with Changes in Food Security among Low-Income Residents of a Former Food Desert? Nutrients 2022, 14, 5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavelle, F.; McGowan, L.; Hollywood, L.; Surgenor, D.; McCloat, A.; Mooney, E.; Caraher, M.; Raats, M.; Dean, M. The development and validation of measures to assess cooking skills and food skills. Int. J. Behav. 2017, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, J.J.; McCaffrey, J.; Schumacher, M.; Kownacki, C.; Prescott, M.P. Community-based nutrition education and hands-on cooking intervention increases farmers’ market use and vegetable servings. Public Health Nutr. 2022, 25, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.L.; Reardon, R.; McDonald, M.; Vargas-Garcia, E.J. Community Interventions to Improve Cooking Skills and Their Effects on Confidence and Eating Behaviour. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2016, 5, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025. 9th Edition. Available online: https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/ (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Rees, J.; Fu, S.C.; Lo, J.; Sambell, R.; Lewis, J.R.; Christophersen, C.T.; Byrne, M.F.; Newton, R.U.; Boyle, S.; Devine, A. How a 7-Week Food Literacy Cooking Program Affects Cooking Confidence and Mental Health: Findings of a Quasi-Experimental Controlled Intervention Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 802940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-T.; Shim, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-J.; Linton, J.A.; Park, B.-J.; Lee, H.-R. Reading nutrition labels is associated with a lower risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: The 2007–2008 Korean NHANES. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpp, K.G.; Berkowitz, S.A.; Sharma, S.V.; Anderson, C.A.; Brewer, L.C.; Elkind, M.S.; Gardner, C.D.; Gervis, J.E.; Harrington, R.A.; Herrero, M.; et al. Food Is Medicine: A Presidential Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurler, K. “Food Is Medicine: Uniting Innovation and Equity”. Tufts Now, Tufts University. Available online: https://now.tufts.edu/2023/06/01/food-medicine-uniting-innovation-and-equity (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Mozaffarian, D. The White House Conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health—A New National Strategy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2014–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Baseline Characteristics (n = 120) | |
|---|---|
| n or Mean (% or SD) | |
| Race | |
| African American | 101 (84.2%) |
| White | 5 (4.2%) |
| Hispanic | 4 (3.3%) |
| Other | 10 (8.3%) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 95 (79.2%) |
| Male | 23 (19.2%) |
| Other | 2 (1.6%) |
| Age | |
| 18–24 | 10 (8.4%) |
| 25–34 | 11 (9.2%) |
| 35–44 | 33 (27.7%) |
| 45–54 | 23 (19.3%) |
| 55–64 | 40 (33.6%) |
| 65 | 2 (1.7%) |
| Referral location | |
| Clinic | 98 (81.7%) |
| Community | 22 (18.3%) |
| Education | |
| Master’s Degree or Higher | 3 (2.5%) |
| Completed College | 7 (5.9%) |
| Some College or Vocational School | 39 (33.1%) |
| High School or GED | 54 (45.8%) |
| Less than High School | 15 (12.7%) |
| Annual Household Income | |
| Less than USD 25,000 | 88 (74.6%) |
| USD 25,000–USD 34,999 | 19 (16.1%) |
| USD 35,000–USD 49,999 | 6 (5.1%) |
| USD 50,000–USD 74,999 | 5 (4.2%) |
| More than USD 75,000 | 0 (0%) |
| Children in Household | |
| 0 | 68 (59.1%) |
| 1 | 22 (19.1%) |
| 2 | 10 (8.7%) |
| 3 | 9 (7.8%) |
| 4+ | 6 (5.2%) |
| Receive WIC/SNAP | |
| Yes | 55 (46.6%) |
| No | 63 (53.4%) |
| Metabolic Conditions | |
| Pre-diabetes | 35 (29.2%) |
| Diabetes | 44 (36.7%) |
| Hypertension | 67 (55.8%) |
| Metabolic Measurements | |
| Average BMI (kg/m2) | 34.85 (9.23) |
| Average Waist Circumference (in) | 42.23 (7.94) |
| Mean PHQ-9 | 6.97 (6.34) |
| Home appliances | |
| Stove/hotplate | 113 (94.2%) |
| Oven | 114 (95.0%) |
| Microwave | 113 (94.2%) |
| Pan | 113 (94.2%) |
| Refrigerator | 118 (98.3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ardoin, T.W.; Perry, E.; Morgan, C.; Hymowitz, J.; Mercante, D. The Design and Impact of a Clinic-Based Community Program on Food Insecurity, Healthy Eating Behaviors, and Mood. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204316
Ardoin TW, Perry E, Morgan C, Hymowitz J, Mercante D. The Design and Impact of a Clinic-Based Community Program on Food Insecurity, Healthy Eating Behaviors, and Mood. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204316
Chicago/Turabian StyleArdoin, Tiffany Wesley, Elizabeth Perry, Chelsea Morgan, Jared Hymowitz, and Donald Mercante. 2023. "The Design and Impact of a Clinic-Based Community Program on Food Insecurity, Healthy Eating Behaviors, and Mood" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204316
APA StyleArdoin, T. W., Perry, E., Morgan, C., Hymowitz, J., & Mercante, D. (2023). The Design and Impact of a Clinic-Based Community Program on Food Insecurity, Healthy Eating Behaviors, and Mood. Nutrients, 15(20), 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204316






